-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Research in Zoology
p-ISSN: 2325-002X e-ISSN: 2325-0038
2013; 3(3): 75-79
doi:10.5923/j.zoology.20130303.02
Incidence of Head Lice (Pediculus humanus capitis) among Primary School Children in Five Rural Schools in Khana Local Government Area, Rivers State, Nigeria
LeBari Barine Gboeloh, Kingsley Elele
Department of Biology, Ignatius Ajuru University of Education, Port Harcourt, Nigeria
Correspondence to: LeBari Barine Gboeloh, Department of Biology, Ignatius Ajuru University of Education, Port Harcourt, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
A total of 726 primary school children (363 males, 363 females) within the age of 6-13years from five rural primary schools in Khana Local Government Area, Rivers State were investigated for the presence of Pediculus humanus capitis by visual examination of their head. Questionnaires were used to assess children’s and teachers’ knowledge about the parasite. Out of 726 school children investigated, 331(45.6%) were found infested with immature and adult head lice. This value was statistically significant (P<0.05). Girls showed a high prevalence (30.3%) than boys (15.2%) and there was no statistically significant relationship between age of children investigated and prevalence. Low socioeconomic status accounted for the high prevalence of the parasite. 94.7% of the children agreed sharing the same bed with others and the major treatment measure was hand picking. All the teachers interviewed had good knowledge of pediculosis and agreed that the infestation is preventable. Risk factors mentioned by the teachers included sharing comb, beddings and contact with head. 100% of respondents mentioned lack of concentration as the major effect of pediculosis among school children. Preventive measures reported by the teachers included personal hygiene, regular washing of hair and use of hair cream containing sulphur.
Keywords: Ectoparasite,Pediculus humanus capitis, School Children, Nigeria
Cite this paper: LeBari Barine Gboeloh, Kingsley Elele, Incidence of Head Lice (Pediculus humanus capitis) among Primary School Children in Five Rural Schools in Khana Local Government Area, Rivers State, Nigeria, Research in Zoology , Vol. 3 No. 3, 2013, pp. 75-79. doi: 10.5923/j.zoology.20130303.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Head Lice (Pediculus humanus capitis) is one of the commonest ectoparasites of man in the tropics and it has been implicated in the transmission of several microbial infections including spirochaetal[1]. Lice are permanent, obligatory ectoparasites spending their entire life cycle on the host[2]. There are three distinct varieties of lice which are specific parasitic for humans. The head louse, Pediculus humanus capitis De Geer (Anoplura: Pediculidae), and the body louse, Pediculus humanus humanus are closely related variants of the same species though they have different habits and habitats. The pubic louse, Phthirus pubis, also called “crab louse” is the third species[3, 4].The adult forms and eggs of Pediculus humanus capitis occur freely on unkempt hair and are disseminated primarily by physical contact, with the incidence being usually more in over-crowded situation[5].It causes a disease called pediculosis which has become a major health concern in both schools and in the wider community. Pediculosis (Pediculosis capitis) caused by Pediculus humanus capitis affects millions of children worldwide, especially those aged 5-13years[6]. Although head lice can infest people of all ages[3], children are more vulnerable to infestations because of their habit of playing in close contact, share hats, head-phones, combs and brushes and clothing[5]. In school-aged children, head lice infestation can cause sleep disturbance, potentially leading to poor performance in school[7]. It is also associated with social distress, discomfort, parental anxiety, embarrassment and unnecessary absence from school[8].Several studies have been carried out on the prevalence of head lice infestation in school children in different parts of the world. In Malaysia, the prevalent rate is reported to be 12.9%[9], in Saudi Arabia, it is 12%[10], in Korea, it is 37.22%[11], in Argentina, it is 61%[12], in Australia, it is 95%[13] and in Belgium, it is 8.9%[14]. In sub-Saharan Africa, high prevalence has also been reported. In Ghana, the prevalent rate was reported to be 49%[15] and in Angola, it was 42.1%[7].In Sub-Saharan Africa, the high prevalent rate and persistence infestation has been associated with high morbidity including secondary infections and impetigo[16]. Scarcity of resources and lack of trained health personnel in this region have resulted in complete neglect of pediculosis, resulting in its prevalence in many areas[17, 18]. The infection is also common in industrialized countries especially among residents of unhygienic environments[19, 20]. In Nigeria, the distribution of head lice in primary and post-primary school pupils in Nsuka, East Central Nigeria was studied[1], other studies on head lice infestation has also been conducted in a rural village in Kwara State[21] and among primary school children in Calabar[22], Cross River State, Nigeria.Head lice infestation is a public health concern in parts of Nigeria. To the best our knowledge, no such study had been conducted in Rivers State, Nigeria, hence this study was conducted to determine the prevalence of P. humanus capitis among primary school children in Khana Local Government Area, Rivers State, Nigeria, in relation risk factors involved, treatment and control of pediculosis.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
- The study was conducted in five selected rural primary schools in Khana Local Government Area of Rivers State. Khana Local Government Area is one of the twenty three local government areas in Rivers State, Nigeria. It lies in the Niger Delta within latitude 40NE and longitude 80NE. It occupies an area of about 990 Square kilometres. The LGA is made up of one urban centre (Bori) and several rural communities. The inhabitants are predominantly Ogonis who engaged in subsistence farming and trading. Household included many low-income earners living in typical mould houses in a hydrocarbon-polluted environment. The study area has several government-owned primary schools. The Primary schools selected for this study included Community Primary school 1 and 2, Beeri, Community Primary school Wiiyakara and Community Primary school 1, Taabaa. The surveys and collections of head lice were conducted within November 2012 and February 2013 from pupils in primary one to primary 5. Oral interview was also conducted.
2.2. Sampling Method
- A total of four hundred and ninety two pupils from the selected primary schools were examined for the presence of Pediculus humanis capetis. Screening of each pupil was done by visual examination the head in sufficient day light, by combing of the hair with toothed comb on a piece of white paper for about 3-5minutes. The hair and scalp were examined by separation of the hair every 1 to 2 cm and eggs, nymph and adult lice identified using a magnifying glass.
2.2.1. Questionaire
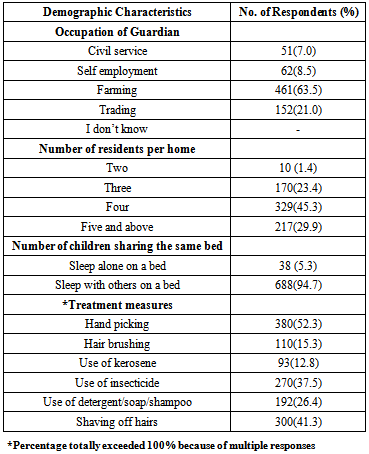
- A cross sectional survey was adopted using questionnaires targeted at the pupils and the teachers. The questionnaire contained multiple choice questions to indicate teachers’ knowledge of head lice infestation, particularly regarding the biology, transmission, clinic manifestations, treatment and prevention. The pupils were interviewed on knowledge and treatment of head lice, socio-demographic factors associated with pediculosis including occupation of guardian, number of persons that sleep on the same, bed, whether other residents had head lice infestation, types of home, number of children in the home and number of people at home with the lice infestation.
2.2.2. Statistical Analysis
- Data analysis was performed using SPSS software, version 18.0 and Chi-square used to determine the relationship between prevalence and independent variables at statistical significant of p<0.05.
2.3. Ethical Consideration
- Before examination of the pupils, the researchers held a meeting with the Head Teacher and staff of each of the schools to explain the objectives of the study. The objectives were also explained separately to the pupils in a meeting. Consent form was included in the study for teachers and pupils who agreed to participate in the study.
3. Results
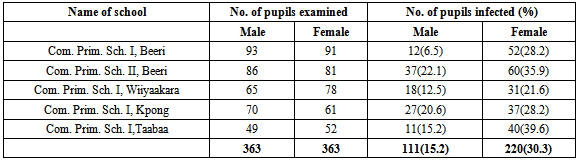
- A total of 726 school children (363 males and 363 females) within the age bracket of 6 and 13years from five rural primary schools were investigated for the presence of Pediculus humanus capitis in the hairs of their head. Out of this number, 331(45.6%) were infected by the parasite (Table 1).The results indicated that out of the 331 pupils infected, 111(15.2%) were males while 220(30.3%) were females (Table 1).Table 2 showed the distribution of head lice infestation in the studied population in relation to age. The parasite was highly prevalent among children within the ages of 8 and 9years (59.0%), followed by children within the ages of 6 and 7years (45.4%) and those within the ages of 10-13years (28.8%).
|
|
|
|
4. Discussion
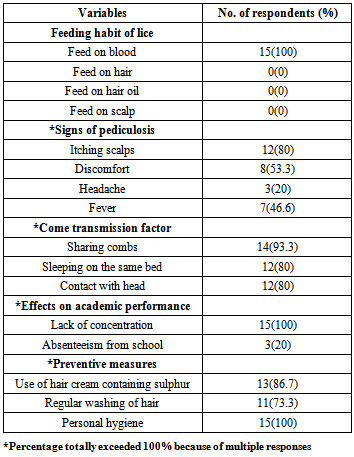
- The present study indicated that the overall prevalence (45.6%) of pediculosis in the study area was statistically significant (P<0.05) among children in all the schools sampled. The result is similar to the 48.1% reported in selected human settlement in Lagos State[18] and slightly lower than the 74.0% recorded in Shanko village in Kwara State, Nigeria[23]. It is however higher than the 26.4% recorded in previous studies among primary school children in Calabar, Cross State, Nigeria[22] and the 29.0% prevalence recorded among rural residence of Kwara State, central Nigeria[21].The high prevalent rate (45.6%) recorded in this study area could be attributed to poor sanitation and personal hygiene as well as leaving in crowded rooms[3, 24].Present study demonstrated that pediculosis was more prevalent in girls (30.3%) than in boys (15.2%). This result is consistent with the previous reports[17, 18, 22].The high prevalence observed in girls could be attributed to gender-related behaviour[16]. For instance, girls have the tendency to have long[13], they also tend to have closer and more prolonged social contact in small groups than boys[7]. The high prevalence could also be as a result of the fact that girls keep braided hairs which are kept for a long time without combing or washing while boys keep short and shaved hairs[22].The present study regarding knowledge, attitudes and practices on Pediculosis humanus capitis infestions showed that the study population have good knowledge of human head lice. Human lice infestation is still perceived as a trivial health problem by the respondents and public health practitioners[23]. This trend could be attributed to the presence of more important parasitic diseases in rural Nigerian communities[21]. The study also revealed that socioeconomic status is a risk factor in the prevalence of pediculosis. Majority of the respondents reported that their parents/guardians were farmers (63.5%) and traders (21.0%). This is an indication that poverty existed among the study population. This is further confirmed by the fact that majority of the children (94.7%) agreed that they share same bed with others, and live in overcrowded home. It has already been demonstrated that if one member of a family is infested with head lice, other family members had a high risk of infestation[7, 16].Other researchers maintained that socioeconomic conditions have great association with head lice infestation because poor economic conditions are likely to result in crowding at home and sharing of beddings and comb[3, 25]. In Delhi, India, It was observed that those who shared both beddings and comb showed a statistically higher significant head lice infestation than others[26].In previous study, age was recorded as one of the risk factors that influence the prevalence of head lice infestation [22]. However, results obtained in the present study indicated no statistically significant (p>0.05) relation between age and prevalence of pediculosis. The differences in infestation rate among the various age groups investigated were not significant. Hand picking (52.3%), shaving off hair (41.3%) and use of insecticide (37.5%) were the most frequently used treatment methods reported by the respondents. This is in consistent with previous studies among school children in Viana, Angola[7], among school children at Quetta city, Pakistan; Jorge[3], in Shanko village of Kwara State, Nigeria[23] and among primary school children in Calabar, Cross River State, Nigeria[22].The teachers have good knowledge about head lice infestation as 100% of the respondents agreed that pediculosis is preventable and head lice feed on blood, 80% reported that itching scalp and discomfort (53.3%) were the major symptoms of pediculosis. The teachers also reported sharing combs (93.3%), sleeping on same bed (80%) and contact with head were the major risk factors in the transmission of pediculosis. This is in agreement with previous study among primary teachers in Viana, Angola[7]. This knowledge could be attributed to their level of education. All the teachers (100%) interviewed reported that head lice infestation among school children deprived them of full concentration hence affects their academic performance. This trend could be attributed to the itching scalp symptoms associated with pediculosis. Regular washing of hair and personal hygiene reported by the respondents as preventive measures have already been reported in other studies[3, 7, 27]. These studies recorded good personal hygiene, regular hair washing and brushing as some of the preventive measures of head lice infestation[22, 28, 29]
4.1. Conclusions
- Our study revealed that school children are more vulnerable to head lice infestation and the prevalence of pediculosis is high in rural primary schools in Khana Local Government Area. It is highly prevalence in girls. Poor socio-economic status and lack of personal hygiene are among the most important risk factors. Although the pupils and teachers tend to have a relatively good knowledge pediculosis, they lack appropriate knowledge about treatment of the infestation. This calls for the need to give adequate public health information on the biology, epidemiology, preventive and treatment measures associated with pediculosis and other ectoparasitic infestation. Emphasis should be placed on personal hygiene and the government should enhance poverty reduction programmes with the view to elevating the standard of living of the study population.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- We appreciate the support given to us by the head teachers, teachers and pupils of the primary schools investigated.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML