-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Research in Zoology
p-ISSN: 2325-002X e-ISSN: 2325-0038
2013; 3(1): 10-14
doi:10.5923/j.zoology.20130301.02
Trials for Isolation of Contagious Pustular Dermatitis Virus (CPDV) from Sheep in Ismailia Governorate
Ahmed A. Said, Sahar I. Mohamed, Nahed K. Abd Elhamid, Wafaa A. Hosny, Eman M. Baheeg
ELISA Research Unit and Viral Strain Bank, Animal Health Research Institute, Giza, Egypt
Correspondence to: Ahmed A. Said, ELISA Research Unit and Viral Strain Bank, Animal Health Research Institute, Giza, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Contagious Pustular Dermatitis (CPD) is a highly contagious, zoonotic, viral skin disease that affects sheep, goatand some other domesticated and wild ruminants. In this study, a total of 60 samples (15 scabs, and 45 serum) were collected from sheep in different farms in Ismailia Governorate during the appearance of skin lesions similar to CPD symptoms. Clinical examination of the affected sheep, show wart-like lesions on the lips, gums, teats, around the anus and dried scabs. Inoculation of scabs supernatant on primary lamb kidney cell culture revealed a cytopathic effect in the form of cell rounding, pyknosis, and cell detachment. Inoculation of the positive cell culture isolates on chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) of emberyonated chicken egg 9-11 days resulted in appearance of thickening in the CAM. Identification of the virus by agar gel precipitation test revealed a clear precipitation line while the morphology of the CPD virion was studied using the negative staining technique and photographed with an electron microscope revealed an electron micrograph of a typical parapoxvirus virions which is consisted of ovoid electro dense structures. The virions had a characteristic crisscross pattern in the outer membrane that gave them a basket-weave appearance. Agar gel precipitation test (AGPT) of the collected serum samples revealed a number of 5 positive samples for the presence of antibodies against CPDV.
Keywords: Contagious Pustular Dermatitis, CPDV Infection In Sheep, CPDV Detection
Cite this paper: Ahmed A. Said, Sahar I. Mohamed, Nahed K. Abd Elhamid, Wafaa A. Hosny, Eman M. Baheeg, Trials for Isolation of Contagious Pustular Dermatitis Virus (CPDV) from Sheep in Ismailia Governorate, Research in Zoology, Vol. 3 No. 1, 2013, pp. 10-14. doi: 10.5923/j.zoology.20130301.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Contagious pustular dermatitis (CPD) is a common epitheliotrophic highly contagious viral disease of sheep, goats, wild ruminants and sometimes other species including wild animals. It is also known as Orf, contagious ecthyma, infectious labial dermatitis, scabby mouth, or sore mouth[17]. The disease is caused by Orf virus genus Parapoxvirus, family Poxviridae[21], it is linear double-stranded DNA epitheliotropic virus 138 kbp[18] and[15]. Parapoxviruses are morphologically distinguished from other poxviruses by their ovoid shape, the crisscross pattern on the particle surface and relatively small size[7].The orf virus infects damaged or scarified skin through rough grazing and replicates in regenerating epidermal keratinocytes. Crusted areas on muzzle, eyelids, oral cavity, feet, or external genitalia are laden with virus[23]. Spread of infection can occure by direct contact or through exposure to contaminated feeding troughs and similar fomites including wheat stubble and thorny plants. The viruses are sometimes transmissible to humans after close contact with skin lesions of infected animals or handling virus-contaminated materials, so the infections are therefore classed as zoonoses[27].CPD virus is very resistant to adverse environments and physical factors except ultraviolet light. It may persist in shed scabs and in lambing sheds from one year to ten years but rapidly loses infectivity when exposed to rain on pasture[8] &[23]. Sheep may also carry the virus without showing lesions and introduce the disease into susceptible flocks[24].In sheep and goat, the disease usually occurs in young animals 3-6 months old, although neonatal lambs and kids aged 10-12 days old can be severely affected as well[13]. In naive flocks the disease can affect also adult animals. Clinical signs include papules, or vesicles and pustules on the non-woolly areas of the skin (around the mouth and nostrils, along the gums and in the oral cavity, on the thigh, axilla, genitalia, lower limbs, coronet and ewe udder and teats) that progress into thick crusts or heavy scabs[6]. Grazing and finishing lambs may develop the mouth form of CPD or more rarely, a condition known as strawberry foot rot. Lambs sucking infected teats commonly develop CPD lesions around the month and nostrils .The lesions usually heal in 2-4 weeks[24]. Infected animals usually exhibit a decrease in feed consumption and some become depressed, anorectic and febrile. Complications of contagious ecthyma include secondary bacterial infections (respiratory, gastrointestinal, integumentary), myiasis, mastitis and lameness[13]. The economic impact of the disease on sheep farmers due to decreases in production and also has a considerable negative effect on animal welfare[9] The morbidity can reach up to 100 % and the case fatality rate usually ranges between 5-15%[8] and[16].The diagnosis of CPD virus is based on the finding of large proliferative lesions on the animal body[19] and virus isolation in lamb testis or kidney cell cultures in combination with laboratory identification assays including electron microscopy, agar gel immunodiffusion (AGID) test, immunofluorescence or immunoperoxidase staining, Enzyme–Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) and PCR[15]. Antibodies can be found one week after the skin lesion appear. Serologic tests include virus neutralization, agar gel immunodiffusion, indirect immunofluorescence and ELISA. Virus neutralization is the most specific serological test, but is not sensitive enough to detect infections in all animals.[20].Genetic heterogeneity of the orf virus isolates circulate in different geographic regions including Europe, the Middle East, the United States, Africa, Asia, Alaska, South America, Canada, New Zealand and Australia has been recorded since the late 19th century and has been reported from most sheep or goat-raising areas[5]. In Egypt Orf virus was isolated from different field cases of sheep and goat[2] and in El Hawamdia, Giza, Egypt during the summer 2006[16].Aim of work:The study aimed for isolation and identification of CPD virus from samples of diseased sheep in Ismailia Governorate.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Samples
- A total of 60 (15 Dried scabs and 45 Serum samples) were collected from different farms in Ismailia Governorate during the appearance of skin lesions similar to CPD symptoms in sheep. Table (1)
|
2.2. Cell Culture
- Lamb kidney primary cell culture was prepared in the ELISA and viral strain bank unit, Animal Health Research Institute (AHRI), grown in Eagles MEM supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum. The cell culture was used for CPDV isolation[23].
2.3. Emberyonated Chicken Egg
- 9-11 days old embryonated chicken eggs supplied from the poultry reference laboratory-Animal Health Research Institute, for CPDV isolation on CAM.
2.4. Reference CPDV Antigen and Antiserum
- It was supplied by Sigma immune chemicals were used for applying AGIDT on the serum samples.
2.5. CPD Virus Isolation
- Virus isolation was achieved from the prepared supernatant of the scab samples .The supernatants were inoculated in the lamb kidney cell culture. The Cell culture examined daily for the presence of cytopathic effect (CPE). Cells were harvested when 50% CPE was observed and kept at -70 C till inoculation onto the (CAM) of emberyonated chicken eggs[16].
2.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy Identification of CPDV Isolates
- Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was applied on the lesions of the CAM for confirmation of CPDV in the Egyptian Organization for Biological Products and Vaccine -Agouza (VACSERA).The morphology of the virions was studied using the negative staining technique and photographed with an electron microscope[25].
2.7. Agar Gel Preciptation Test (AGPT)
- Agar gel Preciptation test (AGPT)test was used for detection of CPD antigen in the isolates and detection of antibodies against the virus in the collected serum samples using reference CPD antigen and positive immune serum[3] and[20].
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Manifestations
- In 2010, wart-like lesions on the lips, gum, teats and around the mouth appeared in different sheep farms in Ismailia Governorate (Fig. 1A ,B& C).
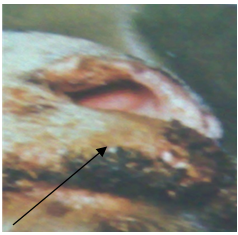 | Figure 1(A). Proliferative lesions of contagious pustular dermatitis virus around the mouth |
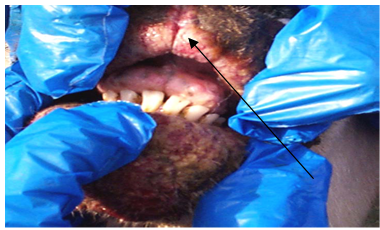 | Figure 1(B). Contagious pustular dermatitis virus lesions in the gum of affected sheep |
 | Figure 1(C). Contagious pustular dermatitis virus lesions on the medial aspect of the ewe’s teats |
3.2. Inoculation of Samples on Primary Lamb Kidney Cell Culture
- The result of inoculation of scabs supernatant on primary lamb kidney TC revealed a cytopathic effect in the form of cell rounding, pyknosis, and cell detachment was observed in 9 samples after 5-8 days of culture inoculation. (Table 2).
3.3. Inoculation onto Emberyonated Chicken Egg( CAM)
- Inoculation of the tissue culture positive isolates on corioallantoic membrane (CAM) of emberyonated chicken egg resulted in thickening in the CAM in 9 samples at 5-7 days from inoculation (Table 2).
3.4. Agar gel Preciptation test (AGPT)for CPD antigen Detection
- Seven isolates by embryonated chicken egg inoculation were positive for the presence of CPD antigen by Agar gel Preciptation test.
3.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy Identification of CPDV Isolates
- The morphology of the CPDV virions was studied using the negative staining technique and photographed with an electron microscope; it revealed electron micrograph of a typical parapoxvirus virions which is consisted of ovoid electrodense structures ranging in size (370x160). The virions had a characteristic crisscross pattern in the outer membrane that gave them a basket-weave appearance. (Figure 2).
 | Figure 2. Electron micrograph of the ORF virus particle showing typicaloval-shaped morphology (370x160 nm) original magnification x70000 |
3.6. Agar Gel Preciptation Test (AGPT) for Detection of Antibodies
- Only 5 from 45 tested serum samples were positive for the presence of antibodies against CPDV with the AGPT test.
4. Discussion
- Contagious ecthyma is a highly contagious, zoonotic, viral skin disease that affects sheep, goats and some other domesticated and wild ruminants. Although a number of proprietary treatments as well as homeopathic preparations are available, the treatment of Orf infections is usually not effective. Moreover the possible beneficial effects of treatment must be weighed against the danger of zoonotic infection[8]. Orf infection can be clinically manifested as simple lesions around the commisures of the mouth. These lesions usually begin as erythema, followed by papules,pustules, which develop into brownish dry scabs. The time span of these stages is usually four to six weeks. Under certain circumstances as in young malnourished kids the disease may take a chronic form, which might take more than six months to heal completely. In such chronic cases, the lesions can spread to other parts of the skin[1] and[6]. ORF virus has been extensively investigated over recent years, owing to its zoonotic importance and ability to cross-infect other species by sporadically evasive mechanisms, that the virus has developed to adapt and grow in the presence of an active immune response and this helps to explain the ability of the virus to repeatedly reinfect the same host. Exposure of Animals to stress or immunosupression as a result of therapy or primary viral infection can accentuate the severity of disease[6] and[15].The diagnosis of CPD is based upon the finding of large proliferative lesions in the animal body. In our study the clinical diagnosis of CPDV in sheep show wart-like lesions which were distributed in the skin of the lips, gums, teat and around the anus (Figure, 1, A, B & C). This agreed with the study which stated that the clinical signs of ORF include multifocal to coalescing papillary, proliferative and ulcerated lesions in the epidermis of the muzzle and lips[22],[24] and[26]. In some cases the lesions appear on and in the nostrils, around the eyes, on the thigh, coronet, vulva, udder and axilla[10] and[11]. Another severe case was reported on the buccal cavity, cheeks, tongue and lips and infection of the hooves which led to lameness and, in some cases, sloughing of the hoof[5].With respect of CPDV isolation on primary lamb kidney cell culture, the results of inoculation of the scab supernatant samples revealed a cytopathic effect, in the form of cell rounding, pyknosis, and cell detachment. CPE was observed in 9 samples after 5-8 days of inoculation (Table 2).This agreed with[20] and[27] where they stating that, CPD isolation can done by inoculation onto cell culture (primary lamb testis or lamb kidney) and the appearance of CPE may take 4–12 days. Another study stated that, the causative viruse can be isolated in lamb testis or kidney cell cultures or in other sheep, goat, or bovine cell lines[13].In addition inoculation of the positive isolates from cell culture on corioallantoic membrane (CAM) of emberyonated chicken egg resulted in appearance of thickening in the CAM in 9 samples (Table 2). This agreed with[16] who stated that Orf virus was clinically diagnosed from different field cases of sheep and goat in Hawamdia, Giza, Egypt during the summer 2006, by inoculation on the chorio-allantoic membrane of embryonated chicken eggs indicated by expressing the characteristic thickening and pock lesions of Poxviridae family.Detection of CPD antigen by Agar gel Precipitation test (AGPT) in the positive isolates from egg inoculation resulted in clear precipitation line in 7 isolates. This agreed with the studies which stated that, AGPT is very simple and can be applied as it requires minimum laboratory facilities and cheaper but it is relatively insensitive[12]. Electron microscopy, is one of the most accurate laboratory examinations of CPDV and it supports the diagnosis of ORFV infection[16] &[23].With revealing to the electron microscopical examination of positive isolates by egg inoculation on chorio-allantoic membrane, using the negative staining technique, CPD virion was studied and photographed revealing an electron micrograph of a typical parapoxvirus virion showing typical oval-shaped morphology (370x160 nm) original magnification x70000 . The virion had a characteristic crisscross pattern in the outer membrane that gave them a basket-weave appearance. (Figure 2). Another studies stated that, the Electron microscopy examination of CPD which is negatively stained showed an oval-shape virus particles trait for members of the genus Parapoxvirus[19],[16], and[14]. In our study, detection of antibodies against CPDV in collected serum samples by Agar gel Preciptation test (AGPT) revealed that only 5 samples from 45 tested serum samples were positive for the presence of antibodies against CPDV. This agreed with the studies which stated that, AGID is very simple and can be applied as it requires minimum laboratory facilities, cheaper but it is relatively insensitive[12],[3] and[20]. Another study, use AGID test for differentiation of antibodies in animals infected with capripox and parapox viruses using sera from sheep with naturally-acquired infections and from sheep experimentally inoculated with orf or capripox viruses showed cross reactions.[4]
5. Conclusions
- Primary lamb kidney cell culture and CAM of emberyonated chicken egg are the best routes for CPDV isolation. Identification of the virus by Electron microscope and AGPT is a reliable method for diagnosis.
References
| [1] | Abu Elzein E.M.E. & Housawi F.M.T. (1997): Severe longlasting contagious ecthyma infection in a goat’s kid. Zentralbl. Veterinärmed., B, 44 (9), 561-564. |
| [2] | Ahmed,M.H.; Mervat M. Mahmoud and Ewes,M.(2001): Isolation and identification of contagious pastural dermatitis virus from infected sheep and goats. Accepted by date 7/1/2001 in J.Egypt.Vet.Med.Ass.,61 (A 6). |
| [3] | Animal Disease Factsheets, (2005): Sheep & Goat Pox.The Center for Food Security & Public Health Iowa State University, Ames, IA, USA. Last Updated: Aug. |
| [4] | Chand, P. Kitching, R. P and Black, D. N. (1994 ) : Western blot analysis of virus-specific antibody responses for capripox and contagious pustular dermatitis viral infections in sheep. Epidemiol Infect. October; 113(2): 377-385. |
| [5] | Couch and Alan John; (1983): "The Development and Host Response to Ovine Contagious Pustular Dermatitis". A thesis submitted to the Faculty of Science of the University of New England, Armidale, N.S.W., in partial fulfilment of the requirements of the degree of Bachelor of Science with Honours. |
| [6] | De la Concha-Bermejillo A., Guo J., Zhang Z. & Waldron D. (2003): Severe persistent orf in young goats. J. vet. diagn. Invest., 15 (5), 423-431 |
| [7] | Delhon G, Tulman ER, Afonso CL, Lu Z, de la Concha-Bermejillo A, Lehmkuhl HD, Piccone ME, Kutish GF, Rock DL (2004 ): Genomes of the parapoxviruses ORF virus and bovine papular stomatitis virus. J Virol, 78:168-177. |
| [8] | Giadinis N. D., G. Filliusis, S. Q. Lafi, N. Panousis, K. Pourliotis, J. Bojkovski, H. Karatzias (2007): Vet. glasnik 61 (5-6) 301 – 312 |
| [9] | Gumbrell RC, McGregor DA(1997): Outbreak of severe fatal orf in lambs. Vet Rec, 141:150-151. |
| [10] | Hawkins CD, Ellis TM, Davies MK, l.(1991): An unusual outbreak of contagious ovine ecthyma. Aust Vet J 68:210–211. |
| [11] | Housawi FM, Abu EE.( 1991): Orf infection following ear tagging in goats. Rev Elev Med Vet Pays Trop 44:277–278. |
| [12] | ImadaT., TsuboiT., TakahashiN., HamaokaT., HaritaniM., MiyamotoT., and MurataH. (1996): Serological survey of 8 bovine viral pathogens in sika deer (Cervus nippon) of northern Japan. Jpn. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 1:42–44. |
| [13] | Jae-Ku Oem, In-Soon Roh, Kyung-Hyun Lee, Kyoung-Ki Lee, Hye-Ryoung Kim, Young-Hwa Jean and O-Soo Lee(2009) :Phylogenetic analysis and characterization of Korean orf virus from dairy goats: case report, virology journal , 16 octobre |
| [14] | Kui Zhao, Deguang Song, Wenqi He , Huijun Lu, Bingbing Zhang, Chao Li, Keyan Chen and Feng Gao,(2010): Identification and phylogenetic analysis of an Orf virus isolated from an outbreak in sheep in the Jilin province of China Veterinary Microbiology Volume 142, Issues 3-4, 19 May, Pages 408-415 |
| [15] | Madhusudan Hosamani, Alessandra Scagliarini, Veerakyathappa Bhanuprakash, Colin J McInnes and Raj Kumar Singh (2009): Orf: an update on current research and future perspectives Expert Review of Anti-infective Therapy September Vol. 7, No. 7 |
| [16] | Mahmoud M, Abdelrahman K, Soliman H.(2010):- Molecular and virological studies on contagious pustular dermatitis isolates from Egyptian sheep and goats.Res Vet Sci. 2010 Oct;89(2):290-294. Epub 2010 Mar 20. |
| [17] | Mercer, A., Fleming, S., Robinson, A., Nettleton, P. & Reid, H. (1997): Molecular genetic analyses of parapoxviruses pathogenic for humans. Archives of Virology Supplementum 13, 25-34. |
| [18] | Mercer AA, Uedaa N, Friederichs S, Hofmann K, Fraser KM, Bateman T, Fleming SB (2006 ): Comparative analysis of genome sequences of three isolates of Orf virus reveals unexpected sequence variation. Virus Research, 116:146-158. |
| [19] | NADIS (2009) :Contagious Pustular Dermatitis (Orf). |
| [20] | OIE Manual of Diagnostic, 2008: Chapter 2.7.14 Sheep pox and goat pox Terrestrial Animals under the heading “Diagnostic Techniques”. |
| [21] | Robinson AJ,and Balassu TC.(1981): Contagious pustular dermatitis (orf). Vet Bull, 51:771-82.  |
| [22] | Smith, GW., Scherba, G., Constable, PD., Hsiao, Behr, MJ., Morin, DE., (2002) Atypical parapoxvirus infection in sheep. J Vet Intern Med16: 287-92 |
| [23] | Stephen M. Apatow (2010):One Medicine: One Health (Zoonotic Disease) Online Course, Biodefense Reference Library Foreign Animal and Zoonotic Disease Center. |
| [24] | Tucson, AZ (2003): Farm animal zoonotic and reportable diseases. VSC/443/543 Research Animal Methods. Class notes for: November 7,03. |
| [25] | Zahur, A. B. Ullah, I A. Rshad, F H. Arooq M. S., Hussain M. and Jahangir, M. (2009): epidemiological investigations of a peste des petits ruminants (PPR) outbreak in afghan sheep in Pakistan, Pakistan Vet. J., 29(4): 174-178. |
| [26] | Zhang Keshan Zhang, Zhongxin Lu, Youjun Shang, Haixue Zheng, Ye Jin, Jijun He and Xiangtao Liu(2010): Diagnosis and phylogenetic analysis of Orf virus from goats in China: Virology Journal, 7:78 C. a case report. |
| [27] | Zeljko Cac, Ana Beck, Tomislav Bedekovic, Zeljko Cvetnic, Branko Sostaric. (2010): Virology Journal, 7:314 Phylogenetic analysis of Croatian orf viruses isolated from sheep and goats Ivana Lojkic1 |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML