-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Materials Science
p-ISSN: 2162-9382 e-ISSN: 2162-8424
2015; 5(2A): 6-9
doi:10.5923/s.materials.201501.02
Surface Characterization and Catalytic Activity for Alumina-Supported Cobalt Acetate
Somia M. Abad-Elwahad 1, Ali F. Bukhzam 2, Gamal A. H. Mekhemer 3
1Chemistry Department, Faculty of Science, El-Marj University, Benghazi, Libya
2Chemistry Department, Faculty of Science University, Benghazi, Libya
3Chemistry Department, Faculty of science Minia University, El-Minia, Egypt
Correspondence to: Somia M. Abad-Elwahad , Chemistry Department, Faculty of Science, El-Marj University, Benghazi, Libya.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Supported cobalt oxide samples were prepared by wet impregnation, using alumina gel and alumina as support materials and aqueous cobalt acetate tetrahydrate as the impregnating solution. Prior to application, the support materials were ground to ≤ 200 µm. The impregnation solution was prepared by dissolving a calculated amount of the precursors CoA of the required loads 3, 5, 10 and 15 wt % CoOx in the final supported oxide materials in a suitable volume of distilled water (25 cc/g support). The catalysts characterized by different technique like X–ray diffractometry, Ex–situ fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. XRD and Ex–situ FTIR spectroscopic analyses of the supported catalysts were performed to get more information about the cobalt oxides loading up to 15 wt% exist as high intensity were results cobalt acetate suggested three bands indicated to formation of the cobalt (II) oxide. The catalytic activity results on the decomposition of Hydrogen peroxide on cobalt acetate suggested that the activity increased with increasing loading levels. Up to however we observe the following descending on catalytic activity order: CoAlOA > CoAlA.
Keywords: Characterization, Cobalt oxide and the catalytic activity results on the decomposition of Hydrogen peroxide
Cite this paper: Somia M. Abad-Elwahad , Ali F. Bukhzam , Gamal A. H. Mekhemer , Surface Characterization and Catalytic Activity for Alumina-Supported Cobalt Acetate, American Journal of Materials Science, Vol. 5 No. 2A, 2015, pp. 6-9. doi: 10.5923/s.materials.201501.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- There are two types of chemical interactions may occur depending on the nature of the transition metal oxide and also the preparation conditions, one leading to the formation of a ‘surface’ metal aluminate spinel form and the other to the segregation of stable oxides [1, 2]. The chemical and textural properties of the support influence the catalytic activity and selectivity of Cobalt nitrate and cobalt acetate catalysts via their modification on the reducibility and dispersion of cobalt or the formation of well fined phases. The synthesis of highly dispersed Cobalt acetate and cobalt nitrate catalysts requires strong interactions between the support and the Cobalt acetate and cobalt nitrate as precursor, but in turn such strong interactions generally lower the reducibility of such precursors [3, 4].Accordingly metal oxides used in the field of heterogeneous catalysis, both as catalysts and as supports for the so-called monolayer-type catalysts. In such applications the performance is determined by parameters like bulk metal oxide, surface area, the surface oxide structure and surface acidity [5, 6-8]. Also metal oxides must have high stabilities as well as high surface areas under conditions of their use both as catalysts and as support materials [9, 10]. Metal oxides containing transition metal ions are versatile materials which have received much attention in both science and engineering technology. They provide several technical applications, such as chemical sensors, heterogeneous catalysts and ion conductors. Among these materials, metal oxides having the spinel-type AB2O4 structure are often utilized as model systems due to their structural features which facilitate tailoring of relevant properties [11]. Cobalt oxide is one of the versatile materials among the transition metal oxides.Besides cobalt oxide supported on alumina catalysts are quite promising, among metal oxide supported catalysts, for the catalytic combustion of the volatile organic compounds (VOCs) [12]. Avariety of supports are used to prepare supported cobalt oxide catalysts depending on the properties required; however the bulk of the literature is concerned with high surface area oxide supports [13].Also cobalt oxides, both unsupported and supported on different oxide support materials (including alumina), have proven their high catalytic activity in the field of air pollution control of CO [14-16] and organic pollutants from effluent streams. It has been found that the obtained system has a high catalytic activity in some oxidation reactions, carried out in an aqueous and in a gaseous phase [17]. These changes could be normally accompanied by possible changes in surface and catalytic activity of the doped catalytic systems. Other physicochemical properties, such as thermal stability and oxidation state of solid catalysts could be modified by the doping process [18]. Supported metal oxides frequently have better catalytic properties than the pure oxide components. In particular, it has been found that mixed oxides can develop very strong surface acidity even when the pure oxide components do not show [4, 19-23].
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
- Thcobalt(II)acetteteterahydrate(CoA),(CH3COO)2Co.4H2O, MERCK, used as a precursor for supported and unsupport CoOX catalysts aluminium hydroxide Al(OH)3.xH2O, dry gel was purchased from SURECHEM Products LTD (SCP, England), used as supplied and high surface area of γ - alumina was obtained by calcinations of alumina gel (SCP) at 870 K for 3 h, in static atmosphere of air. Hydrogen peroxide H2O2: ARJHDTM Guandong Guanghua Chemical Factory CO., Ltd. Shantou, Guangdong, 515021. China, used as probe molecules to investigate the catalytic properties of the catalysts. Bi-distilled water: was employed, whenever water was needed.
2.2. Techniques
2.2.1. XRD
- XRD is a technique used for the identification of the bulk structure of macro–crystalline materials, which is used on measurement of structure–sensitive high energy X–ray radiation. X-ray powder diffractograms were recorded, using Ni–filtered CuKα- radiation (λ = 1.54056 Å); on a JSX – 60 PA Jeol X–ray spectrometer. The generator at 35 Kv and 20 mA, and the diffractometer at 2θ diverging and receiving slits and at a scan rate of 20 mm/ min. The sample ground to a particle size less than 44 μ and packed into the wall of a sample holder, and then mounted in a horizontal position. Diffraction patterns (I/I0 vis. d-spacing (Å)) derived from the powder diffractograms were matched with relevant ASTM-standard patterns. Crystallite sizing (Dhkl) was carried out using the line broading technique in conjunction with Scherrer's formula:
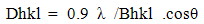 | (1) |
2.2.2. Ex–situ FT–IR Spectra
- Ex–situ FT–IR spectra of supports, unsupported and supported catalysts were taken at frequency range 4000–400 cm-1. This was done at a resolution of 4 cm-1 using a model Genesis–II FT–IR Mattson Fourier-transform infrared spectrometer (USA) and an online PC with win first Lite (V 1.02) software for spectra acquisition and handling. The spectra were taken for thin ( >20 mg /cm ) lightly loaded (> 1–Wt.% ) wafer of KBr–supported test samples. About 1–2 mg of the catalyst as a fine powder was mixed well with spectroscopy pure KBr powder and was finally grinded in agate mortar.
2.2.3. Catalytic Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide
- The catalytic activity was determined in solution. H2O2 decomposition was used to calculate the catalytic alumina supported cobalt oxide catalysts. The reaction was carried out at room temperatures to explore the catalytic activity of test catalysts towards H2O2 decomposition.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. XRD
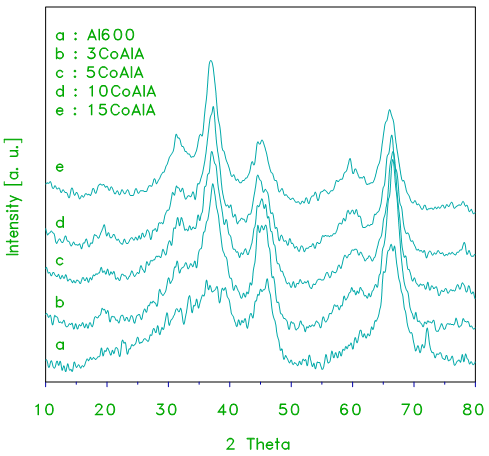
- XRD diffractograms of pure alumina and alumina supported cobalt oxide prepared from cobalt acetate at different loading levels are shown in Figs.1 and 2, respectively. The diffraction pattern exhibited by 3CoAlA (Fig.1) which exhibit a weak peaks for cobalt oxide (Co3O4) of a size (D = 12.3 ± 1nm, Table 2). These peaks grow stronger in the pattern of 15CoAlA, thus indicating formation of more Co3O4 and/or CoAl2O4 particles of larger size (D = 22.1 ± 1nm, Table 2). It is obvious that Co3O4 and/or CoAl2O4 particles established in these catalysts. Diffractograms obtained for CoAlOA catalysts prepared from crystalline oxide (xCoAlOA series) at different loading levels are displayed in Fig.2. XRD patterns of these catalysts reflected the same structure of xCoAlA. The difference is the high crystalline of these catalysts more than xCoAlA. The particle sizes of these catalysts increase with increasing the loading levels up to 15 wt % of CoOx. Also, the particle size of Co3O4 and/or CoAl2O4 in these catalysts are lower than the Co3O4 and/or CoAl2O4 in the catalyst prepared from crystalline alumina.
 | Figure 1. XRD patterns obtained for alumina and the indicated set of alumina-supported cobalt oxide (xCoAlA) catalysts prepared from cobalt acetate and alumina gel used as a support |
 | Figure 2. XRD patterns obtained for alumina and the indicated set of alumina-supported cobalt oxide (xCoAlA) catalysts prepared from cobalt acetate and crystalline alumina used as a support |
3.2. Ex-situ FTIR Spectra Cobalt Oxide Catalyst
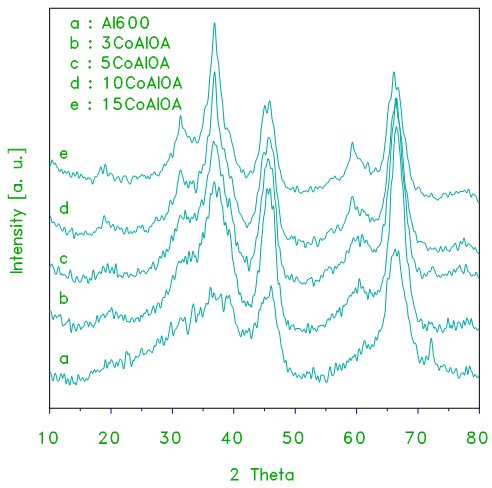
- The IR spectra of alumina supported cobalt oxide prepared from cobalt acetate used as a precursor xCoAlA and xCoAlOA catalysts are shown in Figs.3 and 4. The spectrum of cobalt oxide prepared from decomposition of cobalt acetate at 870 K for 3 h (Fig.3), displays two strong bands at 666, 573 and another weak band at 470 cm-1. These bands are characteristic to Co3O4 and/or CoAl2O4 [10, 20]. IR spectra of alumina supported cobalt oxide prepared from cobalt acetate display similar three bands, the intensities of these vibration bands increase with increasing the loading level of cobalt oxide due to the increase in the crystallinity of Co3O4.
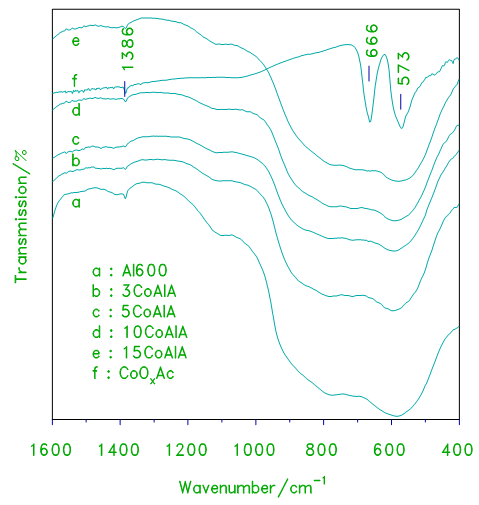 | Figure 3. FT–IR transmission spectra obtained for cobalt oxide, crystalline alumina and the indicated set of alumina supported cobalt oxide prepared from acetate xCoAlA catalysts |
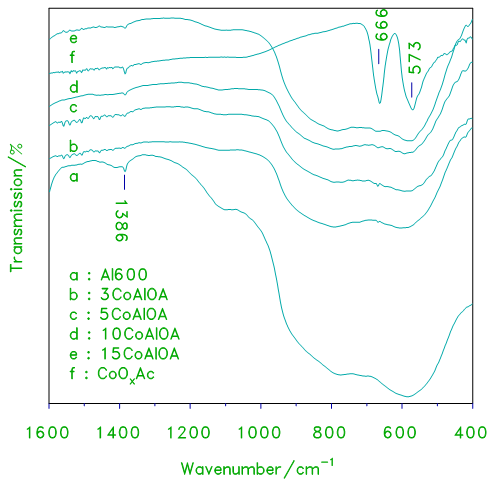 | Figure 4. FT–IR transmission spectra obtained for cobalt oxide, crystalline alumina and the indicated set of alumina supported cobalt oxide prepared from acetate xCoAlOA catalysts |
3.3. Catalytic Activity
- The catalytic decomposition of H2O2 was studied at RT over pure and alumina supported cobalt oxide catalysts prepared from cobalt acetate at different loading level (xCoAlA and xCoAlOA). Figs.5 and 6 show the decomposition of H2O2 on xCoAlA and xCoAlOA catalysts, respectively. Fig.5 display increasing the activity of the catalysts towards decomposition of H2O2 at RT with increasing the loading level of cobalt oxide on alumina. Zero-order kinetics were observed at low loading level (3CoAlA) and First-order kinetics were observed at high loading level (10 and 15 CoAlA). Inspection of Fig.6 revealed that the activity is increased with increasing the loading level similar to CoAlA catalysts. The activity of xCoAlOA is higher than the activity of xCoAlA is due to the formation of active sites Co3O4 on xCoAlOA more than on xCoAlA. These results are agreement with the results obtained from XRD of the supported cobalt oxide catalysts, which shows a sharp increase in intensities of the XRD patterns of Co3O4 phase.
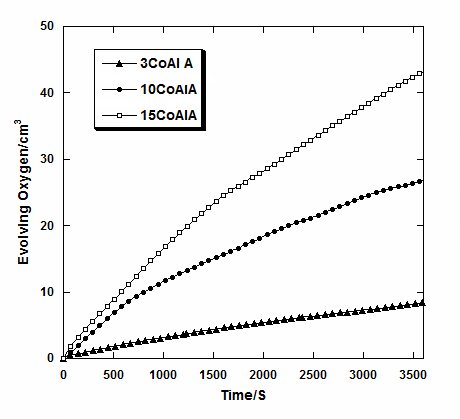 | Figure 5. VO2 – t plots constructed for H2O2 decomposition at RT on the indicated alumina supported cobalt oxide catalysts |
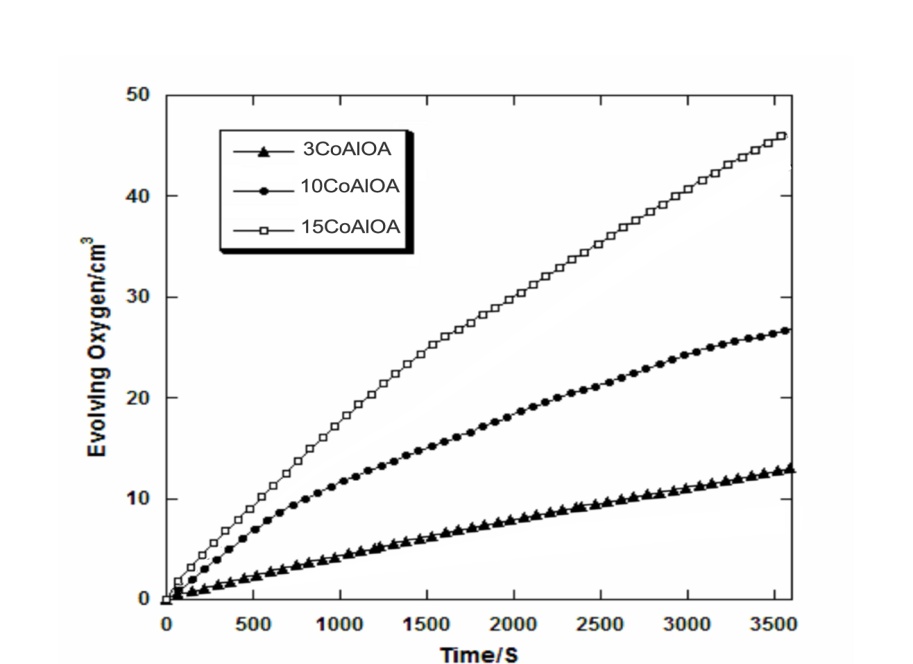 | Figure 6. VO2 – t plots constructed for H2O2 decomposition at RT on the indicated alumina supported cobalt oxide catalysts |
4. Conclusions
- XRD and IR results of cobalt oxide show the formation of crystalline Co3O4 and/or CoAl2O4 increasing the loading level of cobalt oxide (up to 15 wt%). The above presented and discussed results may help drawing the following conclusions:1 – The activity of all samples increase with increasing the loading level of cobalt oxides. 2 – The low loading levels catalysts display zero-order kinetics but higher loading levels catalysts show first-order kinetics.3 – The higher activity of the catalysts is due to the formation of active sites Co3O4. In contrast, the lower activity of catalysts is due to the formation of cobalt aluminate (higher loading level).
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML