-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Research in Zoology
p-ISSN: 2325-002X e-ISSN: 2325-0038
2015; 5(2): 25-31
doi:10.5923/j.zoology.20150502.01

Limnological Parameters and Population Structure of Artemia persimilis Piccinelli and Prosdocimi, 1968 (Crustacea, Anostraca) in La Amarga, a Hypersaline Lake of La Pampa (Argentina)
Echaniz Santiago A., Cabrera Gabriela C., Vignatti Alicia M.
Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales, Universidad Nacional de La Pampa. Avenida Uruguay, Provincia de La Pampa, República Argentina
Correspondence to: Echaniz Santiago A., Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales, Universidad Nacional de La Pampa. Avenida Uruguay, Provincia de La Pampa, República Argentina.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

In the semiarid central region of Argentina, there are many hypersaline lakes that are scarcely studied ecologically. In La Pampa province, La Amarga stands out, which is a lake with particular characteristics that belongs to a virtually inactive fluvial system by anthropogenic action. Since Artemia persimilis Piccinelli and Prosdocimi, 1968, a native species on which information is scarce, has been registeredin La Amarga, the objectives of this study were to determine the main limnological parameters and know the density, biomass and population structure of A. persimilis and its relationship with environmental parameters. Seasonal samplings (January, April, August and October) were carried out during 2007. In situ temperature, dissolved oxygen concentration, pH and transparency were determined. Water samples were taken for the determination of salinity, nutrients, suspended solids and chlorophyll-a and qualitative and quantitative zooplankton samples. The mean salinity was 115 g.L-1 ±19.02 and Cl- and Na+ predominated. Mean transparency was 1.54 ±0.15 m, and despite high concentrations of nutrients (TP: 4.38 ±1.61 mg.L-1 and TKN: 25.32 (±12.29) mg.L-1), the phytoplankton chlorophyll-a concentration was reduced (1.65 ±1.16 mg.m-3). The mean density and biomass of A. persimilis were reduced (1.56 ±2.17 ind.L-1 and 122.43 ±99.3 µg.L-1). The density was minimal in winter (0.04 ind.L-1), but was higher when more biomass was found (240.95 µg.L-1), since larger stadiums (post-larvae and adults) prevailed. No correlations between total density and biomass or those of the different stages and environmental parameters were found. Although A. persimilis has adaptations that allow it to thrive with higher salinities than those of La Amarga, its low density and biomass could be due to scarce availability of food, given the low concentrations of chlorophyll-a and suspended organic solids that were recorded.
Keywords: Artemia persimilis, Hypersaline lakes, La Amarga, La Pampa
Cite this paper: Echaniz Santiago A., Cabrera Gabriela C., Vignatti Alicia M., Limnological Parameters and Population Structure of Artemia persimilis Piccinelli and Prosdocimi, 1968 (Crustacea, Anostraca) in La Amarga, a Hypersaline Lake of La Pampa (Argentina), Research in Zoology , Vol. 5 No. 2, 2015, pp. 25-31. doi: 10.5923/j.zoology.20150502.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Due to the strong gradient east-west of rainfall that is registered in Argentina, many hypersaline lakes [1] exist, especially in arid and semi-arid regions of western central. Most of them have been scarcely studied, with information only existing on some highland saline lakes of the northwest [2, 3], of the Córdoba province or La Pampa [4].Hypersaline lakes are particular environments because an abiotic factor, the salinity, is dominant and produces a strong environmental stress [5]. This makes biodiversity reduced, so that the region can only be inhabited by species with physiological mechanisms to counteract the osmotic stress generated by the high concentration of salts [6].The anostracans of the Artemia genus are some of the few organisms able to withstand the extreme conditions imposed by these environments. In Argentina, the genus is represented by two species: Artemia franciscana Kellogg, 1906 and Artemia persimilis Piccinelli and Prosdocimi, 1968. The first is a North American species that has colonized Argentinean environments for passive income with bird migrations coming from the northern hemisphere. Some birds have carried cysts that allowed the colonization and rapid expansion of A. franciscana [7], since at present its distribution has been expanded to 30°S, having been recorded in Mar Chiquita Lake, in Córdoba [8]. A. persimilis is native and the only species recorded in the province of La Pampa. It has been determined that its distribution could be in decline due to the greater phenotypic plasticity attributed to its cogeneric [9-11], although a possible limitation to the advancement of A. franciscana to the south could be its lower tolerance to low temperatures [12, 4]. Due to the economic interest in that genus, from its naupliar to adult stage, since they are the crustaceans most often used in aquaculture as live food for various fish and other crustaceans of commercial interest [13-15], some biological aspects of A. persimilis have been studied in the laboratory [16-20]; however, there is very limited information on the ecology of this species under natural conditions [4]. In La Pampa province, in the semiarid center of the country, the ecology of hypo to mesosaline lakes [1] is relatively well known, as their chemical composition, trophic status, taxonomic composition of zooplankton and the effects of environmental changes on zooplankton have been studied [21-30]. However, hypersaline lakes have only recently begun to be studied and in this respect, Vignatti et al. [4] registered A. persimilis to the higher salinity (418.5 g.L-1) reported in the world literature, in Guatraché, a large hypersaline lake situated at the southeast of the province.Considering that there are other hypersaline lakes in La Pampa on which there is only hydrological information as they have been poorly studied biologically, and A. persimilis has been registered in some, the aims of this study were to determine the main limnological parameters of La Amarga, an extensive hypersaline lake located at southwest of the province; to determine the density, biomass and population structure of A. persimilis; and to establish relationships between biotic and environmental variables.
2. Materials and Methods
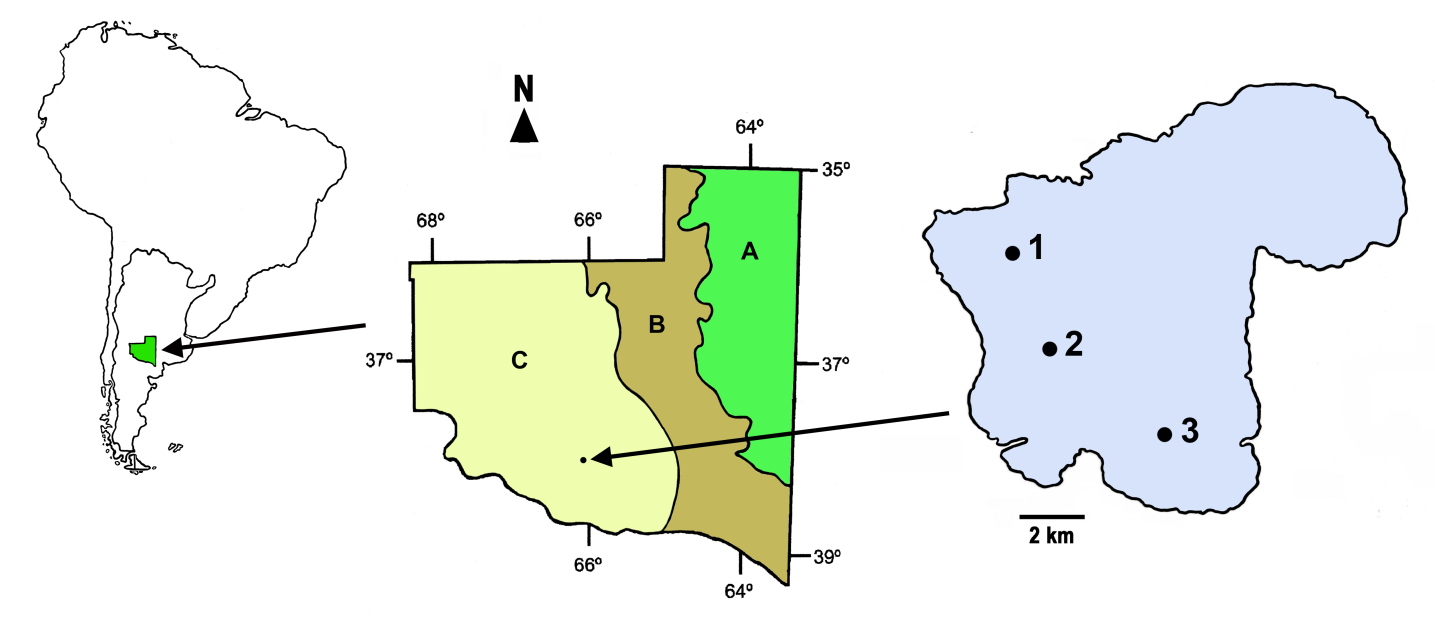
2.1. Study Area
- La Amarga (66º07´W, 38º13´S) (Figure 1), located in the Curacó Department, is the largest natural lake in the province. It has a maximum length of 15,428 m, a maximum width of 9688 m, an area of 11,109 ha and a maximum depth of about 12 m. Mean annual rainfall in the region is around 300 mm and the potential evapotranspiration 750 mm [31]. La Amarga differs in several aspects from most natural lakes of La Pampa. First, its depth is much greater; however, on the other hand, it is not located in a naturally arheic basin, because it is part of a practically inactive fluvial system. In the past, the river Chadileuvú, originating from the confluence of major rivers with a source in the mountain range of the Andes (Atuel, Diamante and Desaguadero) passed by this system. The Chadileuvú river fed La Amarga Lake and the excess water continued on its course to another river, the Curacó, until it reached its mouth in the Colorado River and finally in the Atlantic Ocean. For over 60 years, the rivers Atuel, Diamante and Desaguadero have been dammed in the provinces of Mendoza and San Juan, making natural feeding of the lake very sporadic. Water ingress to La Amarga occurs only on rare occasions when the reservoirs mentioned above are opened. The lake is located in the phytogeographic province of the Monte [32], where low and sparse shrubland of “jarillas” (Larrea) dominates. The arid landscape means that the low human activity in the region is restricted to raising goats. During the study period, the lake lacked rooted vegetation and fish fauna.
2.2. Field and Laboratory Work
- During 2007, seasonal samplings were conducted in summer (January), autumn (April), winter (August) and spring (October) at three sites (Figure 1). The water temperature, the concentration of dissolved oxygen (Lutron® OD5510 oximeter), the water transparency (Secchi disk), and the pH (Cornning® PS15 pH meter) were recorded at each station, and water samples, which were kept refrigerated until analysis, were collected for physicochemical determinations.
- In addition, a qualitative sample of zooplankton was taken by vertical and horizontal dragging, using a net with a mouth diameter of 22 cm and a mesh opening of 0.04 mm, and quantitative samples were taken with a 10 L Schindler-Patalas plankton trap using a net with a mesh opening of 0.04 mm, by means of two vertically aligned extractions, in order to integrate the water column. Samples were anesthetized with CO2 and kept refrigerated until analysis. The maximal depth of the lake was measured by probing and the length and width with a GPS Garmin® E-Trex Legend. The dissolved solids concentration (salinity) was determined by the gravimetric method with drying of 50 ml of previously filtered water at 104°C. The concentration of chlorophyll-a was determined by extraction with aqueous acetone to 90% and subsequent reading in a spectrophotometer [33, 34], total Kjeldahl nitrogen by the Kjeldahl method and total phosphorus using the method of ascorbic acid, and previous digestion with potassium persulfate. The content of suspended solids was determined with Microclar FFG047WPH fiberglass filters, dried at 103-105°C until constant weight and later calcined at 550ºC [35].Counts of zooplankton [36] of each sample were carried out under stereoscopic microscopes in Bogorov chambers. The proportion of stadia of Artemia persimilis was determined in Sedgwick Rafter chambers under light microscope (40-100X).For the calculation of the biomass, a minimum of 30 specimens per stage were measured with a Leitz ocular micrometer. Once analyzed, the samples were fixed with 5% formalin and then deposited at the plankton collection of the Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales de la Universidad Nacional de La Pampa. We used the classification of continental waters based on salinity proposed by Hammer [1]. To represent the water chemistry, we developed a Maucha graph [37, 38]. In order to examine relationships between environmental factors and attributes of zooplankton, nonparametric correlation coefficients of Spearman (rs) were calculated and to improve the exploratory data analysis, Principal Component Analysis (PCA) was performed [39-41].With the aim of characterizing the lake as a function of its transparency, we calculated the relationship between the mean depth and that of the photic zone: Zm/Zphot [42]. For calculation of the depth of the photic zone, we multiplied the reading from the Secchi disk by a factor of 3 [36, 43]. We used Past [44] and InfoStat [45] software.
3. Results
- The water temperature followed a seasonal pattern and varied from a minimum of 6.9°C in winter and 25.8°C in summer (Figure 2). The lowest concentration of dissolved oxygen in the water was recorded in summer (5.2 mg.L-1) and highest in autumn (8.1 mg.L-1) (Figure 2).
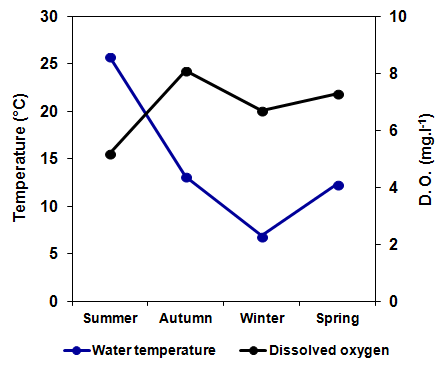 | Figure 2. Seasonal variation of the water temperature and dissolved oxygen concentration in La Amarga Lake during 2007 |
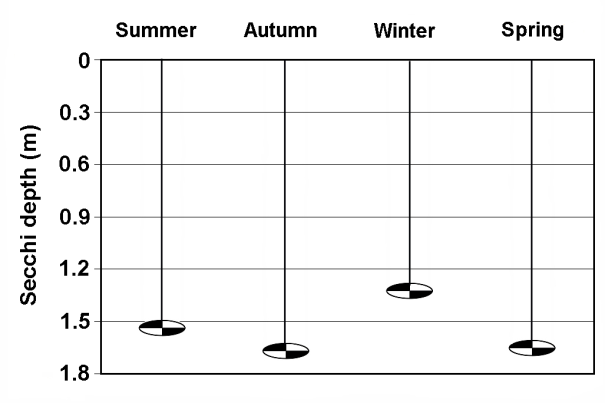 | Figure 3. Seasonal variation in the water transparency in La Amarga Lake during 2007 |
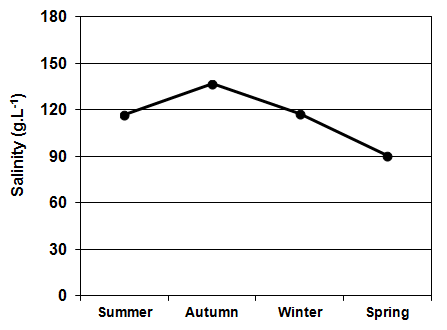 | Figure 4. Seasonal variation in the salinity of La Amarga Lake during 2007 |
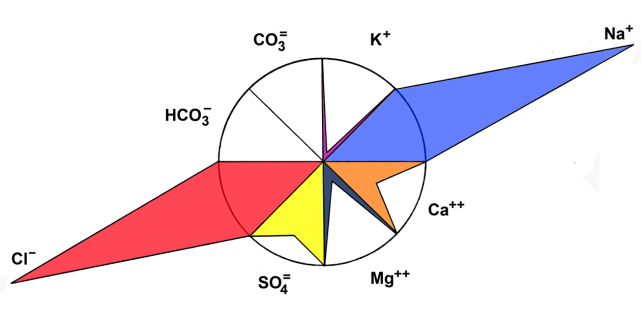 | Figure 5. Maucha´s diagram representing the chemical composition of the water of La Amarga Lake during 2007 |
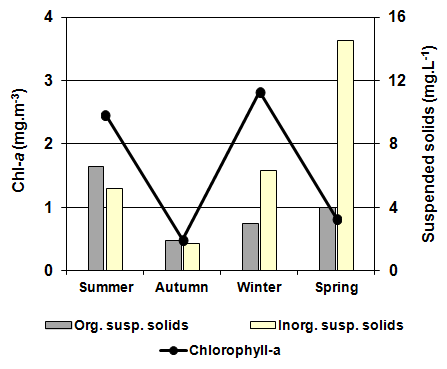 | Figure 6. Seasonal variation of the suspended solids and chlorophyll-a concentration during the study period in La Amarga Lake |
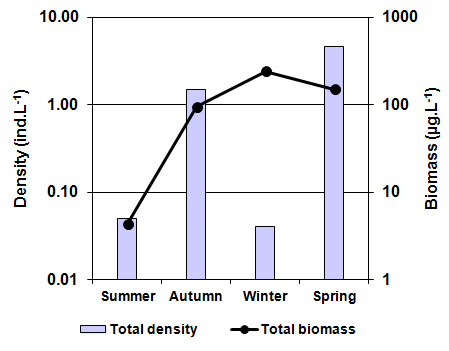 | Figure 7. Seasonal variation in the total density and biomass of A. persimilis in La Amarga Lake during 2007 |
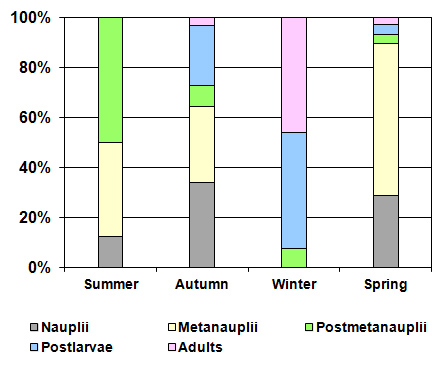 | Figure 8. Seasonal variation of the different stages of de A. persimilis in La Amarga Lake during 2007 |
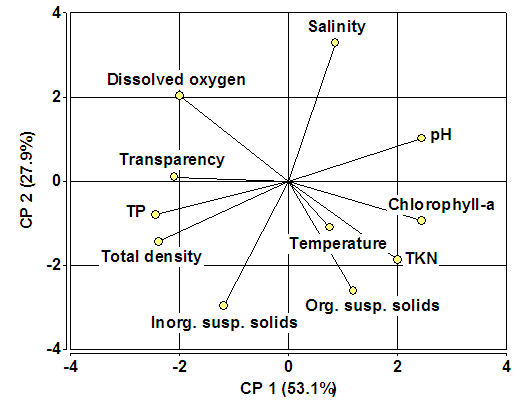 | Figure 9. Biplot with the results of the Principal Component Analysis |
4. Discussion
- As indicated above, water entry to La Amarga occurs only on the rare occasions that the floodgates of the reservoirs in Mendoza and San Juan provinces are opened. In these cases, although the incoming water had relatively low salinity, the evaporation caused the salinity to slowly increase after the cessation of input, such as that which occurred during the 90s [46]. However, this situation was not the same over time. Information from ancient inhabitants of the region indicates that before cutting of the fluvial system, the salinity of the lakes of “Curacó system” (among which it includes La Amarga) was much lower, to the point that there were fish. Among them, Odonthestes bonariensis (silverside) was highlighted, to the point that it came under small-scale commercial fishery [46-48]. The presence of this species suggests that salinity was much smaller in the past, given that its tolerance, although wide, it does not allow it to adequately develop in salinity near the sea water (~33 g.L-1) [49, 50].Despite this, during the study period, the dissolved solid concentration allowed La Amarga Lake to be classified as hypersaline [1]. The particular dynamics of this aquatic ecosystem led to a salinity decline, similar to that which happened in the previous year (2006), during the same period (autumn-spring). This occurs because the water released from the upstream reservoirs, with a relatively low salinity, usually enters at this time [51]. Due to the high concentration of nutrients registered in the water, La Amarga could be classified as hypertrophic. These high nutrient concentrations could be due to the frequent sediment resuspension in shallow areas caused by the effect of strong and frequent winds of the region and the process of accumulation of nutrients favored by the lack of water output from the lake [52]. However, the chlorophyll-a concentration was very low, which characterizes an oligotrophic environment. The reduced development of phytoplankton, represented by the low chlorophyll-a concentration, could be due to a limitation imposed by the high salinity rather than a lack of nutrients or the limitation imposed by any of them. The low concentration of chlorophyll-a as well as the reduced concentration of suspended solids meant that the water of La Amarga had a very high transparency; the same was also registered in Guatraché, another Pampean lake where A. persimilis was found in very low densities [4]. However, there is a remarkable difference with Utracán, another lake of La Pampa, very different from its reduced depth and chlorophyll-a and organic suspended solid concentrations that are almost 26 and 100 times higher, respectively, which led to reduced transparency. Here, this species was found during a hypersaline period (2009-2010) with high densities and biomasses (Echaniz and Vignatti, unpublished data), several times higher than that of La Amarga.The density and biomass of A. persimilis in La Amarga were very reduced and higher in autumn and spring when the water temperature was around 12°C. With the exception of winter, when post-larvae and adults predominated indicating a lower rate of reproduction, in the other stations, the highest proportion was given by the early stages (nauplii, metanauplii and post-metanauplii). This situation is similar to that of Guatraché, where the density of A. persimilis was also very low [4], but contrasts with that recorded in Utracán, where a 40 times higher abundance, represented mainly by post-metanauplii, was found (unpublished data). As mentioned, during the period in which the species was recorded, Utracán differ from La Amarga and Guatraché by high concentrations of chlorophyll-a and organic suspended solids, which could indicate a much larger food supply for A. persimilis.Thus, although A. persimilis is an extremophile species that has efficient mechanisms for both individual and population survival [6], and the salinity of La Amarga could have been within its ranges of tolerance, the lower population density could be due to a reduced availability of food represented by low concentrations of chlorophyll-a and suspended organic solids, as in Guatraché.
5. Conclusions
- La Amarga is a large lake in the province of La Pampa very particular, because it belongs to a river system almost inactive by human action. Until about sixty years ago, the river that fed the lake ran, and salinity was so low as to allow the existence of fishes. As at present the income of water from the river system is sporadic, so it became a hypersaline lake in which Artemia persimilis was recorded. This population differs from others in the region by its low density and biomass. As A. persimilis can thrive with higher salinity than that of La Amarga, its low density and biomass could be due to the limited availability of food, given the low concentrations of phytoplankton chlorophyll-a that were recorded.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- We thank the Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales, Universidad Nacional de La Pampa for the partial financial support of the project.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML