-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Advances in Life Sciences
p-ISSN: 2163-1387 e-ISSN: 2163-1395
2012; 2(3): 65-67
doi: 10.5932/j.als.20120203.04
Genotoxic Effects of Hypericum heterophyllum Vent. in Human Lymphocytes Cultures
Afide Öcal1, Halil Erhan Eroğlu2
1Bozok University, Science Institute, Department of Biology, Yozgat, 66200, Turkey
2Bozok University, Faculty of Science and Art, Department of Biology, Yozgat, 66200, Turkey
Correspondence to: Halil Erhan Eroğlu, Bozok University, Faculty of Science and Art, Department of Biology, Yozgat, 66200, Turkey.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Hypericum species, growing wild in Anatolia, widely used in traditional medicine in . In order to determine the genotoxic effect of Hypericum heterophyllum, human lymphocytes were incubated with the aqueous extracts. The increasing extract concentrations of Hypericum heterophyllum induced micronucleus. The rise of micronucleus shows that Hypericum heterophyllum at high concentrations may become carcinogenic and genotoxic. The positive correlation was observed between micronucleus and age. Also, the positive correlation was observed between micronucleus rates of female and male. Further studies will be needed to determine the effects of the main bioactive components isolated from this species on micronucleus.
Keywords: Hypericum, Genotoxic, Micronucleus
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Traditional oriental herbal prescriptions have become popular over the past decade; they are widely used for the treatment and prevention of various diseases due to their effectiveness[1].The genus Hypericum L. ( Wort, Hypericaceae) includes at the most recent count, 484 species that are either naturally occurring on, or which have been introduced to, every continent in the world, except . These species occur as herbs, shrubs and infrequently trees, and are found in a variety of habitats in temperate regions and in high mountains in the tropics, avoiding only zones of extreme aridity, temperature and salinity[2]. Hypericum heterophyllum Vent., an Endemic Turkish species, is a source of medicinal compounds and well known with its antifungal activity[3]. A micronucleus (MN) is a small extra nucleus separated from the main one, generated during cellular division by late chromosomes or by chromosome fragments. Because of its association with chromosomal aberrations, MN has been used since 1937 as an indicator of genotoxic exposition based on the radiation studies conducted by Brenneke and Mather[4]. Investigations on MN frequencies support the widely accepted assumption that MN is a product of early events in human carcinogenic processes[5]. Evaluation of the genotoxic potential is one of the most important nonclinical safety studies required for registrationand approval for marketing of pharmaceutical products. Furthermore, studies on the genotoxicity of medicinal plants used by the population are needed to identify those which pose mutagenic and carcinogenic risks. In the present work, we attempted to evaluate the genotoxic effects of Hypericum heterophyllum extracts used in traditional medicine in . For this purpose, the extracts were assessed by the micronucleus (MN) on human peripheral blood lymphocytes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of the Extracts
- Aqueous extracts (AE) (decoction) were prepared by boiling the air-dried aerial parts of the plants grounded by mechanical mill in water at 100℃ for 5 min in the case of decoction. Preparations were sterilized through a filter and stored at + 4℃.
2.2. Chemicals
- PB karyotyping medium (Biological Industries, ), colcemid (, ), cytochalasin B (Sigma) and giemsa stain () were used in peripheral blood cultures. PB karyotyping medium is based on RPMI-1640 basal medium supplemented with l-glutamine, foetal bovine serum, antibiotics (gentamycin) and phytohemagglutinin.
2.3. In Vitro Micronucleus Assay
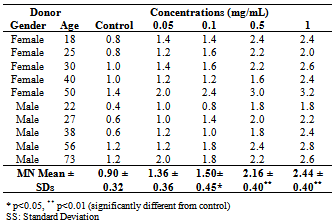
- After getting approval from , heparinized blood samples (0.4 mL), obtained from ten healthy donors, were placed in sterile culture tubes containing 5 mL of PB karyotyping medium. Then, AE were added to obtain the four final concentrations (0.05, 0.1, 0.5 and 1 mg/mL). After mixing the contents of each culture tube by gently shaken, the culture tubes were incubated in a slanted position at 37℃ for 72 h. Cytochalasin B was added at 44 h of incubation at a final concentration of 5 µg/mL to block cytokinesis. After 72 h of incubation, the cultures were harvested and stained according to Fenech and Morley[6].
2.4. Statistical Analysis
- The computer software program SPSS 10.0 was used to analyze the data. The statistical significance of the effects of Hypericum heterophyllum on the MN was assessed using repeated measures of the analysis of variance (ANOVA) and the differences between groups were determined by the Tukey-Kramer test with p < 0.01 and p < 0.05 were considered significant. Correlation and regression coefficients were calculated between two parameters (MN and doses, MN and age, MN male and MN female).
3. Results and Discussion
- Hypericum species, growing wild in , are aromatic plants. In this study, genotoxic and clastogenic effects of Hypericum heterophyllum were investigated in cultured human lymphocytes. The peripheral lymphocytes are one of the best materials for the determination of cytogenetic effects. The MN technique has been proposed as a useful tool for measurement of genotoxicity in vivo and in vitro cultures. MN arises during cell division either from chromosomes that are lagging in anaphase or from chromosome fragments[6]. In living creatures, which are exposed to a mutagen factor, the probability of formation of mitotic and meiotic defects is increased and the rate of MN could increase due to this increase[7]. Alcohol consumption, smoking and viral infections increase MN rates in peripheral blood lymphocytes[8]. The donors chosen for this study did not smoke or consume alcohol. They had not been exposed to X-ray and gamma-ray and they did not have any viral infections.
|
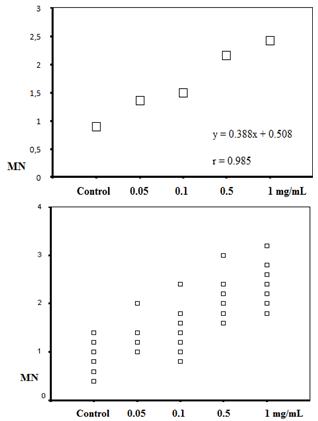 | Figure 1. The positive correlations between micronucleus and the extract concentrations |
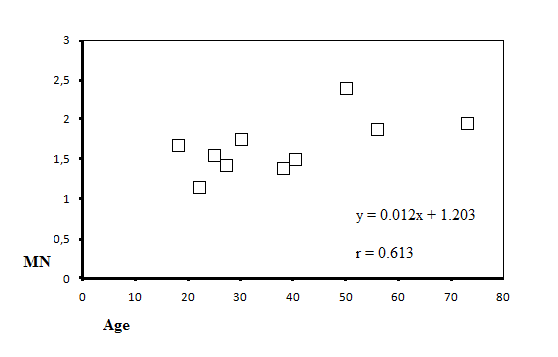 | Figure 2. The positive correlation between micronucleus and age |
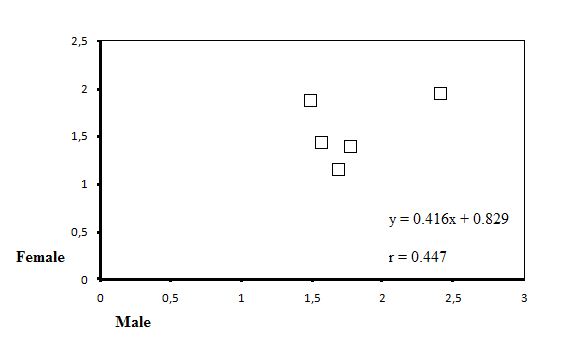 | Figure 3. The positive correlation between MN rates of female and male |
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- This study was supported with research projects (I.F.E-2011/49) by the Scientific Research Projects Fund of Bozok University.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML