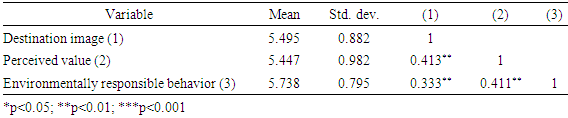-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Tourism Management
p-ISSN: 2326-0637 e-ISSN: 2326-0645
2018; 7(1): 1-9
doi:10.5923/j.tourism.20180701.01

The Moderating Role of Intercultural Service Encounters in the Relationship among Tourist’s Destination Image, Perceived Value and Environmentally Responsible Behaviors
Joseph Si-Shyun Lin
Department of Restaurant, Hotel and Institutional Management, Fu-Jen Catholic University, New Taipei City, Taiwan (R. O. C.)
Correspondence to: Joseph Si-Shyun Lin, Department of Restaurant, Hotel and Institutional Management, Fu-Jen Catholic University, New Taipei City, Taiwan (R. O. C.).
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2018 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Because of the popularity of tourism worldwide, each tourist destination has received more and more international tourists. The increasing tourism activities may result in the change of the environment and ecosystem of the destinations. The environmental destruction caused by the tourists has received attention from all sectors of the community. Studies have shown that destination image is one of the key factors attracting tourists and affecting their behaviors during their trips. The cross-cultural interaction between international tourists and locals, with the increasing amount of international travelers, is also intensified and receiving academic attention. Nevertheless, no research has studied the influence of the cross-cultural interaction in hospitality in the hospitality sectors in tourist’s Environmentally responsible behavior. The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship among the international tourists’ destination images, perceived value and environmentally responsible behavior in Macau. The role of intercultural service encounter during tourists’ visit in the city related to their destination image and perceived value were also examined. Results showed that international tourists’ image of destination were significantly related to their perceived values, as the perceived values was found to play as a mediator between their image of the city and their environmentally responsible behavior. The results also revealed that the international tourists’ experience of service encounters had moderating effect between their destination image and perceived value of the trip. While at the same level of destination image, the tourists who had good experience during their encounters with local service sectors had better perceived value of their trip. Besides, when the international tourists who had higher perception of service encounters, the increase of the tourists’ image of destination could much better enhanced their environmentally responsible behavior, as compared with the ones with lower perception of service encounters. Managerial implications to the local service sectors and authorities are also suggested.
Keywords: Destination image, Perceived value, Environmentally responsible behavior, Intercultural service encounters, Macau
Cite this paper: Joseph Si-Shyun Lin, The Moderating Role of Intercultural Service Encounters in the Relationship among Tourist’s Destination Image, Perceived Value and Environmentally Responsible Behaviors, American Journal of Tourism Management, Vol. 7 No. 1, 2018, pp. 1-9. doi: 10.5923/j.tourism.20180701.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- According to United Nations World Tourism Organization, the number of passenger of global travel has reached 1.2 Billion in 2016, this number has doubled since 2000. It is predicted that the number of international visitor will reach 1.8 Billion in 2030 (Crotti, & Misrahi, 2017). United Nations Secretary-General of the World Tourism Organization, Taleb Rifai, pointed out that Asia is becoming the center of world's tourism, he projected that, in 2030, and the number of international visitor received by Asian countries will reach 535 million. As the number of both international passenger and visiting country grows, it is expected for the members from local hospitality industry to encounter visitors with more diversified cultural backgrounds and have deeper and breather intercultural interactions with the visitors (World Tourism Organization, 2016). Meanwhile, the mass-scale tourist activities are changing the environment and ecosystems of the destinations, which includes the damage and pollution to the geology, land vegetation, water, wildlife, air quality, etc. (Amendah & Park, 2008; Chang, 2010; Cheng & Wu, 2015). UNESCO found that nearly 3000 million passengers poured into Venice in 2015, and with the cruise ship sailed into Venice, has caused serious ecological damage in this area. They warned that Venice would be removed from the list of World Heritage of the United Nations if the local government doesn’t take any action to improve the situation (Gerard-Sharp, 2017). Similar scenarios has been observed in other tourist places around the world (Alessa, Bennett, & Kliskey, 2003; Chin, 2017; Line & Hanks, 2016).In recent years, the study regarding passengers’ sustainable behavior and responsibility during their trips has gained more and more attention. Researchers have investigated, from the subjective point of view of passengers, how their cognition (Chiu, Lee, & Chen, 2014a), perceived value (Chiu, Lee, & Chen, 2014b) and environmental consciousness (Han, 2015; Lee & Jan, 2015), environmental commitments (Lee, 2011), Environmental knowledge (Ardoin, Wheaton, Bowers, Hunt, & Durham, 2015), place attachment (Ramkissoon, Smit, & Weiler, 2013) influence their environmentally responsible behavior. Chiu et al. (2014b) studied the effect of how tourists’ destination image and perceived value shaping their environmental responsible activities; they found that the cognitive image of eco-tourism destination, mediated by the emotional images and perceived values, had enhanced the environmental responsible behaviors. The study also highlighted that passengers’ destination image and perceived value were important antecedents of their environmentally responsible behavior. It is suggested that the image of the destination perceived by the international tourists and their behavior of environmental responsibility are mutually inter-affected, while the tourists’ experience with their service encounters during their stay in the destination may have impact on their image of the destination and behaviors. However, currently, the subject of the study regarding passengers’ environmentally responsible behavior mainly focus on their destination image of tourist attractions such as national forest park, scenic areas and eco-destinations, few study had discussed the city as the destination (Cheng, Wu, & Huang, 2013; Chiu et al., 2014a; Ramkissoon et al., 2013).Researchers have indicated that service encounter elements are thus the antecedents of experiential value and satisfaction (Baker, Parasuraman, Grewal, & Voss, 2002; Bitner, 1992; Hutton & Richardson, 1995; Minor, Wagner, Brewerton, & Hausman, 2004). Fiore and Kim (2007) pointed out that, when service encounter are positively perceived (where the consumption experience exerted by the inputs of environmental variable, individual variables, and person-environment interaction variables or situations), increased their value of experience. Sulek and Hensley (2004) argued that both service employees and consumers influence cognition, emotion and physiological response in the foodservice settings.This study, therefore, aimed to investigate the relationship among the international tourists’ destination images, perceived value and environmentally responsible behavior in Macau. The role of intercultural service encounter during tourists’ visit in the city between destination image and perceived value were also examined.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Destination Image
- Destination image is defined as a set of qualities, attributes and benefits that visitors hold about the destination; it represents the sum of beliefs and impressions that a person has of a destination (Echtner & Ritchie, 1993). Destination image is shaped primarily by the environmental attributes that characterize the tour site (Jenkins, 1999; Obenour, Groves, & Lengfelder, 2006; Turner & Reisinger, 1999), but it also derives from travel promotions, which convey specific features about the destination to the target audience (Baloglu & McCleary, 1999). Thus, destination image is an important influence factor for tourist destination choice.A tourists’ image of destination image is dependent on their subjective perception towards the local environmental resources and supporting site facilities (Gallarza, Saura, & Garcia, 2002). In general, the evaluation of destination image consists of a cognitive and an affective dimension (Baloglu & Mangaloglu, 2000; Hui & Wan; 2003; Kim & Perdue, 2011; Martin & Bosque, 2008). Cognitive evaluation is defined as the belief or knowledge about a destination’s attributes, whereas affective evaluation describes the feelings toward or attachment to these attributes due to experiences related to the scenic spots or wildlife appreciation (Baloglu & McCleary, 1999; Chan & Baum, 2007; Chhetri, Arrowsmith, & Jackson, 2004). Researchers believed that what tourists actually experience, see and feel help them to form impressions of the tourist destination (Echnter & Ritchie, 1993). Previous studies suggest that cognitive image can influence affective image (Beerli & Martin, 2004). In other words, tourist cognition of destination attributes will determine their feelings (positive or negative) about the travel destination.
2.2. Perceived Value
- Perceived value is the feeling consumers have when buying products or services, comparing the input and the output they received (Zeithaml, 1988). The measurement of perceived value encompasses both the acquired object as well as the transaction process (AI-Sabbahy, Ekinci, & Riley, 2004). The value is related to service quality in relation to the costs paid by the customer, in other words, the difference between customer expectations regarding service and actual service received. It reflects the benefits and costs as perceived by customers in relation to both tangible and intangible products, which may include the combination of quality, service and price (Kotler & Keller, 2006).Perceived value can be measured as a multi-dimensional construct, consisting of quality, emotional, price and social aspects (Sweeney & Soutar, 2001), or functional, emotional, epistemic, social and situational dimensions (Sheth, Newman, & Gross, 1991). In the hospitality literature, perceived value is frequently conceptualized as the personal evaluation of the characteristics of travel products, such as service quality, price, emotions and social factors (Petrick, 2004). These factors determine whether product value is worth consumption and influence tourist satisfaction after traveling (Chen & Tsai, 2007). Tourists’ image of destination reflects what they experience, see and feel of destination (Echnter & Ritchie, 1993). The perceived cognitive image can influence affective image of destination received by the tourists will determine their feelings (positive or negative) about the travel destination. Destination image has been modeled as an antecedent variable that correlates with perceived value (Kim, Holland, & Han, 2013; Phillips, Wolfe, Hodur, & Leistritz, 2013), satisfaction (Chi & Qu, 2008; Park & Njite, 2010; Prayag & Ryan, 2012) and behavioral intention (Chen & Tasi, 2007; Ramseook-Munhurrun, Seebaluck, & Naidoo, 2015).Therefore, we proposed that: H1: Tourists’ image of destination is positively related to their perceived value during this trip.
2.3. Environmentally Responsible Behavior
- According to Cottrell and Graefe (1997), environmentally responsible behavior is reflected in an individual’s environmental concern, commitment and ecological knowledge. Environmentally responsible behavior can be expressed through different types of behavior, such as waste recycling and energy management (Iwata, 2001; Lee, Jan, & Yang, 2013; Thapa, 2010). In the context of ecotourism, environmentally responsible behavior is given when tourists understand the impact of their behavior on the environment and abide by the norms in the eco-site (Kang & Moscardo, 2006; Puhakka, 2011). Orams (1995) indicated that tourist satisfaction in ecotourism is dependent upon experiences, and if experiences in ecotourism are satisfactory, it would result in behavioral changes. For instance, Otto and Ritchie (1996) defined satisfaction as the subjective feelings of tourists when they use the services and experience sites. With respect to perceived value and environmental behavior, Russell and Russell (2010) stated that if tourists could gain beneficial experiences in areas requiring payment, they would be more motivated to protect the environment. Moeller, Dolnicar, and Leisch’s (2011) study on eco-travelers showed that the higher the travel expenditures the stronger the environmental awareness. Chiu et al. (2014b) in their study pointed out that the tourists with higher emotional cognition of the destination and perceived higher value during the trip, would increase their concern of the eco-environment of the destination and therefore, enhancing their environmentally responsible behavior.Therefore, we hypothesized that: H2: Tourists’ perceived value is positively related to their environmentally responsible behavior.
2.4. Intercultural Service Encounters -Service Encounter Elements
- Service encounter was studied by researchers to reveal personal interaction because increasing the pleasure of service encounters can ‘‘reduce the perceived risk associated with purchasing a service and improve the buying experience’’ (Julian & Ramaseshan, 1994). It is believed that service encounter elements are thus the antecedents of experiential value.The service encounter elements can be categorized to three components (Bitner, 1992; Baker et al., 2002; Keng, Huang, Zheng, & Hsu, 2007; Wu & Liang, 2009). The first is environmental elements, i.e., consumers interact with intangible and tangible elements in the service environment (e.g., lighting, music and internal and external design, or physical facilities) (Bitner, 1992). The second component comprises service employee factors, including the services to consumers provided by the employee. The interactive relationship between consumers and service employees is important to consumer evaluations, the behavior of service employees, are the key determinants of perceived service quality and also of consumer satisfaction (Andaleeb and Conway, 2006; Wu and Liang, 2005). Keng et al. (2007) found that personal interaction encounters and physical environmental interaction encounters positively influence customer experiential value. The third component is consumer factors such as whether the consumer is influenced by other customers (Bitner, 1992; Baker et al., 2002). The observed behavior of other consumers affects consumer perceptions and can influence consumer service satisfaction, therefore, managers must be sensitive to such interactions (Baker and Cameron, 1996; Brocato and Kleiser, 2005; Sommer and Sommer, 1989). The consumer-to-consumer interaction can be social facilitation, which positively impacts consumer-to-consumer interaction and provides entertainment. However, if the consumer perception that other consumers in the service setting are intruders (for example, smoking or talking loudly), it will has adversely impact on their customer service satisfaction (Baker and Cameron, 1996).Fiore and Kim (2007) presented a conceptual framework for the influences on the consumption experience exerted by the inputs of environmental variable, individual variables, and person-environment interaction variables or situations. The value of experience increases when service encounter (including interactions with service employees or other consumers) are perceived as positive. Hutton and Richardson (1995) proposed that the physical environment may provide cues regarding the influence of consumer perceptions on the brand image of business. Other scholars also pointed that environment influences consumer satisfaction (Baker et al., 2002; Bitner, 1990; Minor et al., 2004). Sulek and Hensley (2004) argued that both service employees and consumers influence cognition, emotion and physiological response in the foodservice settings.Therefore, we proposed that: H3: The international service encounter received by the tourists plays a role of moderator between their image of destination and perceived value.
3. Methodology
- This study examined the relationship between tourists’ image of destination, Perceived value and their environmentally responsible behavior. The interfering effect of tourists’ intercultural service encounters between their destination image and environmentally responsible behavior was also examined (Figure 1).
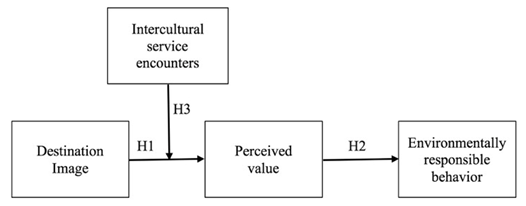 | Figure 1. Frame of research |
3.1. Demographic Information of the Participants
- Descriptive statistics is performed to analyze demographic data of the participants and calculate the information of sample frequency distribution, percentages and mean. Four hundred and twelve valid questionnaires out of five hundred were obtained; the valid response rate is 82.8%. Among the valid responses, 48.9% of the participants were from China, 16.5% from Hong Kong, 16.3% from Taiwan, while 18.2% from other country (including Singapore, Malaysia, Korea, Japanese, France, America, and India). Female participants (59.9%) were slightly dominant over male participants. Participant's age was dominated at 20-29 years old (37.2%) and 30-39 years (22.4%) and 77.9% them had the education level of college and above. Over half of the participants were first time to Macau (62.5%) and their main purpose of this visit was tourism (88.1%). For duration of stay, 54.5% of the participants spent only one day in the city; and for the type of tour. 55% of the participants attended packaged tour.Reliability check of the constructs by Cronbach’s α coefficients showed that the construct displayed ample reliability with the coefficients exceeding 0.90 for four sections of the construct. The Cronbach’s α coefficients for ‘destination image’, ‘perceived value’, ‘environmentally responsible behavior’, and ‘international service encounters’ were 0.978, 0.912, 0.900, and 0.955, respectively. The skewness and kurtosis of the collected data were examined to test the normality of the data. Skewness is a measure of the asymmetry and kurtosis is a measure of 'peakedness' of a distribution (George & Mallery, 2010; Kline, 2014). For sample sizes greater than 300, either an absolute skew value larger than 2 or an absolute kurtosis (proper) larger than 7 may be used as reference values for determining substantial non-normality (Kline, 2014). The result showed that all values for asymmetry and kurtosis for the tested data in this study were within the acceptable range of skewness and kurtosis for normal distribution.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. The Study of the Correlation among Tourists’ Destination Image, Perceive Values, Environmentally Responsible Behavior
- Result of the correlation analysis showed that the international tourists’ destination image was significantly related to their perceived value (β=0.413, p<0.01) and their environmentally responsible behavior (β=0.333, p<0.01). While the tourists’ perceived value was also significantly related to their environmentally responsible behavior (β=0.411, p<0.01). This result supported both H1 and H2.
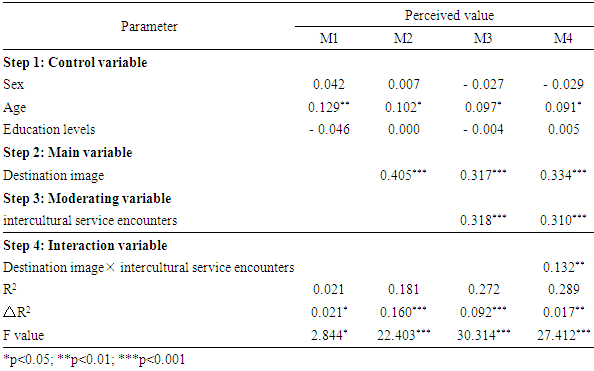
4.2. The Study of the Moderating Role of Tourist’s Intercultural Service Encounters
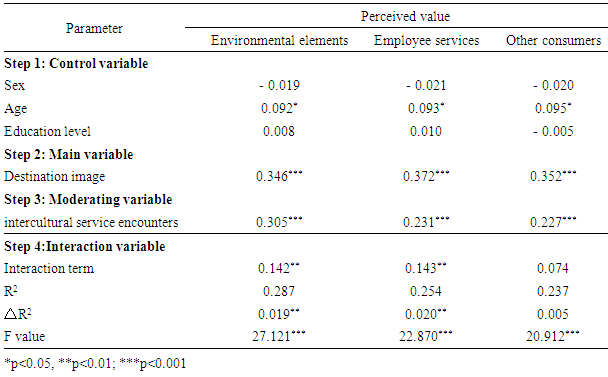
- The method of hierarchical regression was used to identify the moderating effect of tourist’s intercultural service encounters between their destination image and perceived value. Model 2 in Table 2 indicated that, the relationship between tourists’ image of destination (e.g. Macau) was positively related to their perceived value of this trip (b = 0.405, p < 0.001), and along with the result from the correlation (Table 1), it further supported H1. To test for moderating effect, the interaction terms (Destination imageÍ intercultural service encounters) was introduced into the regression model. Model 4 in Table 2 presents the results the interaction of destination image and international service encounters was significant in predicting the tourists’ perceive value (b = 0.132, p < 0.01), as well as the increased R2 of the regression equations from M3 to M4 (△R2 = 0.017, p < 0.01) which help in better predicting the perceived value. This result supports H3.
|
|
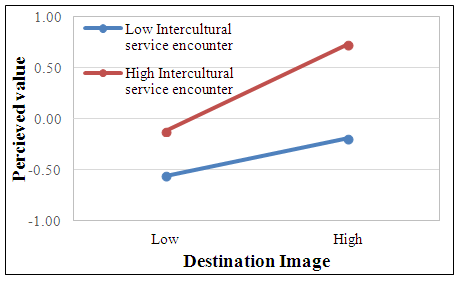 | Figure 2. The interaction between intercultural-service encounters and destination image in predicting perceived value |
|
5. Conclusions
- The purpose of this study was to develop a hypothesized model for destination image and validate its structure in Macau. It is important to gain better understanding of international tourists’ perceptions of destination image, how tourists value their trip experiences and what drives the environmentally responsible behavior.The findings of this study showed that international tourists’ image of destination was significantly related to their perceived values, and the perceived values were significantly related to their environmentally responsible behavior, during their visit to Macau. This finding is consistent with past studies (Chiu, Lee, & Chen, 2014a; Chiu, Lee, & Chen, 2014b; Ramseook-Munhurrun, Seebaluck, & Naidoo, 2015). The results also revealed that the international tourists’ experience of service encounters, as expected, had moderating effect between their destination image of the city and perceived value of the trip. While at the same level of destination image, the tourists who had good experience during their encounter with local service sectors had better perceived value of their trip in Macau. Besides, when the international tourists who had higher perception of service encounters, the increase of the tourists’ image of destination could much better enhanced their environmentally responsible behavior in Macau, as compared with the ones with lower perception of service encounters. Making tourism more sustainable is based not only on managing the negative impacts of the travel industry but also calls for a higher awareness and support for the conservation of the environment among travelers (UN Environment Programme and World Tourism Organization, 2005). Therefore, how to achieve and enhance travelers’ environmentally responsible behavior is an issue that draws the attention of the travel industry in general. It is important for government, private sectors and citizen of a city to realized that the image of the destination perceived by the international tourists had huge influence on their perceived value of their trip to this destination, and further impact their environmentally responsible behavior. The authority of Macau can study and identify what destination’s attributes or propagandas are likely to convey positive ideas or feelings that the tourists can be attachment to (further study). Form a managerial perspective, this study provides the managers with a better understanding of customer’s estimates of perceived value for the service industry. To enhance customers’ perceived values, it’s essential for local service sectors to deliver good experiences to these international tourists. The managers should focus on three service encounter factors, which includes environmental settings, personnel service performance and customer interaction. Thereby, encourage their environmentally responsible behavior during their stay at the city.For example, restaurant owners can enhance the visual appeal of the restaurant by changing furnishings and colors to enhance elegance and comfort. Employee-customer interaction can also be enhanced to improve customer perceived values.This study has limitations that need to be acknowledged. First, the results of this study may not be generalized because the research was conducted in a specific region; data were not collected from different destinations. The characteristic features of the region may also limit the ability to make generalizations. Because this study focuses on cognitive destination image, the findings are evaluated according to this criterion. The findings will be meaningful for similar future studies in this field. Second, examining perceived destination image of both the first-time and return visitors could be considered in future research. It would be important to examine how first and previous travel experience can affect tourists’ perceptions of destination image and their effect on perceived value, service encounters and environmentally responsible behavior.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML