Matrizaeva Gulnara Djumaniyazovna1, Ikhtiyarova Gulchehra Akmalovna2
1Urgench Branch of Tashkent Medical Academy, Uzbekistan
2Bukhara State Medical Institute, Professor, Head of the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Abstract
The frequency of undeveloped pregnancy remains consistently high and amounts to 45-88.6% of cases of spontaneous miscarriages in the early stages. Inflammatory diseases occupy one of the leading places among the causes of premature termination of pregnancy. In our work, we examined women with recurrent miscarriage for up to 12 weeks. Termination of pregnancy was established on the basis of ultrasound examination (abdominal and transvaginal). Immunohistochemistry makes it possible to more accurately diagnose and monitor the effectiveness of hormonal treatment, provides an individual approach to the patient and, therefore, allows optimizing hormonal therapy regimens.
Keywords:
Miscarriage, Inflammatory diseases, Immunohistochemistry, CD 34, Ki 67, hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) hormone, Estrogen and progesterone
Cite this paper: Matrizaeva Gulnara Djumaniyazovna, Ikhtiyarova Gulchehra Akmalovna, Characteristics of Immunohistochemical Investigations During Early Gestation in Marriage of Pregnancy, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 14 No. 6, 2024, pp. 1640-1646. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20241406.36.
1. Introduction
The problem of miscarriage continues to occupy one of the first places among the most important tasks of obstetrics and gynecology and is of great medical and social importance. In the world, spontaneous miscarriage accounts for 180,000 annually, or > 15-20% of all wanted pregnancies. At the same time, according to literature data, the risk of repeat miscarriage after the first is 13-17%, after two failures it increases to 36-38%, and after three to four miscarriages it reaches up to 50%. The frequency of undeveloped pregnancy remains consistently high and amounts to 45-88.6% of spontaneous miscarriages in the early stages [4,5,6].The reasons why pregnancy does not develop are numerous and very often the leading factors cannot be identified. Reproductive loss in 80% of cases mainly occurs in the first trimester of pregnancy [3,9]. Recurrent miscarriage may be associated with the presence of chromosomal abnormalities, antiphospholipid syndrome, as well as immune and endocrine disorders [1,2,14]. Inflammatory diseases occupy one of the leading places among the causes of premature termination of pregnancy [8,15]. However, in 50% of cases the reason for termination of pregnancy remains unknown. For this reason, studying the factors of miscarriage in obstetrics and gynecology is one of the most pressing problems.Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is a method of identifying the exact location of a particular cellular or tissue component (antigen) by binding it to labeled antibodies.CD 34 is a membrane protein, an intercellular adhesion molecule (adhesion between cells), which plays a role in the initial stages of hematopoiesis.Ki 67 is a DNA - binding nuclear protein expressed in proliferative cells that prevents chromosome destruction during division and is considered a marker of proliferation (also known as MKI67) [11]. Present in normal endometrial cells in the proliferative phase, less so in the secretory phase. It participates in the cell cycle, being involved in the biogenesis of ribosomes, and is responsible for the organization of heterochromatin and the separation of mitotic chromosomes [7,13].Estrogen and progesterone: The most important estrogen hormones are estradiol and progesterone. Estrogen is responsible for the growth and enlargement of specific cells in the body that ensure the formation of female secondary sexual characteristics.Progesterone is required to induce progesterone activation. Progesterone is usually the only progestin. Progesterone is secreted primarily by the corpus luteum, which produces it during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle and early pregnancy. After 2-3 months from the beginning of pregnancy, the placenta takes over this function [2].Human chorionic gonadotropin is a hormone that is produced in the membrane of the embryo during pregnancy. It plays a role in stimulating the production of progesterone to maintain pregnancy, which is very important. After conducting rapid tests, including early pregnancy detection, to determine pregnancy at home [10,12].The purpose of the study is to study the immunohistochemical features of the endometrial decidua in order to identify the mechanisms of the causes of miscarriage in early pregnancy in women living in the Aral Sea region for the development of diagnostic methods.
2. Materials and Research Methods
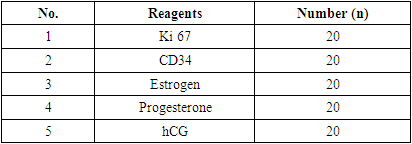
Immunohistochemistry study was carried out at “FBC LLC NGS MEDICAL” pathomorphological laboratory. Scrapings from the uterus were collected at the Perinatal Center of the Khorezm region in the gynecology department from women with recurrent miscarriage after miscarriage in the period 2021-2023.An analysis of data from clinical-anamnestic and laboratory-instrumental methods of examination of women with recurrent miscarriage in the first trimester was carried out depending on the frequency of occurrence.According to the ICD - XI, as well as according to the national clinical recommendations of the ESHRE World Congress of 2023, the diagnosis of recurrent miscarriage is made when a woman has a history of two or more spontaneous terminations of pregnancy for up to 22 weeks. In our work, we examined women with recurrent miscarriage for up to 12 weeks. Termination of pregnancy was established on the basis of ultrasound examination (abdominal and transvaginal). Imaging revealed the absence of motor activity and heart contractions, as well as the discrepancy between the size of the embryo and the expected pregnancy, depending on the last date of menstruation, which was one of the criteria for diagnosing a non-developing pregnancy. In case of spontaneous incomplete miscarriage, ultrasound detects the remains of the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity.A study was made of 156 pregnant women who were observed during pregnancy at the Khorezm Regional Perinatal Center. Among the women examined, the incidence of miscarriage pregnancy history ranged from 1 to 8 cases, the average number was 2.1±0.02 cases.The material for the morphological study was scrapings from the uterine cavity (n=40), including decidual endometrial tissue. The comparison group consisted of a biological substrate obtained from women who decided to terminate an uncomplicated pregnancy in the period from 4 to 12 weeks through an artificial (medical) abortion (n=20). The main group included scrapings obtained from patients with recurrent early pregnancy loss of various etiologies (main group, n = 40).Gestational age was determined by the first day of the last menstrual period.The results of a morphological examination are currently recognized as the “gold standard” throughout the world. In all examined patients, a histological block of cassettes was obtained, taken from the section, and processed for immunohistochemical examination. For the study, a radio transmission of the immune processor Bond Leica Australia (Australia) was used, Ki 67, CD 34, CD 20, CD 3 estrogen and progesterone receptors, hCG monoclonal antibodies (Table 1).Table 1. Number of patients selected from each group for immunohistochemical study
 |
| |
|
3. Results and Discussions
Study of the structure and functional properties of gravidar decidual cells: the components of the endometrium were studied using an electron microscope, the differentiating properties of the cells and their ultrastructure were determined.An extremely important structural transformation in the early stages of uncomplicated pregnancy is the formation of a progressive blood supply to the endometrium, necessary for further prolongation of pregnancy. Due to the spiralization of the vertical branches of the spiral arteries, “vascular tangles” are formed. Gestational remodeling endometrial fragments of the vertical branches of the uterine arteries occur as a result of the first wave of endovascular trophoblast invasion. This transformation of the arteries ensures adequate maternal blood flow, according to the increasing needs of the developing embryo.A study of endometrium obtained from women with an uncomplicated pregnancy revealed that during the first trimester, the “vascular tangles” included a varying number of arteries of varying sizes. A targeted morphological and morphometric study of vessels made it possible to identify large, medium and small spiral arteries.The spiralization of the arteries during 8 weeks of pregnancy is characterized by a quantitative increase (from 8 to 15) and the bringing together of the vessels in “tangles”. Intravascular invasion cytotrophoblast is accompanied by gestational remodeling of the wall of spiral arteries, primarily large and medium-sized ones, which is manifested by focal replacement of wall components with fibrinoid. The restructuring of the arteries is accompanied by an increase in the perimeter of the vessels and an expansion of their lumen.Vascularization of the endometrium at the end of the first trimester of uncomplicated pregnancy is accompanied by quantitative and qualitative changes in the “vascular tangles”. The number of vessels increases to 20, and the location of the arteries relative to each other becomes more compact. The endothelium and connective tissue fibers in large arteries are lysed throughout and completely replaced by fibrinoid. The perimeter of vessels and the lumen area of large vessels are increased by 3.3 and 7.2 times, respectively. In medium-sized arteries, fibrinoid replaces the components of the vascular wall by half, in small ones - focal replacement.Immunohistochemical results studies CD 34 were rated as weakly, moderately and highly positive. The minimum number of cells with a low expression index was detected in very early stages. The maximum proportion of cells with highly expressed expression of CD 34 was detected at the end of the first trimester of pregnancy in the predecidual precursors and the predecidual cells themselves.CD34 expression significantly (p=0.005) increased with increasing gestational age (Table 2).Table 2. Expression of CD 34 in decidual tissue during normal pregnancy
 |
| |
|
Intragroup correlation analysis in uncomplicated pregnancy showed a significant (p < 0.05) highly positive correlation between the Ki 67 indicator, responsible for the proliferation of the endometrial stroma, and the size of differentiating stromal cells (Picture 1).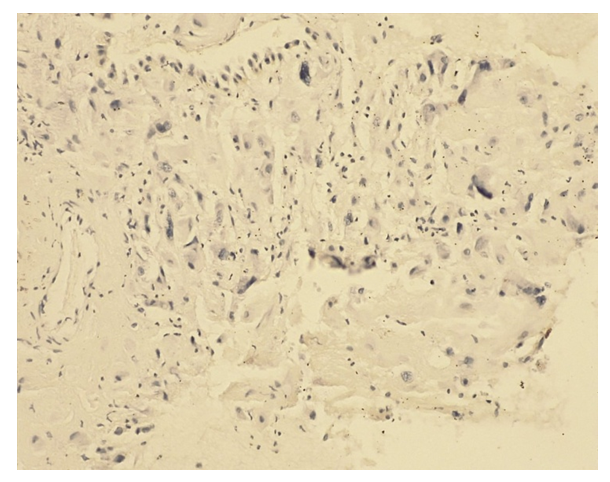 | Picture 1. K i 67 positive reaction. IHC – Dab chromagen. Ob10. Ok40 |
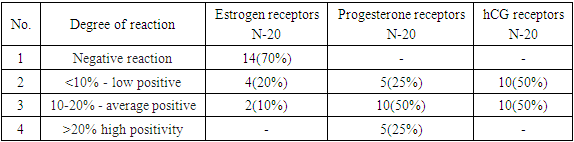
Further immunohistochemical studies with monoclonal labeled antibodies associated with estrogen receptors revealed a positive reaction both in the nuclei of differentiating fibroblast-like cells and in the nuclei of glandular epithelial cells. Moreover, estrogen expression was significantly higher in the glandular epithelium compared to stromal cells.Immunohistochemical study with antibodies that bind to progesterone receptors showed pronounced and moderate staining of the cytoplasm and cell nuclei. The expression of progesterone receptors in the glandular epithelium was significantly higher than in stromal cells (Table 3).Table 3. Expression of hormonal receptors in decidual tissue during normal pregnancy
 |
| |
|
Immunohistochemical A study of antibodies associated with steroid receptors of endometrial cells during uncomplicated pregnancy revealed a significant predominance of progesterone receptors in glandular epithelial cells compared to fibroblast-like stromal cells.Expression of CD20, which is a marker of mature B-lymphocytes, and CD3, a marker of T-lymphocytes, are detected to a small extent around the vessels.Results of studying the structure and functional properties of gravidar decidual cells in recurrent miscarriage in the first trimester of pregnancyAs a result of the study, it was revealed that the morphometric parameters of the area of the cytoplasm and cell nuclei are significantly less than those in uncomplicated pregnancy, by 1.6 and 1.0 times, respectively, which is associated with the predominance of intermediate fibroblastic forms of cells of the first and second types. The stromal cells are located in isolation, without a tendency to approach each other.In the compact layer of the endometrium, along with differentiating fibroblastoid cells, a pronounced focal, with a tendency to form pseudofollicles, and/or diffuse inflammatory infiltration, represented by lymphocytes, leukocytes, histiocytes and plasmacytes, is diagnosed. The number of inflammatory infiltrate cells in the field of view ranges from 89 to 465 over 5-12 weeks, which significantly exceeds similar indicators during uncomplicated pregnancy. The endometrial glands of the compact layer, lined with cuboidal epithelium, are predominantly hypotrophic and have a narrowed lumen (Picture 2).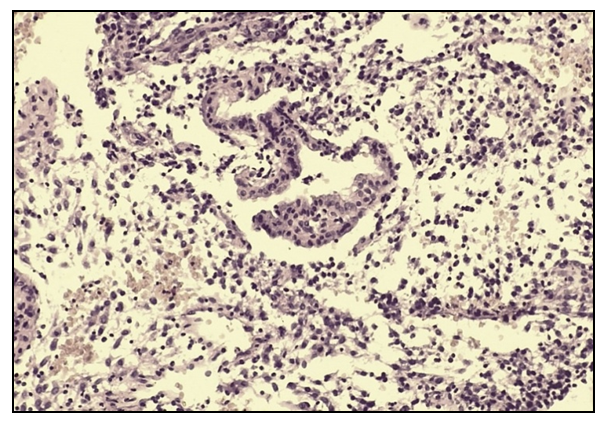 | Picture 2. Microscopic picture of the endometrium during miscarriage. Heme -eosin staining. Ob10hock40 |
The average height of the glandular epithelium was 4.0±0.2 µm, which is 2 times less than that of the comparison group. In the lumen of individual glands, white blood cells and desquamated epithelium are visualized. In the deeper layers of the functional layer of the endometrium there are glands that have a relatively monomorphic rounded shape in the cross section, containing protein and blood cells in the lumens. In the perivascular and periglandular zones, the stromal cells of the compact layer of the endometrium are replaced by connective tissue. The arteries of the compact layer, in a state of spiralization and transformation, with sclerosis of the walls and narrowed lumen, are located among fibrotic connective tissue.In endometrial scrapings of patients of the main group in the placentation territory, a significant (p<0.0001) quantitative decrease in invasive cytotrophoblast cells to 48 was revealed. Histological preparations rarely revealed small hypovascularized anchor villi with scanty proliferative tissue at their bases.The implantation area was characterized by the presence of extensive foci of necrosis, hemorrhages, stromal edema and reactive inflammation.Significant differences from the comparison group are also revealed in the spiral arteries. Thus, in the vast majority of vessels, incomplete gestational restructuring of the vascular wall and insufficient spiralization are found. Some vessels are dilated and full of blood.Thus, based on histological examination and comparative morphometric analysis in the first trimester of pregnancy, a violation of the differentiation of fibroblastopathic stromal cells and vascularization was revealed gravidar endometrium. A decrease in the number of vessels in the “vascular tangles” and a delay in gestational age have been established. remodeling of the vascular wall of small, medium and large arteries with a decrease in the area of their lumen and the perimeter of the vascular wall. The differentiation of fibroblastopathic cells of the stroma is delayed at the level of precursors of predecidual cells, surrounded by intermediate forms that have stopped in their development, which creates a picture of cellular polymorphism.Considering the identified features, it was advisable to conduct additional clarifying research methods.Expression of CD34 in the main group compared to the female group with uncomplicated pregnancy it was 3 times less (Picture 3).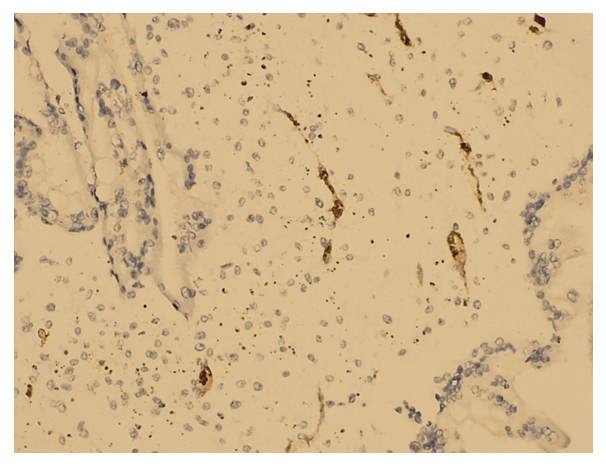 | Picture 3. SD 34 - low positive. IHC – Dab chromagen. Ob10. Ok40 |
An immunohistochemical study of decidual tissue revealed that out of 20 people, 5 patients (25%) had a negative reaction, 55% had a mild positive reaction of vascular density, medium positive expression was in 15% of women and high positive in 5% of women. (Table 4).Table 4. Expression of DM 34 in decidual tissue during miscarriage
 |
| |
|
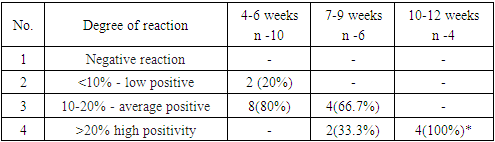
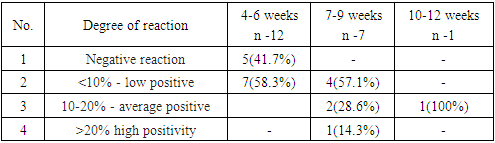
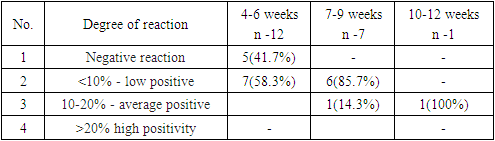
Ki 67 is a protein that determines the proliferative activity of cells and the study evaluated the results in 20 patients. Of 12 patients with 4-6 week of pregnancy, 41.7% of patients had negative staining and 58.3% light staining (Picture 4, 5); a medium and high positive reaction was not observed in women in this group. In patients 7-9 weeks of pregnancy, a low positive reaction was observed in 6 patients, which amounted to 85.7%, and an average positive reaction in 14.3%. The process had an average positive reaction in 1 woman with a period of 12 weeks. (Table 5).Table 5. Expression of K i 67 in decidual tissue during miscarriage
 |
| |
|
Thus, with recurrent miscarriage, the C D 34, K i 67 index of expression of proteins involved in the formation of intercellular channels that control the proliferation and differentiation of fibroblast-like endometrial stroma cells into predecidual cells is significantly reduced. Structural and functional disorders in recurrent miscarriage result in endometrial insufficiency, which contributes to early termination of pregnancy (Picture 4,5). | Picture 4. K i 67 negative expression |
 | Picture 5. Ki 67 Low positive reaction. IHC – Dab chromagen. Ob10. Ok40 |
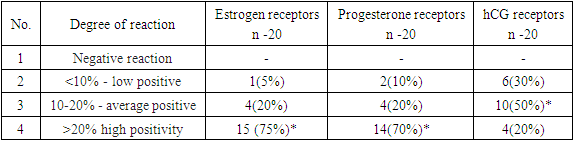
hCG hormone is a hormone that is produced in the membrane of the embryo during pregnancy. All 20 patients were tested for the presence of hCG receptors using the immunohistochemical method, and 100% had a positive reaction. Positive staining was observed in 50% of lungs and 50%. average expression. No negative reaction or high expression was detected.Progesterone – Progesterone is usually the only progestin. Immunohistochemistry revealed a (100%) positive reaction, a highly positive reaction was observed in 15 patients, a moderate positive reaction was observed in 25% of patients, and a mild positive reaction was observed in 25% (Picture 6). | Picture 6. Low expression of progesterone receptors. IHC – Dab chromagen. Ob10. Ok40 |
Estrogen - out of 20 patients, 4 (20%) had a low positive reaction, 2 of them (10%) had an average positive reaction, and in 14 patients 70% showed a negative reaction (Table 6).Table 6. Expression of hormonal receptors in decidual tissue during normal pregnancy
 |
| |
|
 | Picture 7. Estrogen negative. IHC – Dab chromagen. Ob10. Ok40 |
 | Picture 8. Estrogen low positive. IHC – Dab chromagen. Ob10. Ok40 |
The decidual index of the main group of estrogen receptors in the membrane is reduced by 2.1 times when expressed.The membrane level of progesterone in cells 3 and 11, respectively, compared with uncomplicated pregnancies, in decidual receptors of immune expression is reduced by 3 times.Thus, a study of the expression of estrogen and progesterone in the endometrial structures of the study groups revealed significant differences in the form of a significant decrease in indicators in women suffering from recurrent miscarriage, in contrast to patients with uncomplicated pregnancy.To confirm chronic inflammation in the endometrium, an IHC reaction with anti-CD20 was performed. Positively stained CD20 in the endometrium was distributed unevenly, often forming perivascular and peritubular accumulations. Antigen expression in the cytoplasm was assessed as pronounced in all cases.Additionally, a quantitative calculation of cells in the field of view was carried out, confirming a significant increase in lymphocyte cells with CD20 immunophenotypes in the endometrium of women with recurrent miscarriage compared with uncomplicated pregnancy.Expression of CD 20 - 2 women (10%) had a strong positive reaction, 25% had a mild positive reaction, 40% had a moderate positive reaction and 25% had negative results.Of immunophenotypic cells of lymphocytes CD 20 in the endometrium was calculated. Significant cell growth has been established in women with miscarriage compared to women with uncomplicated pregnancies.In chronic endometritis, there was a more than 2-fold increase in the expression of receptors for estrogen and progesterone in the nuclei of glandular epithelium cells compared to normal endometrium. In quantitative terms, expression of progesterone receptors was found on average in a greater number of cells than expression of estrogen receptors. The ratio of steroid receptors ER / PR in the epithelium in chronic endometritis is 0.97, which differs significantly from the values in normal endometrium - 1.42. The E R / PR ratio in stromal cells is 0.41 and 0.58, respectively. The presence of changes in the ratio of steroid receptors in the endometrium indicates, first of all, dysfunctional disorders of tissue reception against the background of chronic inflammation.It is important to note the interdependence of the listed causes of recurrent miscarriage; for example, the level of progesterone has a direct effect on the cytokine system. With low progesterone levels or receptor damage, a low level of progesterone-induced blocking factor was detected. Under these conditions, the mother's immune response to the trophoblast is realized with a predominance of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which have a direct embryotoxic effect and contribute to abortion in the 1st trimester.
4. Conclusions
1. The identified changes require further study of the problem by pathomorphologists, obstetricians-gynecologists, and immunologists to determine the pathomorphological mechanisms of the development of non-developing pregnancy in each married couple. This will allow obstetricians and gynecologists to focus on a detailed examination of married couples and carry out comprehensive prevention of miscarriage.2. The results of the studies made it possible to establish new links in the pathogenesis of miscarriage due to intrauterine infection.3. Immunohistochemistry makes it possible to more accurately diagnose and monitor the effectiveness of hormonal treatment, provides an individual approach to the patient and, therefore, allows optimizing hormonal therapy regimens.
5. Practical Recommendations
The established morphological and immunohistochemical features of the endometrium emphasize the importance and need for a comprehensive study of scrapings and biopsies in the algorithm for examining patients with infertility and miscarriage.
References
| [1] | Matrizaeva G.D. Immunohistochemical aspects of miscarriage problems / Talqin va tadqiqotlar 2022 yil No. 10 182 pages. 184. |
| [2] | Matrizaeva G.D. Immunohistochemical method for examining the endometrium in cases of recurrent miscarriage in the first trimester / The Journal of humanities and natural sciences/vol.I(2023) p. 93. |
| [3] | Matrizaeva G.D., Yusupova M.A. Ultrasound prognostic signs of miscarriage and placental insufficiency in the 1st trimester of gestation. / News of dermatovenereology and reproductive health No. 3-4 (79-80) (1) Tashkent 2017 p. 87. |
| [4] | Matrizaeva G.J., Saparbaeva I.R., Ikramova Kh.S./ To determine the effectiveness of preconception preparation in patients with hyperandrogenism to reduce the incidence of obstetric and perinatal complications/ Biology va Tibbyot muammolari. 2021. №1. 1(126) pp. 188-190. |
| [5] | Characteristics of Natural Killer Cell Interaction with Trophoblast Cells During Pregnancy / DO Bazhenov [et al.] // Current Molecular Medicine. – 2019. – Vol. 19, No. 10. P. 97-104. |
| [6] | Developmental and Functional Control of Natural Killer Cells by Cytokines / Y. Wu, Z. Tian, H. Wei // Front. Immunol. – 2017. – No. 8. – R. 930. |
| [7] | Genetic polymorphisms associated with impaired folate cycle and the risk of thrombophilia in patients with retrochorial hematoma in the first trimester of pregnancy/NB Bushtireva, EI Kuznetsov// With linicalmedicine. – 2015. – Vol. 7, No. 3. – P. 84 – 88. |
| [8] | Investigation of systemic inflammatory response in first trimester pregnancy failure / J. Calleja-Agius, E. Jauniaux, AR Pizzey [at al.] // Hum. Reprod. – 2012. – Vol. 27. – P. 349–357. |
| [9] | Matrizayeva GD, Ikhtiyarova GA/ Immunohistochemical features of the endometrium in miscarriage/ World Bulletin of Publik Health Vol. 17 (2022): WBPH p. 45-62. |
| [10] | Recurrent Pregnancy Loss / eds. S. Mehta, B. Gupta. – Springer Nature Singapore: Pte. Ltd., 2018. P. 431. |
| [11] | Recurrent pregnancy loss: current perspectives / HE Hachem [et al.] // International Journal of Women's Health. – 2017. – No. 9. – R. 331 – 345. |
| [12] | Recurrent Pregnancy Loss and Inherited Thrombophilia / S. Singla,S. Jain // Recurrent Pregnancy Loss / eds. S. Mehta, B. Gupta. – Singapore: Springer, 2018. – R. 113 – 128. |
| [13] | Recurrent pregnancy loss is associated with leaky gut: a novel pathogenic model of endometrium inflammation? / C. Tersigni [et al.] // Journal of Translational Medicine. – 2018. – No. 16. – R. 102. |
| [14] | The distal upstream region of insulin-like growth factor–binding protein-1 enhances its expression in endometrial stromal cells during decidualization / I. Tamura [et al.] // Biol. Chem. – 2018. – Vol. 293, no. – R. 5270 – 5280. |
| [15] | The Elusive Role of Placental Macrophages: the Hofbauer Cell / MZ Zulu, F. O. Martinez, S. Gordon, C. M. Gray // Innate Immun. – 2019. – No. 10. R. 1 – 10. |










 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML




