-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Textile Science
p-ISSN: 2325-0119 e-ISSN: 2325-0100
2025; 14(2): 27-33
doi:10.5923/j.textile.20251402.02
Received: Jul. 27, 2025; Accepted: Aug. 25, 2025; Published: Sep. 3, 2025

Capacity Base Production Plan can Balancing the Resources and Control Manufacturing System as Efficient as Possible in Apparel Industry
Tanvir Ahamed Manik 1, Md. Al Amin 2, Md. Nurunnabi 1, Md Abir Ahmed 3
1Department of Textile Engineering, Dhaka University of Engineering & Technology, Gazipur 1707, Bangladesh
2Department of Industrial and Production Engineering, National Institute of Textile Engineering and Research, Dhaka 1350, Bangladesh
3Department of Apparel Merchandising, BGMEA University of Fashion & Technology, Bangladesh
Correspondence to: Md. Al Amin , Department of Industrial and Production Engineering, National Institute of Textile Engineering and Research, Dhaka 1350, Bangladesh.
| Email: | 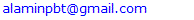 |
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Capacity is the maximum level of output that a company can able to produce and capacity based work and workloads arranging, controlling and optimizing process is capacity planning. This article elucidate a critical role that capacity plan determine what appropriate man, machine and time required to produce current customer demand. So that we can easily execute the future forecast demand and also can balancing available resources (man, machine, materials) that improves productivity, efficiency and reduce production cost. Capacity plan remove overload works so it makes easy production plan and schedule that provide a guide of the future development and growth. If there has not major obstacles of supply chain than hope capacity utilization system will be success approximately. The research analysis those elements to achieve better capacity plan that are number of workers, ability of workers, number of machine, maintenance support, supply chain support, quality control system etc. A case study Jeans 2000 Ltd demonstrates how strategic capacity plan can significantly enhance productivity, efficiency and reduce production cost. The findings underscore the necessity of robust capacity plan in driving productivity, cost savings and sustainable business growth in apparel industry.
Keywords: Capacity plan, Production plan, Balancing resources (man, machine, materials)
Cite this paper: Tanvir Ahamed Manik , Md. Al Amin , Md. Nurunnabi , Md Abir Ahmed , Capacity Base Production Plan can Balancing the Resources and Control Manufacturing System as Efficient as Possible in Apparel Industry, International Journal of Textile Science, Vol. 14 No. 2, 2025, pp. 27-33. doi: 10.5923/j.textile.20251402.02.
1. Introduction
- In apparel industry production plan is very important for on time shipment and growth business. [1] Here capacity plan balancing the resources and arranging, controlling, optimizing all allocated orders so that on time delivery will be easy. [2] According to the product differentiation capacity plan determine the maximum level of output capability and calculate the time which required to produce current forecast demand. [3] If we invest time for any operation process than capacity plan helps to calculate the right target and remove overload works. [4] So it helps to control overtime than production cost will be controlled. [5] Capacity plan ensure how an organization can meet customer demand based on the amount of resources available. [6] Production plan is the act of a guide for design and produce of a product. [7] It coordinates and integrates the manufacturing activities in a production system. [8] Production plan ensure all preproduction steps so bulk production can run smoothly. [9] Capacity based production plan helps the optimum utilization of production capacity and increase productivity. [10] It also reduces idle time by proper scheduling the machine items so that execute on time delivery and reduce wastage. [11]
2. Objectives
- 1. Determine what appropriate man, machine and time required to produce current customer demand.2. Balancing the resources (man, machine, materials) and remove overload works.3. Control overtime and reduce production cost.4. Increase productivity and efficiency.5. Determine the maximum level of output capability based on resource available.6. Calculate the right target and arranging, controlling and optimizing all work and workloads.7. Execute the future forecast demand and control organizations as efficient as possible.
3. Methodology
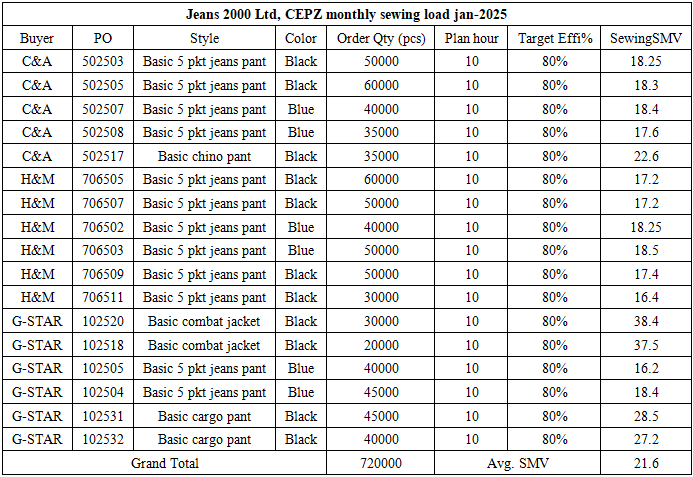
- Here a basic jeans pants and its sewing SMV 18.25 min. Its mean per pcs jeans pant production time required 18.25 min.
 | Figure 1. Flow chart of production planning & control |
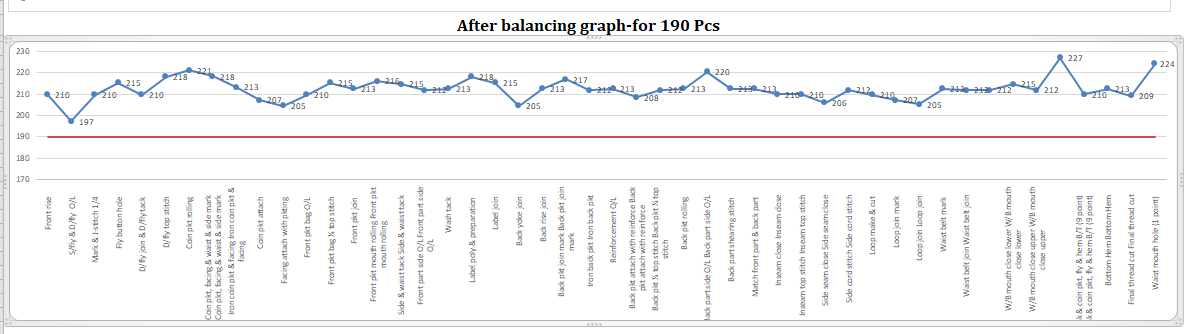
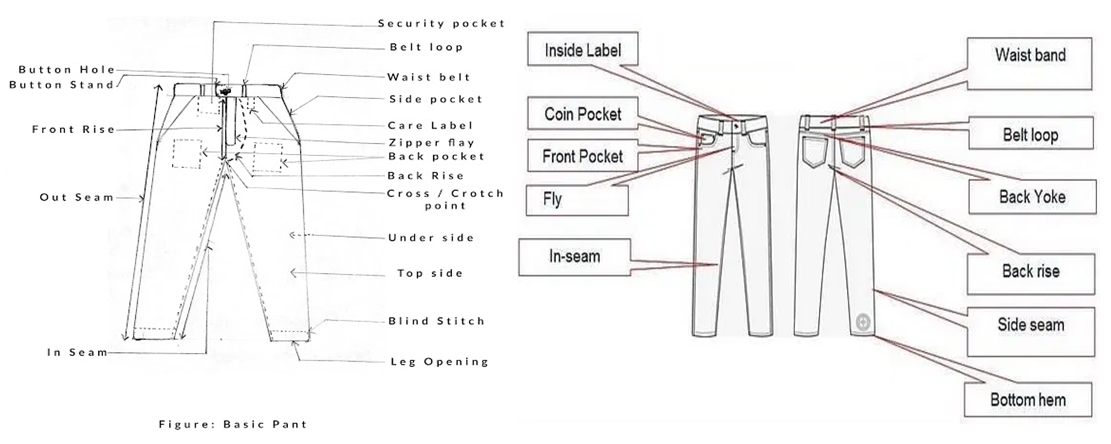 | Figure 2. Basic jeans pant different parts |
|
 | Figure 3. After capacity balancing curve |
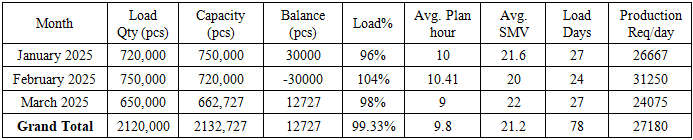
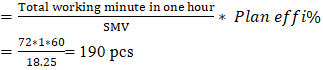 Sewing line capacity balancing:Lowest output point in a sewing production line is called bottleneck. [12] If a sewing line has bottleneck point than we can’t achieve line target so we must need to solve those bottleneck problems. After balancing this line has no bottleneck point and here every operation has more than 190 pcs capacity. So, hope this line target will be achieved easily. [13]Master Plan:Master plan is along termplanning documents and schedule that provide a guide of the future development and growth. [14] In garments industry master plan is very important for improve supply chain, production, efficiency and on time delivery. [15] It arranging, controlling and optimizing all work and activities for future allocated orders. [16] Master plan depends on factory capacity and product SMV. [17] So, it is very important to calculate actual capacity of a company otherwise we can’t execute a proper production plan. [18] Capacity plan helps to keep a sequence of production orders, estimating production as per line wise capacity, achieving targeted production and on-time production and delivery to the customers. [19]Here an example of Jeans 2000 Ltd, CEPZ monthly production plan.Capacity utilization of the plan: Jeans 2000 Ltd, CEPZ a RMG base company has total sewing unit workers 1250January-2025 allocated orders average SMV = 21.6 minPlan working hour/day = 10 hoursPlan working day = 27 dayTarget efficiency = 80%Now January 2025,factory capacity
Sewing line capacity balancing:Lowest output point in a sewing production line is called bottleneck. [12] If a sewing line has bottleneck point than we can’t achieve line target so we must need to solve those bottleneck problems. After balancing this line has no bottleneck point and here every operation has more than 190 pcs capacity. So, hope this line target will be achieved easily. [13]Master Plan:Master plan is along termplanning documents and schedule that provide a guide of the future development and growth. [14] In garments industry master plan is very important for improve supply chain, production, efficiency and on time delivery. [15] It arranging, controlling and optimizing all work and activities for future allocated orders. [16] Master plan depends on factory capacity and product SMV. [17] So, it is very important to calculate actual capacity of a company otherwise we can’t execute a proper production plan. [18] Capacity plan helps to keep a sequence of production orders, estimating production as per line wise capacity, achieving targeted production and on-time production and delivery to the customers. [19]Here an example of Jeans 2000 Ltd, CEPZ monthly production plan.Capacity utilization of the plan: Jeans 2000 Ltd, CEPZ a RMG base company has total sewing unit workers 1250January-2025 allocated orders average SMV = 21.6 minPlan working hour/day = 10 hoursPlan working day = 27 dayTarget efficiency = 80%Now January 2025,factory capacity  January 2025 monthly production plan = 720000 pcs
January 2025 monthly production plan = 720000 pcs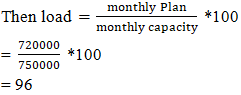 ##January 2025, possible to execute plan up to 750000 pcs. Here load is less than its capacity so it is possible to execute this plan. If company has not any supply chain problems than we hope it will be achieved approximately.February 2025 capacity planning:Let, February 2025 allocated orders average SMV= 20 minPlan working hour/day = 10 hoursPlan working day = 24 dayTarget efficiency = 80%Now February 2025,factory capacity
##January 2025, possible to execute plan up to 750000 pcs. Here load is less than its capacity so it is possible to execute this plan. If company has not any supply chain problems than we hope it will be achieved approximately.February 2025 capacity planning:Let, February 2025 allocated orders average SMV= 20 minPlan working hour/day = 10 hoursPlan working day = 24 dayTarget efficiency = 80%Now February 2025,factory capacity 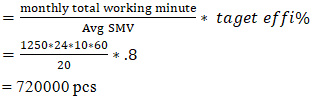 February 2025 monthly production plan = 750000 pcs
February 2025 monthly production plan = 750000 pcs ##February 2025, possible to execute plan up to 720000 pcs. Here load is higher than its capacity so if we want to achieve monthly production plan than we must need to increase plan working hour and efficiency otherwise we can’t achieve this plan.
##February 2025, possible to execute plan up to 720000 pcs. Here load is higher than its capacity so if we want to achieve monthly production plan than we must need to increase plan working hour and efficiency otherwise we can’t achieve this plan.
|
|
 March 2025 monthly production plan = 650000 pcs
March 2025 monthly production plan = 650000 pcs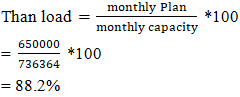 Here march 2025 possible torun factory = plan working day * load%= (27*0.882)= 23.81= 24 daysSo, Factory will be idleatmarch 2025 = (27-24) days= 3 days## March 2025, possible to execute plan up to 736364 pcs. Here load is 11.8% less than its capacity so it has apossibility that factory will be idle 3 days at march 2025. Due to less allocated orders we can’t run this factory full month. In this situation we need to reduce plan working hour otherwise production cost will be high.Now if, plan working hour/day = 9hoursThen march 2025,factory capacity
Here march 2025 possible torun factory = plan working day * load%= (27*0.882)= 23.81= 24 daysSo, Factory will be idleatmarch 2025 = (27-24) days= 3 days## March 2025, possible to execute plan up to 736364 pcs. Here load is 11.8% less than its capacity so it has apossibility that factory will be idle 3 days at march 2025. Due to less allocated orders we can’t run this factory full month. In this situation we need to reduce plan working hour otherwise production cost will be high.Now if, plan working hour/day = 9hoursThen march 2025,factory capacity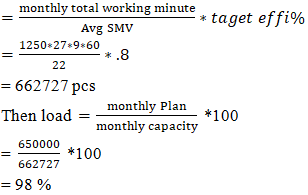 If reduce excess working hours and increase productivity then production cost will be low and efficiency will be high.
If reduce excess working hours and increase productivity then production cost will be low and efficiency will be high.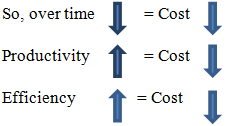
4. Result and Discussion
- 1. Without capacity plan a company can’t determine what appropriate man, machine and time required to produce current customer demand. So it’s not possible to balance the resources (man, machine, materials). Without capacity plan if allocate 1800,000 pcs orders for 3 month master load.
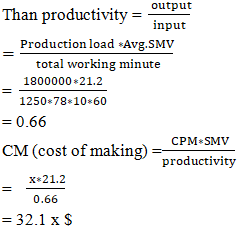 (Here, CPM = x dollar)## Here without capacity plan if allocate more order quantity than its capacity for master load. It will not outcomes a good result due to absence of right target, achievement and capacity base plan. Preparation to balance resources—man, machine, and materials—remains lacking, leading to an inability to determine the required amount of each. As a result, overall productivity, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness suffer significantly.2. With capacity plan table 3, shows that average SMV 21.2 so Jeans 2000 Ltd 3 month sewing capacity 2132,727 pcs and here considered 80% efficiency and 9.8 average working hours. Here load is 99.33% and allocated orders is 2120,000 pcs.
(Here, CPM = x dollar)## Here without capacity plan if allocate more order quantity than its capacity for master load. It will not outcomes a good result due to absence of right target, achievement and capacity base plan. Preparation to balance resources—man, machine, and materials—remains lacking, leading to an inability to determine the required amount of each. As a result, overall productivity, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness suffer significantly.2. With capacity plan table 3, shows that average SMV 21.2 so Jeans 2000 Ltd 3 month sewing capacity 2132,727 pcs and here considered 80% efficiency and 9.8 average working hours. Here load is 99.33% and allocated orders is 2120,000 pcs.
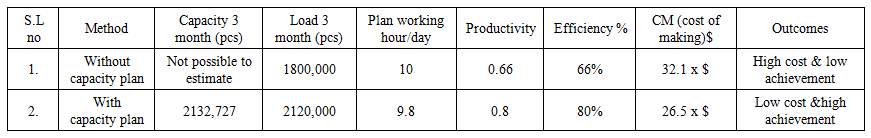 | Table 4. Jeans 2000 Ltd, CEPZ achievement forecast based on capacity plan |
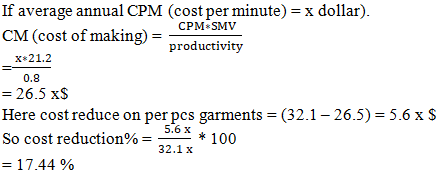 Table 4, shows that productivity and efficiency is significantly higher and cost of making is comparatively very lower with capacity based master plan. Here capacity study and capacity plan determine style wise SMV, manpower and machine requirement to produce current customer demand. It helps to identify and remove the bottleneck areas in a bulk production line so line target and efficiency will achieve easily. It balancing the resources (man, machine, materials) and remove overload works as a result improves productivity, efficiency and reduce production cost. According to capacity plan we can easily calculate monthly, weekly and yearly production capacity of a company. It helps to do a proper master plan that arranging, controlling and optimizing a long term planning documents and schedule. By this process a company can allocate the maximum level of orders that can able to produce. If the allocated order exceeds capacity, it becomes essential to increase planned working hours; otherwise, achieving the target plan will not be possible. Again, if allocated order is too less than its capacity than need to decrease plan working hour otherwise production cost will be high. A case study Jeans 2000 Ltd demonstrates the final outcomes that proper capacity plan able to produce the maximum level of output and reduce production cost.Descriptive Analysis: Table 4, shows that the result of productivity, efficiency and cost-effectiveness with capacity based plan.Master load (pcs): - Mean: (2120,000 + 1800,000) / 2 = 1960,000 pieces.- Range: 2120,000 - 1800,000 = 320,000 pieces. Without capacity-based master load has significantly lower and possible of 85% (1800,000/2120,000) of the capacity-based master load.Productivity: - Mean: (0.8 + 0.66) / 2 = 0.73- Range: 0.8 – 0.66 = 0.14Capacity based productivity has significantly higher and possible of 121% (0.8/0.66) of the without capacity based productivity.Efficiency: - Mean: (80% + 66%) / 2 = 73%- Range: 80% – 66%= 14%Capacity based efficiency has significantly higher and possible of 121% (80/66) of the without capacity based efficiency.CM (cost of making)$: Capacity based cost of making has significantly lower and possible of 82.6% (26.5x/32.1x) of the without capacity based cost of making.
Table 4, shows that productivity and efficiency is significantly higher and cost of making is comparatively very lower with capacity based master plan. Here capacity study and capacity plan determine style wise SMV, manpower and machine requirement to produce current customer demand. It helps to identify and remove the bottleneck areas in a bulk production line so line target and efficiency will achieve easily. It balancing the resources (man, machine, materials) and remove overload works as a result improves productivity, efficiency and reduce production cost. According to capacity plan we can easily calculate monthly, weekly and yearly production capacity of a company. It helps to do a proper master plan that arranging, controlling and optimizing a long term planning documents and schedule. By this process a company can allocate the maximum level of orders that can able to produce. If the allocated order exceeds capacity, it becomes essential to increase planned working hours; otherwise, achieving the target plan will not be possible. Again, if allocated order is too less than its capacity than need to decrease plan working hour otherwise production cost will be high. A case study Jeans 2000 Ltd demonstrates the final outcomes that proper capacity plan able to produce the maximum level of output and reduce production cost.Descriptive Analysis: Table 4, shows that the result of productivity, efficiency and cost-effectiveness with capacity based plan.Master load (pcs): - Mean: (2120,000 + 1800,000) / 2 = 1960,000 pieces.- Range: 2120,000 - 1800,000 = 320,000 pieces. Without capacity-based master load has significantly lower and possible of 85% (1800,000/2120,000) of the capacity-based master load.Productivity: - Mean: (0.8 + 0.66) / 2 = 0.73- Range: 0.8 – 0.66 = 0.14Capacity based productivity has significantly higher and possible of 121% (0.8/0.66) of the without capacity based productivity.Efficiency: - Mean: (80% + 66%) / 2 = 73%- Range: 80% – 66%= 14%Capacity based efficiency has significantly higher and possible of 121% (80/66) of the without capacity based efficiency.CM (cost of making)$: Capacity based cost of making has significantly lower and possible of 82.6% (26.5x/32.1x) of the without capacity based cost of making.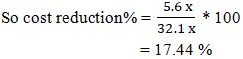
5. Conclusions
- Capacity plan is very important for arranging, controlling and optimizing all work and workloads of a company. [20] It helps to determine how services are offered and what appropriate time and manpower required to produce current customer demand. [21] So it is the act of balancing available resources to satisfy customer demand that improves productivity, efficiency and reduce production cost. Capacity planning is the best way to invest time for any operation process that makes easy to achieve target and remove overload works. [22] Man and machine ratio totally depends on capacity plan. Here capacity plan is the best way to remove and balancing the bottleneck points in a production line. [23] In garments industry without capacity utilization we can’t execute the maximum level of output. So in modern industrialization its importance is very much. [24] It helps to execute the future forecast demand and also control organizations as efficient as possible. [25]
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML