-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Research in Zoology
p-ISSN: 2325-002X e-ISSN: 2325-0038
2018; 8(1): 6-11
doi:10.5923/j.zoology.20180801.02

Spatiotemporal Activities of Eidolon helvum (Kerr, 1792) a Near-Threatened Species (Côte D’Ivoire, West Africa)
Niamien Coffi Jean Magloire1, Dago Dougba Noel1, Kadjo Blaise2, Koné Inza2, N’goran Kouakou Eliézer2
1Department of Animal Biology, UFR of Biological Sciences, Peleforo Gon Coulibaly University of Korhogo, Korhogo, Côte d’Ivoire
2Laboratory of Zoology and Animal Biology, URF Biosciences Félix Houphouët-Boigny, Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire
Correspondence to: Dago Dougba Noel, Department of Animal Biology, UFR of Biological Sciences, Peleforo Gon Coulibaly University of Korhogo, Korhogo, Côte d’Ivoire.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The spatiotemporal activities of straw-colored fruit bats, Eidolon helvum (Kerr, 1792) a near-threatened species has been studied in the Commune of Plateau in Abidjan from August 2012 to July 2013. The present survey carried out by direct observations aimed in monitoring the straw-colored fruits bats population with the purpose to discriminate their circadian rhythm activities patterns in terms of time and space by processing behavioural pattern frequencies as well as by identifying distribution discriminant factors. Results showed that daily activity pattern was characterized by (i) sleeping activity from 07:00 Am to 05:00 Pm, (ii) awaking (05:00 Pm-05:30 Pm) and (iii) grooming in the early evening (05:30 Pm-06:00 Pm) and (iv) dispersion from 06:00 to Pm-07:00 Pm. Activities patterns varied with food availability, reproduction and season. A right integration of presently processed data into the biodiversity system preservation strategy should contribute to ensure and guarantee a rational and as well a sustainable management with regard these near-threatened species.
Keywords: Straw-colored fruit bats, Behavioural pattern, Distribution factors, Season effect, Conservation,Côte d’Ivoire
Cite this paper: Niamien Coffi Jean Magloire, Dago Dougba Noel, Kadjo Blaise, Koné Inza, N’goran Kouakou Eliézer, Spatiotemporal Activities of Eidolon helvum (Kerr, 1792) a Near-Threatened Species (Côte D’Ivoire, West Africa), Research in Zoology , Vol. 8 No. 1, 2018, pp. 6-11. doi: 10.5923/j.zoology.20180801.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Bats have systematical [1, 2], ecological [3, 4], pharmacological [5], medical and veterinary [6, 7], economical [3, 8-10] and conservation value [6, 9, 11, 12]. In spite of those interests, few ecological data about them are available because of their nocturnal lifestyle and their ability to fly which makes difficult their study [1, 2].In Côte d’Ivoire, the Commune of Plateau (Abidjan) shelters a great population of straw colored fruit bats, Eidolon Helvum (Kerr, 1792), a near-threatened species [12]. That population use the urban site respectively as roosting site, maternity and nursery. Despite their great ecological interests, these bats colonies have been less studied [9, 13-19]. Indeed, bat significantly contribute in flower pollination process and as well in forest ecosystem reconstitution after natural and anthropogenic disturbance [1, 3, 4, 6, 10]. In addition, these frugivorous also insure seed dispersion and favor seed germination of Iroko (Milicia excelsa Welw. Moraceae), which is a threatened forest gist in West Africa [20, 21]. Thus, basing on these evidence, the Commune of Plateau, because of the remarkable presence of the important community of fruit eater straw-colored bats should be considered a strategical site for biodiversity conservation. However, activities patterns of straw-colored fruit bats resulted marginally studied. Then, with the purpose to contrast this tendency the present study aims (i) to identify the spatial and time distribution of behavioural patterns of Eidolon helvum and (ii) to examine season influence and/or impact on these activities in above mentioned site (Plateau Commune in Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire) in order to draw a practical applications guarantying their conservation.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Area
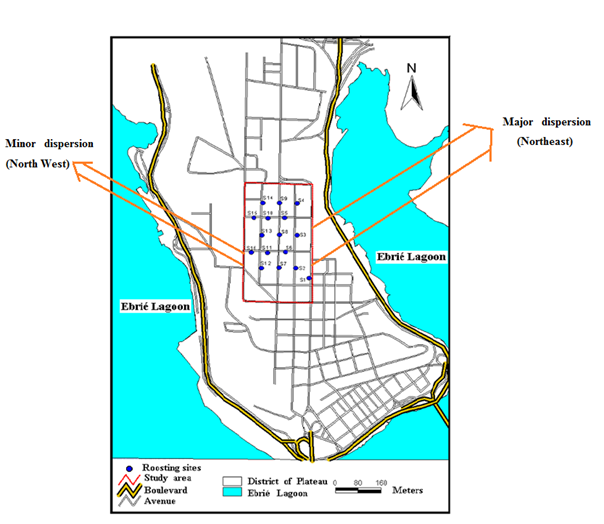
- Our experimental site (Plateau Commune in Abidjan, Southern of Cote d’Ivoire) stretches out between longitudes 4°10’ and 4°50’ West and latitudes 5°10’ and 5°80’ North, on a surface area of 2.5 km² (Figure 1). Also, core area of presently process experimental site avenues are characterized by different species of tree which are used as roosting sites (Figure 1) by straw-colored fruit bats [13, 15-18].
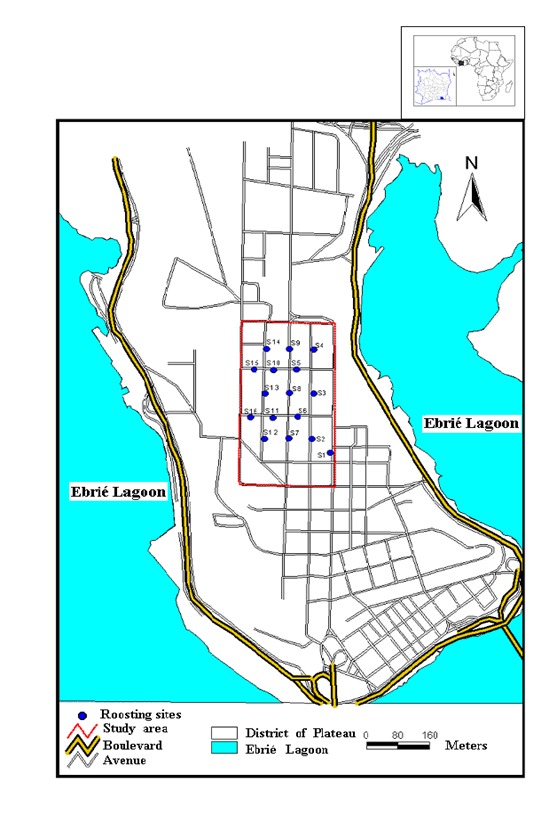 | Figure 1. Cartography of 16 roosting sites of straw-colored fruit bats in the District of Plateau in Abidjan from August 2005 to July 2006 |
2.2. Data Collection
- Data were collected from August 2012 to July 2013. Visits were made on Saturdays, to take into account poaching activities, which take place on other non-working days [9]. To study the spatiotemporal activities of the straw-colored fruit bats in Plateau Commune, observations were made thanks to binoculars from 7:00 Am to 07:00 Pm., respectively, in all identified roosting sites and in the study area (Figure 1). We stopped our observations at 7:00 Pm. because of the darkness [1]. Bats activities in the corresponding time ranges were recorded to determine the behavioural pattern frequencies. In addition, the modalities of dispersal of fruit bats in relation to food availability, reproduction and season were also observed. In this study, the monthly availability of food was assessed by presence and/or lacking of fruit, epiphyte or defoliated fir tree and as well food resources tree species [24] previously identified by of the National Floristic Center of the University Félix Houphouet-Boigny in Côte d’Ivoire [15, 17].
2.3. Statistical Analysis
- Before any analysis, data was normalized using the X + 1 transformation. The Generalized Linear Model was done to compare behavioural occurrence frequencies and to test the effect of the season on the distribution of activities. The present analysis was performed by using STATISTICA software (version 7.1).
3. Results
3.1. Activities
- Observations made in experimental site (Plateau commune in Abidjan) from August 2012 to July 2013 recorded four circadian rhythm activities in straw-colored fruit bats population: (i) sleeping activities from 07:00 Am to 05:00 Pm (Figure 2), (ii) awaking from 05:00 Pm to 05:30 Pm and (iii) grooming from 05:30 Pm to 06:00 Pm and (iv) dispersion activities from 06:00 Pm to 07:00 Pm (Figure 3).
 | Figure 3. Dispersion of straw-colored fruit bats outside the Plateau Commune for forage from August 2012 to July 2013 |
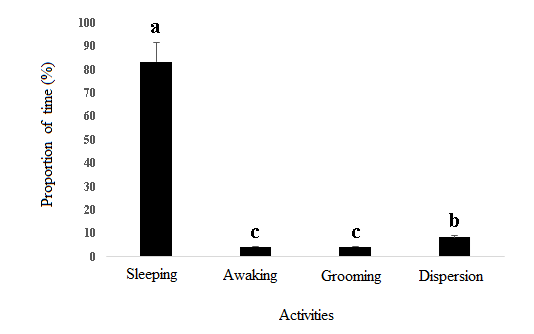 | Figure 4. Activities of the straw-colored fruit bats in the Commune of Plateau in Abidjan from August 2012 to July 2013 (a: major activity; b: average activity and c: minor activity) |
3.2. Dispersion Patterns
- Straw-colored fruit bats dispersion survey highlighted different patterns in relation to food availability and reproduction activities.
3.2.1. Food Availability
- Availability of food resources around roosting sites incite some female bats movement from peripheral zone to dormitories sites and vice versa. This pattern has been observed when the trees used as roost were not fruit trees and/or fruit trees without fruits (Figure 5).
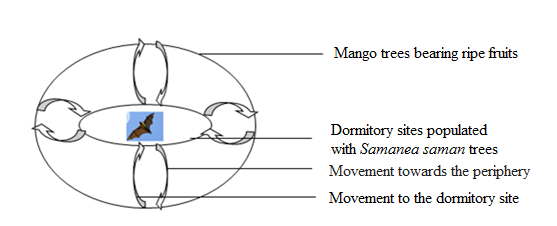 | Figure 5. Dispersion of bats from dormitory sites to peripheral mango trees bearing ripe fruits in Plateau Commune from April to July 2013 |
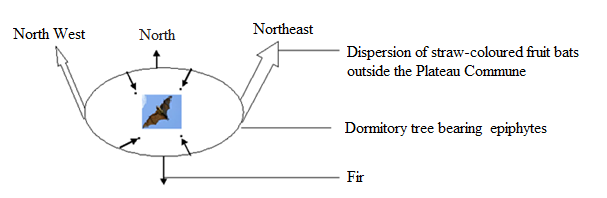 | Figure 6. Dispersion of straw-colored fruit bats in Plateau commune in exploiting fir Araucaria excelsa and epiphytic plants Platycerium sp leaves from June to July 2013 |
3.2.2. Food Unavailability
- When the food resources exploited by a part of the population within processed site area are exhausted, fruit bats population dispersed outside Plateau Commune along the north-west and north-east directions (Figure 7).
 | Figure 7. Dispersion of the population of straw-colored fruit bats outside the study site for foraging when food resources are depleted in the Plateau Commune |
3.3. Effect of the Season on Behavioral Dispersal Patterns of Eidolon helvum
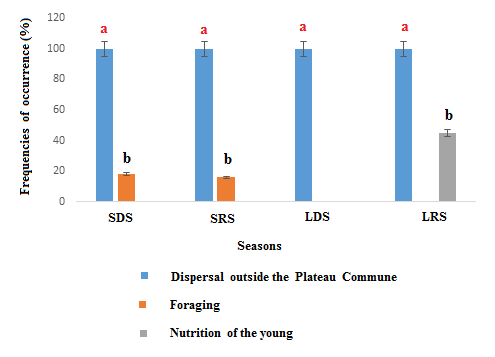
- Three dispersal behavioural patterns were observed during the different seasons; (i) dispersal outside Plateau Commune, (ii) foraging and (iii) young nutrition activities (Figure 8). Globally, comparison analysis with regard behavioural pattern frequencies by Generalized Linear Model survey revealed the preeminence of dispersal activity in all seasons followed by foraging activities during small dry and small rainy seasons. Also, it is noteworthy to underline that young’s nutrition activities increase (second more important dispersal behavioural pattern) during long raining season. Generalized linear model confirmed these observations suggesting season factor as significantly influencing presently analyzed straw-colored fruit bats population dispersal patterns (ddl=3; W=8.45; p < 0.05).
4. Discussion
- Observations on straw-colored fruits bats behavior in Plateau Commune area in Abidjan, Southern of Côte d’Ivoire allow to record and/or identify four activities. Then, these results contrast with previous study that discriminated only two activities (day rest and nocturnal activity) in the same area [13]. This difference could be linked and/or due to briefs performed observations. However, our findings in agreement with [13] study indicated sleeping phase as the most important activity feature.Concerning fruit bats dispersion movement with the purpose of foraging, our findings are in agreement with those of [13]. This observation suggested an involvement of biological clock in determining the above mentioned fruit bats activity dispersal moment. Round-trip activity appears to be executed by fruit bat female individuals. In according to that suspect, our findings suggested that, several fruit bat females’ dispersing in the evening, with the purpose of forage, do not return to their daily roost site, unless they have young taking care [25]. It’s has been revealed that leaves turn out to be an important nutritional resources of straw-colored fruit bats because of fruit rarity and/or lacking in the presently processed experimental area (Plateau Commune quartier). Indeed, various studies showed that both fruits and flowers rarity and/or unavailability in frugivorous bats inhabited areas influence their diet changing resulting in leaves and buds feeding [15, 17]. In addition, fir leaves (Araucaria excelsa) and epiphytic plants (Platycerium sp) have been identified as straw-colored fruit bats food resources in Plateau Commune area in Abidjan [17].Straw-colored fruit bats population dispersed outside of Plateau Commune site to forage. Also, it has been reported that restriction with regard food resources availability contrast with normal bodily maintenance needs value. Hence, to overcome this issue, individuals migrate and/or check for food abundance area with the purpose to satisfy their high energy needed [11, 18, 26-29]. Seasonal dispersal behavioural patterns result to be strongly correlate with food availability in space and time. According to optimal foraging theory, individuals should minimize travel distance, time and energy expenditure to locate food patches while maximizing food intake [2, 30, 31]. Thus, variations in the seasonal dispersal patterns of straw-colored fruit bats in Plateau Commune would be associated to the seasonal availability of food resources in space and time [15-18, 29].
5. Conclusions
- The study of the spatio-temporal distribution of behavioural patterns of straw-colored fruit bats, Eidolon helvum, a near-threatened species in Plateau Commune in Abidjan, recorded sleeping, awaking, grooming and dispersion as main activities and highlighted sleeping activity as the most important (83.34%). Dispersal patterns have been associated to food resources availability and reproduction. Three types of dispersal behavioural patterns were observed during the different seasons: dispersal outside processed area, foraging and young nutrition activities. Findings advised the preeminence of dispersal activity outside Plateau Commune (100%) in all season suggesting seasonal influence on Eidolon helvum dispersal behavioural patterns in above mentioned area (Plateau Commune in Abidjan Southern of Côte d’Ivoire). To maintain the integrity of the population of that near-threatened species, the protection of the roosting and breeding sites must be strengthened during the daily sleep, phase during which these megachiropteran are the most vulnerable. Thus, human will be able to benefit from the important ecosystem services provide by this specie for his well-being.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML