-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Architecture Research
p-ISSN: 2168-507X e-ISSN: 2168-5088
2014; 4(1B): 1-12
doi:10.5923/s.arch.201402.01
Towards a Different Architecture in Cooperation with Nanotechnology and Genetic Science: New Approaches for the Present and the Future
Didem Akyol Altun, Bora Örgülü
Department of Architecture, University of Dokuz Eylul, Izmir, Turkey
Correspondence to: Didem Akyol Altun, Department of Architecture, University of Dokuz Eylul, Izmir, Turkey.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Technological advancements and scientific researches, especially in nanotechnology and genetic engineering in the latter part of the 20th century, encourage new approaches for the architecture of the future at present. There have been many studies on genetic algorithms, nano-materials, nanostructures and “searching a new architecture” with the help of interdisciplinary relationships between architecture and nanotechnology and genetics. This study categorizes contemporary works in this field into three main approaches: the form-finding strategies helped by genetic algorithms, the hybrid designs with nano-materials or nano-sensors and the living architectures. Thus, the aim of this paper is to introduce new architectural approaches generated with the interdisciplinary domains of genetics and nanotechnology and to discuss them in the context of the future of architecture.
Keywords: Architecture of the Future, Genetic Architecture, Nanotechnology, Living Spaces
Cite this paper: Didem Akyol Altun, Bora Örgülü, Towards a Different Architecture in Cooperation with Nanotechnology and Genetic Science: New Approaches for the Present and the Future, Architecture Research, Vol. 4 No. 1B, 2014, pp. 1-12. doi: 10.5923/s.arch.201402.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The Information Age, which is regarded as the third grand social revolution of mankind [1], began with the rapid development of microelectronics and computer technology and also spread over all scientific fields. Technological advancements and scientific researches, especially in nanotechnology and genetic engineering in the latter part of the 20th century, encourage new approaches for the architecture of the future at present. There have been many studies on genetic algorithms, nanomaterials, nanostructures and “searching a new architecture” with the help of interdisciplinary relationships between architecture and nanotechnology and genetics from the 1990s to today [2].The science of genetics substantially developed over a short time by analyzing the genetic code of humans when the Human Genome Project was completed in 2000. From the developments within genetic science, a nano revolution occurred in the 21st century. Nanotechnology is the science of manipulating matter on an atomic and molecular scale, deals with structures measuring 100 nanometers or smaller, and involves developing materials or devices within that size. When the dimensions of materials are reduced to a nanometer criterion, quantum behaviors supersede the declared traditional behaviors, and physical properties begin to change. Electronic properties such as electric conductivity are changed conspicuously with the adherence of foreign particles to the existent nanomodel. When the foreign atom is a transition element, the nanomodel adheres to and can gain magnetic properties. For example, even though a diamond crystal constructed by carbon atoms is not normally a good conductor, the one-dimensional carbon atom chain can be rendered a fairly good conductor by means of nanotechnology [3]. Thus, if we could manipulate the molecular structure of matter on an atomic scale, either we would have new and moldable materials or the real genetic codes would take the place of digital codes and would be reshaped by the designer the user needs in the future.As we have seen, genetics and nanotechnology, which are the most transformative technologies we have ever faced, have the potential to radically alter our built environments and our lives. Both of them take their power from nature. Their main characteristics are based on the laws of nature. Thus, we can mention new architectural approaches built on genetics and nanotechnology, which are related to nature, natural principles, and life.However, the basis of these approaches goes back to computer technology and computational techniques that developed after 1960. Computer software called CAD/CAM technologies, which transfer the designs to drawings, making use of 3-D digital modeling and rendering, enable new design forms. These forms have complex types of geometry determined by mathematical functions and parametric algorithms and have a new vectoral geometry, which is not Euclidian. Different forms which haven’t been designed can be produced from different mathematical functions [4].Emerging computational design techniques enhance the interdisciplinary relationship between architecture and the sciences of mathematics, geometry, electronics, genetics and biology. Thus, new design practices were generated by transferring various notions or techniques from scientific fields to architecture, such as NURBS curves, spatial bubbles (Blobs) or pits (Blebs) or twisted surfaces (Folds), genetic algorithms and parameters, evolutional approaches, animation techniques, artificial intelligence, robotics, etc. We can see that the mentioned approachments are variously termed in the media: evolutionary architecture, genetic architecture, parametric design, algorithmic design, biomorphogenic architecture, recombinant architecture, cyberspace architecture, hypersurface architecture, non-linear architecture, etc.At the present time, the use of nanotechnology and genetic technologies in architecture has generated various materials, equipment, forms, and design theories. When the potential of biological science was associated with a complete transformation of computer technology, firstly, the resulting architectural outcomes were included morphological aspects. Engineers can describe the genetic codes of DNA in a mathematical process -with the help of genetic algorithms- and recode it for new requirements in the virtual platform. Hence, the new nature-inspired organic forms could be digitally derived and some of them produced. Some other architects model genetic or evolutionary processes in designs and produce new forms that show natural characteristics. In addition, innovative nanomaterials and nanosensors already give designers a renewed palette. As George Elvin said, “Advances in biomaterials and biocomposites converge with advances in nanotechnology, and an increase in their application to construction seems certain to emerge in the future” [5]. Nanostructures’ materials represent an interesting development in the construction sector, showing higher-level performances and a lower consumption of energy resources when compared to traditional cement-based products [6].On the other hand, there are few studies on the possibility of a building that is self-generated by its own DNA like an organism, growing, surviving and even dying though using the opportunities of genetics and nanotechnology.Most architects consider this effort as a utilitarian experience which might be a way for them to develop eco-friendly and livable architecture derived from the nature for a sustainable environment. According to them, it is not only a romantic concept of “back to the nature” or searching for different, attractive forms; it is about reducing dependence on environmental resources, improving our decadent ecosystem, and the desire for a sustainable world.The studies on the relationship between architecture and nanotechnology or genetics continue in both universities or research centers and in freelance architectural offices, such as the Institute for Genetic Architecture at the GSAPP in Columbia University, New York, and architectural studio METAXY; Biodigital Architecture Program at ESARQ, Universitat Internacional de Catalunya, Barcelona; master’s program of University of the Alexandria; and the architectural offices of Greg Lynn, John Frazer, Marcus Novak, and others.It has been reviewed from the literature that there is a complexity about both the theoretical and practical fields. Each architect generates their own experiences; conceptual terms and production techniques are varied. It is hard to classify or label the present approachments academically. On the one hand, they based on a common scientific foundation and are derived from interrelated scientific areas such as genetics, biology, nanotechnology, microelectronics, computational techniques, etc. On the other hand, the outcomes of these approachments are different from each other in practice. For example, the words of genetics and genetic algorithms sound the same, but in fact, there is a serious difference between real DNA and computational DNA. In this respect, it is hard to determine a design product and settle in a class. For many designs –those mentioned in this paper too- it is undecided whether these are yet genetic architecture or, rather, still architecture about genetics. It is hard to easily separate which design has real “aliveness”, which is only computational versus biological or nature-mimetic, which is utopian or virtual, which is actual or applicable to the real world. Definitions are changeable from person to person, and the questions of “According to what?” and “According to whom?” are subsequently conjured up.There is also not a clear and comprehensive classification in the literature. This study could be considered as a classification dissertation. However, it is not possible to mention sharp borders in between the categories; they are intertwined. Three main approaches are described in contemporary architecture at the intersection of genetics or nanotechnology:• The form-finding strategies helped by genetic algorithms• The hybrid designs with nanomaterials or nanosensors• The living architecturesThe first of these focuses on the form finding which uses the digital computational techniques in computers. The second of these discusses the developments in materials and the effects of nanotechnology on architecture. And the last one deals with the interrogative works that question the possibility of a really living building with a hope and concern for the future. Some works in this classification are only utopic and stay in the virtual environment, but some of them are produced in real life. Consequently, the aim of this paper is to introduce new architectural approaches generated with the interdisciplinary domains of genetics and nanotechnology and to discuss them in the context of the future of architecture. The selected works -spaces or buildings- are generated through genetics or nanotechnology in a virtual or real environment.
2. Form-finding Strategies with the Help of Genetic Algorithms
- The new hospital shall offer an environment specifically designed with patients in mind. The new hospital shall use natural light, therapeutic colours and distinguishable finishes to assist way finding and provide a restful, relaxing environment. The rooms shall have daylight and views to ensure patients are in touch with the outside world, even in the basement areas. Consideration shall be made to ensure high levels of infection control in the clinical rooms and reception areas including anti-bacterial finish; and ledges and protrusions shall be kept to a minimum. In the architectural field, the major impact of cooperation with biotechnologies, including genetics, genomics and transgenic engineering, is on the architectural imagination. So, most of the studies on genetics and architecture have served to provide form-finding strategies. Genetic science first met architecture in a virtual platform. The genetic body -of all organics, human, animal, plant- contains multiple and creative animated forms, figurative principles and evolutionary systems that can be given architectural expansion [7]. Hence, a different form -generating process that is based on biological evolution came to the fore by moving genetic technology to the computer with new software. This software uses the genetic algorithm method, which is inspired by Darwin’s theory of evolution. Genetic algorithm, suggested by John Holland in the 1970’s, is a search and optimization method based on canonical selection rules. This method works according to probability rules, synchronously searches all of the population, and reaches the optimum solution for a complex problem in a short time [8]. Genetic algorithms used in the software that generates design forms in the architectural area last 10 years. Biological evolution processes, such as the crossover of genes, reproduction, mutation and natural selection run in software codes. The best genomes are perpetually selected and transferred to the next generations. At the end of the process, new forms that are members of same family and have little differences are generated [9]. Architects can see the outcomes of designs and operate them as requested. The British architect John Frazer, both an educator and the writer of the book The Evolutionary Architecture, is among the earliest researchers to investigate generative design systems using genetic algorithms. His research suggests nature’s evolutionary model as the generative process for architectural morphology: Interactivator (1995) (Figure 1). In this context, a seed in a computer model transfers its genetic codes to the other seeds by cell division and then disperses to all models. According to the fitness value which is calculated for the computer medium, successful genes in genetic algorithms are selected as in nature. Then these genes are exposed to crossover and mutation operations, and different architectural forms are produced in a working process of the model. The goal of this approach is to create artificial life due to evolutionary processes and to simulate nature’s behavior in a built environment [10].
 | Figure 1. Derivation in the Interactivator model (Frazer, 1995) |
 | Figure 2. [Above] Generating forms for Embryological houses / [Down] 3-D Embryological house prototype (www.glform.com) |
 | Figure 3. Different planets of Planetary Automata (Gregory Chaitin, http://www.futurefeeder.com/wp-content/6chuCorr.pdf) |
 | Figure 4. [Above] Aegis Hyposurface / [Downt] Muscle Body project |
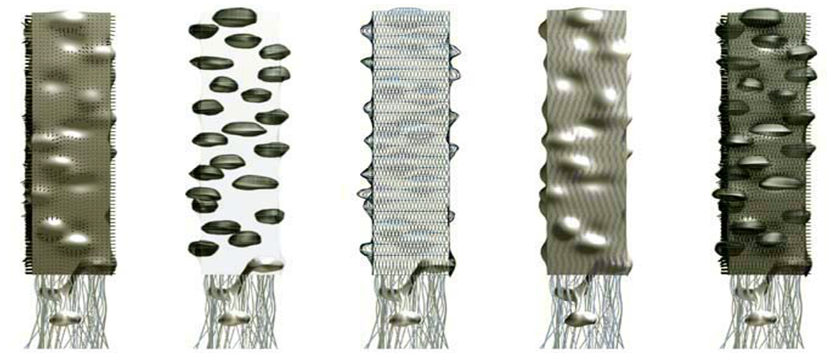 | Figure 5. UN Plug Office (www.glfor m.com) |
 | Figure 6. The eTree structure, covered by a monocoque facade and chainmail-like components, can take on environmental performance duties such as filtering and ventilation |
3. Hybrid Spaces in Cooperation with Nanotechnology and Architecture
- Contemporary architecture has more opportunities than just creating genetic algorithms for form finding. It can adopt material investigations for generative design approaches. The works in this title are generally helped by nanotechnology.Many nanomaterials are already available, and also, nanoparticles could integrate into conventional materials to attain multifunctional nanocomposites and have new properties. Nanostructured materials are constituted as traditional materials -steel, cement, glass, polymers-admixed in a mass or surface with nanomaterials (nanocomposites) or modified in its chemical and physical structure at the nanoscale level (nanoengineering) [18]. In the near term, the nanocomposite reinforcement of steel, concrete, glass, and plastics will dramatically improve the performance, durability, and strength-to-weight ratio of these materials. For example, a nanocomposite steel that is three times stronger than conventional steel, is already on the market.Many intelligent materials are also researched based on the development of nanotechnology such as shape-memory alloys, which return to the original shape at a particular temperature after stretching; piezo-electric materials, which can be widened and narrowed by voltage; composite materials, which have properties of two or more materials; and also some materials which can copy themselves, change their transparency and colors, and transmit information, sound, and light to each other through sensors [19]. Furthermore, it is claimed that in the future, external surfaces of buildings would be changeable according to computer instructions; would change between liquid, solid, and gas states of matter; and would sometimes be dull and solid or sometimes be transparent and liquid [6].An example of this is Aerogel that has a density of three times that of air but has considerable strength and insulation capabilities [20]. Aerogel, currently used in solar collectors, is a solid, but it is so transparent that it looks like a hologram. Another is carbon nanotubes, which have a significant potential for use in the future. They could bring unprecedented strength and flexibility to our buildings with their power. It is said to be 100 times stronger than steel because of its “molecular perfection” [21]. In addition, carbon atoms can act as a switchable conduit, a light source, a generator of energy, and even a conveyor of matter by bonding with other forms of matter. Carbon nanotubes—sheets of graphite just one atom thick, formed into a cylinder—are not only 50 times stronger than steel and 10 times lighter, but they are transparent and electrically conductive to boot. Nanotubes are already the building blocks for hundreds of applications and are used to reinforce concrete and deliver medication to individual cells [22] (Figure 7).
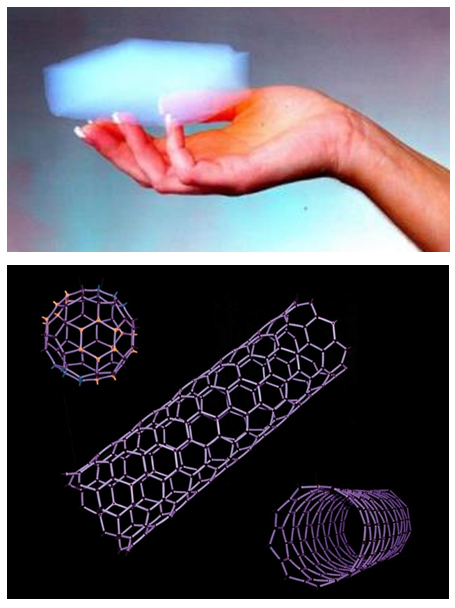 | Figure 7. [Above] Aerogel (http://stardust.jpl.nasa.gov/images/technology/aerogelhand.jpg), [Down] Carbon nanotubes (http://www.nanoscience.ch/nccr/nanoscience/pictures/gallery_01/gallery_01_03) |
 | Figure 8. Nanohouse (http://www2.arch.uiuc.edu/elvin/nanohouse.htm) |
 | Figure 9. Nano Skin System |
 | Figure 10. Megapyramid |
 | Figure 11. Nano Towers |
 | Figure 12. Nano Vent Skin |
4. Shaping a Living Architecture
- We know that architecture has adopted many concepts from the nature throughout history, for example, Ancient Egyptian columns, modeled on palm trees and lotus plants; the Geodesic Dome of Fuller, generated by his researches on plants and human neural systems; the Living Pod of Archigram; the IMAX Theater of Santiago Calatrava, shaped like an eye, and other designs of Calatrava inspired by birds or structures of trees; the Sydney Opera House of Utzon, inspired by seashells. All of these, inspired by natural forms, have organic characteristics and are named in literature as analogical or biomimetic design [28]. But the architecture that has recently been suggested is different from them. Genetic architecture, suggested by a group of architects, is based on the philosophical notion of genesis [31]. Its aim is not exactly to imitate nature or designs in the nature, but plasticize with nature and, moreover, design nature. The architects try to achieve an architectural approachment which is a real and living piece of natural life by making use of the opportunities in genetic principles and nanotechnology. Nature is not only a source of inspiration but also raw material for them. Accordingly, the works in this category are born out of the desire to design self-growing, living buildings operating by their own DNA.John M. Johansen, in the late 1960s, envisioned the building as an organism whose structure is determined by genetic processes. Buildings, in his imagination are self-organizing, self-regulating structures with the capabilities of self-diagnosis and self-healing and have a central nervous system. The Molecular Structure House and the Multi-Storey Apartment Building designed by Mohamad Alkhayer and John M.Johansen for the year 2200 are already utopic but impressive futuristic designs. Everything would start by placing a “seed” of artificial DNA, the molecular modeled code designed by the architect, in the ground and into a vessel filled with special liquid chemicals. The order of the processes are as follows: taproots, which would compose the basis of the building, followed by the upper building, inside-outside horizontal skeleton, grid system, inside-outside walls, and platforms or flats, with gaps and mechanical systems then being completed via molecular divisions in nine days (Figure 13). The construction starts with an excavation for placing large vessels he calls “assembly vats.” The second day, the vats and ingredients are delivered and placed on the site by pumping. Then “The Code” comes on day 3. He describes the code as a representation of a very old combination of architectural drawings, specifications, and strategies of construction management. The code is placed in the vat. The fourth day is when molecular growth begins. A vascular system develops, with roots germinating from the mixture in the vat and reaching the ground level. The roots (also beams of the ground floor) then start forming a superstructure by weaving a ground-floor platform by extending themselves across each other. The structure grows during the fifth day by extending its vertical ribs and forming necessary lattices of the structure. He also mentions that a neural network joins the structure at this phase. During the sixth day, the boundaries of the molecular-engineered house start functioning, mimicking membranes of living cells. When membranes receive electric currents, molecules disengage, and exterior membranes open while letting inhabitants permeate the house. The seventh day is for the growth of interior finishes that are simply called “body support”. The next day brings us an artificial organic shelter which Johansen refers to as a cocoon. Day 9 is the grand opening: he house is a flexible, self-sufficient molecularly engineered living space which can be rearranged or demolished and recycled [30].
 | Figure 13. The growing process of the Molecular-engineered House of Johansen |
 | Figure 14. Fab Tree Hab |
 | Figure 15. STEMcloud v2.0 |
 | Figure 16. Hydrogenase vessels |
 | Figure 17. Production diagram and 3d model of Fibrous Tower |
- It can be said that these design experiments include the first two categories together. They intend to be living architecture in terms of both form and materials. Although it is impossible to demarcate between categories, these works differ from others by their production techniques, formations, and materials. For instance, designs in the second category are determined as hybrid systems which are constituted by integrating the nanomaterials or special techniques on conventional buildings. They seem like ordinary architecture sanctified by scientific technology. On the other hand, the designs in third category have the potential to point out architecture of a different age. However, they have an even lower probability of realization, as they are still utopic. Accordingly, there is a requirement for much more research on real DNA, not computational.
5. Conclusions
- In the 20th century, Le Corbusier metaphorically likened the house to a living machine. In the 21st century, it is predicted that buildings will really be living organisms, not like machines but like organics. Actually, this idea contains aims of designing buildings in harmony with nature and protecting the symbiotic equilibrium as mentioned above. Architects have thought about a better and more sustainable environment and space quality in the future because the resources of the world have become restricted, and ecology has gained more and more importance. They would also have to cooperate with other disciplines, obtain information, and gain experience in scientific developments. It is possible to mention that there is a conceptual confusion in theoretical areas and classification problems with design works. In addition, it requires querying some aspects. First, architects should show regard to the fact that imaginer’s attraction to biogenetic forms in architectural media does not mean that they suggest satisfactory spatial organization for users. In our age, many things could easily be used to serve consumption and with the facts distorted even in scientific areas. It is known that the sustainability of many energy-efficient techniques or systems is arguable. Many commentators recognized too that the genetic technologies or sustainability and energy policies are part of a new capitalist paradigm that becomes a special object for politics and the financial production-consumption process. So being fascinated by the trends and keeping track of them could not be the best way every time and might bring only commercial success. Second, all these developments have unknown effects on humanity. For example, would people really be comfortable sitting in a house supported by columns having almost the diameter of a needle? Or what would be the effects of living buildings with their changeable materials on us? The social and psychological effects of the foreseen architecture of the future must be researched synchronously with the design process. Living architecture might be a solution for the loneliness or alienation of our metropolis and might strengthen our sense of belonging. But the situation of being in an organism and having mutual interactions with space are main research topics. Despite all the developments of the processes, we live in great white hope for the future. Constructing a living building which grow like a plant is still theoretical. But in the future, the fields of microelectronics, genetics, nanotechnology, and molecular engineering represent a new frontier in architecture. When these approaches are evaluated, it can be claimed that specifically genetics, molecular-nanotechnology, and robotics could start a radical revolution in architecture as in many other areas. And as a result, architecture could reach a very different stage from where we are now. Ray Kurzweil, in his 1999 book ‘The Age of Spiritual Machines’, stated that if the technology develops with that speed, computers would pass the human brain in terms of memory capacity and operation speed. As a matter of fact, today’s computers that are integrated into buildings can observe some conditions such as temperature, air circulation, energy consumption and wind load using their sensors and can respond if they have already been programmed. Although we crawl on all fours, living buildings or cities constructed by robots could be made possible with the coordination of architecture, science, and technology when considering the development of mankind in the last two centuries. Therefore, a more livable environment could be constructed from real living buildings. To express with Johansen’s words [30], “Much of yesterday’s fiction is now reality, and much of today’s fiction may be reality of the future.”
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML