-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Microbiology Research
p-ISSN: 2166-5885 e-ISSN: 2166-5931
2014; 4(6A): 10-17
doi:10.5923/s.microbiology.201401.02
Infection and Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria in Developing Countries: A Genetic Review
Effat Al-Judaibi
Department of Biology, King Abdul Aziz University, Jeddah, KSA
Correspondence to: Effat Al-Judaibi , Department of Biology, King Abdul Aziz University, Jeddah, KSA.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
About 90% of deaths due to infection worldwide are caused by antibiotic-resistant microorganisms. Multidrug-resistant bacteria have become a major health concern. With new generations of virulence and resistant bacteria, we need to improve our understanding and produce novel techniques to control these pathogenic bacteria. In our review, we focus on five pathogenic bacteria with completed genome sequences, which provide a better target for a new generation of antibiotics.
Keywords: Resistant, Antibiotic, Bacteria, Genetic, Infection disease
Cite this paper: Effat Al-Judaibi , Infection and Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria in Developing Countries: A Genetic Review, Journal of Microbiology Research, Vol. 4 No. 6A, 2014, pp. 10-17. doi: 10.5923/s.microbiology.201401.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Infections cause 45% of deaths in low-income countries, and half of all deaths worldwide. Furthermore, about 90% of these deaths are due to one of the following diseases: respiratory infections (mainly pneumonia), HIV/AIDS, TB, malaria and measles [1].Infections caused by antibiotic-resistant microorganisms have become a major problem. Infections from resistant bacteria are now too common, and some pathogens have even become resistant to multiple types or classes of antibiotics. The loss of effective antibiotics will impair our ability to fight infectious diseases and to limit complications that are common in patients undergoing chemotherapy for cancer, dialysis for renal failure or surgery, and especially organ transplantation, for which the ability to treat secondary infections is very important. If infection from resistant pathogens is not effectively treated because of resistance, microorganisms can persist and spread, thereby expanding the problem. The emergence of new forms of resistance that have not been previously encountered also remains a risk. Today, there are about six different deadly bacteria that have strains resistant to all or virtually all antibiotics: Enterobacteriaceae (especially Escherichia coli, Salmonella spp., and Klebsiella pneumoniae), Acinetobacter spp., Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterococcus spp., Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and Neisseria gonorrhoeae [2-5].Although resistance of bacteria to antibiotics can be natural, bacteria can also become resistant to an antibiotic through a genetic mutation or by acquiring resistance from another bacterium. One type of mutation, a spontaneous change in the bacteria's genetic material that provides a different type of resistance, is rare and only occurs with a ratio of about 1:106 to 1:107. Mutations can impact bacterial cells in different ways. Some mutations enable bacteria to produce enzymes or other active chemical compounds that inactivate antibiotics, whereas others remove target cells that are attacked by antibiotics, close up entry ports that allow antibiotics inside cells, or produce pumping mechanisms that block antibiotics from reaching their target [6-12]. Bacteria can acquire antibiotic-resistant genes from other bacteria in several ways; Conjugation in bacteria can transfer genetic material from a donor to an acceptor, which can include antibiotic-resistant genes found on plasmids and transposons. Viruses can pass resistant genes between bacteria by bacteriophages. For example, clonal variants of the severe Haemophilus influenzae biogroup aegyptius disease have been shown by PCR-based genome hybridization to contain both plasmid and chromosomal regions that have been transported by bacteriophages [13]. Bacteria also have the ability to acquire free DNA from their environment. Using these methods of transfer, bacteria acquired from a resistant gene become resistant to one or more antibiotics depending on the timing and quantity of the genes that have been transferred [14].Populations of antibiotic-resistant bacteria can spread vertically by passing on resistant gene or genes to new generations, or horizontally by exchanging genetic material from one bacterium to another or between different bacterial species. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria lose acquired resistant genes more slowly than they were acquired when conditions favorable to antibiotic resistance are removed. If these resistant genes are lost, new generations of the bacteria will respond to antibiotics [10, 11].In this review, we focus on antibiotic-resistant bacteria in developing countries, genes that have mutated in several of the most important antibiotic-resistant bacteria, and ways to prevent infection with these resistant bacteria.
2. Transfer of Microorganisms and Infections
- Diseases can be spread directly or indirectly from one person to another. Zoonotic diseases are infectious diseases of animals that can be transmitted to humans, most of which are caused by viruses, protozoa or fungi [10, 15].In epidemics, there are often extensive interactions within centers or groups of infected individuals, and other interactions within discrete groups of susceptible individuals. Despite low interaction between discrete groups, diseases can be transmitted to and spread in susceptible individuals via a single or a few interactions with an infected person. Thus, infection rates in small networks can be reduced somewhat if interactions between individuals in infected groups are controlled [16]. Pathogenic microbes can be transmitted through insect or animal bites or from exposure to organisms in the environment; for example, in Legionnaires disease caused by Legionella pneumophila, a human pathogen might have developed in air conditioning systems in houses [6]. There is also an increase in foodborne infections, promoting concern about drug resistance in the pathogens Salmonella and Campylobacter [1]. Water is one of the most important sources of contamination with pathogenic microbes. Epidemics can be caused by flooding or irrigating crops with water contaminated with fecal material. For example, Campylobacter jejuni, the Shiga-toxin-producing strain E. coli O157:H7, and other haemolytic–uraemic syndromes infect agricultural animals, and can then obtain access to humans through food, milk, water, or direct animal contact [17]. Other enteric pathogens including vibrios that cause classic cholera (the re-emerging serogroup O139 cholera), and the zoonotic protozoa Cryptosporidium parvum and Cyclospora cayetanensis come from the environment or from animals through human ‘faecal–oral’ transmission through water [18]. According to the World Health Organization, half of the population of developing countries is suffering from waterborne infectious diseases in a given year, and 3.4 million people die annually from consuming fecally contaminated water; most of these are children and infants [1]. In a study of isolated bacteria from drinking water samples from Karachi that were tested for their susceptibility and resistance to 14 commonly used antibiotics, Klebsiella, followed by Pseudomonas, were the most common bacteria found in the drinking water samples, whereas E. coli and Staphylococcus aureus were the least common. Almost all isolated bacteria were found to be resistant to Ampicillin (99%), and sensitive to Amikacin (96%) and Imipenem (96%) [19]. Another major problem is the hospital acquired infection "nosocomial" that causes about 40,000 deaths a year in the USA, which is almost always caused by drug-resistant microbes [20].
3. Drug Resistant Bacteria
- Recently, several bacteria have become the most deadly source of infection by microorganisms. For example, the fatal S. aureus USA300 identified in 1998 is thought to be the primary strain that causes community-acquired staph infections in the United States, Canada and Europe. In 2006, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported that 64% of methicillin-resistant S. aureus isolated from infected patients was caused by the USA300 strain that contains the cytotoxin Panton-Valentine leukocidin, which targets leukocytes and contains modulin, a phenol-soluble peptide that is capable of lysing neutrophilic granulocytes. These toxins cause progressive fatal conditions such as necrotizing pneumonia, fasciitis, and severe sepsis, which kills an estimated 20-40 thousand people annually [21]. Moreover, the new strain of E. coli O104:H4 caused a foodborne illness in 2011, mainly in northern Germany. The illness was characterized by bloody diarrhea and had a high frequency of serious complications including hemolytic-uremic syndrome. It was caused by an enteroaggregative E. coli strain that had acquired genes to produce Shiga toxins [22]. Below, we focus on the genome composition of some antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
3.1. Escherichia Coli
- E. coli are normal microflora in the intestines of healthy humans and animals. Most E. coli varieties are harmless or cause relatively brief diarrhea. But a few specific strains are fatal, such as E. coli O157:H7, which causes severe abdominal cramps, bloody diarrhea, and vomiting.E. coli has a circular plasmid, and a circular chromosome with about 4,600 kb, 4,300 potential coding sequences, and only 1,800 known E. coli proteins. The chromosomal DNA has been completely sequenced; 70% of the chromosome is composed of single monocistronic genes, 6% is polycistronic genes, and about 30% of the sequenced open reading frames (areas that look like they could be protein coding genes) have unknown functions [23, 24]. There are many different strains of E. coli that have different genotypes from the wild-type E. coli. The genotype affects the phenotype, physiology, and life cycle expressed in each strain, which is reflected in their ability to live in different kinds of animals. The variety of strains of E. coli is mostly caused by mutation in genomes, although E. coli can also transfer its DNA through bacterial conjugation with other related bacteria to produce more mutations and strains.The evolution of the E. coli O157:H7 genome shows a divergence into two distinct lineages (I and II), which appear to have different ecological characteristics. Microarray comparative genomic hybridization was used to identify genomic differences between the strains 31 and O157:H7, which have different lineage-specific polymorphism assay types. Lineage I strains are more commonly associated with human disease than lineage II. The genomic composition of these subgroups suggests that genomic differences and side gene transfer have contributed to E. coli evolution. In addition, the genomic differences between lineages I and II may contribute to our understanding of the epidemiology and ecology of different strains of E. coli such as O157:H7 [25-27].
3.2. Staphylococcus Aureus
- The most complete genome sequence compared to other microbial species is that of the S. aureus genome. Its map is based on the strain NCTC 8325, and there are six other completed strains: COL, N315, Mu50, MW2, MRSA252, and MSSA476. The circular genome map of the strain NCTC 8325 showed ~2,900 open reading frames, 61 tRNA genes, 3 structural RNAs, and 5 complete ribosomal RNA operons. Similar to other S. aureus strains, it has 33% GC content and a gene length of about 824 nucleotides with 85% as the coding sequence; the coding sequence is mostly composed of two parts, each of which is located on one replichore. Differences in S. aureus populations appeared by a combination of mutation, recombination, and horizontal gene transfer [29-32].Virulence factors in S. aureus can be encoded by phages, plasmids, pathogenicity islands, or the staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec, whereas increased antibiotic resistance can be encoded by the transposon Tn1546, which is inserted into a conjugated plasmid that also encodes for resistance to disinfectants. The methicillin-resistant S. aureus transfers to the modified penicillin-binding protein encoded by the mecA gene that is located on plasmids or other similar DNA [33, 34].
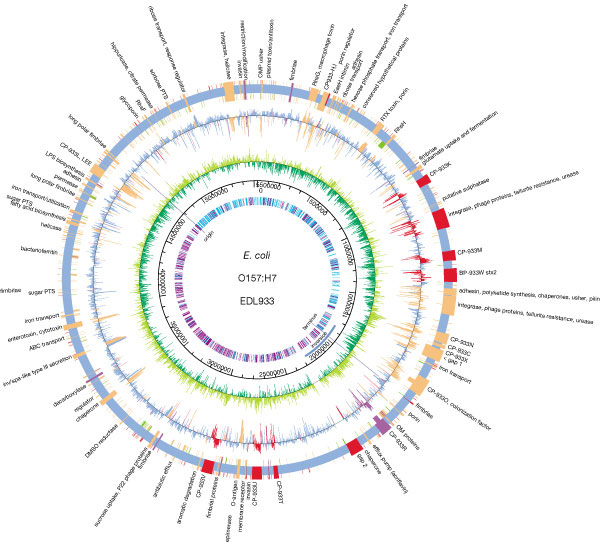 | Figure 1. Escherichia coli O157:H7 genome [28] |
- In 2006, the genome sequence of S. aureus USA300 was conducted to obtain a single circular chromosome of 2,872,769 base-pairs and 2,560 genes, which contained 3.1 and 27 kb plasmids, respectively. Further, the genome contained genes encoding for the cytotoxins phenol-soluble modulin and Panton-Valentine leukocidin, and for the arginine catabolic mobile element that had been acquired by USA300 from S. epidermidis by horizontal gene transfer, which explains the spread of Staph infections through the skin [35].
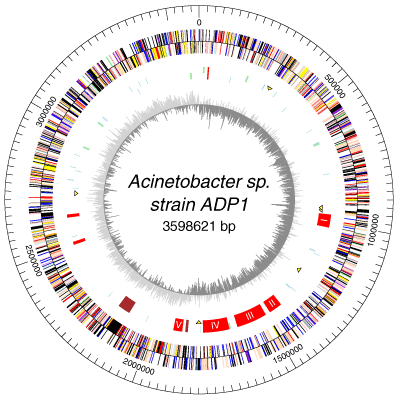
3.3. Acenatobacter Baumannii
- The single circular chromosome of A. baumannii contains 3,976,747 base pairs, in which 3,454 are used for protein coding. The strain AYE contains an 86 kb resistance island called AbaR1, which is made up of 45 resistant genes, and 25 genes that code for resistance against the antibiotics tetracycline, aminoglycosides, cotrimoxazole, and chloramphenicol [37, 38]. Class 1 integrons, which are chromosome sections capable of recombination, expression, and integration, have 14 resistant genes. The presence of amino acid sequences in common with other organisms demonstrates genetic exchange. Of a total of 88 genes, 39 are originally from Pseudomonas spp., 30 from Salmonella spp., 15 from Escherichia spp., and 4 from other bacteria [39, 40]. Mobility elements were found on 22 open reading frames. The A. baumanni AYE strain has three plasmids, but none contain resistant markers [41].
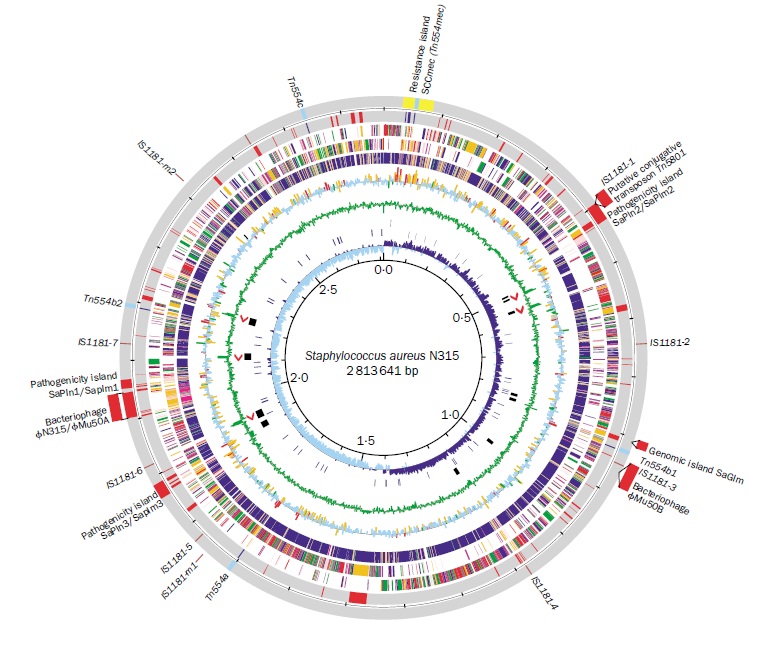 | Figure 2. Staphylococcus aureus N315 genome [36] |
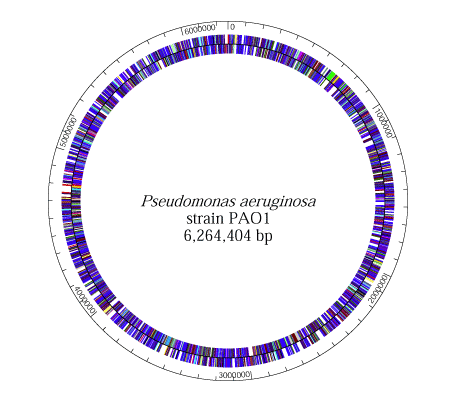
3.4. Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
- PA01 and PA14 are the two strains of P. aeruginosa with complete genome sequences. They are nearly identical; 96.3% of the DNA sequence of PAO1 is in PA14, and 92.4% of the PA14 DNA sequence is in PA01 [43, 44].The P. aeruginosa genome contains about 5.2 to 7 million base pairs with 65% GC content combined with variable amounts of accessory fragments and a conserved core. The highly variable accessory genome is characterized by a set of tRNA-integrated islands and islets, whereas the core genome consists of a low level of nucleotide divergence of 0.5% and a conserved synteny of genes that are in the same chromosome [45]. P. aeruginosa has a supercoiled circular chromosome in the cytoplasm. It also has a lot of chromosome-mobilizing plasmids that are significant to the organism’s pathogen. The plasmids, TEM, OXA, and PSE, for example, are encoded for extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs) production, which is necessary for its resistant antibiotics, thus allowing P. aeruginosa to be an enormous pathogen [46-48].
3.5. Vibiro Cholerae
- V. cholerae El Tor N16961 genome has been sequenced, and contains two circular chromosomes; one has 2,961,149 base pairs with 2,770 open reading frames and the other with size of 40% of the entire genome has 1,072,315 base pairs with 1,115 open reading frames. The larger chromosome contains crucial genes for toxicity, the regulation of toxicity, and important cellular functions such as transcription and translation [49-51]. The determination of the second chromosome is different from that of a plasmid or megaplasmid due to the inclusion of housekeeping and other essential genes in the genome including essential genes for metabolism, heat-shock proteins, and 16S rRNA genes. A significant proportion of the genome is replicon [49]. In addition, V. cholerae contains a genomic island of pathogenicity and is lysogenized with phage DNA. The pathogenicity of the bacteria may become integrated into the bacterial genome with the virus genes [52].
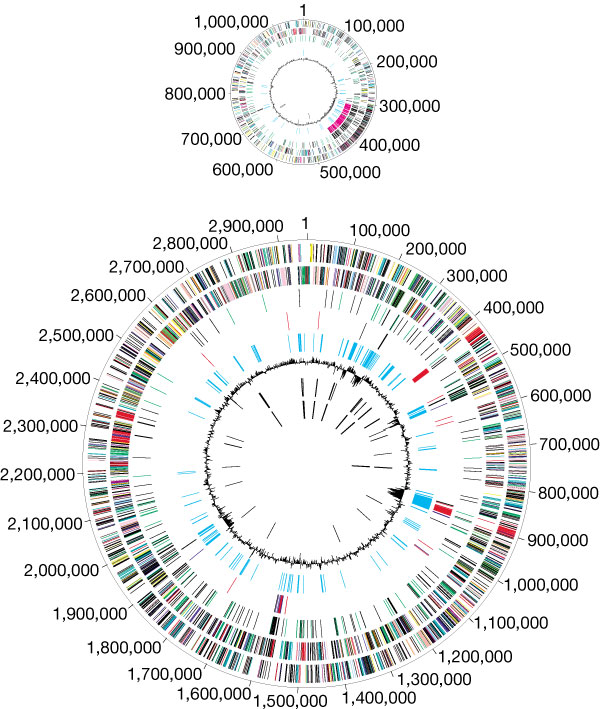 | Figure 5. Vibiro cholerae PA01 genome [49] |
4. A Promising Future
- Since the discovery of microbial pathogens, science is developing new antimicrobial agents, and with the new scientific revolution, several methods including molecular techniques have been developed. Identification of the bacteria genome structure provides an accurate understanding of the virulence of pathogenic bacteria and of the properties controlling the pathogens, thereby preventing infection. However, we still need to develop new promising medications including antibiotics and vaccines, and new methods for chemotherapy and organ transplants.With $30 million annual funding over five years, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Antibiotic Resistance Initiative has succeeded in reducing antibiotic resistance associated with: 50% of C. difficile, which saves 20,000 lives, prevents 150,000 hospitalizations, and reduces healthcare costs by more than $2 billion; 50% of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae infections; 30% of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas, a common cause of infections; 30% of invasive methicillin-resistant S. aureus; and 25% of multidrug-resistant Salmonella infections [53].
5. Conclusions
- Multidrug-resistant bacteria have become a major health issue. With new generations of virulence and resistant bacteria, we need to improve our understanding and produce novel techniques to control these pathogenic bacteria. In our review, we focused on five pathogenic bacteria with completed genome sequences, which provide a better target for a new generation of antibiotics.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML