-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Environmental Engineering
p-ISSN: 2166-4633 e-ISSN: 2166-465X
2015; 5(1A): 39-44
doi:10.5923/s.ajee.201501.06
The Daily Cycle of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer Heights over Pasture Site in Amazonia
Theomar T. de A. T. Neves 1, Gilberto Fisch 2
1Centre of Weather Forecast and Climate Studies, National Institute of Space Research, São José dos Campos, Brazil
2Science and Technology Aerospace Department, Aeronautics and Space Institute, São José dos Campos, Brazil
Correspondence to: Gilberto Fisch , Science and Technology Aerospace Department, Aeronautics and Space Institute, São José dos Campos, Brazil.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
A better descriptions of the atmospheric boundary layer (ABL) properties in Amazonia, such as its time evolution is necessary, especially for studies involving weather forecast and climatic simulation. The objective of this work was integrate and comparing data of the ABL characteristics made by different techniques in RaCCI/LBA experiment, held in southwestern Amazonia pasture site during the dry-to-wet seasons of 2002. For daytime it was possible to observe that there is an abrupt growth of the Convective Boundary Layer (CBL) between 08 and 11 Local Time (LT) with a stationary pattern between 14 and 17 LT. The maximum heights at late afternoon were around 1500 m. The onset of the Nocturnal Boundary Layer (NBL) occurs before the sunset (18 LT) and its height is very stable during the whole night (typical values around 180-250 m). The erosion of the NBL lasts for 2 hours and it is complete at 08 LT.
Keywords: Nocturnal and daytime boundary layer, Radiosondes, Tethered balloon, Amazonia
Cite this paper: Theomar T. de A. T. Neves , Gilberto Fisch , The Daily Cycle of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer Heights over Pasture Site in Amazonia, American Journal of Environmental Engineering, Vol. 5 No. 1A, 2015, pp. 39-44. doi: 10.5923/s.ajee.201501.06.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- In the last decades a great effort has been made by the scientists from micrometeorology and boundary layer for a better understanding of the dynamics and the description of the properties of the atmospheric boundary layer (ABL). As an example, the studies on the atmospheric transport and diffusion of pollutants [1, 2], mountain-valley and land-sea breezes [3], turbulence and wind regime [4] and parameters of climate models and general circulation [5] can benefit from the knowledge improvements about ABL. An important feature of ABL is its height, which dictates the volume where the source of pollutants can disperse, being an important parameter for the modeling of atmospheric dispersion. [6] describe the ABL as the layer adjacent to the earth’s surface with significant turbulent transfers of heat, mass and momentum occurring over a period of the order of an hour. It has atmospheric processes due to the thermal and mechanical convection during daytime and suppressed turbulent conditions which persist and evolves during the nighttime. The heights of the atmospheric boundary layer during unstable atmospheric stability (mainly daytime) are named CBL (Convective Boundary Layer), whereas those obtained during the period of stable stability (mainly nighttime) will be denominated NBL (Nocturnal Boundary Layer).The observational evaluation of CBL and NBL is a broad field of study, since those atmospheric processes in the lower atmosphere have an important impact on society and in the environment. Despite its importance, the logistics of the observations of atmospheric boundary layer is usually complicated [7] and with this problematic its height are considered many times as fixed in some climatic and forecast models. Also, this study different to the usual that contributes for medium latitudes will contribute for both scientific and practical applications [8-10] in lower latitudes (tropics), as it gives some new information for computational modelling and strategy designfor field experiments. Thus, the objective of this work is to integrate and compare data from the heights of ABL measured or estimated by several different instruments as radiosonde, tethered balloon and SODAR deployed on RaCCI/LBA experiment. This data tends to be representative for the daily cycle evolution of CBL and NBL over a pasture area at southwest Amazonia during the transition of the dry to the wet season.
2. Data and Methods
- The measurements were made at Nossa Senhora Aparecida farm (10° 45' S, 62° 22' W; 293 m), Figure 1, a cleared/pasture area, which has been used in LBA´s micrometeorological field campaigns since the 90s [12].
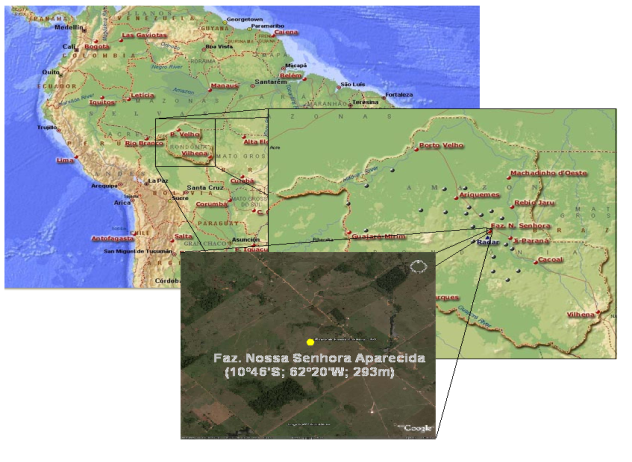 | Figure 1. Site location |
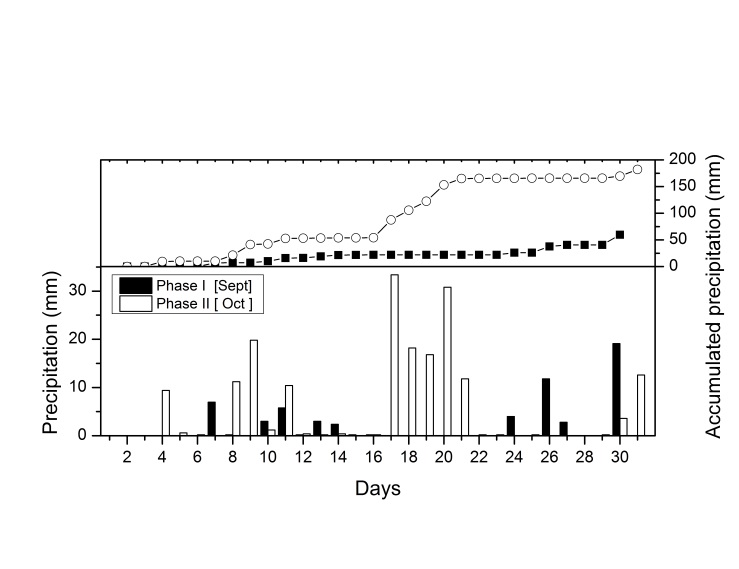 | Figure 2. Time series of the rainfall (daily and accumulated precipitation) during the transition from dry (represented by Phase I) to rainy season (Phase II) |
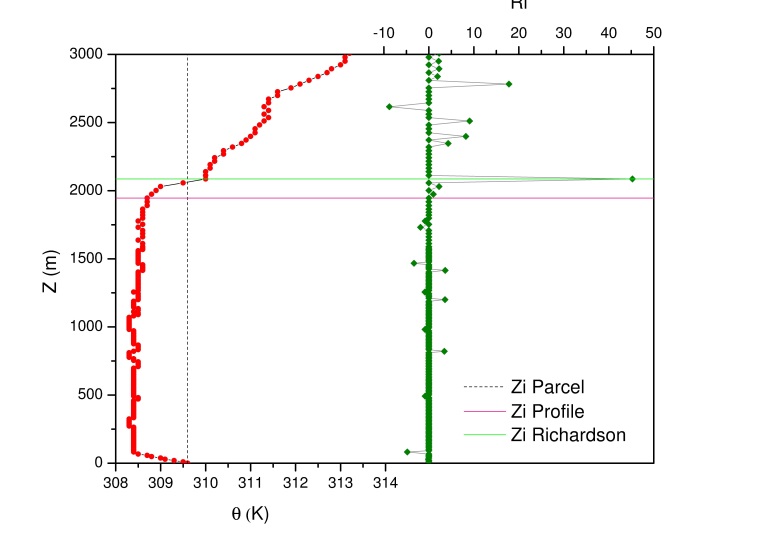 | Figure 3. Schemes of the methods to obtain the convective boundary layer height. As an exemple was used the day sept/20 at 17 LT |
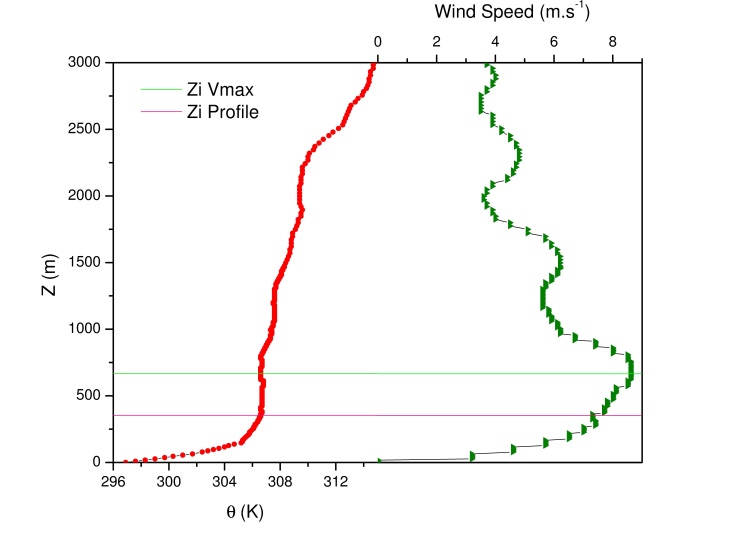 | Figure 4. Schemes of the methods to obtain the nocturnal boundary layer height. As an exemple was used the day sept/20 at 02 LT |
3. Results and Discussions
- Figure 5 shows the hourly average ABL´s heights for the Phase I (which represents the end of the dry season). The daytime (convective) and nighttime (stable) conditions were separated by vertical lines in 06 and 18 LT as well a dashed line was included to identify the end of NBL erosion.
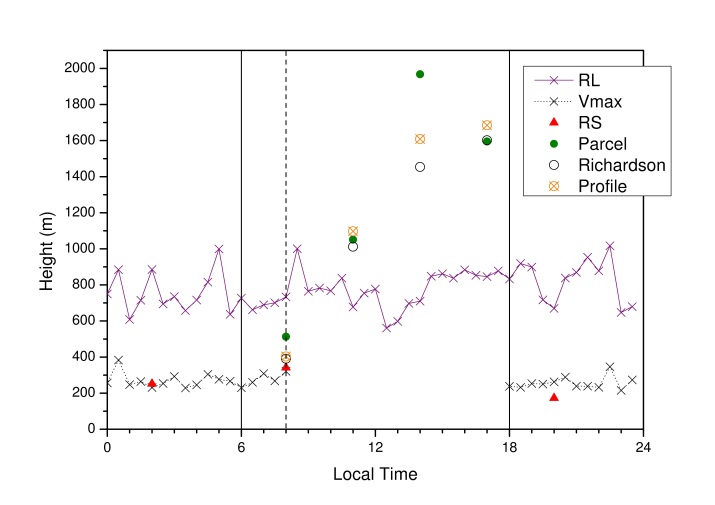 | Figure 5. ABL heights during the Phase I of LBA/RaCCI 2002 experiment |
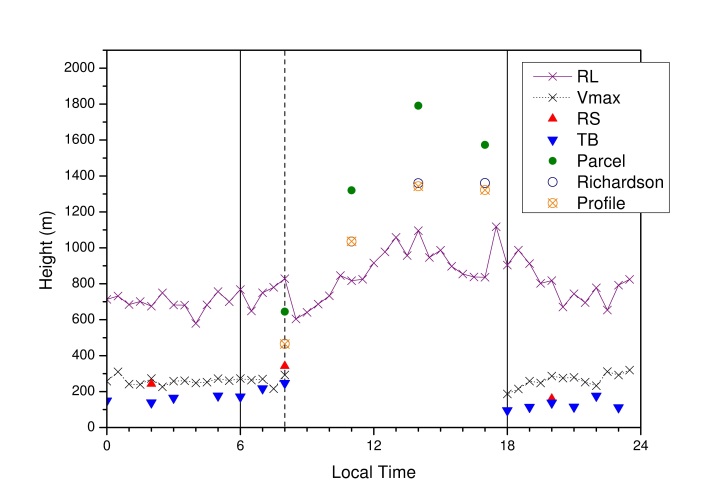 | Figure 6. ABL heights during the Phase II of LBA/RaCCI 2002 experiment |
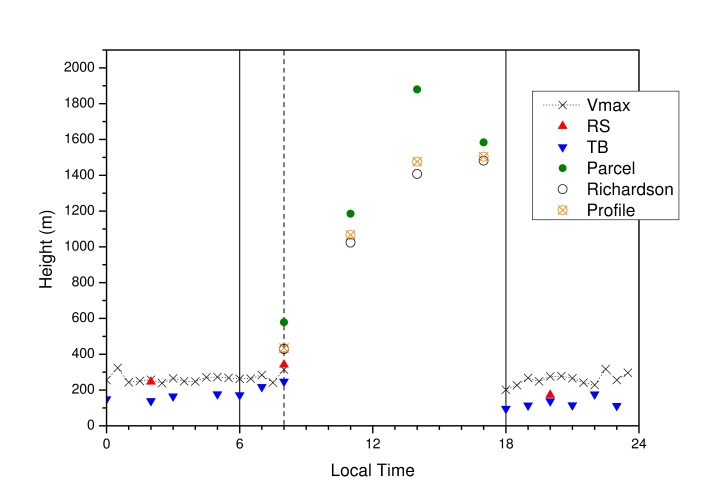 | Figure 7. ABL heights during the LBA/RaCCI 2002 experiment |
4. Conclusions
- The daily cycle behavior of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer heights in a deforested area (pasture site) in south-western Amazonia (Rondônia) was derived using different instruments/methods (radiosondes, tethered balloon and sodar measurements). Typical values for the daytime / convective (CBL) and nocturnal / stable (NBL) boundary layer depth were determined for a field campaign held during the transition period from the dry to wet season in the region (LBA/RACCI 2002 Experiment): for the CBL is around 1500 m and ranged from 180-250 m for the NBL. An additional result is that the commercial software from REMTECH for the height of the boundary layer for nighttime does not represent the true depth but instead the height of the residual layer. An alternative method (height of the maximum windspeed) was proposed using the SODAR data-set and the results are compatible with the estimates using radiosonde and tethered balloon.According to [15], he presents a classical figure of the ABL development in his book, which even referring to a development mean of the atmospheric boundary layer it was very similar to the Figure 7. Although, as can be seen in [16], the pattern changes due to local characteristics, reforcing the idea of ABL’s height study as important. Also, different parameterizations can be created using different measurements and observations methods, resulting in significant model errors [17]. These errors may be produced mainly by lack of local average (observational) knowledge.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors acknowledge the CNPq by the support to this work, process number 131165/2009-7, during the master degree.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML