-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Research in Zoology
p-ISSN: 2325-002X e-ISSN: 2325-0038
2012; 2(5): 47-59
doi:10.5923/j.zoology.20120205.02
Oogenesis,Vitellogenesis and Cocoon Secretion in Two Freshwater Leeches from Assiut, Egypt
Hanaa A. Gouda
Zoology Department, Faculty of Science, Assiut University, Assiut, Egypt
Correspondence to: Hanaa A. Gouda , Zoology Department, Faculty of Science, Assiut University, Assiut, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The organization of the ovisacs, fine structure of the oogenesis, vitellogenesis and formation of cocoons were studied in two freshwater leeches; Alboglossiphonia levis (Glossiphoniidae) and Barbronia assiuti (Barbronidae). Each of them was composed of two elongated ovisacs of germ cells' clusters. The ovisacs, in the studied species, were meroistic (nutrimental), without regionalization and mitotically dividing oogonia, germ cells entering the meiosis prophase as well as trophocytes, prominent cytophores and growing oocytes were occurred. During late previtellogenesis/early vitellogenesis, the oocytes detached from the cytophore and floated in the coelom; they are usually enveloped by the peritoneal epithelium and associated with blood vessels. Meantime, the activity of clitellar gland cells in both studied leeches could be distinguished. Both light and electron microscopy revealed two types of clitellar gland cells. These exocrine gland cells were responsible for the formation of cocoons which enclosed the fertilized ova. The organization of ovisacs and the course of oogenesis in the two genera were studied ultrastructurally and compared with other related leeches.
Keywords: Alboglossiphonia, Barbronia, Oogenesis, Vitellogenesis, Ultrastructure, Egypt
Cite this paper: Hanaa A. Gouda , Oogenesis,Vitellogenesis and Cocoon Secretion in Two Freshwater Leeches from Assiut, Egypt, Research in Zoology, Vol. 2 No. 5, 2012, pp. 47-59. doi: 10.5923/j.zoology.20120205.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Ooogenesis in leeches begins with the release of epithelial cells from the walls of specialized coelomic sacs. The released oogonia float freely in the lumen of the coelomic sacs wherein they undergo mitotic divisions followed by meiosis and the haploid nuclei eventually are found arranged around the periphery of an anucleate cytophore to which the gametes remain connected[1]. Multiple oogonia, many trophocytes and a number of growing oocytes are formed[2,3]. Trophocytes (nurse cells) are connected by inter-cellular bridges and form clusters. Only one within each cluster differentiates into an oocyte and continues the meiosis. Trophocytes are mostly responsible for rRNA synthesis and its transport to oocytes[4]. Early studies[5-7] and other modern[8-20] on leech oogenesis have shown that the course of this process and the spatial relationship between different kinds of cells (oocytes, trophocytes and follicle cells) inside the ovary vary considerably among various families. Moreover, only glossiphoniid leeches produce many large yolky eggs[15,21], whereas leeches in the remaining families lay small and yolk-poor eggs[15]. Like other clitellates, leeches possess a clitellum, the saddle-like glandular region associated with cocoon deposition in the anterior portion of the body. Theprominence of the clitellum is variable in leeches (usually somites X to XIII; that is, the eighth through eleventh true segments) and often is not evident externally in most species[22]. Various studies of oogenesis have been restricted mainly to glossiphoniids[8-11,15,17-19], little in hirudinids[1], piscicolids[23]. So far, no ultrastructural studies investigated the gametogenesis in Barbroniida. The present study is aimed to study the oogenesis, vitellogenesis and secretion of cocoons in Barbronia assiuti (Arhynchobdellida: Barbronidae) as well as, Alboglossiphonia levis (Rhynchobdellida: Glossiphoniidae).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
- Sexually mature leeches of Alboglossiphonia levis Gouda, 2010 and Barbronia assiuti Hussein and El-Shimy, 1982 were collected from Al-Sont canal
 , near Assiut governorate.
, near Assiut governorate.2.2. Techniques
- Nine leeches from each studied species were relaxed in % 8 ethanol, specimens were examined at the clitellum and gonopores to detect their maturity. Two specimens of both spp., were processed and stuck onto a holder in ventral and dorsal surfaces using a suitable glue then and photomicrographed with Jeol SM (JSM-5400 LV scanning electron microscope), at the EM Unit. The other seven specimens were cut into two halves at a level below the ovisacs. The anterior halves of both Alboglossiphonia levis and Barbronia assiuti were fixed in formol saline (1 g calcium chloride + 100 ml neutral formalin) for 48 hrs. Four specimens were used for paraffin sections and three for the transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Paraffin tissues were processed routinely for light microscopy based on[24]. Tissues were sectioned at 6 um at the clitellar region. Some histological procedures were performed to distinguish the different types of clitellar cells in both studied species. Neutral mucosubstances were demonstrated by the periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) reaction. Neutral and acidic mucosubstances were revealed in the same section by staining with a combination of the PAS reaction and Alcian blue. The section was first stained with Alcian blue at pH 2.5 and Alcian blue-positive acid mucosubstances that were also PAS positive will not react with PAS. Only neutral compounds were PAS positive. Also, toluidine blue could stain metachromatically the acidic mucus and sulphated compounds. After examination, photomicrographs were taken by a digital camera (Canon G6) fixed on a binocular Zeiss light microscope. For transmission electron microscopy, three anterior halves of A. levis and B. assiuti were placed in 2.5 % glutaraldehyde in 0.1 M phosphate buffer at pH 7.2 for 3 hrs. at room temperature. The specimens were post fixed in 1% buffered osmium tetroxide at pH 7.2 for 3 hours at 4 °c. They were then dehydrated and embedded in Epon. Semithin sections of 0.5 um were cut and stained with toluidine blue for examination under a light microscope. Ultrathin sections from selected areas of the trimmed blocks were made and collected in copper grids. The ultrathin sections were contrasted in uranyl acetate for 10 minutes, lead citrate for 5 minutes and examined under transmission electron microscope JEM, 100 Cx11 TEM, at Assiut University.
3. Results
3.1. Gross Morphology of the Ovisac
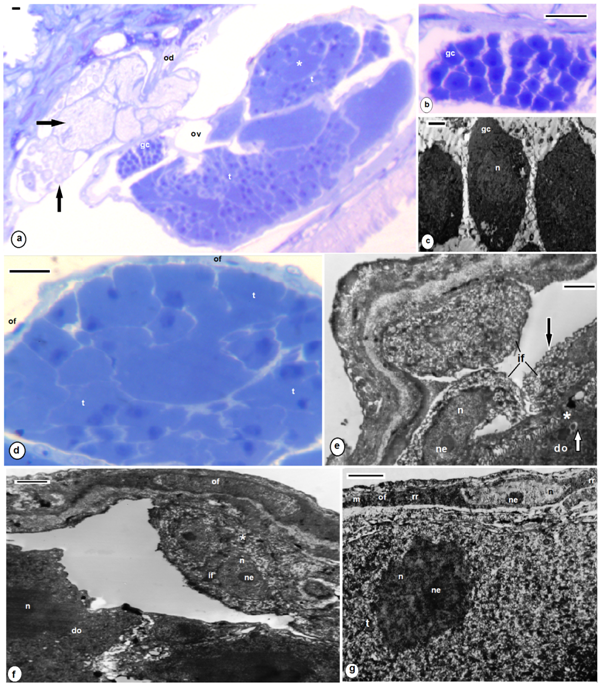
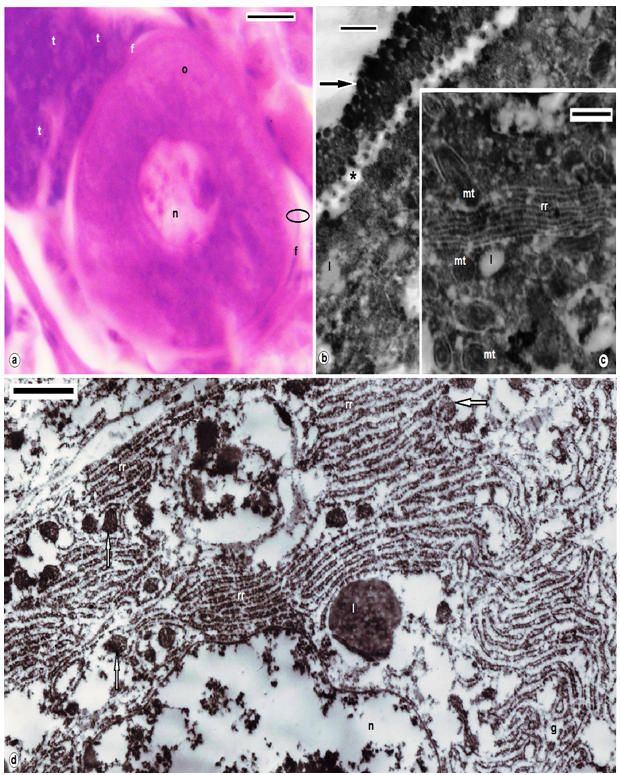
- Both Alboglossiphonia levis (Fig. 1a) and Barbronia assiuti (Fig. 2a) have similar pair of elongated ovisacs. Inside the ovisacs, numerous germ cells were arranged in solid cords (Figs. 1a-c, 2a).
3.2. Oogenesis
- Histology showed ovisac of both current species was composed of cords of germ-cell line, cords are non-polarized; i.e. no zones with consecutive stages of oogenesis could be found within ovary cords. During oogenesis three types of cells; enveloping follicle cells, numerous trophocytes and few developing oocytes, could be detected clearly. During previtellogenesis, each trophocyte is connected with an anuclear cytoplasmic mass, the cytophore, by a cytoplasmic bridge. Organelles such as mitochondria, cisternae of rER, Golgi complexes and ribosomes are transported via intercellular bridges and the cytophore towards the growing oocytes (Figs. 3a-h).
3.2.1. Follicle Cells
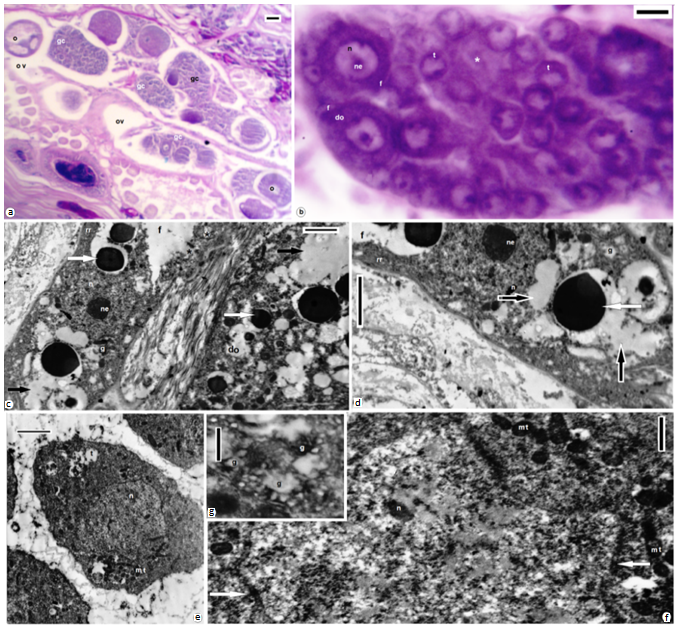
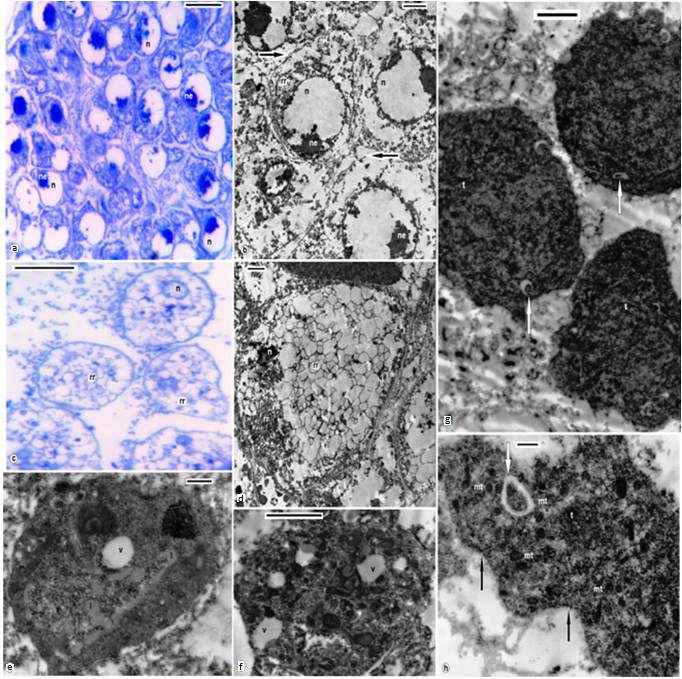
- In A. levis there were outer follicular cells surrounding the trophocytes and oocytes (Figs. 1d,f,g) as well as inner follicular cells between the developing oocytes (Figs. 1e,f). Outer follicular cells differed considerably from inner ones. The outer follicular cells were thin and elongated except for the nuclear region, which was much broader, oval nucleus, rounded prominent nucleolus and rich in mitochondria and rough endoplasmic reticulum especially at the extremities (Fig. 1f,g). No evident signs of synthetic activity by these cells were observed in A. levis. Inner follicular cells were found in groups (2-3), between the developing oocytes (Figs. 1e,f). These cells appeared oval in shape, with oval nucleus and rounded prominent nucleolus. These cells showed great synthetic activity and their cytoplasm were filled with huge amounts of electron dense cortical granules. These granules occurred between the microvilli and periphery of oocytes via exocytosis (Figs. 1e,4b). Furthermore, cortical granules constituted a condensed layer around large oocytes (Fig. 4b). As the oocytes enlarged, the inner follicular cells became much thinner (Fig. 4b). At the end of oogenesis, when the cortical granules are formed, follicle cells detached from the oocytes and degenerated. In B. assiuti there were only outer follicular cells surrounding the oocytes (Figs. 2b-d,5a) and the inner follicular cells could not be detected. Follicular cell in B. assiuti was greatly similar, in structure and shape, to the inner follicular cell of A. levis. The cells were rich in rough endoplasmic reticulum and golgi complex (Figs. 2c,d). Various sized vesicles of both clear and electron dense secretions were found in follicle cells of B. assiuti (Figs. 2c,d). At the onset of vitellogenesis, the follicle cells tightly enveloped the oocytes (Figs. 3h,4b,5a). The plasma membrane of follicle cells appeared smooth towards the ovisac wall but slightly protruded towards the oocyte (Fig. 2c), which seemed to form gaps filled with hemocoelomic fluid. At late vitellogenesis, some various sized yolk beside few cortical granules were found.
3.2.2. Trophocytes
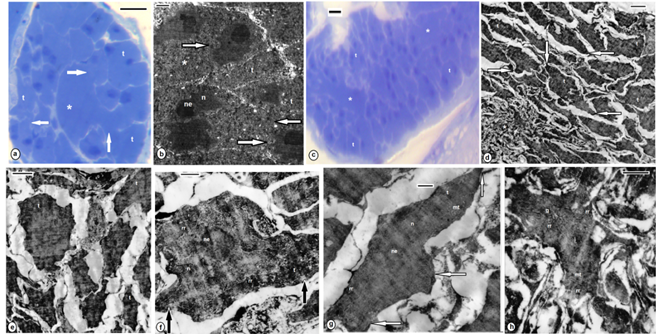
- The remaining pro-oocytes stopped meiosis and differentiated into trophocytes. Being initially spherical in shape (Figs. 1a in A. levis, 2b in B. assiuti), and amoeboid while growing (Figs. 1d,a-g in A. levis, 2e in B. assiuti). Moreover, their initially spherical nuclei seemed amoeboid in shape as well, became large (Figs. 3a-g in A. levis, 2e in B. assiuti) and bounded by porous undulating nuclear envelopes (Figs. 2e,f). Rounded prominent nucleolus could be detected easily (Figs. 2b-d,3b,f). Trophocytes contained distinctively well-developed Golgi complexes, which were accompanied by well-developed vacuoles (Fig. 2g). At this stage (Figs. 2e,f), the cytoplasm in trophocytes was rich in elongated mitochondria (the number of which increased as the cells grew) , ribosomes, rough endoplasmic reticulum (Fig. 3f,g). Initially, trophocytes were close to each other and formed chains of cells connected by intercellular bridges (Figs. 3a,b). As they grew, however, they moved apart and their connections became elongated forming cytoplasmic (trophic) cords (Figs. 3c-g). These structures contained cytoplasm and such cell organelles as mitochondria, ribosomes, microtubules, microfilaments and storage material (Fig. 3h). The connections among cells (the cytoplasmic cords) might branch and produced complicated patterns of cytoplasmic bridges which could be regarded as a cytophore (Figs. 3b,d). Trophocytes were associated with oocytes via cytoplasmic bridges. Tens of trophocytes were similarly connected with the cytophore in A. levis via numerous cytoplasmic bridges (Figs. 3a-d ). Whereas fewer ones in B. assiuti (Fig. 2b).
3.2.3. Oocytes and Vitellogenesis (Yolk Formation)
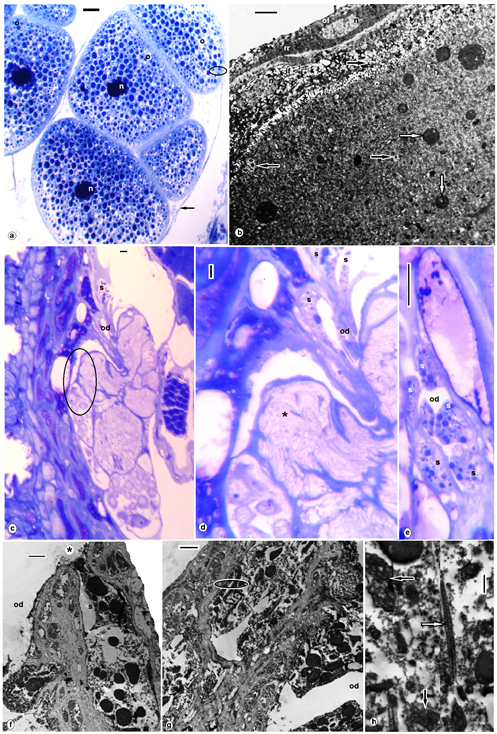
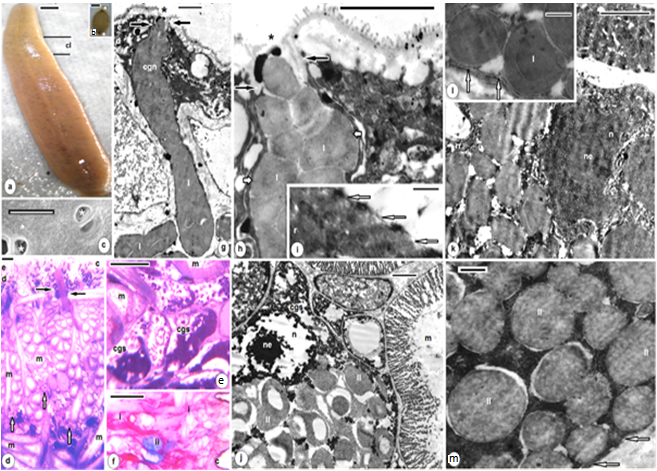
- Some of the pro-oocytes differentiated into oocytes, began previtellogenesis and finally underwent vitellogenesis. Young, previtellogenic / developing oocytes were small, spherical in shape and contained poorly differentiated ooplasm and rounded nucleus (Fig. 2b) in B. assiuti. While large rounded oocytes with large and ramified nucleus (Fig. 1f) in A. levis. As oocytes grew and increased in size, the ooplasm housed elongated, rough endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria (Fig. 5a-d). While numerous dictyosomes of Golgi complexes were well developed (Fig. 5d). Ooplasm became granular as numerous protein yolk and lipid storage materials were aggregated in oocytes in the form of spheres of different sizes and electron densities (Figs. 3h,4a,b,5d). In these cells the cytoplasmic membrane produced fine microvilli. At bases of microvilli, cortical granules were evident in the oocytes of A. levis (Figs.3h,4b). Conversely, in B. assiuti oocytes appeared surrounded by longer microvilli and no cortical granules could be detected; besides an acellular sheath (zona pellucida) was found at the periphery of the oocyte under the base of the microvilli. (Fig.5b). Large oocytes lack connections with trophocytes. The latter was degenerated (Fig. 1a). In B. assiuti, some degenerated trophocytes appeared with enlarged nuclei, ruptured plasma membrane and fragmented endoplasmic reticulum (Figs. 6a,b). Others with reduced nuclei and crystalloid reticulated endoplasmic reticulum (Figs. 6c,d). In A. levis, degenerated trophocytes were reduced in size, the plasma membrane became undulating, their nuclei disappeared, numerous fat droplets and vacuoles were occurred, besides the presence of some rickettsia-like microbes (Figs.6e-h). Fully developed oocytes with clearly seen cell nuclei endowed with nucleoli were released into the coelom. As oogenesis proceeds the growing oocytes gather nutrients which are known as vitellogenesis. Vitellogenic oocytes gradually protruded into the ovisac cavity and float freely in haemocoelomic fluid whereas the ovisac cords degenerated.The present work detected some glandular cells at the lining of the oviduct (Figs. 4c-h). Semithin sections revealed different sized proteinaceous secretion which discharged in the lumen of oviduct (Figs. 4c-e). TEM showed different sized electron dense rounded secretory granules (Figs. 4f-h), besides groups of signet ring and ladder like structures.
3.3. Secretion of Cocoons
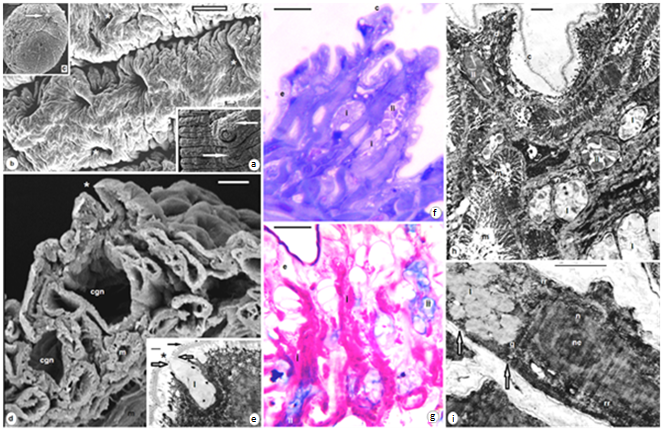
- Mature leeches could be distinguished externally by swallowing gonopores and presence of elevations surrounding them at the clitellar region (Fig. 7a). Light and electron microscopy showed clitellar gland cells only located at the ventral surface in A. levis (Figs. 7b,d-h), while at both dorsal and ventral surfaces in B. assiuti (Figs. 8a,c,d,g,h). Before laying egg, the leech A. levis searched for a hard substrate and attached to it by its anterior and posterior suckers. Behind the gonopores the parent widened and had thin lateral margins which inflected downwards and inwards, forming a trough around the coming eggs to protect them. Eggs were deposited individually, each egg was attached by a thin, flexible, transparent cocoon with short cord, by which it attached to the parent venter (Fig. 7c). Cocoon of B. assiuti (Fig. 8b), was outlined as a lemon with anterior and posterior short plugs. Its wall was membranous, transparent and light brown in color. The cocoon was secreted from both dorsal and ventral sides around the clitellum and slipped out, meantime, the fertilized ova (1- 4) fell in the cocoon with nutritive albumen, secreted by some clitellar gland cells, for the developing embryos. Immediately after deposition, the cocoon was shaped by the mouth of the parent leech and became more rigid. The cocoon was comprised of a free dorsal convex side and other ventral flat one by which attached to the submerged objects as plastic sheets, stones, snails' shells or even wall of the jar. Histologically, the clitellar gland cells were located deeply within the musculature below the body wall, where each cell was comprised of a relatively wide oval cell body (Figs.8e,j,k) and a characteristic elongated narrow process or ductule (Figs.8,d,g,h). Each cell was provided with large basal ramified nucleus, prominent rounded nucleolus (Figs. 7i,8j,k), vesicles of golgi complex (Fig. 7i) and cisternae of rough endoplasmic reticulum were occurred (Figs. 7i,8k). The characteristic elongated ductule winded its way within the musculature of the body wall and finally opened at the body surface through clitellar pores (Figs.7b,d,e,8e,j,k). TEM revealed the occurrence of longitudinal sections of microtubules just at the plasma membrane of the ductule (Figs. 7i,8i,l,m). Permanent metachromasia and combined PAS and Alcian blue techniques revealed two types of secretions within the clitellar cells in both studied spp. Alcian blue - positive acid mucosubstances stained blue, while neutral compounds were PAS – positive stained pink (Figs.7f,g in A. levis and Figs. 8d,e,f in B. assiuti). Ultrathin sections detected two types of secretory granules inside the ductules. In A. levis (Figs. 7h,i) electron lucent granules (type I) and electron dense granules (type II). In B. assiuti (Figs. 8k,l,m) polygonal electron dense granules (type I) surrounded by 3-7 peripheral lamellae or rings and rounded clear granules (type II). TEM revealed a constriction at the ductule's end near the site of exocytosis (Figs. 7d,8g,h ) .
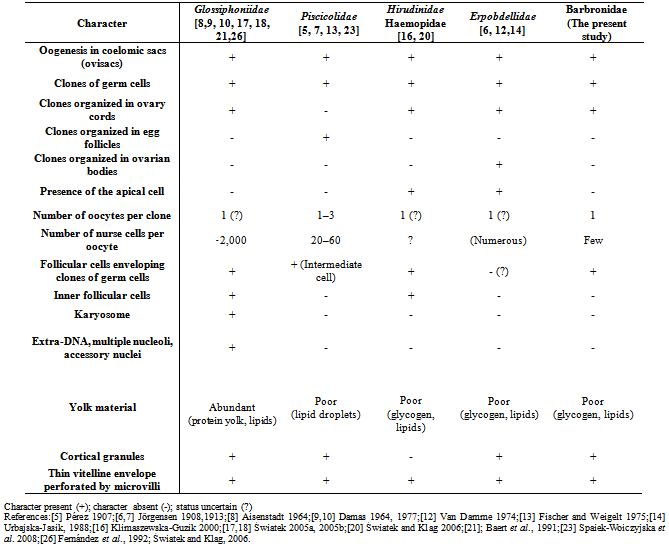
|
4. Discussion
- In Euhirudinea, four different types of ovary organization were recorded. Non-polarized ovary cords were found in glossiphoniids, egg follicles were described in piscicolids, ovarian bodies were characteristic for erpobdellids, and polarized ovary cords in hirudiniforms. Ovary organization in both current leeches revealed the same style of glossiphoniids. In all cases oogenesis is nutrimental: trophocytes (nurse cells) are engaged in nourishing oocytes. Oogenesis in the present two species is meroistic, as other Hirudinea, i.e. some mitotic divisions of oogonial cells are followed by incomplete cytokineses, and as a result, syncytial cysts (clusters) of interconnected germ cells (cystocytes) are formed[25]. Table (1) summarized the most important characteristics of oogenesis among main families of Hirudinea. In Glossiphoniidae, Hirudinidae and Haemopidae the ovary cords occurred. The ovary cords were composed of several huge (Glossiphoniidae) or smaller (Hirudinidae and Haemopidae) clones with dozens germ cells surrounded by flat somatic cells. Growing oocytes gradually protruded into ovary cavity and eventually detached from the cord and flew freely in coelomic fluid. In Hirudinidae and Haemopidae the cords were polarized; their club shaped end contained oogonia, developing clones of germ cells and one huge apical cell, which has been never observed in the current glossiphoniid and barbronid spp. Outer follicular cell was detected in most leech families, while inner follicular cell was detected in Glossiphoniidae, Hirudinida and Haemopidae but absent in Piscicolidae, Erpobdellidae and Barbronidae (the present study). In Piscicolidae each clone of germ cells was embedded in a cytoplasm of a single follicular cell (intermediate cell), which, in turn, was enveloped by several flattened somatic cells. Such organized egg follicles float freely in an ovary cavity. In Erpobdellidae in each ovisac there are several (5– 7) spindle-shaped bodies, ovarian bodies. Ovarian bodies are polarized; their top is occupied by oogonia and developing clusters of germ cells, whereas the lower parts are filled with differentiating germ cells and developing oocytes. Oocytes persist within the ovarian bodies as late as they reach I meiotic metaphase. During gametogenesis in Hirudinea and in other Clitellata, an anuclear mass, the cytophore, mediates between the trophocytes and oocytes. The cytophore is especially well developed in spermatogenesis, where it performs many functions; for review see[26]. In glossiphoniids and hirudiniform leeches, where ovary cords occurred, the cytophore was huge and has many branching but its overall characteristics were the same as in Piscicola[16-20]. The current study showed trophocytes were close to each other and formed chains of cells connected by intercellular bridges which were rich in cell organelles. Tens of trophocytes were similarly connected with the cytophore in A. levis via numerous cytoplasmic bridges (intercellular bridges). Whereas fewer ones in B. assiuti. In Piscicola the ‘‘young’’ cytophore (when germ cells entered meiotic prophase) consisted mainly of the membrane labyrinth; later it became more voluminous and oval shaped when trophocytes' cytoplasm was transferred to it. At the end of oogenesis the cytophore disappeared together with the trophocytes, and its cytoplasm was engulfed by the growing oocyte. The present work traced these changes gradually through the development of trophocytes and oocytes; this may explain the alteration in the size and shape of initially spherical trophocytes with rounded nucleus into amoeboid trophocytes with ramified nucleus while growing in both A. levis and B. assiuti. The plasma membrane of the intermediate cell (outer follicular cell in others) facing the growing oocyte forms also wide intracytoplasmic channels, and together those cells presumably have a system of intracellular channels. Such a phenomenon has been described in glossiphoniids[15,18,19,] and in some malacostracan Crustacea[27,28]. The plasma membrane of follicle cells in the present B. assiuti appeared smooth towards the ovisac wall but slightly protruded towards the oocyte which seemed to form gaps filled with hemocoelomic fluid through which the synthetic activity transferred to the oocyte. In glossiphoniids and Crustacea such follicular cells were suggested to be involved in transport of some macromolecules (yolk precursors) from the ovarian cavity to the oocytes[27,28]. Although in Piscicola oocytes are yolk-deficient cells[20]. As in glossiphoniid leeches and many other annelids the oocyte surface in Piscicola is equipped with microvilli projecting through the vitelline envelope. The vitelline envelope is thin and is produced by oocyte exocytosis. The same oocyte surface organization has been described in Polychaeta and Oligochaeta[29-33] and in Glossiphoniidae[19]. At the end of oogenesis in the cortical ooplasm of A. levis , the present work detected small electron dense cortical granules. After fertilization they disappeared from the ooplasm. In Annelida, cortical granules have been described mainly in Polychaeta[31-33]. In Hirudinea, stratified granules lying in the peripheral ooplasm were described as cortical granules only in Glossiphonia hetroclita[19]. Unlike glossiphoniids, piscicolid leeches do not produce yolky eggs; instead, they lay only one ovum in a cocoon[34], while in the present barbronid the cocoon enclosed 1- 4 fertilized ova. The main nutrient materials we observed were lipid droplets. In addition, the oocyte is well equipped with numerous mitochondria and long ER cisternae. Recently it has been shown that the Glossiphonia heteroclita oocyte nucleus (germinal vesicle) has numerous domains such as the karyosome, extra-DNA bodies, multiple nucleoli, and accessory nuclei[17]. In Piscicola the germinal vesicle behaves in a totally different manner. Meiotic chromosomes did not condense into a karyosome, the single prominent nucleolus is present till the end of oogenesis, and no other prominent nuclear domains were observed similar to that of the current spp. In glossiphoniids (Hirudinea) the direct communication between the cytoplasm of trophocytes and oocyte via cytophore allows transport of large molecules and even organelles[15].Serial semithin sections showed the presence of clitellar cells at the clitellum in both the dorsal and ventral surfaces of B. assiuti, while restricted to the ventral surface in A. levis. This distribution seemed suitable to the formation of cocoons in both leeches. In B. assiuti the cocoon was secreted around the clitellum and the leech wriggled out backward to release the cocoon then attached it to any substrate. In A. levis, the cocoon was secreted, attached directly and individually only to parent's Venter. Moreover, two types of clitellar gland cells in A. levis, and B. assiuti. All types could be distinguished (based on the nature of the secretion within the cells) by different histological stains, as well as TEM. This may reflect the importance of these secretions. This agreed with the findings of[35]. TEM revealed microtubules located at the periphery of the smooth plasmalemma of both clitellar gland cell soma and its ductule in both studied leeches. The microtubules served in maintaining cell structure (cytoskeleton) and forming channels along which the secretion transferred[36,37].[38] suggested that microtubules provide structural support to ductules and may ease secretory granule transportation through the ductule.
5. Conclusions
- The organization of ovisacs and fine structure of oogenesis in Alboglossiphonia levis (Glossiphoniidae) appeared typically as the glossiphoniid style, while Barbronia assiuti (Barbronidae) was related to the glossiphoniid style. A. levis produced large ova rich in yolk, conversely, those of B. assiuti were small and poor in yolk. Clitellar cells were located in both dorsal and ventral surfaces of B. assiuti, while restricted to the ventral surface in A. levis. This distribution seemed suitable to the formation of cocoons in both leeches.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML