-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Tourism Management
p-ISSN: 2326-0637 e-ISSN: 2326-0645
2014; 3(1): 17-31
doi:10.5923/j.tourism.20140301.03
Profile of Chinese Outbound Tourists: Characteristics and Expenditures
Rakotonanahary Fanomezantsoa Nasolomampionona
College of Economics and Management, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing, China
Correspondence to: Rakotonanahary Fanomezantsoa Nas, College of Economics and Management, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing, China.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The number of international tourists from China has remarkably increased in the past two decades; a continued growth is with an increase in household income and discretionary time. This paper aims to understand the trend in Chinese outbound pleasure travelers by identifying their travel motivations, the historical, political and economic circumstances in the development of Chinese outbound tourism, the profile, characteristics and strategies used to penetrate the Chinese Outbound Travel Market. China was selected in the research because it is currently the largest outbound tourist generating country in the World. Hence, the characteristics of travelers from China are very important and complicated, which deserve to be studied; being a fundamental key market for the world tourism industry.
Keywords: China, Chinese Outbound Tourism, Approved Destination Status, Gross Domestic Product, Geography, Strategy, Marketing
Cite this paper: Miao Jian-jun, Rakotonanahary Fanomezantsoa Nasolomampionona, Profile of Chinese Outbound Tourists: Characteristics and Expenditures, American Journal of Tourism Management, Vol. 3 No. 1, 2014, pp. 17-31. doi: 10.5923/j.tourism.20140301.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- China has the world’s fastest growing economy, with real GDP average growth rates of 10 percent for the past 30 years (Steven Barnett, 2013). China’s emergence creates tremendous growth opportunities and redraws the lines of force of the global tourism. China has the world’s largest population with 1.35 billion people, and occupies the third largest surface area after the Russian Federation and Canada. In 2010, China surpassed Japan to become the world’s second largest economy after the United States of America. While the tourism industry is weakened globally, the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) stated a very optimistic prospects offered by this emerging market: About 100 million Chinese tourists are expected to travel abroad by 2020 to 130 million international tourists in China. In 2013, the Chinese made 97 million outbound trips in the world.The rapid development of an inbound and outbound Chinese tourism is a wonderful positive sign within thirty years in the Chinese history. The policy of economic reforms implemented by Deng Xiaoping, in the early 1980s, has given the emergence of a middle class, open to culture, leisure and desperation to discover the outside world. Several approaches are possible to understand the evolution of the Chinese outbound tourism in the world, but we privilege the study of current mutation, because ever since the Chinese government in Beijing has been permissive in travel and never will leave traveling abroad has never been so strong in the minds of Chinese people. This mutation presents a significant challenge, while barriers to expansion already on the horizon.This topic instead the Chinese population in the heart of reflection. Guide policy to promote tourism to Chinese tourists is it relevant? What strategies and tools to use to reach them? To answer these questions, we relied initially on articles and scientific articles that have allowed us to better understand the topic identify points of conflict and identify issues. In a second step, we employed a participant observation as a methodology. Participant observation is in some ways both the most natural and the most challenging of qualitative data collection methods. It connects the researcher to the most basic of human experiences, discovering through immersion and participation the how and whys of human behavior in a particular context. The advantage is clear in terms of production data: This method allows us to live the reality of the observed subjects and to understand some mechanisms decrypting difficult thing for anyone in a position of exteriority remains. By participating in the same way as actors, researchers have a privileged access to inaccessible information. Participant observation is a process consisting of phase and strategies of integration starting with the contact phase has direct participation in activities with individuals observed. There are not here to expose the details of investigations obtained during different missions field results, but to show what methodological tools we use for the construction of scientific knowledge in the context research work on Chinese outbound Tourist.International tourism is democratized in the Chinese population, and develops to reach many destinations. It was previously unauthorized by the Chinese government. Chinese tourism is now accepted in over 146 countries or regions of the world, negotiations to obtain the “ADS” (Approved Destination Status) have multiplied in recent years between foreign and Chinese government.We hope, through the demonstration of the importance and weight of the Chinese population in tourism, observe how destinations meet new demand. Opportunities open to the Chinese middle class, which resonate as challenges to overcome. Hence these problems: "The Chinese middle class it represents a major opportunity for the global tourism industry? What will be the effect of the agreement (Approved Destination Status) on the Chinese outbound tourism and the tourism industry? Another question will be How do professionals prepare for the likely invasion of Chinese outbound tourism and how are they prepared?Historical and sociological approaches are necessary first to understand who the new tourists are: Where do they come from, how many and who are they, where are they going, what are their capabilities, their behavior and their expectations?We then make analysis of the policy of the Chinese outbound tourism and the implementation of agreements ADS (Approved Destination Status).The study of Chinese tourism abroad has a double interest: First, it allows appreciation of the evolution of the Chinese society, that is to say, including measuring the increase in purchasing power, to probe his desire to learn about other cultures, to study its ability to adapt to other cultures and observe his reports with the rest of the world.Second, it will show that Chinese tourists are a necessary means to foreign countries to decrypt the Chinese society and understand its march towards modernity. In a globalizing world, knowledge becomes a priority: this society does not quickly be called upon to play a leading role in the international community? Would a rate of sustained economic growth and the emergence of a middle class simply that give a new dynamism in the Chinese tourism industry, today become the strength development of the global tourism industry?
2. Historical and Sociological Approach to Chinese Outbound Tourism: New Customers for the Global Tourism Industry Weakened
- We try to draw in this part an overview of the Chinese outbound tourism: what are the main stages of its construction, who constitute the Chinese tourists, and which international destinations do they prefer?
2.1. Dévelopment of the Chinese Outbound Tourism
- For a long time, tourists from mainland China remained strangers to customs of other countries though they openly receive tourists; this is for the simple reason that international tourism has not existed in the People's Republic of China until the early 1990s.It will be important to point at the exceptional circumstances that allowed the foreign private travel of the largest population in the world to develop such as tracing the history of the first trips from the mainland and then on by analyzing the gradual introduction of Chinese outbound tourism.
2.1.1. The Historical, Political and Economic Circumstances
- a. From locking to opening of China to the worldThe Chinese, with their thirst for knowledge, for new experiences, culture and shopping, are in the process of becoming the first world travelers of many countries.Since the beginning of the Dengist Era, the Chinese government has gradually released its tight grip on the population to allow its citizens to travel abroad, because it is incompatible with the requirements of the new market.Laws restricting the mobility of Chinese in their own country, driven by the almighty hukou system1 (户口), a kind of residence booklet, have been revised. Introduced in the late 50s, this system of social control of the population remains in effect until mid-80s, to be relatively released afterwards. This “birth certificate” booklet, given at birth, in which the name of the place of birth and class of every Chinese mobility are inscribed, made only one scenario possible: " from bottom to up and horizontally."(TROLLIET Pierre, BEJA Jean-Philippe, 1986). For example, a Chinese rural Sichuan (South west) could not go and live in another city, or province, even less of Municipalities in directly under the Central Government, because his hukuo (户口) indicated his city Authorities which town is his original village. He are only allowed to live and work in another village within his province. Beijing residents, and residents of the major cities, were better served because their hukou (户口) allowed them to move horizontaly and down. The hukou (户口) system did not allow inter-class marriages because it limited rural people within their boroughs separately from city people confined in their cities. So, the hukou (户口) system somehow froze the Chinese company, in which the geographic mobility of people was very limited and where the various categories had social trends become endogamous. The need for the hukuo system found various justifications: for the government, it is possible to avoid an uncontrolled urbanization, but for others, he obeyed political motivations, because "it allowed to reinforce the authorities' control over the movement of the Chinese people, which hukou (户口) was initially granted, to know landowners and rich peasants.At first, only the officials of the State, theoretically was allowed to travel in China and abroad, only for official purposes. Then, the policy of reform implementation in the early 80s, initiating a "socialist market economy" has resulted in an overall increase in the standard of living of the Chinese. Pressured citizens became affluent, willing to work wherever demand is and to discover their country. They became stronger, to compel the authorities to relieve unofficially.Authorization to Travel gradually generated intra Border permits to allow the ability for Chinese tourists to move beyond boundaries.The gradual relaxation of the hukou (户口) system since the era of economic reforms has enabled the Chinese people to move first in the country, and partly to become consumers of leisure and tourist travel, then the world according to strict migration rules, framed by the agreements "ADS" (Admitted Destination Status) systematically signed between China and the countries concerned.b. Emergence of a middle classChina is a traditional agricultural society. For fifty years, and especially during the last thirty years, Chinese society has witnessed various changes, induced by the process of transformation from a traditional society to a modern society, from an agricultural society to an industrial society, as well as the conversion process from a planned economy to a market economy. These changes are reflected in changes in the structure of social classes. There were the steady declines in the number of agricultural workers since 1978. In 1978, farmers accounted for 67.4% of the workforce whereas in 1999; the number represents only 44% of the total workforce (UNWTO, 2003).So, Chinese leave campaigns for looking for work, to township enterprises or villages, by educating more and because of the urbanization of their villages to improve their social status. Due to the annual decline in the number of farmers, lower social classes and middle classes shrink. It is the same for industrial workers for whom the modernization of enterprises and the adoption of new technologies have had a positive impact on their standard of living, by passing in the middle class, whose we are witnessing the emergence and training. The number of private entrepreneurs, managers, owners of small industrial and commercial enterprises, people working in the service, is constantly increasing. This class that controls or directly operates on the economic resources of the country will take off and growth. The number of managers and private contractors also has known continuous growth.The explosive growth of China’s new middle class has brought sweeping economic change and social transformationIn China, the middle class is defined by all the people whose incomes are between 25,000 and 100,000 yuan. Its increase was due to many factors, but perhaps the most important is that the high level of literacy of the population, also the entertainment and leisure. From 2005 to 2010, its workforce has increased by 46%. It represents 57% of the Chinese population in 2010, against 39% in 2005. (SERRA André, 2014)The rapid growth of the middle class will be the most powerful in the development of China over the coming years, and deeply change the conditions of the planetary balance.Today, the consumption structure of urban and rural residents is dramatically changing, the proportion of spending on culture, education, tourism, recreation or sport gradually increases from 12.3% to 14% between 1999 and 2000, and urban residents aspire less survival as the search of entertainment and some development. (UNWTO, 2003).To increase the development of its economy through consumption, China has introduced the concept: Paid holidays. Introduced in 1998, these holidays mark an important turning point in the evolution of Chinese tourism. The three "Golden Weeks", "黄金 周" (Huangjinzhou) now allow a wide segment of the population to travel inside the country, and outside the Chinese border. Originally the term "Huangjinzhou""黄金 周" was used by the Chinese travel agencies to designate the Japanese’s holiday week of May, during which they are particularly many people to go abroad and especially in China. The term has been diverted by travel agencies to describe the Chinese official paid holidays: one week for the Spring Festival, which takes place between January and February, according to the date set by the lunar calendar, one week on the occasion of Labor Day, May 1st, one week for national day on October 1st. In general, persons belonging to upper and middle classes move at least three times during the year, both inside and outside the country, if the middle and lower classes make possible migration during the spring festival.
2.2. China: Country Issuer of Tourists
- In 1990, China Officially Opened Its borders, allowing its people to start visiting the world. The issuer market was initially developed to Hong Kong and Macao is growing rapidly since its inception.
2.2.1. History of Travel from Mainland China
2.2.1.1. Opening of China to the World: Hong Kong and Macao
- Visiting relatives and friends living in Hong Kong and Macao are the source of the first trips in these British and Portuguese ex-colonies. On the 15th November 1983, in order to simplify the movement of Chinese mainland who wished to visit their relatives or friends in Hong Kong and Macao, Guangdong Provincial Travel Corporation began to organize “Tours for visiting relatives in Hong Kong and Macao”. In 1984, the State Council approved the organization of tours to Hong Kong and Macao for visiting relatives for mainland residents. This was the prelude to the outbound tourism of Chinese citizens.In 1992, the Hong Kong and Macao Affairs Office of the State Council gave approval to Fujian Overseas Travel Corporation and Hua Min Travel Company to do this business. In 1998, the Hong Kong and Macao Affairs Office of the State Council and theGovernment of Hong Kong Special Administrative Region decided to increase the volume of tourists to Hong Kong and China International Travel Service Head Office was given approval to operate tours to Hong Kong and Macao. On January, 1st, 2002, the Hong Kong government and China National Tourism Administration decided to abolish the quota system regarding travel to Hong Kong. As a consequence, the number of travel companies increase to do outbound travel business. Now, there are over 531 travel agencies in mainland China accredited by the CNTA to organize tours abroad, who arrange tourist trips to Hong Kong and Macao.
2.2.2. Travel in the Border Areas
- In November 1987, China National Tourism Administration and the Ministry of Foreign Trade and Economic Cooperation gave approval to the border city of Dandong in Liaoning Province to operate one day tours to the border city of Sinuiju in the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea. By June 1998, the seven provinces and autonomous regions of Heilongjiang, Inner Mongolia, Liaoning, Jilin, Xinjiang, Yunnan and Guangxi have been approved by the government to operate border area travel with the Russian Federation, Mongolia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Myanmar and Vietnam.UNWTO notes that, after a development of twenty years, many changes have taken places with border tourism:- More and more people who do not live in the border areas make border travels.- The border travel routes have extended from border cities to the inland. For instance, border travel to D. P. R. Korea has not only extended to Pyongyang, but also reached Panmunjom at the 38th parallel, the demarcation line.- The stay of the border tourists in the foreign countries has become longer, such as from one day to 8 days. Actually, to a certain extent, there is no big difference between border travel and outbound travel.
2.2.3. Travel to Foreign Countries
- Travel to foreign countries by Chinese citizens has evolved from visiting relatives in foreign countries. In 1988, approved by the State Council, Chinese citizens were allowed to go to Thailand for visiting relatives and travel, provided their relatives paid for their expenses and offer guarantee for them. In October 1990, Singapore and Malaysia were added to this list, followed by the Philippines in July 1992.On July, 1st, 1997, “Provisional measures concerning the administration of outbound travel of Chinese citizens at their own expenses” was jointly promulgated by the China National Tourism Administration and the Ministry of Public Security and approved by the State Council. Thus outbound travel by Chinese citizens officially started and implemented the Approved Destination Status. Then, the government approved new destinations for outbound travel:
 ‖ 1999: Australia, New Zealand, South Korea;
‖ 1999: Australia, New Zealand, South Korea;  ‖ 2000 Japan;
‖ 2000 Japan;  ‖ 2001: Vietnam, Cambodia, Myanmar, Brunei;
‖ 2001: Vietnam, Cambodia, Myanmar, Brunei;  ‖ 2002 Indonesia, Malta, Turkey, Nepal, Egypt, Laos, Germany;
‖ 2002 Indonesia, Malta, Turkey, Nepal, Egypt, Laos, Germany;  ‖ 2003: Maldives, India, South Africa, Croatia, Cuba;
‖ 2003: Maldives, India, South Africa, Croatia, Cuba;  ‖ 2004: Europe, Switzerland, Denmark, 10 new European countries, Tanzania, Zimbabwe.
‖ 2004: Europe, Switzerland, Denmark, 10 new European countries, Tanzania, Zimbabwe. ‖ 2012: Madagascar, Columbia
‖ 2012: Madagascar, Columbia ‖ 2013: 146 destinations around the world signed the bilateral tourism agreement with China, called Approved Destination Status “ADS”
‖ 2013: 146 destinations around the world signed the bilateral tourism agreement with China, called Approved Destination Status “ADS” 3. Profiles and Characteristics of Chinese Travellers
- To provide a clear description of Chinese tourists traveling abroad, it is necessary to define who they are, by gender, age, socio-professional category, their reason for leaving and their mode of travel - group or individual, the duration of their stay, their spending or their type of accommodation.The vast majority of outbound trips, excluding those to Hong Kong and Macao, more than 70% of the market, are handled by travel agents. In 2010, 1,070 travel agencies in China were licensed to sell international travel, up from 672 in 2005. For travel outside China, people prefer to rely on travel agents, not only for the convenience (government regulations require travelers to some destinations to obtain visas, and applying can be an uncertain and tedious process) but also because agents help bridge cultural differences and language barriers.The main travelling periods for tour groups sold by travel agents are around the two remaining national holiday periods: the so-called “Golden Weeks”. These are the Spring Festival during the Chinese New Year and the National Day Holiday (first week in October). January or February is the most popular month, depending on when the Chinese New Year falls as this is the major holiday period for Chinese travelers.
3.1. Gender and Age
- The percentage of Chinese travelers by gender is changing. The proportion of males and females is becoming balanced.According to the statistics of tourism offices in Thailand, Singapore and Malaysia, from 70 to 80% of Chinese tourists were men in the late 80s and early 90s. Then the percentage of women rose year by year to reached 43.9% in 2000. The earlier Chinese travelers abroad were very often government on official missions traveling with public funds; it was therefore more men than women. Thereafter, with the increase of passengers traveling at their own expense, the proportions of men and women are becoming balanced. In Europe, there is a trend towards feminization of Chinese tourists. For example: In France, 51% of Chinese tourists are women in 2012. Chinese travelers aged 25-44 make up 65% of all outbound travelers. This represents an important increase since 2007 when this age group accounted for around 50% of all outbound tourists. Younger tourists account for 21% of overseas travelers, while tourists aged 45 and above account for 15%. It is worth noting, however, that the latter age group accounts for a higher proportion of long-haul travelers, especially to Europe and Australia. This group is also expected to increase its share of outbound travel in the future, as the Chinese population ages.In China, seniors are not generally willing to travel overseas due to the traditional cultural reasons and health problems. Guo et al (2004, 2007) examined the reasons for the lower participation in outbound travel by people over 50 years old. First, senior residents are living frugally and like saving their money. Travel, especially overseas travel, is seen as a luxury. Second, most have retired from work and live on pensions, which may not be high enough to afford overseas travel. Third, travel agencies do not provide tailored products to this group. Finally, many elderly people lack the physical strength to travel far. Therefore, in this study, the age groups of 50-65 and over 65 were combined together in the category ―over 50 years old‖ in the following analysis. Hsu et.al (2007) also found that many older people felt taking holidays was socially irresponsible, a view shaped by their childhoods in a Maoist period of China‘s history. However, some seniors do take holidays, when either they visit family overseas and / or their children pay for the holidays.The rapid escalation in social and economic mobility in China has brought a relatively rapid increase in discretionary income available for travel. Chinese travelers are therefore more eager than westerners to increase their spending on travel. But Chinese travelers differ from their western counter parts in ways that are significant for the companies that serve them. For instance, demand for travel in china comes mostly from active young adults eager to visit new places, whereas demand in the west is driven by senior citizens, who tend to have more time and money for travel.The young (18-25 years) and seniors (over 50 years) are more likely to participate less in overseas travel than middle aged groups (26-35 years and 36-49 years). In addition, people who are single are more likely to be non-participants when compared with married people. Income level plays an important role, as lower income earners (under RMB 5,000) are less likely to participate in overseas travel. A more plausible explanation, again, could be the high correlations among age, marital status and income. Single people are mostly young with relatively lower income, and the individuals usually earn their highest levels of income in their middle or senior years. With regard to occupation, company employees and managers are more likely to be participants. On the other hand, students are mostly unlikely to take overseas vacations due to lower incomes and perhaps because of time pressures.While outbound travel for Chinese mainland citizens is still dominated by group tours, its growth is slowing when compared to the meteoric rise of independent tourism. Fully independent outbound tourism is growing even faster than foreign travel in general, and the market is still in its infancy. This trend goes hand-in-hand with a demographic sea change for China: a second generation of affluent consumers coming of age. The six characteristics that define this next generation of Chinese travelers- Younger: 60% are in the consumer “sweet spot” between 25 and 45 years old.- Richer: Over 80% have an annual income over 60,000 RMB. The average for urban consumers is 24,000 RMB.- More educated: The vast majority at least have bachelor’s degrees.- More sophisticated travelers: fully independent tourists usually aren’t on their first trip abroad. Many study or have studied in other countries. Even when they aren’t fluent in foreign languages, they aren’t afraid to deal with locals on their own. Younger Chinese are worldlier than their parents, but still proudly Chinese.- More connected: The internet is the main source of information for independent tourists. They see internet and social networking access as a major necessity. They often consult friends for travel advice and use first-hand travelogues in blogs when planning a trip.- Demanding: This whole generation of only children that grew up in relative abundance is accustomed to high quality and attentive service.
3.2. Modes of Travel
- Outbound tourism by Chinese citizens is a recent phenomenon (Zhang, 2003). Before China‘s economic reform and openness to the outside world, the purpose of Chinese overseas travel was primarily related to foreign affairs with an annual outbound departure of 2 million.Strictly speaking, this was more in the nature of diplomatic activity rather than outbound tourism in a real sense. Chinese visitors usually travel in a tour group because of restrictions placed on individual travelers by both the Chinese and destination’s governments. Group travel remains the preferred mode of travel for Chinese tourists in both Asia and Europe. If this mode of travel is now selected in Asia, group travel is imposed in Europe. The vast majority of Chinese tourists traveling in groups: 70% according to a latest report of the tourism agency of China. This number tends to decrease but still remain strong for many reasons:- Language barrier: many Chinese do not speak English or French prefer traveling with a guide. - The issues Visa: agencies take care of everything and facilitate obtaining a VISA - Fear of adventure for the most part they have never been out of China, the travelers are inexperienced, and naturally afraid of the unknown. - Group: Chinese like to be in a group, influence of Asian culture. For reasons-price travel with a travel agency is much cheaper than from single or small group.It is a trend that the percentage of group tourists is decreasing. According to the Statistics of Singapore Tourism Board, in 1993, Chinese group tourists made up 73%.The figure dropped to 56.6% in 1997. It was 60.4% in 2000. The statistics of Macao Government Tourism Office show the percentage of group tourists from the mainland. In 1995, it was 78%; in 1996 it was 67.2%; in 1997 the figure was 67.6%; in 1998 it became 58.15 % and it dropped to 36.5% in 1999.In France, 51% of Chinese tourists are women (2012) and 49% of them traveling alone and addicted to luxury shopping (VIGOUREUX Thierry, 2012). Women executives of private companies include more represented than before and have a high budget personal expense.The opportunity for Chinese to travel outside Mainland China for leisure travel purposes is fairly recent. However, Chinese in the middle and top incomes are already starting to consider travel a ‘birthright’ (World Travel and Tourism Council, 2006, p.15) and there have been an increasing number of Chinese taking outbound trips (China National Tourism Administration, 2006). There is general agreement that the growth of China’s economy is leading to a rapid increase in international travel from a burgeoning middle class. The Chinese Government loosened the restrictions on the outbound tourism market in 1983 with the introduction of the Approved Destination Status (ADS) scheme. As a result of the open door policy and the rapid economy’s expansion, Chinese outbound tourism has strongly developed.China has been recognized as a major emerging outbound tourism markets in the world and in 2012, 83.2 million Chinese engaged in outbound travel (China National Tourism Administration). There has been a growing interest in researching outbound Chinese tourists.
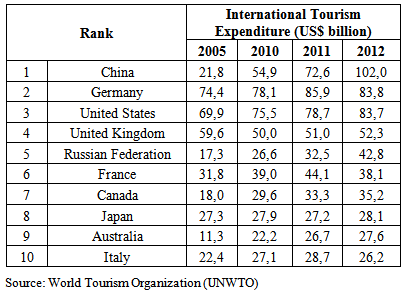
3.3. Chinese Travelers: The Biggest International Tourism Spender
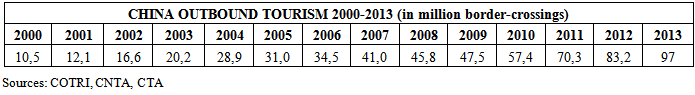
- Expenditures by Chinese travelers are exponentially increasing. Between 2000 and 2012, expenditure abroad of Chinese tourists was multiplied by eight, as the number of international travel, which increased from 10 million to 83 million over the past twelve years. The purchasing power of Chinese tourists is also higher than that of Americans.In two years, Chinese tourists could be spending as much as $194 billion a year in Europe, the US, Asia and other vacation spots.That figure speaks of the appreciation of their currency and the growing economic clout of China’s middle class. In 2012, Chinese travelers became the world’s biggest spenders, shelling out about $102 billion overseas, 40% more than 73 billion in 2011 and $ 48 billion in 2010. According to a new report by the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), Chinese travelers are now the top source of tourism cash in the world.
|
|
3.4. Chinese Tourists: Off Season Customers
- In general, the demand in terms of tourism services is growing: the composition of this demand is constantly changing for several years, and this demand generally influences the timing and space rentals. (Maddison, 2000). The rapid growth of tourism demand is caused by an increase in leisure time, partly due to an aging population, along with a general increase in the purchasing power of households. (IET, 2003).This parallel increase in income and leisure time is an explanatory cause of the growing number of Chinese tourists. Anyway, there is a period defined for the displacement of Chinese tourists. For Chinese travelers, these trips happen most often during the "low" and "off season", towards Europe as the largest destination region. Based on the WTO definition "seasonality is attending a site or a device on a season or part of the year due, in part, to the specificity of a site or equipment and secondly, the constraint of the school calendar and dates of paid holidays."This definition of seasonality, ultimately gives us three types of tourist seasons, based on different levels of annual travel. These seasons are three fold: first, the high season tourism having a maximum occupancy level; second, the low season which refers to a small number of visitors and revenue ; third, the average season is almost similar to the high season months, but with an occupancy level of approximately 60 %. (UNWTO, 2001). Based on climatic phenomena but also the dates of national school holidays, the summer months have traditionally been the month to go on vacation. (Markant, 1991). For most tourists, the main traveling season is still the summer months (July and August) going to mainly Europe, United States, Canada and the others country. (Familitur, 2003).It is recognized that tourism seasonality has two origins: the first is known as natural seasonality and the second, institutional seasonality. (Baron, 1975). For China, the origin of tourism seasonality is institutionalized and is based on Chinese culture: The main travelling periods for tour groups sold by travel agents are around the two remaining national holiday periods: the so-called “Golden Weeks”. These are the Spring Festival during the Chinese New Year and the National Day Holiday (first week in October).January or February is the most popular month, depending on when the Chinese New Year falls as this is the major holiday period for Chinese travelers. So, it is very important to study the evolution of the Chinese work schedules and public holidays to know the availability of time because People who want to travel are not only dependent on their disposable income, but also the availability of time.A six-day work policy, equal to 48 working hours per week, had been implemented since the establishment of PRC. With industrialization and the progress of IT based technologies, the working hours have been reduced in the past decades. The Chinese government effectively cut working hours from 48 to 44 in May 1994 and then to 40 hours, when the two-day weekend was introduced in China in early 1995, which made the pursuit of leisure activities a reality. Golden Weeks were first initiated on the occasion of the 1999 National Day public holiday ("Status Report on China's Golden Weeks Public Holidays", 2007). Soon after in 2000, Chinese citizens were entitled to seven days of national holidays on May Day (from May 1st), National Day (from October 1st) and Spring Festival (in January or early February), as a measure to encourage holiday spending and improve the national standard of living, as well as allowing people to make long-distance family visits. In fact it is a 3-day paid holiday, and the surrounding weekends are re-arranged so that Chinese nationwide have seven continuous days of holiday (Wikipedia, 2008, February 14). The resulting seven-day holidays are called ―Golden Weeks‖ and have become peak seasons for travelling. An estimated 28 million Chinese travelled during the first National Day Golden Week in 1999. In 2007, this number has increased to around 146 million with the tourism income of 55.9 billion Yuan (CNTA, 2007).In order to ensure the supply and demand for holiday tourism and settle tourists ‘complaints, the Coordination Meeting Office (or called "National Holiday Office") was established and the tourism statistical information system was put into practice during ―Golden Week Holidays‖. In total, the annual official holidays have been extended to more than 110 days, including two-day weekends and three golden weeks (Yu & Ge, 2006, May 6). This holiday entitlement has stimulated the dramatic growth of both domestic and outbound tourism in China. It has also changed the seasonality of the Chinese tourism market.Travel is concentrated around the three Golden Weeks. However, many see this as a deterrent, and would like to see a move towards paid holidays (Clsa, 2005), which is now a topical issue. Many experts as well as the public are calling more than before for a "paid holiday", as people complain about congestion when travelling around in the country on the ―big‖ holidays of Labour Day, National Day and Spring Festival. The Labour Law of China, which took effect in 1995, stipulates that all employees enjoy the right to take paid holiday once a year after working for one year, but in practice it performs no function without enforcement. The ETC-WTO joint research on China (2002) mentions that China will introduce the system of paid holidays for the working people in the next five years.According to the survey by Ctrip, the biggest consolidator of hotel accommodation and airline tickets for China's individual travelers, of all the 2200 respondents, about 14 percent of the respondents supported abolishing all three "Golden Week" holidays. Though 49.4 percent wanted to abolish or change the May Day and National Day "Golden Weeks" and retain the Spring Festival holiday. If the government abolished one or more week-long holidays, 60.1 percent favored compulsory paid vacation (Ctrip, 2007).Then, in November 2007, regulations about paid holiday were approved by the Chinese government based on public opinion and these came into effect from January 1, 2008 (Yu, 2007). In the regulation, it is clearly stated that all employees are entitled to have paid holidays after working for the same unit for over one year. The paid holidays vary from 5 to 15 days according to the length of service in the unit. The public holiday and weekends are not counted as paid holidays. It is expected very soon that clear stipulations are going to be added to the current Labour Law, so as to ensure employees' right to their paid holidays. A sample survey by the China National Tourism Administration and State Statistical Bureau indicates that if the "paid holiday" system should be implemented, around 80 percent of urbanites could decide for themselves their time to travel to avoid the peak travel season, which would greatly relieve the pressure on transportation, tourism, commercial and catering sectors (China Daily Online, 2004, May 11). But a question inevitably comes up as to whether the paid holiday system can be effectively carried out. One concern is that unethical employment practices might take place in some companies, whereby employees are denied their paid holidays.Meanwhile, public holiday arrangements are also being changed. There was no 7-day May Holiday in 2008 according to the new regulation from State Council (China News, 2007, December 18), that is to say, 3 days are expected (1st of May and 2-day weekends). Meanwhile, people will have, for the first time, traditional Chinese holidays including Dragon Boat Festival, Mid Autumn Festival and Pure Bright Festival (Tomb Sweeping Day), which regulations are believed to enhance an awareness of Chinese traditional culture. Nevertheless, the 7-day National Day Holiday in October will still remain the same. The above measures will undoubtedly have an impact on the seasonality of travelling overseas by Chinese citizens, because tourist movements are, to a large extent, affected by tourist-generating countries ‘holiday periods. The two main periods of Chinese national holiday during the Spring Festival Chinese New Year (January or February) and the day of the National Day (first week of October) fell to the low tourist season and "out of the tourist season" in destination countries.In general, Chinese travelers visit Europe "out of the tourist season", the largest destination region for them with over 3 million trips (4.4%) in 2011. The Americas follows with almost 2 million (2.7%) Chinese departures, while Africa was the destination of almost 1 million departures (1.4%). They prefer to go in the spring, during the Chinese New Year or in autumn during their holidays. The main issues in the tourism sector are to fill the gaps of activity and Chinese tourists in my opinion are a perfect complement activity for the majority of enterprises in tourism. The rapid escalation in social and economic mobility in china has brought a relatively rapid increase income available for travel. Chinese travelers are therefore more eager than westerners to increase their spending on travel
4. Strategies to Attract the Chinese Consumers Travels how to Achieve the China Market’s Tourism Potential?
4.1. Admitted Destination Status Scheme “ADS”
- In 1995 the Chinese Government introduced the Approved Destination Status (ADS) Scheme. An AD is an administrative measure by means of which the Chinese Government permits its residents to travel to selected countries for personal and leisure purposes: usually on all-inclusive based package tours. The ADS is a bilateral tourism arrangement between the Chinese Government and a foreign destination, whereby Chinese tourists are permitted to undertake leisure travel in groups to that destination. One hundred fourty six destinations around the world signed the bilateral tourism agreement with China, called ADS in 2013. An ADS was first introduced in the early nineties for destinations in Southeast Asia such as Singapore, Thailand and Malaysia. Prior to ADS, travelling abroad was only allowed for business purpose and official visits with government approval needed for every single visit. ADS policy was created to account for the growing interest of Chinese citizens in foreign travel and the fast increase in disposable income. An AD is granted to overseas destinations through a bilateral government agreement. The ADS only concerns tourism groups handled by assigned Chinese local travel agencies. The ADS scheme is an important part of this inbound tourism growth. Chinese visitors can travel on non-ADS visa’s for free independent travel, business and government delegations or official travel, study groups etc. However this travel must still be booked through an approved outbound agent. The purpose of ADS is to have a control mechanism on the organizing parties on both sides (local travel agencies and international tour operators) in order to guarantee safe and reliable tourism services for the Chinese customers.An important issue within ADS is to avoid possible illegal immigration through tourism channels. All tourism groups travelling within the ADS framework are supposed to be monitored by both Chinese and foreign authorities to ensure they return to China. Embassies and consulates apply different methods to monitor the return of the Chinese tourists. Whenever a tourism group member does not return to China, the local travel agency is held responsible and sanctions are applied.Only certified ADS travel agencies are allowed to promote and organize tourist groups including visa application and payment of foreign currency to foreign parties. Each of the certified travel agencies must assign special couriers to handle the visa application procedure. Countries without an ADS agreement are not allowed to receive tourism groups from China or to promote their destination in China for tourism and are restricted to business and official travel groups only.A key factor affecting Chinese outbound travel is the ADS system. This system has two critical features. First, it limits the number of countries to which Chinese residents can easily travel. That is not to say that people cannot travel to other countries, but in such cases the process of obtaining a visa is considerably more complex and costly. Second, the ADS system also controls the negative impact of outbound travel on the Chinese economy by requiring that partner countries agree to a balance of payments in terms of arrivals and expenditures between the ADS destination and China. This can act to neutralize the economic incentive of pursuing Chinese outbound tourism.
4.2. Know the Customer
- Nowadays, China is required on almost every table in the global landscape. With a population of 1.3 billion, China recently became the second largest economy and is increasingly playing an important and influential role in the global economy. China has the world’s biggest online presence; China has more internet users than any other country putting it ahead of the United States as the world’s biggest Internet market. Online shopping taking up almost in various areas and it grows too in Popularity in Rural China.In 2012, there were 1 billion tourists who have traveled abroad. This is a record. In this billion, the parts from Chinese tourists are more important each year. Indeed, they were 16.6 million in 2002 and they numbered 83 million in 2012 with travelers under the age of 45 accounting for 90% of the market over the past decade.China is the largest outbound tourism market in the world: A total of 97 million Chinese tourists left the country in 2013, up 14 million from the previous year. Business travel is also developing, Chinese go out increasingly of their continent and spend significant sums of money in their Business TripChinese travelers are now, on their spending, the top source of tourism cash in the world. According to the World Tourism Organization, China has surpassed Germany and the US as the world's largest source of tourism by expenditure. Spending abroad has increased almost eightfold since 2000, reaching US$102 billion in 2012, representing an increase of 30% from 2011. This is a trend that country and the tourism industry cannot avoid and cannot ignore. But, the majority of tourism stakeholders can not be known, and do not know to attract these new travelers.However, though very promising, the Chinese market is particularly rather complicated. Some knowledge of the customer's expectations and modes of very specific life is therefore necessary to effectively address it.It is important, therefore, to understand the Chinese culture, priorities, lifestyle, consumption ... analyze, understand, explore and create, innovate, implement actions to bring the company as close as possible to consumers .This is a difficult problematic if we do not know the market, culture, habits and customs of the Chinese people and their needs and their major trends. What are their behaviors? How to receive them? How to trade with them? What are their needs, both for Tourism (Accommodation, Transportation, Dining, Activities ...) for the Culture: what support do they need during a visit? How to address them for the promotion of cultural events and sites? How to capture the attention of these customers? What strategies propose to conquer the Chinese tourism market?Understanding how do the Chinese travelChinese tourists are very different from other usual travelers like Indians, Europeans and even Africans. They pay much attention to the basic tourism facilities and service such as transport, accommodation and Chinese-speaking staff as well as the safety and weather in the destination. They place secondary importance on tourism attractions. This is understandable because many Chinese people do not have high level of overseas experience. Going to a foreign country is attractive to them. However, which country they are going to does not really matter so much for many of them. Among the outbound passengers, the young and middle-aged employees tend to have their outbound tours in the peak season, while senior citizens prefer to travel during off-season because of the cheaper price and better service offered.On the whole, the peak season for outbound travel is the three golden weeks, especially the Spring Festival. The public holidays in these golden weeks last seven days each, but May and October are in the busy season and employees will not be allowed to ask for leave in addition to the public holidays. The Spring Festival is however in the off-season and some enterprises have longer holidays than the public holidays. Some employees would utilize their unused holidays or weekends in the Spring Festival. So the real holiday is longer than a week.According to Hofstede (1980), Chinese people tended to avoid uncertainty rather than adventure seeking. They tend to have a high need for security and a strong belief in experts and their knowledge. They think conflict should be avoided. On the other hand, people with low uncertainty avoidance are more willing to accept risks associated with the unknown and take initiatives in life and work.
4.3. Geographic Strategy
- In order to enhance the cooperation between China and the rest of the world and to better attract travelers to China, the world should have a better understanding of China's geography. China has a vast territory, with 9 600 000 km2 land area and ranking 3rd in the world after Russia and Canada. Besides, it also has a sea area of 3 000 000 km2. China has 23 provinces ( Qinghai, Sichuan, Gansu, Heilongjiang, Yunnan, Hunan, Shaanxi, Hebei, Jilin, Hubei, Guangdong, Guizhou, Jiangxi, Henan, Shanxi, Shandong, Liaoning, Anhui, Fujian, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Taiwan, Hainan), 5 autonomous regions (Guangxi Zhuang, Inner Mongolia, Ningxia Hui, Xinjiang Uighur, Tibet), 4 municipalities directly under the central government (Beijing, Chongqing, Shanghai, Tianjin) and 2 special administrative regions (Hong Kong, Macau), with Beijing as its capital.China accounts for the largest population in the world. By January 6th of 2005, the national population had amounted to 1.3 billion. At present, China’s population exceeds 1.3 billion. Chinese people now constitute about 22 % of the world’s population.It is observed that there are many differences both in the degree of economic development and income per capita: income inequality between urban and rural, inequality in the industrial and urban development, there are differences between town and country, between trades between different regions between coastal regions and inland areas and even within cities and within the country.To know, therefore, the main emitting provinces and cities Chinese tourists, studies and surveys have leaded by different services and published in the paper written by the UNWTO in 2003:- According to the statistics of the Entry and Exit Administrative Bureau of the Ministry of Public Security, the ten first provinces and municipalities according to traveler volume are: Guangdong, Beijing, Shanghai, Fujian, Heilongjiang, Inner Mongolia, Liaoning, Shandong, Yunnan and Xinjiang.- According to the criteria of the UNWTO in terms of their economic development, quality of life, social structure, population quality, and public order the top ten provinces and municipalities in China are Beijing, Shanghai, Tianjin, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Guangdong, Liaoning, Fujian, Shandong and Heilongjiang.- The other survey, conducted with Chinese travel agencies tells us that Guangdong, Yunnan, Guangxi, Liaoning, Heilongjiang, Fujian, Shanghai, Beijing, Inner Mongolia and Zhejiang are the main areas emitting Chinese tourists, whether for travel towards the borders or to travel abroad. Both surveys reveal that the more developed areas of China is the more outbound tourists it generate.
4.4. Online Strategy
- China has more internet users than any other country putting it ahead of the United States as the world’s biggest Internet market. According to the latest semiannual report from the official China Internet Network Information Center, 590.56 million people in China were using the internet at mid-2013. By comparison, the U.S. has the second-most internet users -254 million, according to the Harvard Business Review, but that’s less than half as many as China (DESILVER Drew, 2013). China holds the first place in terms of online shoppers: 242 million people in china were doing the online shoppers. Online shopping taking up almost in various areas and it grows too in Popularity in Rural China.
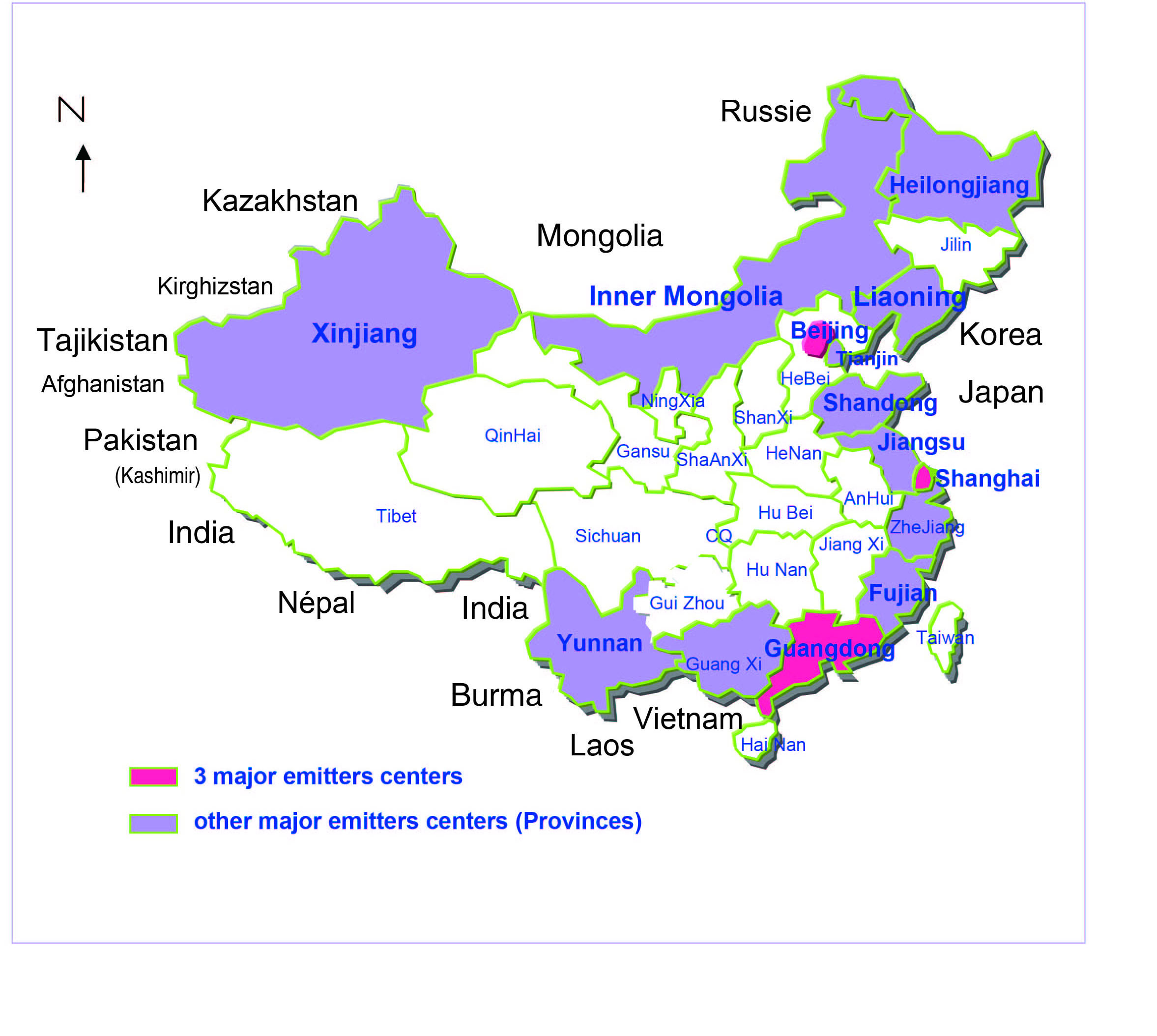 | Figure 1. Centers emitters of Chinese tourists |
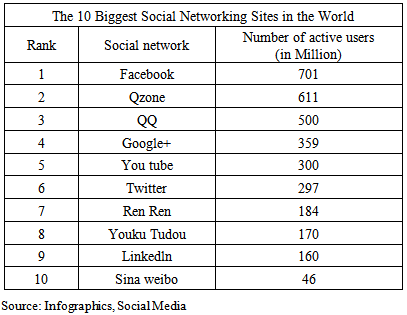
- The Chinese market is technologically savy with over 590.56 million regular internet users today and an estimated online audience of 750 million by 2015. This strong growth in internet usage has led more Chinese to rather book their travel online instead of traditional way. In 2010, online travel bookings in China reached 6.2 billion, a 58 per cent increase from 3.9 billion in 2009. By 2014, online travel bookings are expected to exceed 20 billion. The internet was the most popular source of information for Chinese travelers.It should be noted that the Chinese travelers do not speak much English nor French. They only use their mother tongue. It is therefore essential for the tourism industry (hotels, incoming agency, and destination) to offer services tailored to Chinese customers. So, Chinese language websites attracted more Chinese travelers. Thus a company wishing to attract Chinese tourists must have a website, always in the Chinese language, adapted to the needs and habits of the Chinese. The website in Chinese language must also be optimized to open access to Chinese internet search which usually block Western internet.Search engines are different, and the leading search engine in China is Baidu. Having a site hosted in China is not only important to be able to respond to censorship, but also for the download speed of your pages, as well as the optimal indexation in search engine Baidu has more than 80 % market share in China. It is therefore necessary to optimize the website for Baidu and then work on referencing it. SEO is a very good way to attract the targeted users who do these searches. SEO is to perform work on the keywords and content of the website, then bring them up with external links and link exchanges with other sites.This reinforces the importance of providing consumers with informative and easy access to online options.Online distribution of travel products and services may be the opportunity for service providers in developing countries access to tourism markets international, directly targeting potential tourists like Chinese travelers. Most consumers use the Internet to search for travel information. ICTs also help destinations and providers of tourist services to develop, manage and sell their offerings worldwide. In connection with the reorganization of the tourism market, the effective use of ICT could enable developing countries to build their own brand, to develop new products, promote their tourism resources and increase their base consumers to increase foreign tourism revenues and contribute to local development. The application of ICT in industry-driven information as a key business driver for the organization and marketing of destinations developing countries illustrates the potential of ICT for economic and social development.In fact, the Internet can be divided into several categories: website, forums, social networks, online advertising:- Web siteChina has the world’s biggest online presence. Tourism companies cannot be perceived as market leaders if they do not have a web presence. They thus are making efforts to move more business activities online to best meet the requirements of Chinese customer for online service, because online services are attracting customers and guiding tourism activities.An online tourism service can be characterized under seven functions: general tourism service information publicity; advertising tourism product or service; advertising tourism product/price with price information; email enquiry for tourism information and service; online booking for tourism product and service; online payment; tourism web site registration with user ID.Web site should offer more functions: presenting scenic information, tourism news, offer special local product and souvenir information, provide email address to allow customers to make enquiries about products and services, provide brochures map and other associated tourism information. The web site can offer online booking, including room booking and ticket booking.Tourism companies should use the web to build customer relationships by having customers register directly and then getting information from customers to create customer profiles that can be used in new tourism product development. The tourism web site content could have a promotional direction and a customer oriented design. They could help users in finding “Where to go”, “Where to stay”, “what to do”, “How to go there” and, in general plan a trip. So, the characteristics of tourism web site should be: very helpful, trustworthy, dependable, reliable, and ensure that the information content provided on the web is useful, up to date and can meet customers need and link relevant sites to users.In general, a tourism activity involves the six basic tourism elements: Eating, accommodations, traveling, wandering, relaxation, and shopping. Tourism web site users would like to get relevant information for the six elements from a destination web site before they go on tour. Tourism web site thus should be built with sufficient links to other relevant sites and have the ability to develop various packages that integrate a group of relevant services.In China, there are two categories of tourists: private and group travelers. The two categories of tourists have different travel purposes and requirements concerning travel and accommodation. Tourism web sites thus are expected to offer services to different target groups of tourists.The first key factor for developing a successful online application is to correctly define users’ requirements. Allowing users to email requests and replaying to questions on time are important functions in web site design and an effective way to attract online customers. This is also a strategy of business management. The third most important factor for a successful tourism is a good information interaction. An interaction function is important to allow sharing experiences capture valuable information and taking part in consultations. A lot of users are interested in online chat, online consultation and email facilities. The users prefer a combination of information content such as a tourism guide and community involvement such as a web consultation. Normally, Chinese travelers like to get other opinion of scenic places before they go on tour. They thus wish to talk with other tourists via the web sites. Tourism web sites are expected to provide an interactive space to customers and service providers. Customers would like to share ideas, experiences, opinions and suggestions with others online.- Social Networking SitesFacebook is an online social networking service and the world’s largest social network, but the Chinese are not allowed to use facebook. The fact that China’s government control outgoing information is not just technological but rather economical.China’s government exerts control over every significant business in the country. Companies in China must be majority owned by a Chinese citizen, and even then are heavily regulated by the government. All the major corporations in China, including telecommunications and media companies, are state owned entities or are majority owned by the state. This exerts a significant level of state influence on how people receive and send information. Facebook is the world’s largest social network, but to appreciate its feat, we also need to know how other social networks across the world fare against it.
|
4.5. Travel Agency
- Outbound tourism by Chinese citizens is a more recent phenomenon. Therefore, Chinese travelers want to continue using a travel agent for the arrangement of their holiday. It is true that the Chinese people are already used to making a travel package purchase online. But for their trip abroad, they always trust a travel agency because the opportunity for Chinese to travel outside Mainland China for leisure travel purposes is fairly recent. In addition, they neither have enough knowledge or experiences of the place of destination. So, Human contact is important for the majority of Chinese travelers and they must entrust their trips to travel agencies. Travel agencies support clients, advise on best and popular destinations, provide information on hotels and logistics. Furthermore, travel agencies seek the most suitable solution to tend to their client’s needs to fit into their budgets and aspiration. They also check for the availability of different services such as transport, accommodation, catering, rentals and excursions ...Travel agencies make reservations; ensures IT transactions and trade (quote, order tracking, invoicing and payment collection). They write and send tickets; fulfilled contracts and travel diaries .They manage claims and reimbursements as well.In China, business travel agencies are under strict state regulations. They hold a license issued by CNTA (China National Tourism Administration), after proven to possess managerial professional competence, financial security and professional liability insurance.The China National Tourism Administration is the government body in charge of the tourism industry and as such is an organization at ministerial level reporting directly to the State Council. The responsibilities of such entity can be summarized as follows:
 Drafting plans policies, laws and regulations about the tourism industry.
Drafting plans policies, laws and regulations about the tourism industry. Opening the industry to overseas investors, promoting the growth of tourism enterprise groups and the tourism market.
Opening the industry to overseas investors, promoting the growth of tourism enterprise groups and the tourism market. Approving travel-service companies, guiding the rating of tourist hotels; overseeing tourism service quality, directing tourist safety and entertainment.
Approving travel-service companies, guiding the rating of tourist hotels; overseeing tourism service quality, directing tourist safety and entertainment. Coordinating the management of national tourism resources, approving tourism investment projects, supervising national tourism resorts, organizing the development of tourist products, providing related information and statistics and tapping into international tourism markets, regulating outbound travel by Chinese citizens, and approving and administering overseas offices and foreign tourism institutions in China.The CNTA is competent for inspecting travel agencies and punishing those offering illegal or unauthorized overseas travel services and unapproved destinations.Travel agencies still have their place in China. This is attested by the increase in the number of travel agencies; in 2010, 1,070 travel agencies in China were licensed to sell international travel, up from 672 in 2005 ( UNWTO, 2012).The Internet is a current tool used to teach, plan, discuss, share, and take decision about travelling. However travel agencies still hold an important distribution channel for purchasing Final Act, particularly because of the convenience to get the visa as regards to complex packages to destinations.
Coordinating the management of national tourism resources, approving tourism investment projects, supervising national tourism resorts, organizing the development of tourist products, providing related information and statistics and tapping into international tourism markets, regulating outbound travel by Chinese citizens, and approving and administering overseas offices and foreign tourism institutions in China.The CNTA is competent for inspecting travel agencies and punishing those offering illegal or unauthorized overseas travel services and unapproved destinations.Travel agencies still have their place in China. This is attested by the increase in the number of travel agencies; in 2010, 1,070 travel agencies in China were licensed to sell international travel, up from 672 in 2005 ( UNWTO, 2012).The Internet is a current tool used to teach, plan, discuss, share, and take decision about travelling. However travel agencies still hold an important distribution channel for purchasing Final Act, particularly because of the convenience to get the visa as regards to complex packages to destinations.5. Conclusions
- This study aimed at to better understanding travel motivation, constraints and decision behavior in the context of China pleasure travelers to overseas destinations. These variables play a significant role in influencing future travel behavior. Push and pull motivational factors associated with Chinese outbound pleasure travelers are discovered. The results supported previous studies that motivation is multi-dimensional.Outbound tourism by Chinese citizens is a more recent phenomenon. Successful economic reforms, especially in urban areas, more openness to the outside world and increasing disposable money and time have all contributed to rising demand by Chinese to see the world. A part from that, Chinese outbound leisure travel is expected to rise quickly in the coming years. The easing of passport procedures, the introduction of Approved Destination Status for many destinations and the installation of national “Golden Weeks” holidays, many impediments to travel are disappearing rapidly for the middle class Chinese individual.This trend started with tours to visit friends and relatives in Hong Kong and Macao in the early 1980s. This was followed by an increase in cross border day trips in the late 1980s to the frontier areas of Russia, Korea, and Mongolia.China outbound leisure tourism to destinations outside Asia started with the first ADS groups going to Australia and New Zealand in 1999. Since then, the total number of Chinese citizens leaving Mainland China’s population grew within five years from less than 10 million to almost 30 million, an increase of 313%. Outbound traffic reached almost 97 million in 2013. The degree of development in its outbound tourism is a symbol of the economic growth of the country and the indicator of the increase in the livelihood of the people.Throughout the world in 2012, with the fast economic growth in the past decade, China has become the largest spender on international tourism, surpassing both the second largest spender United States and topping spender Germany (both exceeding US$ 80 billion in 2012). In 2012, Chinese travelers spent a record US$ 102 billion in international tourism, boosted by an appreciating Chinese currency. Expenditure by Chinese travelers abroad has increased eightfold since 2000. As in the majority of the world’s source markets, outbound travel from China heads predominantly to regional destinations. The Asia and the Pacific destinations accounted for 91% of all outbound Chinese trips in 2011. Beyond Asia and the Pacific, Europe is the largest destination region for Chinese travelers with over 4.4% in 2011. The Americas follows with almost 2.7% Chinese departures, while Africa was the destination of almost 1.4% departures. In general, at present, the main outbound travel products are sightseeing tours conducted in groups. In recent years, in Beijing, Shanghai and Guangdong, where travelers are relatively matured, travel agencies started to develop new products according to the demand of the passengers. But, thanks to rapid urbanization, second-tier cities are also emerging as sources of growing demand. With the continued opening up in China, the generating areas can be expanded from Beijing, Shanghai and Guangdong to Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Shandong, Yunnan, Tianjin and other provinces.Making Chinese travelers feel welcome is pivotal to enhancing the Chinese travelers’ experience. At the most basic level, this involves providing better Chinese signage and information and more Chinese-speaking staff at visitor information centers and tourism attractions.To develop stronger links with China, it is a must to increase the number of Chinese speakers and improve the Chinese cultural literacy and awareness. This is particularly important for tourism operators so they can meet the needs and expectations of Chinese travelers.The rapid evolutions of technology, particularly in the Internet and telecommunications have an influence on the field trip. The rapid developments of the Internet increases the amount of information available on the Internet becomes the place where travelers get travel information, more, choose the destinations, planning the route, finding the accompanying. This stimulates further growth of the trip. 68% of Chinese outbound travelers search the web for information before deciding on the destination, but only 13% of Chinese travelers using the Internet to make travel bookings. Therefore, travel agency is an important distribution channel for purchasing Final act because online travel booking is still underdeveloped in China.Although international trip volume has grown rapidly over the past two decades, it is still modest relative to the size of China’s population (China has the world’s largest population with 1.35 billion).Given the favorable socio-economic environment, Chinese tourists’ propensity to travel abroad is expected to continue rising in the coming decades.The President of People’ Republic of China , Xi Jinping, during the 2013 Annual Conference of Boao Forum in Hainan (7th April), said in his keynote speech at the opening ceremony that China will continue to promote friendship and partnership with its neighbors and ensure that its development will bring even greater benefits to its neighbors. In the coming five years, China will import commodities worth around US$10 trillion, invest US$500 billion in foreign countries, and have probably over 400 million tourists traveling abroad.
Note
- 1. A hukou is a record in the system of household registration required by law in the People's Republic of China (mainland China). The system itself is more properly called "huji", and has origins in ancient China.A household registration record officially identifies a person as a resident of an area and includes identifying information such as name, parents, spouse, and date of birth. A hukou can also refer to a family register in many contexts since the household registration record is issued per family, and usually includes the births, deaths, marriages, divorces, and moves, of all members in the family.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML