-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Textile Science
p-ISSN: 2325-0119 e-ISSN: 2325-0100
2017; 6(2): 49-56
doi:10.5923/j.textile.20170602.04

Cost and Time Savings of Apparel Industry through Elimination of Non-valuated Process in Cutting Section
A. T. M. Mohibullah1, Umme Magreba Takebira1, Zinia Anjuman Ara1, Md. Maksudur Rahman2
1Department of Apparel Manufacture & Technology, BGMEA University of Fashion & Technology, (BUFT), Dhaka, Bangladesh
2Merchandising Department, Medlar Apparels Ltd., Dhaka, Bangladesh
Correspondence to: A. T. M. Mohibullah, Department of Apparel Manufacture & Technology, BGMEA University of Fashion & Technology, (BUFT), Dhaka, Bangladesh.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

In this post-modern world, all of the activities of apparel industries focus on proceeds. But a major percentage of proceeds are decreased by the inadequate management of cost and time. The research is to reduce the non-valuated performance in cost and time consumption at cutting section. It focuses on the cutting section of apparel industry for simplification and elimination of non-valuated process of cutting. The apparel manufacturers, along with the closely associated activities of cutting section continue to be one of the driving forces of industrialization throughout the developing world. The research reflected that the industry has to minimize its cost and improve internal throughput time. It also facilitates to gain higher productivity and profitability with improved quality product by eliminating non valuated process. It also minimizes cost and improves internal throughput time. The concern with the following research started during a study of apparel industry in cutting section. To achieve these research goals, the data has been collected on the basis of recorded data and study of cutting process. On the basis of this information, cutting process wise time, space and overhead were calculated. The data captured through cutting simplification techniques revealed that exclusion of non-valuated process of cutting section of the apparel industry. The recommendations primarily include training and education of cutting personnel, standardizing documentation requirements of the company and having a standard operation procedure (SOP), information and communication technology (ICT) and strengthening of information and apparel manufacturing systems, performance appraisal with respect to key result areas (KRAs).
Keywords: Non valuated activities, Cutting section, Cutting methods, Simplification of cutting section
Cite this paper: A. T. M. Mohibullah, Umme Magreba Takebira, Zinia Anjuman Ara, Md. Maksudur Rahman, Cost and Time Savings of Apparel Industry through Elimination of Non-valuated Process in Cutting Section, International Journal of Textile Science, Vol. 6 No. 2, 2017, pp. 49-56. doi: 10.5923/j.textile.20170602.04.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The fabric cutting methods available in the industry cutting stationary lays using the straight knife and one way fabric lying is only considered as elimination of the non valuated process when developing the methodology. The research endows with productive process in cutting section. It also decreases wastage of non productive activities in cutting section which can be avoided that can result in drop in lead time as well as cost and time. Therefore, the cutting process is one of the main values adding process in a factory [1]. The cutting section of apparel manufacturing industry supplies the cut panels required in the sewing section for the production modules. There are several functions in a cutting section like fabric spreading, cutting, numbering and bundling of cut panels [2]. Though there are different costs involved in cost reductions internally spent by an industry through findings wastages, avoiding and improving faulty work would end in vest reserves [3, 5]. Any productive procedures focused on any action that buyers and customers are ready to pay for that. Non productive activates designated that the customers do not consider as adding value to their products ( for example, waiting time, inspection time, no proper cutting plan, improper cutting machine used, sharing of working instruments, absence of operations, workers’ fatigue etc.) [3, 4]. A readymade garments industry consists of three main sectors named cutting, sewing and finishing [5]. Most of the garment factories implement lean manufacturing to develop their processes. Reducing work in progress by on time delivery is one area that they focus on under the lean concepts [6, 7]. The factory can capitalize less cost and more savings by responding faster cutting. To find out the non valuated activities, it is important for cutting, planning accurately and thereby to reduce lead time and cost involved in the cutting process.
2. Methodology
- The study was intended to confine the current status of all the system of cutting room management where we will find out the potential method of cutting. Primary research was carried out to collect quantitative data to eliminate of non-valuated process in terms of cost and time savings in cutting section. The survey was designed to collect information directly from different factory on what support needed to improve their process sequence. The sections provided working definitions and assumption related in the study, followed by detailed descriptions of the data collection methods was used. A questionnaire was developed with questions to collect recent problem of cutting process sequence based on interview. Each problem led to a hypothesis. The purpose is to determine the current state of what is available in the field and the research identified problems of cutting process that may exist. The study was anticipated to confine the current status of all the systems of process sequence in cutting section of both printed & non printed of knit garments where we find out the elimination system of non valuated process in cutting section. In this research, time study for each and every activity was done. The process of cutting section, equipment used, parameters, materials movement was tracked and analyzed. A centralized cutting section of a factory was selected for an experiment and the main product of this factory was non printed knit t-shirt. The experiment provided a simplification process in cutting section which helped to eliminate of non-valuated process in terms of cost and time savings in cutting section. It has improved overall efficiency of the cutting section and reduced the wastage of the fabric. The new cutting layout introduced depend on the specific conditions. The marker efficiency is good but still there is a scope for improvement in terms of wastage reduction. Sorted cutting room by visual aids, marking and remnant storage reduces the wastage of time and this study also improved a better material flow by consuming less movement and time.
2.1. Cutting Process Flow Chart: Node
- The following processes convert raw materials into sewing input. It will be difficult to maintain the industry if production is not up to the mark if the preproduction phase of preparation of material is not properly carried out.
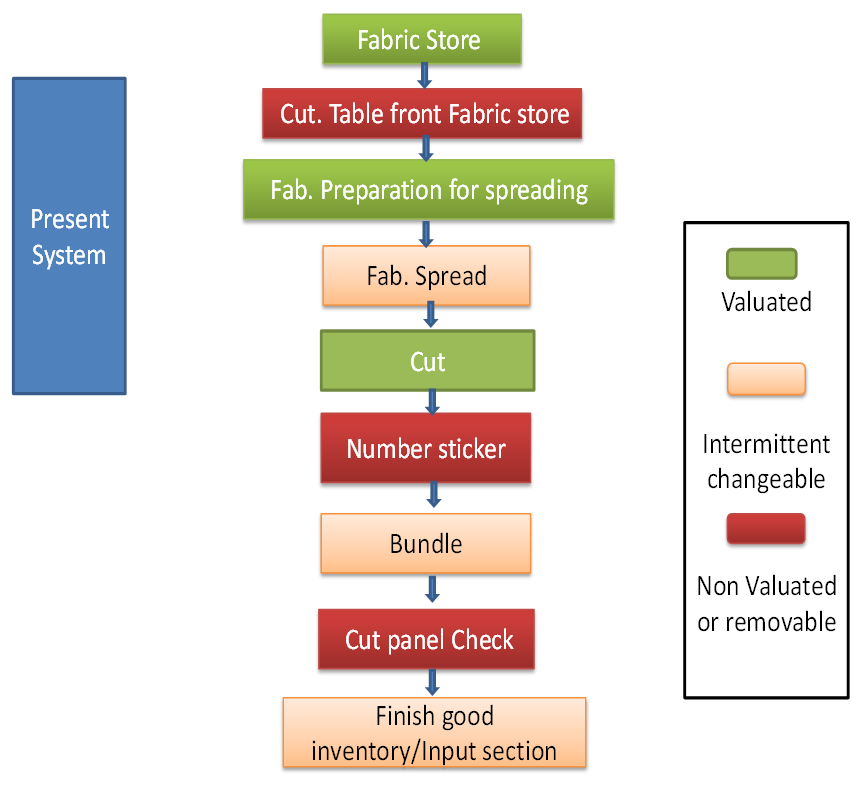 | Figure 1. Process sequence in cutting section of knit garments |
2.2. Cutting Process Simplification
- By maintaining invoice copy the store in charge collects the required fabrics as per booking of merchandiser. When a merchandiser booked fabrics for completing order, the dyeing section takes necessary action to collect the grey fabrics and dye it as per buyer recipe. Then the store collects the dyed fabrics by maintaining a proper raking for fabrics by using bin card or swatch card as per order quantity. As per order ship date the cutting in charge collects the fabrics from store and feeds the fabric to cutting floor. The store authority maintains proper record for fabrics in housed and out housed. When cutting in charge collects fabrics from store they record the quantity of fabrics as per order. The cutting authority collects their required fabrics for cutting and stored it in front of cutting table. As per cargo receive date (CRD) of an order or as per production planning team the cutting in charge store the fabrics in priority basis. The cutting helper prepares the fabrics for spreading accordingly. The fabrics are coming in a role wise and it is wrapped by poly to protect any kind of destruction. The cutting helper aligns the fabrics role for lying in cutting table. The fabrics in-charge double check the fabrics dimension per buyer requirement for better use of marker. The cutting helper spread the shade wise fabrics for cutting on the cutting table. The role of fabrics input in fabrics spreader for spreading the fabrics easily. It will be more useful and time saving way. After the fabrics load in spreader machine then the cutting helper start the spreading machine. Problematic part is removed by scissoring, repair by overlapping as per lay chart. This is the main process of cutting section. This is combined by fabrics pull, marker place, tapping etc. The cutting helper laid the fabrics from spreader. They pull the fabrics from spreader very smoothly. This lay consists of marker length. Helpers pull the length of fabrics. Then separate the fabrics from role. The cutting helper collects the marker from technical section and put on the fabrics lay. The lay quantity depends on fabrics GSM. Sometimes it consists of garments order quantity. Tape use for fabrics attaching with cutting table. This is very helpful to run the cutting machine easily. Suppose the fabrics cutting table width is 56" but the fabrics width is 57". At this time the cutting helper removes the extra fabrics from fabrics lay. When the marker put on the fabrics lay, the helper set the cutting machine accordingly of marker line. Then finally cutting personnel starts the cutting as per marker. Number sticker is the time consuming work in cutting section. As per cutting parts the cutting helper gives number sticker. At this point, the cutting helper gathers the cut panel from the cutting area. Sometimes garments use extra table for cut panel. There are three or more cutting personnel who attach the number sticker on cut panels by using number machine or by using manual process. Manual process is more time consuming than using machine. The cutting helper bundles the cut panel by different parts of garments. For example- they bundle the sleeve parts in one bundle. Cutting personnel collects the bundling card from store officer as per requirement of cut panel. The cutting in-charge prepares the card as per cut panel bundle. Then the cutting helper prepares the bundle panel as per bundle card. Finally he stocks all bundle panels in internal quality checking area for inspection. Cut panel checking is the pre inspection of sewing. This checking is important for smooth sewing in sewing line. If a panel miss in the bundle then the inspector detect it. The inspector checks the bundle and sorts out the defect parts of the bundle. They give the defect/red sticker on defective panels. The quality helper counts the defective panel. The inspector ensures the total defect, because the defective panels hamper in the sewing operation. The internal quality checking personnel checks the all part of bundle as per number. Cutting section arranges the defective panel accordingly. It’s huge time consuming and costly for a factory. After recovery of defective panel from cutting section then the selected sewing section make an inventory of cut panel. The sewing line in-charge makes a challan as per collection of cut panel bundle. At this time, the line supervisor ensures the pair of a garment. Like as pairing the sleeve panel or front and back panel of garment body. After the pairing of panel the supervisor stake all panel in front of the sewing line. In this position the sewing line starts their sewing from the stake panel as per lay out confirmation by IE section.
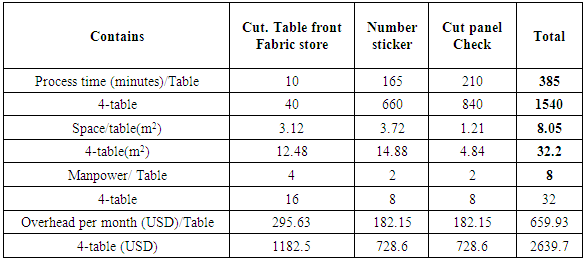
2.3. Cutting Process Wise Time, Space and Overhead Calculation
- An order 1,00,000 pieces quantity for t-shirt (non-printed). Garments color- Orange, single jersey fabric, GSM: 180-200 and fabrics width 57". 1 kg. fabric needed for 4 pieces garments. For this research paper we assume that in a garments vendor has four cutting table, every cutting table’s width- 5 feet, and length-30 feet, total cutting personnel 72. There are 40,000 quantity garments needed 10000 kg. where marker length is 19.45 yards for this specific size. Now we are going to see the evaluation of this order/size.From the above chart, we see the total evaluation from fabrics store to input in a sewing line. There are lots of time consume for this system. Such as, from the chart we see the number sticker process needed 660 minutes with lots of money. There are four cutting table used for this order execution, where the chart show the total USD 6282.72 consume and total 280.22m2 space needed from cutting table front fabrics store to input in line. Total 72 man power works and they need 3696 minutes to complete the whole process. Also refer the chart, there are 18 personnel doing their job in 924 minutes. The garments factory needs to set the one cutting table in 70.05m2 square space and USD 1570.68 for cutting personnel. So we see the total evaluation multiple with one cutting table evaluation.
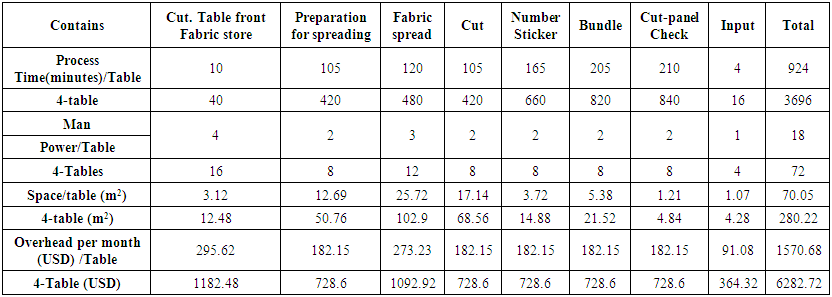 | Table 1. Cutting Process wise time, space and overhead calculation |
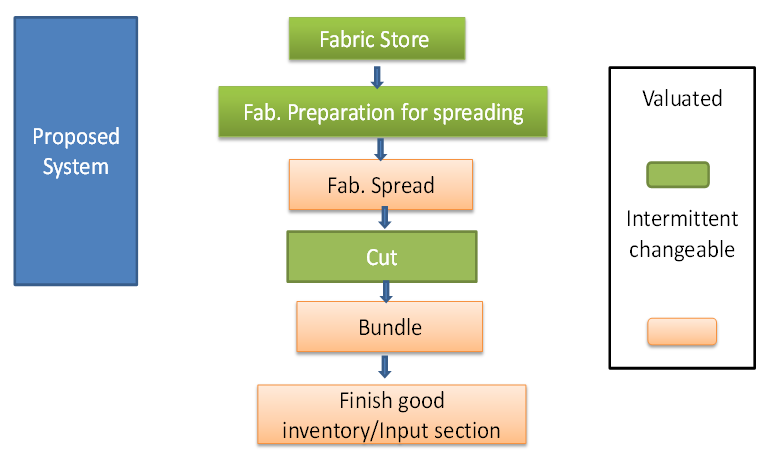 | Figure 2. Proposed process flow chart Process sequence in cutting |
3. Result and Discussion
- For passing the fabrics very smoothly this type of fabrics store is used in front of cutting area. Initially, challan wise fabric check and store department receive the fabrics quantity as per fabrics order. The dyeing section prepares a challan and sends the store. Store manager check the challan very carefully and inspect the fabrics. Secondly, Maintain 6S for fabric store 5S modified to 6S by adding S=Safety, the store concern uses the modern procedure to maintain storage of fabrics. In present system, fabrics are stored in front of cutting table for directly feeding to cutting table. Here we proposed the cutting management to feed the fabrics directly to the cutting table. Subsequently, the cutting concerns align the fabrics role accordingly color or part of an order quantity. It’s very important for saving valuable time and hassle. Afterward Role wise check and ensure quality after alignment, the concern checks the role wise fabrics to meet better quality. Lastly, alert for feed to next position the cutting sections have a plan on a month or week. So, they know the cutting feed yet they arrange the fabrics of next order or color or same cutting fabrics. In this position they save huge time. They are not in back log. Before cutting, fabrics spreading are the basic process. Fabrics are spread by using proper length of cutting table and marker length. Fabrics are loaded by the machine, the cutting concern takes the fabrics role to input in spreader as per shade variation of fabrics (If have any role to role shade variation use loose threads or loose fabric or paper for role to role separation). Need to spread fabric accurately and make lay chart. At this process, the cutting helper pull the fabrics on cutting table accordingly of marker length. And cut the fabrics. By this, it’s make fabrics lay such as 100 lay, 80 lay etc. Need to use sticker for problem indicator maintain document for its quantity. From the spreading fabrics the cutting inspector must indicate the defect area and mark it by sticker. Also maintain a quantity. Lastly use scissor for whole part removing after indicating the defect the cutting helper must cut the defect hole by scissoring. The main process of the cutting section is cutting. For this process, the sections do lots of work. The observed cutting times were multiplied by the rating factors in order to calculate the basic times according to the British Rating Standards [8]. Performance levels of operators were decided by their individual skill levels and the level of training that they have in the relevant field [9]. Efficient cuttings have to reduce the garment wastage. Pull lay from spread position from the spreader machine, the cutting helper pass the fabrics for making lay which is dependent on the garment order quantity. Place marker in fabric and tape after completing the lay, the fabrics in charge put the marker length on the lay and give the tape on marker to bond with fabrics for efficient cutting. Trim and Cut Such as a fabrics length 54" but the cutting table width is 53". Then the cutting personnel trim the extra 1". After trimming they start the cutting as per marker. After cutting the garment cut panel need to bundle for proper feeding in sewing line. Bundle helps to detect the part of the garment easily. The cutting helper makes bundle panel by panel of garment. Put together Panel wise bundle. The cutting helper makes bundle of the cut panel by using looses thread. They do not mix up with every panel of a garment. This bundle make by size wise. If have shade problem then maintain lose thread wise bundle although an inspection occur before cutting, yet some problems found in cutting panels. If there is shade problem, then the cutting person marks it by using loose thread. Must be sincere in bundling before bundling, must be sincere about every panel of garment, shading, defect area etc. An inspection is helped all time to reduce the time wastage and detect the defect pieces of garment panel. Also helps to proper input in sewing line. Maintain proper raking completing the all bundle. And it has to be set up for a proper raking in front of sewing line. A proper raking save the valuable time to input the sewing line. 6S have modified 5S by adding a new “S” to create 6S systems. One of the most common of the 6S systems results from adding Safety to 5S. This is sometimes called 5S+, 6S, lean 6S, 6S safety, or lean 6S safety. In this modern system the concerned person easily notice the proper bundle. Alert for line feed after bundling the panel, production manager notice the related person for feeding the goods in line allocated line. Finally, documentation is very important for safety to be shortage in required quantity. The related person makes the document as per bundling.
3.1. Non Valuated Process
- It is identifiable that the non valuated processes (table front fabric store, number sticker and cut-panel check) require to be removed to increase the productivity. It is preferable that the store loader bear fabric from fabric store to cutting table front place. Number sticker is needed for size and shade wise to assemble the parts and also maintain country wise packing ratio and cut panel check used for faulty parts sort out and replacement.The chart shows the non-valuated process details. There are lots of money saved to complete the whole process in making garments to remove the non-valuated process. Not only money but also time, men power, space for front fabrics store etc. The factory can use this savings in other operation. From the chart, 1540 minutes are totally non-valuated. To use this time in other process, we have to improve our productivity. In a garments factory, the space is very important to ensure effective lay out. By taking away the non-valued process we can save 8.05m2 for one table and 32.2m2 for four tables. The proposed process is able to save USD 2639.7 by reducing those three processes.
|
3.2. Way to Manage without non valuated Process
- We don’t want to use numbering system. Using loose thread, fabric, paper differentiate role to role shade variation then role wise maintain bundle, otherwise hole check is one bundle. It should be strongly monitored bundle wise production. We don’t want to cut fabric check. We use error sticker in fabric spreading preparation stage. Error is counting in fabric spreading process cause of needed replacement. But we sort out faulty fabric from sewing, printing, or embroidery section.
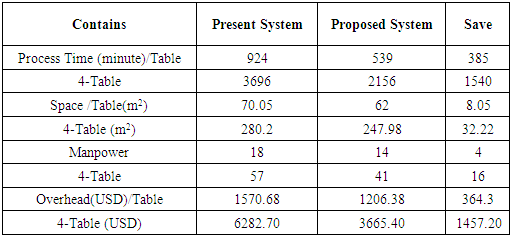
3.3. Statistics between Present System and Proposed System
- The present system uses 924 minutes to complete the whole process, on the other hand proposed system will complete the total process in 539 minutes. This will save 385 valuable minutes. In financial way, the proposed one complete by USD 3665.40 but running one use USD 6282.70. In an equation of manpower, 18 (Running) - 14 (Proposed) = 04, the proposed system reduce the manpower. In distinguish two processes, 8.05m square spaces save easily. So the research provided the new process by reducing the non-valued process which reduces the time, space and money as well as manufacturing cost of a garment.
|
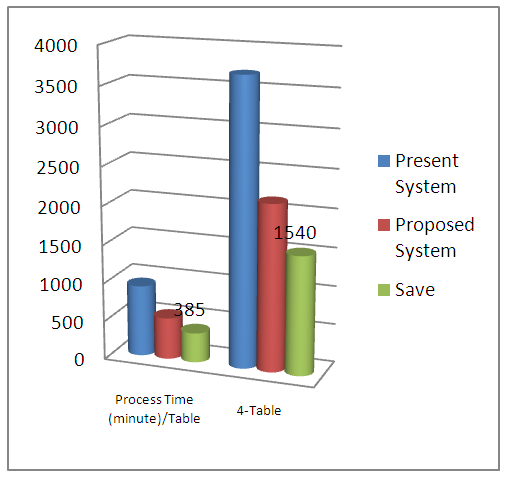 | Figure 3. Present and Proposed time of processing in minute |
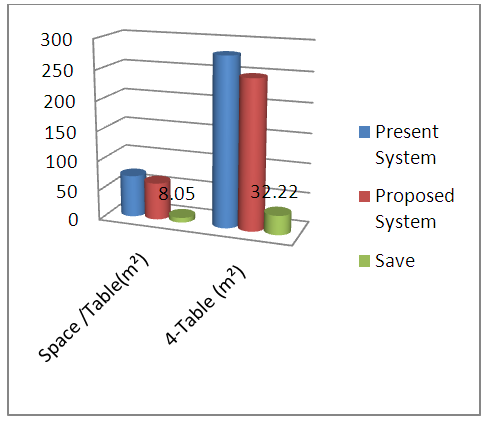 | Figure 4. Present and Proposed Space of processing |
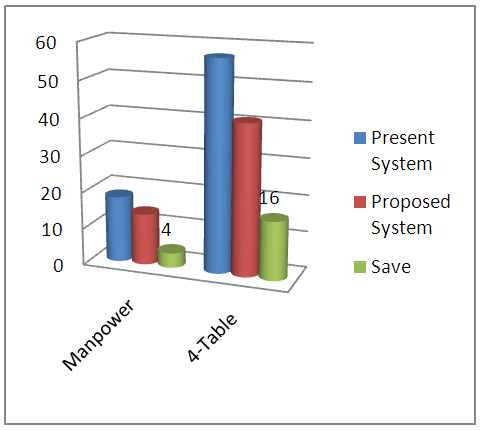 | Figure 5. Present and Proposed Manpower for processing |
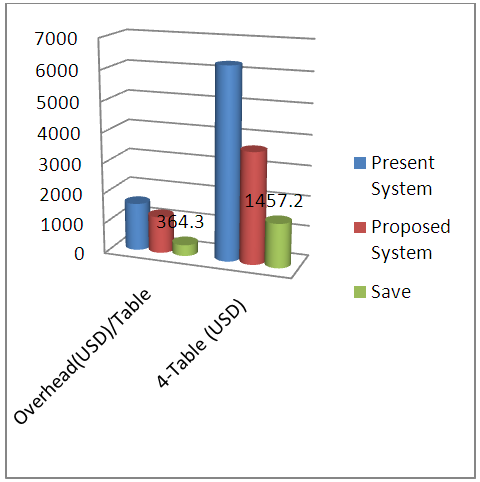 | Figure 6. Present and Proposed Overhead Cost in USD |
4. Conclusions
- The study clearly indicates that by reducing non valuated activities in the cutting section’s time and cost are saved which have an important impact on overall factory financial system. The suggestive tools developed in this research paper shroud an extensive series of perspective in decreasing cost and time in the cutting section of apparel industry by ensuring quality cutting. By eliminating non productive activities, it was observed that the time was saved and cost related to time was utilized properly. As additional and continuous improvements are required, the work study department can specify a methodology to follow when cutting a lay. This research paper also helps an industry for the development of cutting quality and cutting production rate by decreasing non valuated activities.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- This research paper was supported by Rasel Haque, IE executive, Masco Group & Sajjad Hossain, IE executive, Windy group. We would like to thank our colleagues of BGMEA University of Fashion & Technology who provided insight and expertise that greatly assisted the research. We would also like to thank Rajpoti Das, Asst. Manager of IE department for his continued support and for giving us the opportunity to work on the application of industrial engineering in garments cutting section where many of the ensuing ideas were created. We would like to express gratitude the members of the industrial engineer department who kept us honest in our manufacturing idealism. We would like to show gratitude Devashis kumar saha Executive Director Fakir Apparels Ltd. and Emarat Hossain HR admin & compliance Fakir Apparels Ltd. whose insight and ideas helped us to see how to apply industrial engineering in garments cutting section. Finally, we must acknowledge with due respect the constant support of parents.
Appendix
- Please note before beginning to respond1. Answer every question. (
 )2. All questions evaluate the subject outcome and the future requirements to develop the result of the subject area.3. Carefully read the definitions provided below and keep them in mind as you answer the survey question. This is important to ensure the subject outcome and its future requirement and also its lack /deficiency. 4. Each question has a comments area where you can provide additional information about your answer.Definition Non printed: A printed T-shirt or graphic T-shirt is a T-shirt bearing a design, image or lettering on it. Printing is done with textile printing. Various types of printed T-shirts exist.1. Write your gender, position & total working experience in cutting section. Comments: 2. What do you know about cutting process in the RMG INDUSTRY? Comments: 3. Do you think that the knit cutting process (printed & non printed) should be different? a. yes ( )b. no ( )Comments: 4. Do you think Cut. Table front fabric store is necessary for knit non printed cutting process?a. yes ( )b. no ( )Comments: 5. Do you think Numbering Sticker is needed for knit non printed cutting process?a. yes ( )b. no ( )Comments: 6. Do you think Cut-panel check is needed for knit non printed cutting process?a. yes ( )b. no ( )Comments: 7. Do you agree the elimination of non-valuated activities has organizational benefits? a. Strongly disagree ( )b. Neither agree or disagree ( ) c. Strongly agree ( )Comments: 8. What are the awareness level of cutting in your organization? a. Only top-level managers ( )b. Ton and mid-level managers ( )c. Top and mid level managers and supervisors ( )d. Top-level managers, mid-level managers, supervisors and operator ( )Comments: -----------------------------------------------------------------THANK YOU FOR YOUR RESPONSPlease ensure that you have answered all questions and that your responses are consistent.
)2. All questions evaluate the subject outcome and the future requirements to develop the result of the subject area.3. Carefully read the definitions provided below and keep them in mind as you answer the survey question. This is important to ensure the subject outcome and its future requirement and also its lack /deficiency. 4. Each question has a comments area where you can provide additional information about your answer.Definition Non printed: A printed T-shirt or graphic T-shirt is a T-shirt bearing a design, image or lettering on it. Printing is done with textile printing. Various types of printed T-shirts exist.1. Write your gender, position & total working experience in cutting section. Comments: 2. What do you know about cutting process in the RMG INDUSTRY? Comments: 3. Do you think that the knit cutting process (printed & non printed) should be different? a. yes ( )b. no ( )Comments: 4. Do you think Cut. Table front fabric store is necessary for knit non printed cutting process?a. yes ( )b. no ( )Comments: 5. Do you think Numbering Sticker is needed for knit non printed cutting process?a. yes ( )b. no ( )Comments: 6. Do you think Cut-panel check is needed for knit non printed cutting process?a. yes ( )b. no ( )Comments: 7. Do you agree the elimination of non-valuated activities has organizational benefits? a. Strongly disagree ( )b. Neither agree or disagree ( ) c. Strongly agree ( )Comments: 8. What are the awareness level of cutting in your organization? a. Only top-level managers ( )b. Ton and mid-level managers ( )c. Top and mid level managers and supervisors ( )d. Top-level managers, mid-level managers, supervisors and operator ( )Comments: -----------------------------------------------------------------THANK YOU FOR YOUR RESPONSPlease ensure that you have answered all questions and that your responses are consistent. Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML