-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Tourism Management
p-ISSN: 2326-0637 e-ISSN: 2326-0645
2018; 7(1): 19-23
doi:10.5923/j.tourism.20180701.03

Competitiveness of Young Entrepreneurs of Local Graduate in Pekanbaru Shopping Tourism City
Fatkhurahman, Bambang Suroto, Hadiyati
Economic Faculty, Universitas Lancang Kuning, Pekanbaru, Indonesia
Correspondence to: Fatkhurahman, Economic Faculty, Universitas Lancang Kuning, Pekanbaru, Indonesia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Development human resources from entrepreneurship side become important issue, that needs the competitiveness. Competitiveness of young educated entrepreneurs in particular the local community becomes a priority that needs to be empowered, especially in connection with the development of tourist city. Given the competition and also the local community became the base of economic growth and also the main foundation of the economy and social capital of local communities. Through the research with descriptive approach, that do from survey to malay youth spread in Pekanbaru City taken from youth of undergraduate education from local government owned university as much as 69 people taken randomly using online questionnaire and data analyzed by descriptive the result of research sgows that competitiveness of young entrepreneur of local graduate in the development human resourch also see a chance in Pekanbaru city as shooping city shows it is low, especially, relationship with knowledge and skill. So, through enpowering skill and knowledge work together in development competitiveness human resources.
Keywords: Competitiveness, Young Entrepreneur Educated, Shopping Tourism City
Cite this paper: Fatkhurahman, Bambang Suroto, Hadiyati, Competitiveness of Young Entrepreneurs of Local Graduate in Pekanbaru Shopping Tourism City, American Journal of Tourism Management, Vol. 7 No. 1, 2018, pp. 19-23. doi: 10.5923/j.tourism.20180701.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The educated workforce becomes an interesting phenomenon, the younger generation's interest in continuing to a higher level of education creates a new challenge. Indonesia's labor force also has an enormous opportunity to fill increasingly open employment, given the 43 percent of Indonesia's population and the workforce of 125.3 million people in 2014, an increase of 5.2 million from last year (Transmigration & Sari 2015). Education should be oriented to the competencies required by the workforce as the percentage of unemployed among educated people continues to increase (Muhson et al., 2012).One of the challenges to an educated workforce is to become a young entrepreneur, the variables associated with personality, instruments, and demographics together significantly determine the intentions of entrepreneurship. Although, it is only able to explain 28.2% for Indonesia, 14.2% for Japan and 24.8% for Norway (Indarti 2008). This shows that personality, instrument and demografis together significantly determine in developing entrepreneurship in an educated workforce.Young entrepreneurs also have an active role in the framework of national economic development, will only increase the employment rate itself, because it does not affect the improvement of living standards of Indonesian people, especially workers who do not have educational certification such as workers imported from China, even Vietnam which is no better the level of welfare of its workers from Indonesia. If Indonesia is not ready, then the free flow of goods, services, investments, skilled labor and capital, is seen as a threat rather than an opportunity. Immediately improve themselves to prepare a competitive and global quality Human Resources (Unika & Mandala 2015).But with the tight competition in order to enter the era of ASEAN Economic Community (AEC) then of course be a challenge and also opportunities. Explained by the Judge that global competition requires the readiness of the Indonesian nation to improve competitiveness. Entrepreneurship education based on the cultural values and character of the nation is one of the important and strategic aspects to enhance the competitiveness (Judge 2012).With regard to the phenomenon of educated labor and also related to the problem of young entrepreneurs as a challenge and as well as opportunities in order to build competitiveness and character of the nation, it is necessary to put attention to the concept of competitiveness itself. In the study of human resource management as well as entrepreneurial studies on competitiveness related to the concept of competence that leads to the competitiveness of entrepreneurship. When viewed from several issues that exist in private universities, where the slogan used to attract prospective students and parents is to make entrepreneurs and or young entrepreneurs are reliable.This shows that personality, instrument and demografis together significantly determine in developing entrepreneurship in an educated workforce. Provide different opportunities for local youth to respond. Some data show that less than 30% of college graduates as well-educated workers included in the market of young entrepreneurs are still not ready for competition (Indarti 2008). The role of youth is very important in building the economy and this condition makes the reason for the need to improve the competitiveness of youth in viewing the new city opportunities as a shopping city. So need to look more detail about the ability of the young entrepreneur in the framework of evaluation of learning programs in universities and also for the development of competitiveness theory of human resource management.This study is also a development of previous research which says that many parents are less interested in making their children enter the business world that is only 38.2% want graduates to be a reliable entrepreneur. So this needs to get attention and evaluation from the institution.From the results of previous research with regard to entrepreneurship is the biggest catalyst for innovation and job creation. Studies undertaken in Africa in order to build entrepreneurship, the role of government in making policy in the form of promotion is done coupled with the developments in the entrepreneurs themselves. Competition is tight, lack of employees with the right skills, and difficulty in finding adequate facilities to start their business. Being a support given by the government in Africa (Ven Sriram 2010).Entrepreneurs in need of support from the electronic side, such as e-business, e-mail, website, e commerce and organizational traspormasi. This is intended to improve business performance that becomes an important thing (Taylor et al., 2004). Then in terms of this entrepreneurship, the factor of self-support that is owned as a form of competitiveness also becomes a necessity and needs to be developed. Mokter Hossain explains that open innovation on SMEs improve their overall innovation performance (Mokter Hossain 2016). Then entrepreneurship behavior becomes an important part as a reference in growing entrepreneurship in a State (Pasanen 2006).As a form of competence or competitiveness, it also requires attitude and motivation for entrepreneurs to move and become more advanced (Lee & Tai 2011). Research in Pakistan deals with the human capital of entrepreneurial entrepreneurs in business such as education, experience, training, personal skills, skills, attitudes, stability, health and fulfillment. They all become an important part of human capital development into entrepreneurship (Mubarik et al., 2016).Building entrepreneurship is also related to college, which according to Lewrick that entrepreneurship education and innovation come from an established university curriculum and the context is a set of concepts and tools used in the business world. The challenge of turning a start-up company into a business success requires different abilities. It goes beyond the development of ideas and the writing of a comprehensive business plan (Lewrick et al., 2011).Research conducted in Singapore deals with the characteristics of migrant migrant entrepreneurs and establishes a successful business community in Nigeria. The general quality between Lebanese and Nigerian entrepreneurs is compared and contrast given the Lebanese adaptive ability in the face of obstacles. The host country is encouraged to create an enabling environment for domestic and foreign investors (Mambula 2010).Based on the description of the existing entrepreneurs in different parts of the world and has the characteristics of competence or competitiveness itself in order to make successful entrepreneurs face various challenges they face.According to Palan cited by Fatkhurahman that competitiveness has five characteristics, among others: 1) Knowledge, knowledge refers to information and learning outcomes, such as a surgeon's knowledge of human anatomy; 2) Skills, skills refer to a person's ability to perform an activity, such as the skill of the surgeon to perform the surgery; 3) Self-concept and values, self-concept and values refer to one's attitudes, values and self-image. Examples are confidence, one's belief that he can succeed in a situation, such as a surgeon's confidence in carrying out difficult operations; 4) Personal characteristics, personal characteristics refers to the physical characteristics and consistency of responses to situations or information. Good vision of the personal characteristics that the surgeon needs, as well as self-control and the ability to remain calm under pressure; 5) Motives, motives are emotions, passions, psychological needs or other encouragement that triggers action. For example, surgeons, with high interpersonal orientation take personal responsibility to work with members (Fatkhurahman 2010).The novelty of this study leads to the use of the competitiveness dimension of the synthesis results of Palan (2007) and Mubarik (2016), where Palan previously explained the competitiveness dimension of human resource management consists of five dimensions: knowledge, skills, self-concept, personal and motive. But more interesting for the competitiveness of educated young entrepreneurs coupled with a dimension of communication ability. Because the ability to communicate becomes a must owned by a young entrepreneur educated to establish a partnership and good cooperation with customers, as well as with suppliers and with the government and the banking world.This becomes a unique for young educated business entrepreneurs especially for youthful malays in Pekanbaru City. Seeing the progress and opportunities that exist and making them judged ability to improve competitiveness and win the market and tourism is a necessity and also a struggle.
2. Methodology
- The research method used in this research is descriptif. Types of data kuantitatif to be collected and used in this study are: Primary data, primary data in this study obtained from survey results through the spread of questionnaires online to youth, related to the competitiveness of young entrepreneurs face business competition ranging from knowledge, skills, self-concept, personal characteristics and motives up to the personal ability to communicate. Secondary Data, Secondary data in this research is library resources, journal and scientific atrikel, data and report which is recomended related to problem raised.The population in this study were educated youth from local communities who had studied in colleges built by the local government. Especially run business ie from 2012 to 2016 that as many as 214 people. Due to the relatively large number of population then the samples taken probability using simple random sampling. Calculation of sample using slovin formula, as many as 69 people. This research was conducted in Riau Province. Data collection techniques used questioner. Then the questionnaire is data collection conducted by distributing a list of pertayaan to respondents related to the purpose of research and documentation techniques that perform data collection by studying and analyzing the documentation associated with research data.This research uses a descriptive method. Descriptive method is a method in researching the setatus of a group of people, an object, a set of conditions, a system of thought, or a class of events in the present. The purpose of this descriptive study is to make deskipsi, picture or painting in a systematic, factual and accurate about the facts, traits and relationships between the phenomena investigated.
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Result
- Based on the results of surveys conducted in the field with respect to local youth competitiveness in implementing entrepreneurial activities in particular capture shopping opportunities in Pekanbaru City by using dimension dimensions: knowledge, skills, self concept, character, motive and communication. Obtained information as that when viewed from the characteristics of respondents in giving the response that seen from the length of business, the type of business is run and also the number of employees used in running business activities. When viewed from the long youth of young entrepreneurs run their business. Youth as many as 84.3% have experience trying to be seen from the length of their business open under 5 years and this shows that youth still not enough experience in the effort and this will have an impact on the business it runs. Then can also be seen from the type of business run youth, where it is known that the current type of business what the trend and become an interest than the existing business.That the type of trading business becomes something that the youth are interested in trying. This trading business can be done by providing good service to its customers. Furthermore, seen from the number of employees used in running their business and this is related to the absorption of workers who successfully donated young entrepreneurs is known that 84.3% of youth use labor of less than 5 people and only 9.8% others use labor 5-10 people. This shows that youth through their business have absorbed enough labor to help the government reduce unemployment.Based on the data obtained in the field related to young entrepreneurs and the evaluation of the success of educational institutions implement the program it can be seen from the following figure 1:
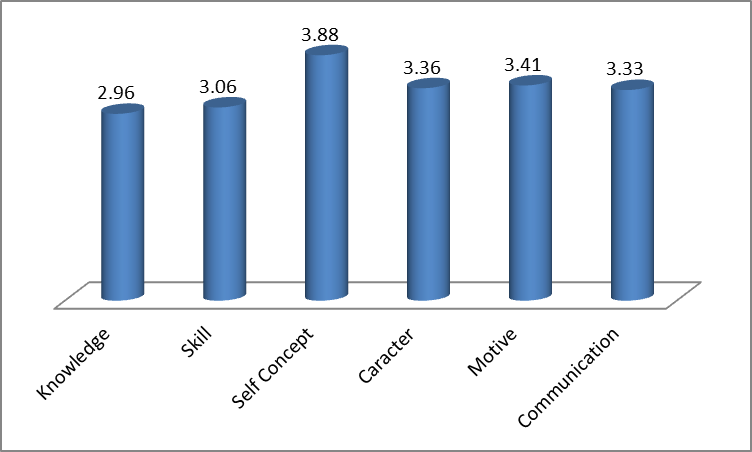 | Figure 1. Competitiveness of Young Entrepreneurs Educated Local |
3.2. Discussion
- The competitiveness of young entrepreneurs is especially educated on youth who come from the land of Malay is very good, where the self-concept and also the motive of the spirit is more dominant than the knowledge and skills possessed. When viewed from the indicator of knowledge can be seen that the knowledge is still included in the lower category compared with other indicators and this indicates that the lack of stock obtained in campus so far. In addition, through education that some opinions submitted by young entrepreneurs related to these include:a. Lack of knowledge of business strategies, such as: direct marketing strategies directed to beginner business, as well as selling strategies through social media.b. Lack of field experience in order to add broad insight so as to know the practices that occur around. Also the improvement is more clarified ways of developing a business opportunity by presenting experienced speakers in the field of entrepreneurship.c. Lack of knowledge about product quality and quality as well as business development. Science should be studied in lectures more to applied science. Directly useful in the world of work. Expected on campus is given semimar or entrepreneurship training training.d. Lack of knowledge in organizing as well as how to get business capital that is the practice of directly applying for credit loans to the bank.e. Lack of financial management practices in processing figures, budgets and revenues related to business in the field ie in the form of real practice.f. Business literature and entrepreneurial sources to complete.Some of these findings in an attempt to improve the competitiveness of knowledge in the future. Then seen from the side of skills owned by young entrepreneurs in running their business is also still low compared with other entrepreneurial indicators. Some of the notes found in the field include: Training to make a proposal to get capital aid, entrepreneurship training, study banding to company, self motivation, mental-building exercises for business entrepreneur as well as starting a business from ZERO capital, Entrepreneurship Field practice, Training on how to build an entrepreneur's character. Cooperate with UMKM entrepreneurs to increase student interest to become entrepreneurial profession, Total marketing training, Training to make something useful and there is selling price training to increase sales turnover, Pratek job training, Training on marketing strategy, Opening booth selling the participants of the students, while training students Become an entrepreneur, Training to open a business, Providing simulations to science, Training interests and talents of students and students. The training takes the business opportunities that are available today by following the development of technology, Training service excellent, Financial management training.Then seen from the indicators of medium and better conditions, among others, character and communication with a good score and also provides an easy entrepreneurial picture has a good character and able to communicate effectively in running their business.Lastly when it is associated with self-concept and motive becomes a high answer, where young entrepreneurs are equipped with seven values of Unilak namely religious, honest, visionary, wise, discipline, dignity, cooperation with faith based and piety. Pengekalan value is characteristic of the Malays and also makes the Malays still have a high spirit because the business is run not only aim at turnover and profit but as a form of amaliah form of piety and faith to the creator.Constraints faced need to be addressed wisely, it has become a challenge for young entrepreneurs to demonstrate the ability of lucky and able to contribute to the government in tax donations. In addition, entrepreneurial mentality becomes more challenged through this condition.
4. Conclusions
- This research resulted in a conclusion that the competitiveness of youth entrepreneurs is still low, utilizing the six dimensions of competitiveness ie knowledge, skills, self concept, character, motive and communication which is the result of synthesis of opinion Palan and Mubarik shows that the low competitiveness of Malay youth in entrepreneurship because of the knowledge and insight and skills possessed in the business is still low. While other factors such as self-concept, character and motive as well as communication is high. The inhibiting factors that are known based on the results of this study relate to mental problems trying to become a necessity with a variety of very tight competition. Competition not only comes from within the country but also from abroad such as foreign workers make young entrepreneurs should have a strong mental attitude. Then also the support of the government is a factor inhibiting the success of young entrepreneurs. Where the government with tax policy is very young entrepreneurs are hampered to create and produce new innovations. Because some online businesses require the owner to have a tax number that is for beginner entrepreneurs become an obstacle.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- A big thank-you to the Dean of the Faculty of Economics, Lancang Kuning University, who has provided funding support for this research to produce research results that can be utilized for the benefit of the institution. Similarly, to Young Entrepreneurs who have participated in filling out this research questionnaire.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML