-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Materials and Chemistry
p-ISSN: 2166-5346 e-ISSN: 2166-5354
2013; 3(A): 8-15
doi:10.5923/s.ijmc.201303.02
Silk Fibroin/Calcium Phosphate Silicate Composites: In vitro Bioactivity
Lachezar Radev1, Todor Gerganov2, Hristo Georgiev3, Antony Kolev4, Violeta Vassileva4, Rumiana Iankova5, Ekaterina Cholakova1
1Department of Fundamental Chemical Technology, University of Chemical Technology and Metallurgy, Sofia, 1756, Bulgaria
2Department of Silicate Technology, University of Chemical Technology and Metallurgy, Sofia, 1756, Bulgaria
3Department of Polymer Materials, University of Chemical Technology and Metallurgy, Sofia, 1756, Bulgaria
4Department Leather and Textile, University of Chemical Technology and Metallurgy, Sofia, 1756, Bulgaria
5Department of Inorganic Chemistry, Assen Zlatarov University, Bourgas, 8000 Bulgaria
Correspondence to: Lachezar Radev, Department of Fundamental Chemical Technology, University of Chemical Technology and Metallurgy, Sofia, 1756, Bulgaria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Keywords: Abstract Composite materials of Silk Fibroin (SF) and Calcium Phosphate Silicate (CPS) ceramic in the 15CaO-6SiO2-0.5P2O5 system were prepared by method of mixing different percentage of component weight. The structure was characterized before and after in vitro test by FTIR, SEM. The concentration of Ca, Si and P after in vitro test was analysed by ICP-AES. FTIR of the composites before in vitro test depicts that random coil and β-sheet structures co-exist in the composites. CPS ceramic has a significant effect on the secondary structure of SF. SEM observed that CPS particles uniformly dispersed in SF matrix. FTIR of the composites after in vitro test revealed that carbonate containing hydroxyapatite (CO3HA) was formed on the surface. B-type CO3HA preferentially formed in the sample with 75 wt. % CPS ceramic. SEM proved that hydroxyapatite (HA) formed in a high level. ICP-AES showed that HA precipitation were similar for the three c
Cite this paper: Lachezar Radev, Todor Gerganov, Hristo Georgiev, Antony Kolev, Violeta Vassileva, Rumiana Iankova, Ekaterina Cholakova, Silk Fibroin/Calcium Phosphate Silicate Composites: In vitro Bioactivity, International Journal of Materials and Chemistry, Vol. 3 No. A, 2013, pp. 8-15. doi: 10.5923/s.ijmc.201303.02.
1. Introduction
- It is well known that natural bone is a typical inorganic/organic composite comprising approximately 80 % HA and 20% collagen matrix. It is also known that the bone shows a porous structure, containing multiple levels of organization where HA crystals in nanolevel scale are embedded in collagen matrix.The biomimetical strategy, based on the idea of mimicking natural bones composition offers great promise for the design and fabrication of biomaterials for healing bone defects. Therefore, growing interest has been focused on the integration of HA ceramic with bio-organic polymers, such as collagen[1], gelatine[2], alginate[3], polylactic acid [4], polyamide[5] and silk fibroin (SF)[6-14]. Among them SF is of practical interest due to its excellent intrinsic properties utilizable in the biotechnological and biomedical fields. It is known that SF is composed from 17 aminoacids. It has been proved to be good biocompatible material and it has been successfully used for various medical applications. X. D. Kong et al.,[6] demonstrated that silk fibres could induce HA nucleation on the surfaces proteins in simulated body fluid (SBF) solution at pH=8 at room temperature. FTIR results proved that the HA crystals are CO3HA. On the other hand they also detected that there are strong chemical interactions between HA and SF protein. The presence of these bonds can be derived from the blue shift of amide II bond. For this reason, a co-precipitation method was often used to synthesize silk powder/HAnanocomposites[6-14]. For instance, L. Wang et al.[9] deposited HA on SF microspheres thorough the co-precipitation method. Others developed a HA/SF composite, where SF was modified with organic compound[15]. In other article, R. Kino et al.[16] reported that regenerated SF films containing calcium were coated with HA after soaking in 1.5 SBF solution for 6 hours. Y. Li et al.[17] proved that SF can induce HA deposition at 37℃ in 1.5 SBF. The effect of pH and initial Ca2+-H2PO4- concentration on the crystal growth of HA in the presence of SF is studied by Y. Ren et al.[12]. The authors evaluate the effect of pH and initial Ca-P concentration on the products of SF mineralization. They also demonstrated that that pH=7 promotes the transition of dicalcium phosphate dihydrate (DCPD) to HA. X. Kong et al. observed that SF can accelerate the phase transmittance of amorphous calcium phosphate to the crystal hybrid between DCPD and HA[18]. L. Li et al.[19] prepared SF/Calcium Phosphate (CP) composite by adding the different amount of Na2SiO3 to assess the effect of silicon on the HA formation in the composite. Based on the obtained results they proved that the addition of silicon could accelerate the HA crystal formation. SF/Wollastonite composite scaffolds were prepared by H. Zhu et al.[20] via freeze-drying method. The obtained results showed that the composite scaffold was in vitro bioactive, because it induced the formation of CO3HA on the surface after soaking in SBF for 5 days. Four type of hybrid films were fabricated from N. Vachiraroj et al.[21]. These materials include gelatin conjugated SF, HA/SF, HA/Gelatin conjugated SF and HA/Chitosan. The synthesized films were investigated in terms of in vitro adhesion, proliferation and oestrogenic differentiation with preosteoblast cell lines (MC3T3-E1) and rat bone marrow derived stem cells (MC3). The authors proved that MC3T3-E1 showed higher proliferation rate. In our previous works, we prepared some in vitro bioactive ceramics in the CaO-SiO2-P2O5[22-24], and CaO-SiO2-P2O5-MgO systems[25] through different ways. Furthermore, we have synthesized in vitro bioactive composite materials in the presence of collagen[26-28] and gelatin[29, 30] with the prepared ceramics powders. The purpose of the present article is preparing new bioactive composite by addition of SF with calcium phosphate silicate (CPS) ceramic and evaluating its bioactivity in 1.5 SBF solutions.
2. Experimental Part
- CPS ceramic powder in the system 15CaO-6SiO2-0.5P2O5, as an inorganic part of the composites, has been synthesized via polystep sol-gel method. The synthesized procedure and structure evolution is documented in Ref.[23]. SF without sericin was dissolved in 9M LiBr at 60oC for 4 hours and then dialyzed against with distilled water at room temperature for 3 days using cellulose membrane (MWCO 12000 Da) for 72 hours to remove the salts[21]. The final concentration of SF solution was 3 wt. %, which was determined in accordance with[20]. SF/CPS composites were prepared by mixing method without binding agents. Briefly, a certain amount of CPS powder was added into the SF solution under stirring for 4 hours in order to disperse the CPS particles uniformly. The obtained mixture was poured into plastic cup. The mixture was dried in the microwave oven for 10 minutes. In the present work, three kind of samples were made with the weight ratio of SF:CPS of 75:25, 50:50 and 25:75 (in wt. %), described as 75S25C, 50S50C and 25S75C.In vitro bioactivity of the prepared composites with different weight ratio of SF and SPS were evaluated by examining the apatite formation on their surfaces in 1.5 SBF solutions. 1.5 SBF solution was prepared from reagents as follows: NaCl=11.9925 g, NaHCO3=0.5295 g, KCl=0.3360 g, K2HPO4.3H2O=0.3420g, MgCl2.6H2O=0.4575g, CaCl2.2H2O=0.5520 g, Na2SO4=0.1065 g and buffering at pH=7.4 at 36.5℃ with TRIS=9.0075 and 1M HCl in distilled water. The synthesized composite materials were immersed in 1.5 SBF at human body temperature (36.6℃) in polyethylene bottles, in static conditions for 12 days. The samples were removed from the fluid after soaking, and gently rinsed with distilled water, then dried at 37℃ for 6 hours. To prevent a homogeneous apatite formation in the solution, it is known that 1.5 SBF needed to buffered at 7.25, as it is highly supersaturated and consequently unstable[31].The structure and the in vitro bioactivity of the synthesized SC composites were monitored by FTIR, ICP-AES and SEM.FTIR transmission spectra were recordered by using a Brucker Tensor 27 Spectrometer with scanner velocity 10 kHz. Diluted pellets of KBr were prepared by mixing of ~1 mg of the samples with 300 mg KBr. Transmission spectra were recordered using MCT detector with 64 scans and 1 cm-1 resolution. The samples were immersed in sealed test tubes containing 10 ml of 1.5 SBF solution for 12 days. The experiment was maintained at 37℃ in sterile polyethylene containers in static conditions. After immersion in 1.5 SBF for 12 days the samples were retrieved, gently rinsed with water, and dried at 37℃ for 6 hours. The ionic concentrations of Ca, P and Si of these solutions were determined by Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-AES), Iris 1000, Thermo Elemental, USA.Morphological studies of the obtained composite materials before and after in vitro test for 12 days have been done by using SEM. The samples were gold-sputter coated and viewed in the secondary electron mode with a field emission gun. Scanning electron Microscope (Philips 515) operated at an accelerating voltage of 2.5 kV.
3. Results and Discussion
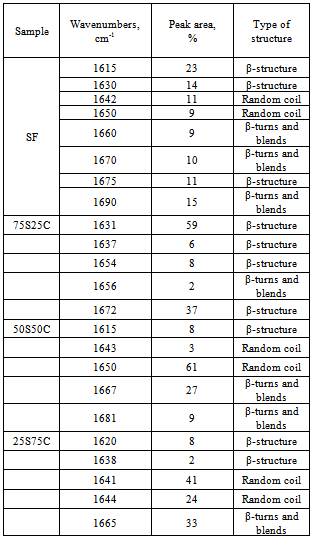
- FTIR spectra of SF and SC composites before in vitro test are shown in Figure 1 in the spectrum range 2000-400 cm-1.SF proteins exists in three conformations, namely random coil, silk I (α-form) and silk II (β-sheet). The absorption band posited at 1644 cm-1 for SF can be ascribed to the amide I mode, associated with random coil conformation occurring in the range of 1640-1650 cm-1, 1534 cm-1 for amide II in the random coil and the β-sheet conformations and 1240 cm-1 for amide III[19, 20, 31]. From the depicted in Fig. 1, a FTIR spectrum, we can assume that both random coil and β-sheets conformation are presented in the structure after microwave treatment of SF. On the other hand, three spectra of the composites with different wt. % of the SF and CPS (Fig. 1, b, c and d) show the peak shift from 1644 to 1638 cm-1 (for 75S25C sample), 1640 cm-1 (for 50S50C sample) and 1641 cm-1 (for 25S75C sample). In the case of 75S25C (fig. 1, b) the observed “red shift” could be ascribed to the conformational transition from random coil to β-sheet, i. e. antiparallel β-sheet conformation[32]. L. Li et al. reported that the same result can be observed, when the composite material synthesized through biomimetic way[19]. There is another possible interpretation, from our point of view : the depicted “red shift” can be assigned to the C=O: group which may interact with Ca2+ from partially dissolved CPS ceramic powder in SF solution under the preparation conditions of the composites. The same results can be observed for amide II and amide III region. New bands at 714-430 cm-1 appear in addition to the characteristic amide I, II and III absorption bands, after preparation of the samples, were assigned to the presence of CPS ceramic[23].
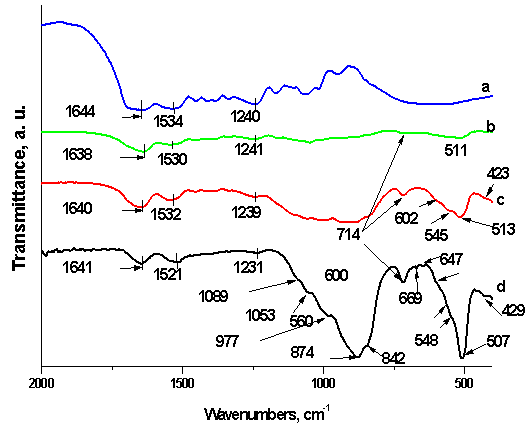 | Figure 1. FTIR spectra of SF (a), 75S25C (b), 50S50C (c) and 25S75C (d) before in vitro test |
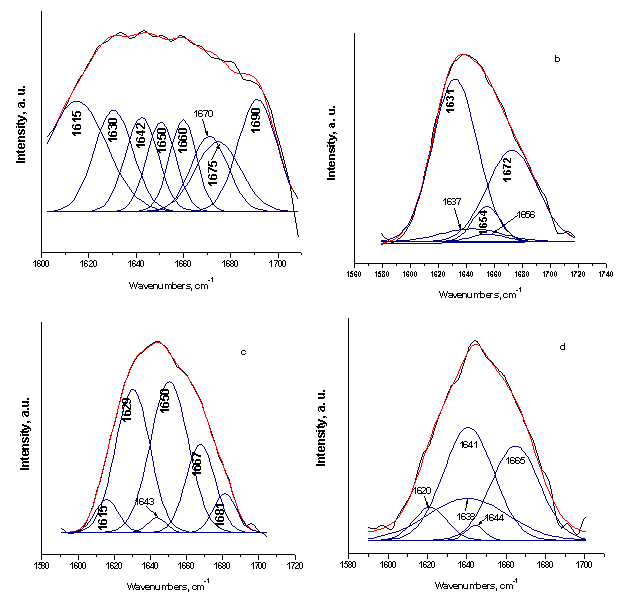 | Figure 2. Curve-fitting results of the FTIR spectra in the amide I region for the SF (a), 75S25C (b), 50S50C (c), and 25S75C (d) |
|
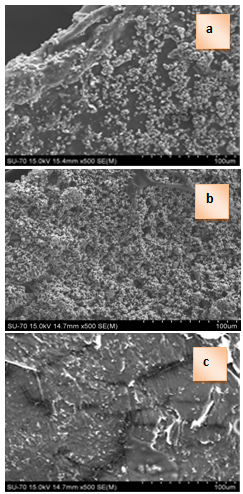 | Figure 3. SEM of 25S75C (a), 50S50C (b) and 75S25C (c) before in vitro test in 1.5 SBF |
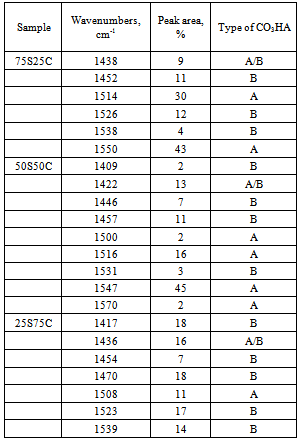
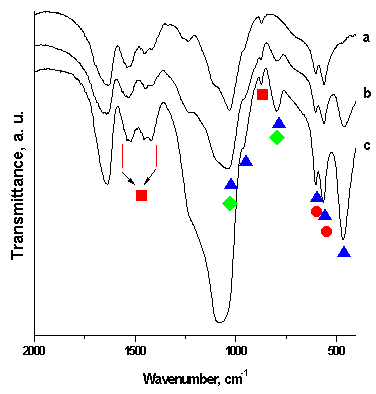 | Figure 4. FTIR spectra of the SF/CPS composites: 75S25C (a), 50S50C (b) and 25S75C (c) after in vitro test in 1.5 SBF for 12 days in static conditions |
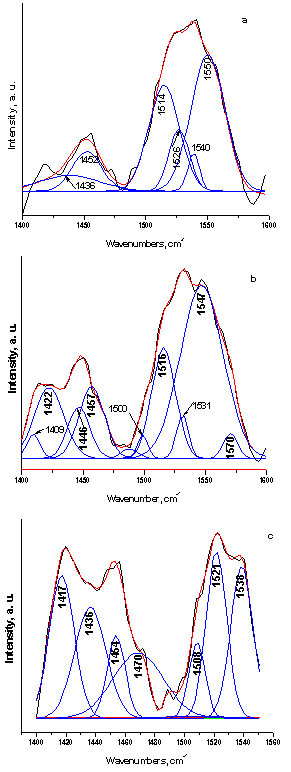 | Figure 5. Curve-fitting spectra of the type of CO3HA, formed on the surface of SF/CPS composites: 75S25C (a), 50S50C (b) and 25S75C (c) after in vitro test in 1.5 SBF for 12 days in static conditions |
|
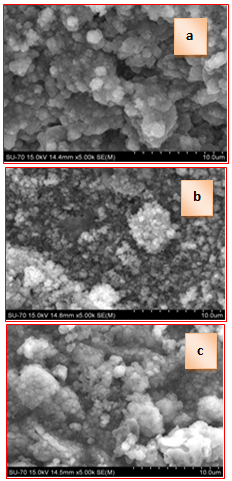 | Figure 6. SEM images for 75S25C (a), 50S50C (b) and 25S75C (c) after soaking in 1.5 SBF solution for 12 days |
4. Conclusions
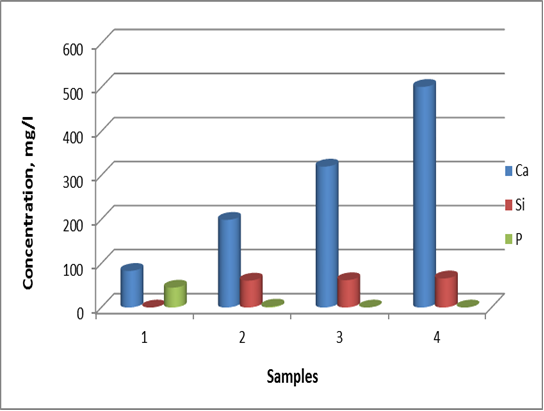
- The purposes of the presented article were to prepare and to evaluate in vitro bioactivity of composites between SF and CPS ceramic powder. The SF, denoted by S, was mixed with CPS ceramic powder, denoted by C, to prepare 75S25C, 50S50C and 25S75C composites. The obtained mixtures were treated in microwave oven to evaporate the water solvent. After drying, the prepared composites were soaked in 1.5 SBF for 12 days in static conditions to evaluate their in vitro bioactivity. The obtained composites were characterized by FTIR and SEM. The ionic concentration of Ca, Si and P were examined by ICP-OES technique.FTIR data of the composites before in vitro test proved that the “red shift” of amide II band becomes larger in comparison to amide I and II. These findings suggest that the chemical interaction exists between SF and CPS ceramic powder. After soaking of the synthesized samples in 1.5 SBF for 12 days FTIR results proved that B-, A- and A/B-type CO3HA are deposited on the surface. ICP-AES measurements have shown that the rates of Ca realize are ordered as follows: 25S75C>50S50C>75S25C. For the three samples, the Si concentration increased and P concentration decreased after immersion. Based on these results we suppose that Si-CO3HA may be formed on the composite surface. SEM of the immersed samples proved that there is high concentration of HA phase on the surface.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML