-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Microbiology Research
p-ISSN: 2166-5885 e-ISSN: 2166-5931
2014; 4(2): 112-116
doi:10.5923/j.microbiology.20140402.11
Isolation and Identification of Yeasts from Local Traditional Fermented Camel Milk, Chal
Barat Ali Zarei Yam , Morteza Khomeiri , Alireza Sadeghi Mahounak , Seid Mahdi Jafari
Department of Food Science and Technology, Gorgan University of Agriculture Sciences and Natural Resources, Gorgan, 49138-15739, Iran
Correspondence to: Barat Ali Zarei Yam , Department of Food Science and Technology, Gorgan University of Agriculture Sciences and Natural Resources, Gorgan, 49138-15739, Iran.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The yeasts in 9 samples of the Iranian traditional fermented camel milk, Chal, taken from farms and households were identified on the basis of their physiological and morphological properties. From the 9 samples, a total of 18 different yeast species were identified including Pichia. anamala, Pichia. jadinii, Debaryomyces. hansenii, Pichia. guilliermondii, Kluyvermyces. marxianus, Candida. fermentati, Pichia. ciferrii, Torulospora. delbrueckii, Candida. versatilis, Kluyvermyces. lactis, Candida. kefir, Saccharomyces. pastorianus, Saccharomyces. serevisiae, Candida. friedrichii, Kluyvermyces. polysporus, Rhodotorula. musilaginosa, Candida. lipolytica and Candida. lusitaniae. All of them could assimilate the glucose as carbon source and liquefacted the gelatin, but could not production starch, tolerated 1% acetic acid, growth in the presence of Nacl 16% (except Debaryomyces. hansenii), anassimilateed the nitrat (except Rhodotorula. musilaginosa) and had not Septate hyphae. Results showed within the yeasts species isolated from Chal samples, Kluyvermyces. lactis (8.57%) and Kluyvermyces. marxianus (8.57%) were the predominant. This study revealed Chal contained a wide variety of yeasts that predominanted at Chal in the 48 h fermentation.
Keywords: Chal, Camel Milk, Fermented Milk, Yeast, Identificaton
Cite this paper: Barat Ali Zarei Yam , Morteza Khomeiri , Alireza Sadeghi Mahounak , Seid Mahdi Jafari , Isolation and Identification of Yeasts from Local Traditional Fermented Camel Milk, Chal, Journal of Microbiology Research, Vol. 4 No. 2, 2014, pp. 112-116. doi: 10.5923/j.microbiology.20140402.11.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Chal is a nutritious fermented camel milk which is prepared by spontaneous fermentation of camel milk at ambient temperature and consume in many areas such as Africa, Arabic countries [12], and in many regions used against diseases [28]. Due to acidic pH, dairy products are favorable environment for growth of yeasts [38-30]. The yeasts usually adopt themselves to coexistence with lactic acid bacteria in dairy products. The yeasts play usefull effect upon the bacteria due to change in pH and secretion of biological substance such as vitamins, enzymes, amino acids etc [7]. Yeast species mainly the genera Candida (C. sphaerica), Debaryomyces, Mycoderma, Saccharomyces (S. dairensis. S. unisporus) and Rhodotorula by lactose assimilation decrease quality of dairy products and Some representatives of the genus Rhodotorula cause staining and give bitter taste to the products [17-23-39].The most isolated species from different dairy products belonged to Species of Candida, Debaryomyces, Galactomyces, Fellomyces, Pichia and Saccharomyces [38-18-37-32]. The yeasts isolated from dairy products are different, but the most frequently described strains belong to the genera Saccharomyces, Kluyveromyces, Debaryomyces, Issatchenkia and Yarrowia [33-34-21]. The nature of fermented dairy products varies from one region to another.The yeasts occurr in many dairy related products [10], [14] and in the human gastrointestinal tract [16], [8], and have probiotic potential. Saccharomyces boulardii is the yeast commercialized as probiotic in human medicine [31], [8], but also in several studies strains such as Kluyveromyces lactis, K. marxianus, Isaatchenkia orientalis, S. cerevisiae and Debaryomyces hansenii have shown antifungal, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and antitumoral activity [25-9-19].Candida albicans, C. parapsilosis, D. hansenii, I. orientalis, K. lactis, S. cerevisiae and S. boulardii were isolated from infants’ gastrointestinal tract and feta cheese [36-2-26]. Many in vitro investigation proved the potential probiotics of the S. cerevisiae 832 and S. boulardii KK1 due to acid and bile tolerance and cholesterol removal ability [27]. The aim of this study was isolation and identification of yeasts from Chal sold in Golestan province of Iran.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
- A total of 9 sour camel milk (Chal) samples (A to I) were randomly collected from different house holds and retail markets with different sanitation levels in the original container from Golestan province. The areas under investigation were Gonbad, Aghghala and Bandar Torkman cities.
2.2. Compositional Analysis
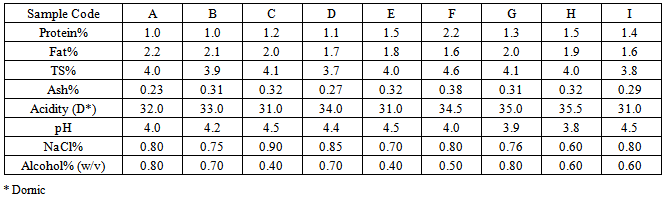
- The Chal samples were analyzed for Fat [29], ash [20], pH, Nacl, Alcohol (after 48 h fermentation) [6], Protein, TS and Acidity content [3].
2.3. Isolation and Identification of Yeasts
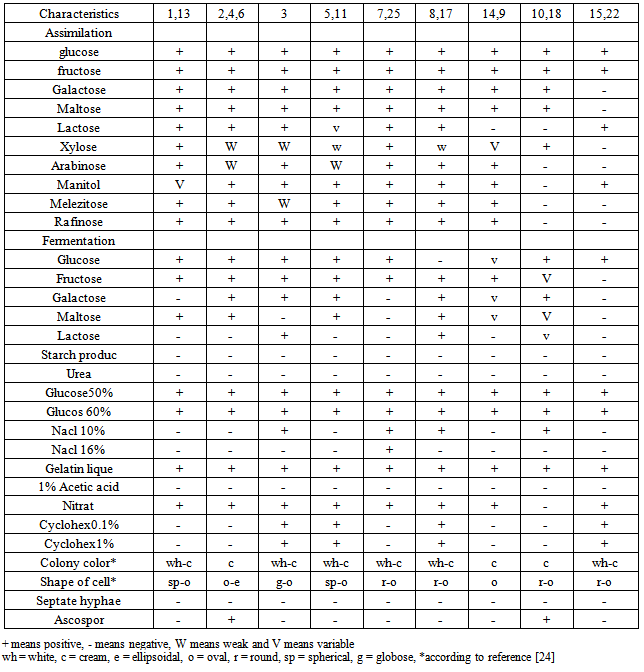
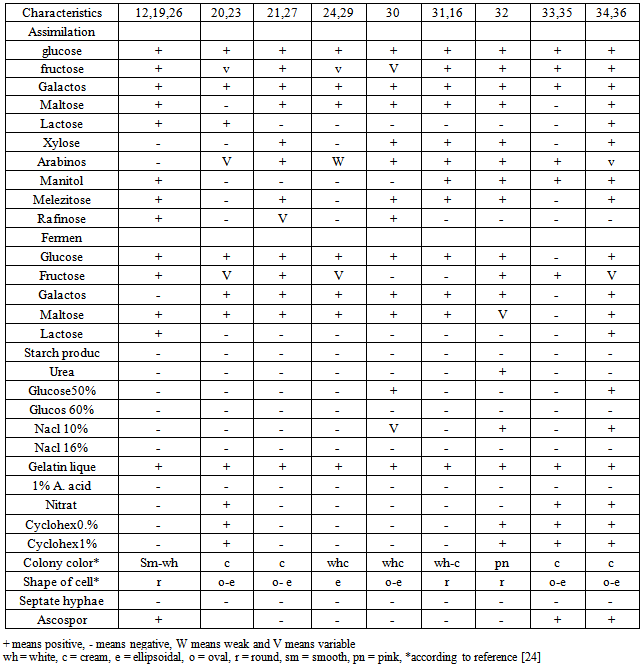
- One milliliter from each samples was serially diluted in distilled water and spread- plated onto YGC agar (Mirmedia, Iran) to isolate the yeasts. The plates were incubated at 25°C for 5 days. Colonies with distinct morphological differences such as colour, shape and size were picked and purified by streaking. The purified isolates were stored on YGC agar slant at 4°C under liquid parafin before identification. The colonies were tested and described based on morphological characteristic on Yeast- Mold Agar (YMA) and YM broth as following:Yeast fermentation base medium containing 2% one of Carbohydrates (glucose, fructose, galactose, maltose, lactose, sucrose, xylose, arabinose, trehalose, manitol, melezitose and rafinose) as a sole carbon source for testing the assimilation of carbon sources for a month, gas production from carbohydrates 5% (glucose, fructose, galactose, maltose and lactose) by using durham tube for three weeks, production of extracellular starch compounds, urease test for hydrolyzation activity, growth in the presence of D-glucose (50 and 60%) and NaCl (10 and 16%), gelatin liquefaction and tolerance of 1% acetic acid according to [35], and investigation of the assimilation of nitrat, growth in the presence of cycloheximide (0.1% and 1%) with modified method according to [15], using disk inoculum- solid medium method were achiened. The isolate were identified according to protocol described by [13-4-32-18-17]. In all tests sensitive compounds to heat such as carbohydrates, cycloheximide, yeasts nitrogen base medium, yeasts fermentation base medium were sterilized using 0.23µ Millipore Filter apparatus.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Copositional Analyses
- Chemical properties of chal given in Table 1.Our results revealed that the pH was ranged from 3.8 to 4.5. Although lower pH has inhibitory effect on the vegetative cells of pathogenic microorganisms, but it is favorable for growth of yeasts [1].
3.2. Identified Yeasts
- All the results have been shown in Tables 2, 3 and Figure 1.
|
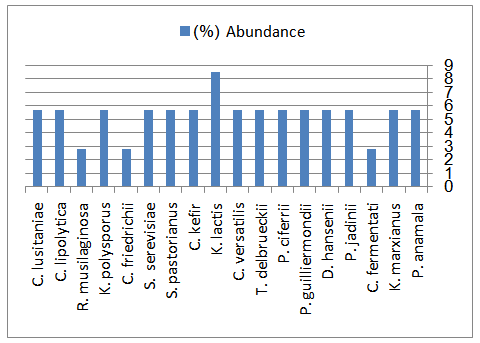 | Figure 1. Estimation of yeasts species isolated from Chal samples |
|
|
4. Conclusions
- Thirty five yeast species belonging to 18 genera were isolated and identified from samples of chal. Results showed Chal contained a wide variety of yeasts that are predominanted at Chal after the 48 h fermentation.Chal was made from raw camel milk, but the presence of yeasts indicates the contamination of the product by air, water or persons who are engaged in the preparation and transportation. This study recommended that increasing the hygienic level in Chal production be effective to decrease the yeast contamination.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support of the Iran National Science Foundation for their interest in and support of this research.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML