-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Advances in Analytical Chemistry
p-ISSN: 2163-2839 e-ISSN: 2163-2847
2013; 3(A): 1-8
doi:10.5923/s.aac.201307.01
Mathematical Modelling and Numerical Simulation of the Processes in Noninvasive Potentiometric Method of Evaluating Antioxidant/Oxidant State of Skin
Khiena Z. Brainina1, Leonid G. Galperin2, Maria G. Markina1, Natalia Yu. Stozhko1
1Department of Physics and Chemistry, Urals State University of Economics, Ekaterinburg, 620219, Russia
2Department of Industrial Heat-Power Engineering, Ural Federal University named after the First President of Russia B.N. Yeltsin, Ekaterinburg, 620002, Russia
Correspondence to: Khiena Z. Brainina, Department of Physics and Chemistry, Urals State University of Economics, Ekaterinburg, 620219, Russia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Abstract The article proposes theoretical and experimental justification for using potentiometry as a new noninvasive method of evaluating antioxidant/oxidant state (oxidative stress) of a skin. Since the inductor of oxidative stress is an overall deficit of electrons accessible to cells, electrochemical methods of evaluating this parameter are naturally considered as fully corresponding with the nature of the phenomenon. A mathematical model is proposed that describes the processes determining analytical signals in the ‘skin-gel-electrode’ system. The signal occurs as a result of interaction between antioxidants/oxidants diffusing from the epidermis of the skin into the gel and the mediator system oxidised or reduced component introduced into the gel. The information source with regard to AOA/OA (antioxidant/oxidant activity) is the electrode potential shift. It occurs when the gel comes into contact with the skin. The series of potential determining substance-time dependences was obtained as a result of numerical simulation and experiment. Typical relationships between different parameters (chemical reaction rate, gel layer thickness, time) and concentration equal to antioxidant or oxidant activity, (AOA or OA) were found. An agreement between the calculated and experimental data was obtained. Findings analysis enables to forecast features of the experimental relations and provided an opportunity to choose experimental conditions ensuring the most reliable results.
Keywords: Potentiometry, Noninvasive Method, Skin, Antioxidant, Oxidant, Oxidative Stress
Cite this paper: Khiena Z. Brainina, Leonid G. Galperin, Maria G. Markina, Natalia Yu. Stozhko, Mathematical Modelling and Numerical Simulation of the Processes in Noninvasive Potentiometric Method of Evaluating Antioxidant/Oxidant State of Skin, Advances in Analytical Chemistry, Vol. 3 No. A, 2013, pp. 1-8. doi: 10.5923/s.aac.201307.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The study of causes and development of oxidative stress (OS) in the human skin, its association with skin diseases and other types of diseases has been conducted by scientists in different fields: medicine, chemistry, biology[1–3]. Oxidative stress contributes (or appears) significantly to the development of some nervous, lung, eye, and blood diseases as well as aging, coronary deficiency, strokes; take part in progressive damage in cardio-surgery, transplantation of tissues and organs and lungs surgery. Oxidative stress contributes to adverse effects on the skin, expressed as erythema, edema, wrinkling, photoaging[4], inflammation, autoimmune manifestation, hypersensitivity, keratinization abnormalities, preneoplastic lesions and skin cancer[5], psoriasis[2,6,7], vitiligo[8,9] seborrheic dermatitis[10].The negative role of free radicals in human health is described in[2,11,12]. On the other hand, reactive oxygen (ROS) and reactive nitrogen (RNS) substances play a crucial role in the body, ensuring good metabolism and performance of vital functions in cells. Previous studies in this field[13-16] allow thinking that AOA/OA (antioxidant/oxidant activity) of the skin can provide information on AOA/OA of the whole body. Thus, developing a method of evaluating this parameter will enable to create a noninvasive method of assessing human health.Antioxidant determination methods are widely reported in the literature[17-19]. Actually, proposed methods are invasive: they require blood taking or homogenate preparations of the analyzed tissue. The data about non-invasive methods used for determining antioxidant activity of biological objects are limited[19–21].Because of inductor of oxidative stress is an overall deficit of electrons accessible to cells, AOA/OA body balance has the electrochemical nature that is why electrochemical methods of evaluating this parameter are naturally should be considered as fully corresponding with the nature of the phenomenon. In[22] we described a potentiometric method of skin AOA/OA measurement. Advantages of the proposed approach are as follows: skin AOA/OA can be measured as integrated parameter by a direct, highly sensitive, user friendly and selective method. However, the following problem arises: the investigated ‘skin-gel-electrode’ system is complicated in comparison with the ‘water solution- electrode’ system used in the early described method[15–16] and it is not obvious, that the same approach and calculations can be used in applying a new method.To justify the correctness of approach and conformity assessment of the measured value of AOA/OA to actually existing in the sample, it is essential to provide theoretical background to the processes occurring in the system, to create a mathematical model that takes into account a range of parameters such as the thickness of the the gel containing the mediator system; the rate of the chemical reaction between skin antioxidants/oxidants and compounds of the mediator system in the gel.
2. Theoretical Considerations
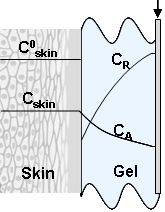
- The method proposed in[22] is based on the interaction between antioxidants/oxidants diffusing from the skin epidermis into the gel and the mediator system introduced into the gel which is applied on the skin. The information source with regard to AOA/OA is the electrode potential shift in the mediator system K3[Fe(CN)6/K4[Fe(CN)6], which is observed when the gel comes into contact with the skin as a result of changing concentration of oxidized or reduced forms of the mediator system in the gel. These changes in the concentration result from reaction (1) for antioxidants and reaction (2) for oxidants:
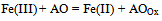 | (1) |
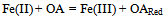 | (2) |
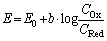 | (3) |
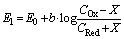 | (4) |
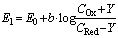 | (5) |
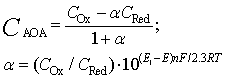 | (6) |
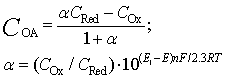 | (7) |
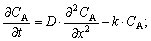 | (8) |
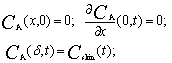
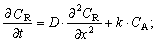 | (9) |
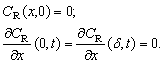 The mathematical model is added by the equation of the material balance of substance AO in the skin. The similar behavior is observed in the case of oxidants. The only difference is that the change in concentration of Fe(III) is considered instead of Fe(II).
The mathematical model is added by the equation of the material balance of substance AO in the skin. The similar behavior is observed in the case of oxidants. The only difference is that the change in concentration of Fe(III) is considered instead of Fe(II).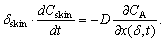 | (10) |
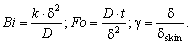 | (11) |
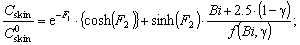 | (12) |
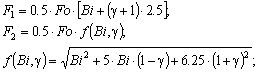
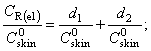 | (13) |
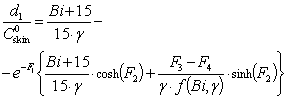 | (14) |
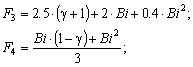
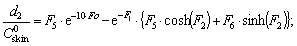 | (15) |
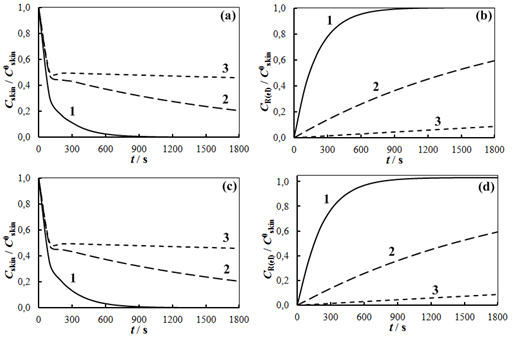
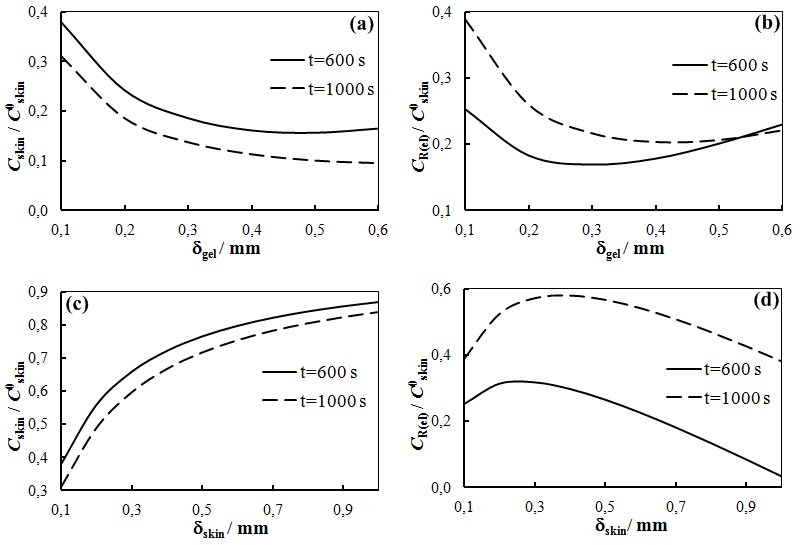
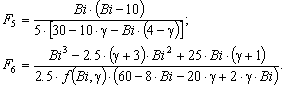 The solution enables to obtain the key correlation between the parameters which define characteristics of the processes occurring in this system, namely, to find the functions Cskin/C0skin and CR(el)/C0skin depending on the arguments δskin-epidermal thickness, δgel-thickness of the gel layer and t-time. In this case CR reflects CAOA, as substance R (Fe(II)-reduced form of the mediator system) results from Reaction (1) which is running in the gel. In case of oxidants CR will reflect COA as substance R (Fe(III)-oxidized form of the mediator system) results from Reaction (2) Let us once again focus on a very important fact: CR is an increment (rather than an absolute value) of the concentration of reduced (Eq. 1) or oxidized (Eq. 2) forms of the mediator system.CR(el) – increment (rather than an absolute value) of concentration at the electrode surface determines a measuring signal that is recorded as a shift of the electrode potential in the mediator system, initially introduced into gel.Ideally, CR(el)/C0skin should approach to 1.Since the mathematical model and calculations in the cases described by Equations (1) and (2) do not differ, the value of CR(el) will be used for further considerations. The general profile of dependence of Cskin/C0skin and CR(el)/C0skin on non-dimensional parameters, including the above given arguments, is shown in Figure 2.
The solution enables to obtain the key correlation between the parameters which define characteristics of the processes occurring in this system, namely, to find the functions Cskin/C0skin and CR(el)/C0skin depending on the arguments δskin-epidermal thickness, δgel-thickness of the gel layer and t-time. In this case CR reflects CAOA, as substance R (Fe(II)-reduced form of the mediator system) results from Reaction (1) which is running in the gel. In case of oxidants CR will reflect COA as substance R (Fe(III)-oxidized form of the mediator system) results from Reaction (2) Let us once again focus on a very important fact: CR is an increment (rather than an absolute value) of the concentration of reduced (Eq. 1) or oxidized (Eq. 2) forms of the mediator system.CR(el) – increment (rather than an absolute value) of concentration at the electrode surface determines a measuring signal that is recorded as a shift of the electrode potential in the mediator system, initially introduced into gel.Ideally, CR(el)/C0skin should approach to 1.Since the mathematical model and calculations in the cases described by Equations (1) and (2) do not differ, the value of CR(el) will be used for further considerations. The general profile of dependence of Cskin/C0skin and CR(el)/C0skin on non-dimensional parameters, including the above given arguments, is shown in Figure 2.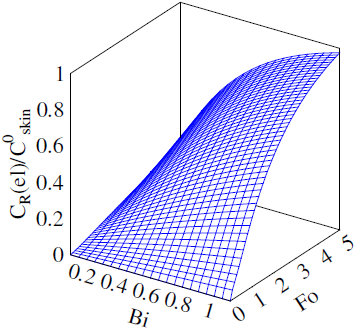 | Figure 2. Dependence of CR(el)/C0skin on non-dimensional parameters Bi and Fo |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
- • K4[Fe(CN)6], K3[Fe(CN6)], KH2PO4, Na2HPO4·12H2O, ascorbic and uric acids, cysteine and glutathione of high purity grade or chemically pure were obtained from Reachim, Russia.• Mixture of K3[Fe(CN6)] and K4[Fe(CN)6] served as mediator system.• Unimax, highly conducting gel (Geltek-Medica, Russia) and adhesive plaster Silkofix PE 2500 were bought in Pharmacy store.
3.2. Investigated Subject
- The surface of human skin in the wrist area served as the subject of investigation. The investigated area of skin was washed with deionized water. Gel, containing ascorbic acid, cysteine or glutathione served as model systems.
3.3. Instruments
- Potentiometric measurements were performed using potentiometric analyser Taion (Tomanalyt Ltd, Tomsk, Russia) with a two-electrode electrochemical cell. Platinum screen-printed electrode (IVA, Ekaterinburg, Russia) and ecg electrodes H92SG Ag|AgCl, KCl (Arbo, Kendal, USA served as working and reference electrodes. Silver/silver chloride electrode (Ag/AgCl/3 M KCl), EVL -1M type (Gomel Measuring Equipment Plant, Gomel, Republic of Belarus) was used as reference electrode in kinetics experiments.
3.4. Methods
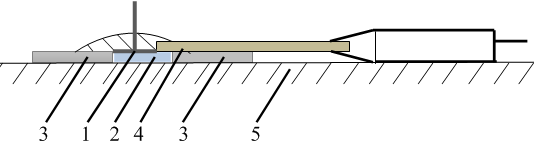
- Measurements of chemical reactions rate using model systemsFour ml of the gel and 0.2 ml of an aqueous solution of the mediator system containing a mixture of 10-3 M K3[Fe(CN)6]) + 10-5 M K4[Fe(CN)6] were placed in a glass cell. Electrodes were immersed in the mixture and the potential (E) was measured after 60 s. Then the electrodes were removed from the cell and 0.2 ml of an aqueous solution of an antioxidant was added. The concentrations of the solutions in the cell were 2∙10-5 M ascorbic acid or 4∙10-5 M glutathione. The electrodes then were again immersed in the cell and the change in the potential was recorded until its value stabilized. Concentration of antioxidants in gel was calculated using Equation 6 and assuming ΔE=E-E1, where E was the electrode potential in the gel containing the mediator system; E1 was the potential in the gel containing the mediator system and antioxidant at a given time t. Value of found antioxidant concentrations at the end of the measuring process and at a half-time of that were used to calculate constants of chemical reaction rate. Form of the curves is shown on the Fig.6.Skin investigationIn order to study the effect of thickness of a gel layer on potentiometric measurements two plates were placed on the tested skin area at a distance of 1cm from each other (Fig.5). The gel containing mediator system, platinum screen-printed and ECG H92SG electrodes were placed in the space between the plates, as shown in Fig. 5. The layer thickness was controlled by the number of pieces of hypoallergenic adhesive plaster (from 1 to 5) located on each other. The thickness of plates were measured with a micrometer.
4. Results and Discussion
- Fig. 6 presents the dependence of E-t, obtained experimentally and AOA-t, calculated applying Eq. 6. All experimental results given below were obtained in this way. Sudden changes in the potential and AOA were observed in the range 0–500 s, which is consistent with the results of the calculations (Fig. 3). After 600 s measurements the potential change in time was slow. For example, the difference between the experimental values of AOA (Fig.6) during 600 s and 783 s was 0.3∙10-6 M-eq, or 0.8%. Further measurements were carried out during 600 s.
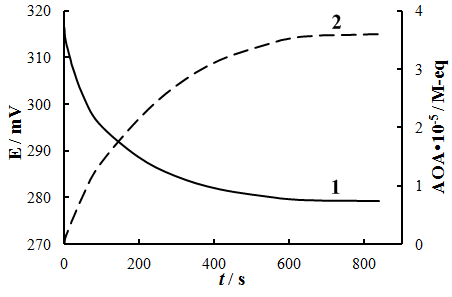 | Figure 6. Time dependence of potential (1) and antioxidant activity (2) measured on human skin |
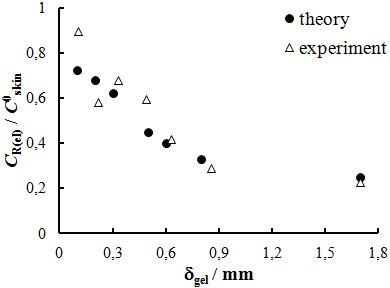 | Figure 7. Calculated and experimental dependence of CR(el)/C0skin on thickness of gel layer; k=0.01 s-1, δskin=0.1mm |
5. Conclusions
- The existing relationship between the internal state of a human body and skin pathology suggests that skin AOA/OA can be a source of information regarding common health problems. Skin AOA/OA can also constitute the basis for developing new methods of analytical chemistry that can be used for monitoring levels of human health and population screening in order to identify, in particular, groups of risk, and detect diseases in an early stage. Decreasing antioxidant content in the skin reflects the emergence of imbalances in the body's antioxidant defense system, i.e. oxidative stress. Oxidative stress has an electrochemical nature that is why electrochemical methods of evaluating this parameter may be considered as fully corresponding with the nature of the phenomenon. Potentiometry is one of the most easily implemented electrochemical method. Moreover, it is widely used in sensors for medical diagnostics. The article elaborates upon the theory of non-invasive method of potentiometric determination of antioxidants and oxidants in the skin. The method is based on measuring an electromotive force produced when electrodes are placed in the gel applied to skin. A good agreement between theoretical and experimental results allows using the calculated results as a source of information regarding selection of experimental conditions, evaluation and interpretation of the results.The advantages of the method are as follows: skin AOA/OA is measured as an integral parameter by direct method; results can be obtained quickly; the method is non-invasive and painless. The measurements are highly sensitive and show good selectivity. Hardware design is simple and accessible and provides possibility to work in the field, in the hospital or at the bedside.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- Authors express their deep gratitude to the financial support of the RFBR (Projects # 12-00-14037_Ir and 13-08-96-050).
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML