-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Surgical Research
2016; 5(1): 8-14
doi:10.5923/j.surgery.20160501.03

Kinetics of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration, Minimum Bactericidal Concentration and Minimum Fungicidal Concentration of Vernonia amygdalina (Bitter leaf) on Microorganisms Isolated from Wound Infections
Ifeanyi Onyema Oshim 1, Chikezie Onyebuchi Desmond 2, Reuben Anyi Udeozo Nwobu 3, Uchenna Modestus Ezugwu 4, Evelyn Ukamaka Urama 1
1Medical Microbiology Option, Department of Medical Laboratory Science, Faculty of Health Sciences and Technology, Nnamdi Azikiwe University, Awka, Nigeria
2Department of Medical Laboratory Science, Faculty of Health Sciences and Technology, Nnamdi Azikiwe University, Anambra, Nigeria
3Applied Microbiology and Brewing, Nnamdi Azikiwe University, Awka, Nigeria
4Chemical Pathology Option, Department of Medical Laboratory Science, Faculty of Health Sciences and Technology, Nnamdi Azikiwe University, Awka, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Ifeanyi Onyema Oshim , Medical Microbiology Option, Department of Medical Laboratory Science, Faculty of Health Sciences and Technology, Nnamdi Azikiwe University, Awka, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Wound infection occurs when one or more of the contaminants evade the cleaning effect of the host’s defenses, replicate in large number, attack and harm the host. It has remained a major cause of morbidity and mortality and a major source of worry to both the patients, doctors, hospitals and the community as a whole. This present study was aimed to investigate the phytochemical analysis and in-vitro antimicrobial activities of crude ethanol and methanol extracts of the leaves of Vernonia amygdalina (bitter leaf) on five clinical wound isolates (Staphylococcus auerus, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Candida albicans using agar well diffusion method. The phytochemical constituents of this medicinal plant was carried out using standard methods. The Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal/fungicidal concentration (MBC/MFC) of the plant extracts on the test isolates were determined by the agar dilution method. Ciprofloxacin and fluconazole (positive controls) were used in comparison with crude extract of Vernonia amygdalina leaves while Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) was used as the negative control. The ethanolic extract of Vernonia amygdalina showed antimicrobial activity with the mean inhibitory zone diameter of 6 - 18 mm against Staphylococcus auerus, 12 – 24 mm against Escherichia coli, 2 – 12 mm against Klebsiella pneumoniae, 4 – 16 mm against Pseudomonas aeruginosa but showed no antifungal effects on these microorganisms. Candida albicans was only found to be resistant to crude extracts of Vernonia amygdalina leaves. Ethanolic extract of Vernonia amygdalina was observed to be more potent, inhibiting all the bacterial isolates thus showing higher antimicrobial activity than the methanolic extract and positive control (ciprofloxacin). The minimum Inhibitory Concentration and Minimum Bactericidal Concentration of the extracts on the test organisms also increased in the following order; methanol < ethanol. In conclusion, this plant extracts could be used as broad spectrum antibiotics in the treatment of wound infections since this leaf extracts has antimicrobial effects on bacterial pathogens. Secondary metabolites of these plant extracts could enhance rapid healing of wound infections.
Keywords: Antimicrobial activity, Phytochemical analysis, Vernonia amygdalina, Agar well assay, Ethanolic extract
Cite this paper: Ifeanyi Onyema Oshim , Chikezie Onyebuchi Desmond , Reuben Anyi Udeozo Nwobu , Uchenna Modestus Ezugwu , Evelyn Ukamaka Urama , Kinetics of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration, Minimum Bactericidal Concentration and Minimum Fungicidal Concentration of Vernonia amygdalina (Bitter leaf) on Microorganisms Isolated from Wound Infections, International Journal of Surgical Research, Vol. 5 No. 1, 2016, pp. 8-14. doi: 10.5923/j.surgery.20160501.03.
1. Introduction
- A wound is an abrasion in the skin and the exposure of subcutaneous tissue following the loss of skin integrity which provide moist, warm and nutritious environment that is conducive for microbial colonization and proliferation [1]. Wounds can be classified as open or closed. They can further be classified as accidental, pathological or post-operative according to its nature [2]. Wound and other open lesions are liable to infection with a multiplicity of organism from the body surface or environment [2]. Infection occurs when one or more of the contaminants evade the cleaning effect of the host’s defenses, replicate in large number, attack and harm the host and may best be described as colonization [3]. Wound infection may be endogenous or exogenous. Endogenous infection or auto-infection is caused by organism that has been living a commensal existence in the patient’s body [3].While exogenous infections are spread from person to person, this may occur after accident or intentional trauma of the skin or other tissue which is also called surgical or post-operative sepsis. Surgical site infection constitute a global health problem both health and human term [4]. Most bacteria enter the wound bed through external contamination from the environment, dressings, the patient’s body fluids, or the hands of the patient or health care provider [5].Organisms commonly found in infected wounds include Gram positive cocci such as S.aureus, Streptococcus spp, Gram negative bacilli mostly Enterobacter, E. coli, Proteus spp, P. aeruginosa and Klebsiella spp [5].With the increasing emergence of multiple antibiotics resistance, wound isolates are posing enormous public health concerns thus making the need for exploring possible alternatives a necessity. Herbs and spices are very important and useful as therapeutic agent against many pathological infections [6]. Increasing multidrug resistance of pathogens has led the research for alternative compounds for treatment of infectious diseases.[6] Traditional preparations and medicinal plants with antimicrobial activities have been extensively used in the West African regions [7].Traditional treatment of circumcision wounds and chronic skin ulcers with locally prepared herbs and other natural occurring substances has been known for generations [8]. These medicinal plants have been shown to be quite effective even where antibiotics treatments have failed [9].Vernonia amygdalina commonly called bitter leaf in English, “oriwo” in Edo, “ewuro” in Yoruba, “shikawa” in Hausa, and “olubu” in Igbo [10]. Vernonia amygdalina, a perennial shrub of 2-5m in height that grows throughout tropical Africa. It belongs to the family Asteraceae, has a rough bark with dense black straits, and elliptic leaves that are about 6 mm in length. The leaves are green and have a characteristic odor and bitter taste [11]. In many parts of West Africa, the plant has been domesticated. Vernonia amygdalina is drought tolerant (though it grows better in a humid environment). The plant has also been shown to contain appreciable quantities of ascorbic acid and caroteinoids [11]. The extracts displayed potent antimicrobial activity against some pathogenic organisms [12]. The bitter taste is due to anti-nutritional factors such as alkaloids, saponins, tannins, and glycosides [13]. The leaves are used as green leafy vegetable and may be consumed either as a vegetable (leaves are macerated in soups) or aqueous extracts used as tonics for the treatment of various illnesses [14].It is effective against amoebic dysentery [15], gastrointestinal disorders and has antimicrobial [16] and antiparasitic activities [16].The plant is scientifically classified as belonging to the Kingdom Plantae. It is an angiosperm, of the order Asterales, of the family Asteraceae, genus Vernonia, and species V. amygdalina. The full binomial name is Vernonia amygdalina [17].The leaves are widely used for fevers and are known as a quinine–substitute in Nigeria and some other African countries [18].S. aureus forms a fairly large yellow colony on rich medium and is often hemolytic on blood agar. Staphylococci are facultative anaerobes that grow by aerobic respiration or by fermentation that yields principally lactic acid. The bacteria are catalase-positive and oxidase negative. S. aureus is a major cause of hospital acquired (nosocomial) infection of surgical wounds and infections associated with indwelling medical devices. Although Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus auerus (MRSA) have been entrenched in hospital settings for several decades, MRSA strains have recently emerged outside the hospital becoming known as Community Associated- MRSA (CA-MRSA) or superbug strains of the organism, which now account for the majority of staphylococcal infections seen in the Emergency Room or clinics.Hospital strains of S. aureus are usually resistant to a variety of different antibiotics. A few strains are resistant to all clinically useful antibiotics except vancomycin, and vancomycin resistant strains are increasingly-reported. Methicillin resistance is widespread and most methicillin-resistant strains are also multiple drug-resistant [19]. P.aeruginosa has become increasingly recognized as an emerging opportunistic pathogen of clinical relevance. Several different epidemiological studies track its occurrence as a nosocomial pathogen and indicate that antibiotic resistance is increasing in clinical isolates [19].Furthermore, it is constantly reintroduced into the hospital environment on fruits, plants, vegetables, as well by visitors and patients transferred from other facilities. Spread occurs from patient to patient on the hands of hospital personnel, by direct patient contact with contaminated reservoirs, and by the ingestion of contaminated foods and water [20].The spread of P. aeruginosa can best be controlled by observing proper isolation procedures, aseptic technique, and careful cleaning and monitoring of respirators, catheters, and other instruments.P. aeruginosa is notorious for its resistance to antibiotics and is, therefore, a particularly dangerous and dreaded pathogen. Only a few antibiotics are effective against P. aeruginosa, including fluoroquinolones, gentamicin and imipenem, and even these antibiotics are not effective against all strains [20]. Theodor Escherich first described E. coli in 1885, as Bacterium coli commune, which he isolated from the feces of newborns. It was later renamed Escherichia coli, and for many years the bacterium was simply considered to be a commensal organism of the large intestine.Over 700 antigenic types (serotypes) of E. coli are recognized based on O, H, and K antigens.At one time serotyping was important in distinguishing the small number of strains that actually cause disease. Thus, the serotype O157:H7 (O refers to somatic antigen; H refers to flagella antigen) is uniquely responsible for causing HUS (Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome). Nowadays, particularly for diarrheagenic strains (those that cause diarrhea) pathogenic E. coli are classified based on their unique virulence factors and can only be identified by these traits.Hence, analysis for pathogenic E.coli usually requires that the isolates first be identified as E.coli before testing for virulence markers [21]. Klebsiella is a genus of Enterobacteriaceae, a frequent cause of nosocomial pediatric infection. Klebsiella can cause infections of the urinary tract, lung, and central venous catheters in high-risk newborns and immunocompromised older children. Klebsiella organisms were named for Edwin Klebs, the noted German bacteriologist [22].K.pneumoniae accounts for less than 10 percent of hospitalized cases of pneumonia in adults. Klebsiella spp now are in greatest evidence as opportunistic nosocomial pathogens of the urinary tract, respiratory tract, biliary tract, and bloodstream.In one survey of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the infection rate of nosocomial K.pneumoniae was 16.7 infections per 10,000 patients discharged [23]. Hand-carriage generally is regarded as the common mode of transmission [24]. Environmental sources of Klebsiella spp. include contaminated blood-pressure monitoring equipment [25], ventilator traps, [24] dialysate [26], ultrasound coupling gel [27], and dextrose solution [28].Candida albicans cause the superficial fungal infections known as oral thrush, which occurs on the surface of the tongue and inside the mucus of the cheeks. It appears as white patches known as “plaques” which resemble milk curds [29].Outbreaks of thrush in older children may also be the result of an increased use of antibiotics and steroids, which disturbs the balance of microbes in the mouth. Burnt patients are another population at high risk; the wound site is susceptible to colonization by opportunistic fungi such as Candida, but nowadays this is generally well managed and Candidiasis in burnt patients may originate in the gastrointestinal tract or from intravenous catheters [30].This present study investigated the antimicrobial efficacy of Vernonia amygdalina extracts on Staphylococcus auerus, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Candida albicans and in comparsion with ciprofloxacin and fluconazole in an attempt to further give further scientific backing to various tradomedical claims and uses of the leaves of Vernonia amygdalina.
2. Materials and Method
- Source and maintenance of test organismsThe wound isolates of Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Candida albicans were obtained from patient’s samples in the surgical wards at NAUTH while Pure cultures of standard strains of Staphylococcus aureus (NCTC 6571) and Escherichia coli (NCTC 10418), (control organisms), were obtained from Department of Pharmaceutical Microbiology and Biotechnology, Nnamdi Azikiwe University, Awka, Nigeria.Ethical approval: The study was approved by the institutional ethics committee at Nnamdi Azikiwe University Teraching Hospital (NAUTH), Nnewi, Anambra, Nigeria. (the ethical approval number: NAUTH/CS/66/VOL.6/99). The study design in November, 2015.Collection and identification of plant sampleFresh leaves of Vernonia amygdalina was harvested from farms in Anambra State, Nigeria and identified in the Department of Botany, Nnamdi Azikiwe University, Awka by Mr Paulinus Ugwuoke.Preparation of ExtractionFresh leaves of Vernonia amygdalina was air dried after washing in distilled water at room temperature, grounded into fine powder with a mechanical grinder. Weighed 320 g of Vernonia amygdalina grounded powder and macerated in each 95% ethanol and methanol respectively for three days. After maceration, the solution of the plant extracts were filtered through No. 1 What- man filter paper and the resulting solutions dried in a rotary evaporator at 60°C. The dried extracts recovered were placed in sterilized screw-capped bottles and stored at 4°C.Phytochemical AnalysisThe phytochemical analysis of methanol and ethanol extract of Vernonia amygdalina (bitter leaf) was carried out using standard methods as described by [31].Preparation of stock solutionsFor the primary antimicrobial screening of the plant extracts, stock solutions were prepared by dissolving 400mg of the extracts in 2mL of DMSO (to make 200mg/mL). Also, in the determination of the minimum inhibitory concentrations of the plant extracts, stock solutions were prepared by dissolving 2000 mg/mL in 4mL of DMSO (to make 500mg/mL). These were stored in screw capped tubes at 4°C for further use.In-vitro screening of antimicrobial activities of the plant leaf extractsThe agar well diffusion assay method described by [32] was used to evaluate the antibacterial and antifungal activities of the crude extracts of Vernonia amygdalina against the test microorganisms. Dilutions of 100, 50, 25, 12.5, and 6.25mg/mL were prepared from the 200mg/mL stock solution of the plant extracts in a 2-fold dilution process. Twenty (20) mL of molten Mueller Hinton Agar (MHA) and Sabouraud Dextrose Agar (SDA) (for bacterial and fungal isolates respectively) were poured into sterile Petri dishes (90 mm) and allowed to set. Standardized concentrations (McFarland 0.5) of overnight cultures of test isolates were swabbed aseptically on the agar plates and holes (6mm) were made in the agar plates using a sterile metal cork-borer. Twenty (20µl) of the various dilutions of the plant extract and control were put in each hole under aseptic condition, kept at room temperature for one hour to allow the agents to diffuse into the agar medium and incubated accordingly. Ciprofloxacin (5μg/mL) and fluconazole (50µg/mL) were used as positive controls in the antibacterial and antifungal evaluations respectively; while DMSO was used as the negative control. The MHA plates were then incubated at 37°C for 24 hours, and the SDA plates were incubated at room temperature (25-27°C) for 2-3 days. The inhibition zones diameters (IZDs) were measured and recorded. The size of the cork borer (6mm) was deducted from the values recorded for the IZDs to get the actual diameter. This procedure was conducted in triplicate and the mean IZDs calculated and recorded.Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) of the plant leaf extracts on test isolatesThe Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of the plant extracts on the test isolates were determined by the agar dilution method as described by [33]. The stock solutions (500mg/ml) were further diluted in a 2-fold serial dilution to obtain the following concentrations: 250, 125, 62.5, 31.25, 15.625, 7.8125, 3.91, 1.95, and 0.98 mg/mL. Agar plates were prepared by pouring 4 mL of molten double strength MHA and SDA (for bacterial and fungal isolates respectively) into sterile Petri plates containing 1mL of the various dilutions of the extract making the final plate concentrations to become 100, 50, 25, 12.5, 6.25, 3.125, 1.5625, 0.78, 0.39, and 0.19 mg/mL.The test isolates which were grown overnight in broth were adjusted to McFarland 0.5 standard and streaked onto the surface of the agar plates containing dilutions of the extract. The MHA plates were then incubated at 37°C for 24 hours and the SDA plates were incubated at room temperature (25-27°C) for 2-3days, after which all plates were observed for growth. The minimum dilution (concentration) of the extracts completely inhibiting the growth of each organism was taken as the MIC. This procedure was conducted in triplicate.Determination of Minimum Bactericidal/Fungicidal Concentrations (MBCs/MFCs) of the plant leaf extracts on test isolatesThe MBC/MFC of the plant extracts was derived by sub culturing portions of the agar from plates that showed no growth in the tests for determination of MICs. These agar portions were transferred respectively into plates containing freshly prepared MHA and SDA [33]. These plates were incubated at 25-27°C for 2-3 days and were observed daily for growth. The absence of growth at the end of incubation period signifies total cell death. The minimum concentration of the plant extracts that produces total cell death is taken as the MFC.
3. Results
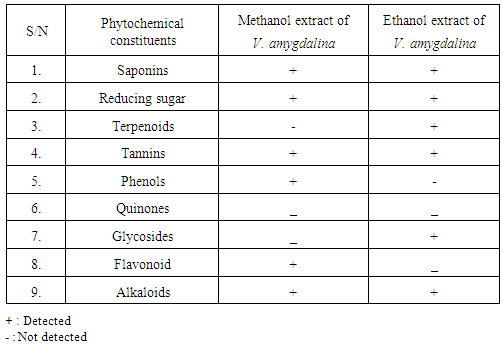
- Qualitative phytochemical analysis detected the presence of tannins, reducing sugar and saponins in all plant extracts (Table 1).
|
|
|
|
4. Discussion
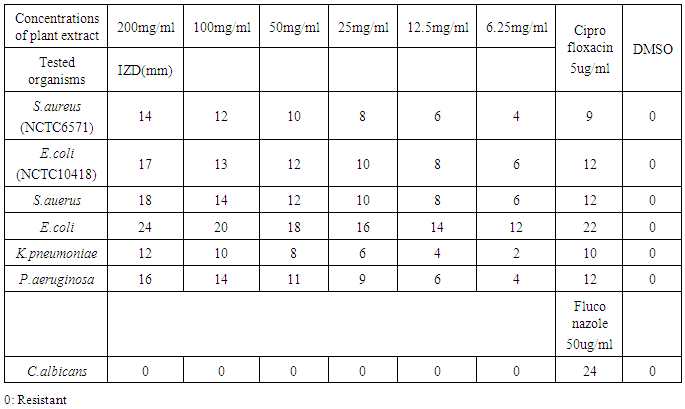
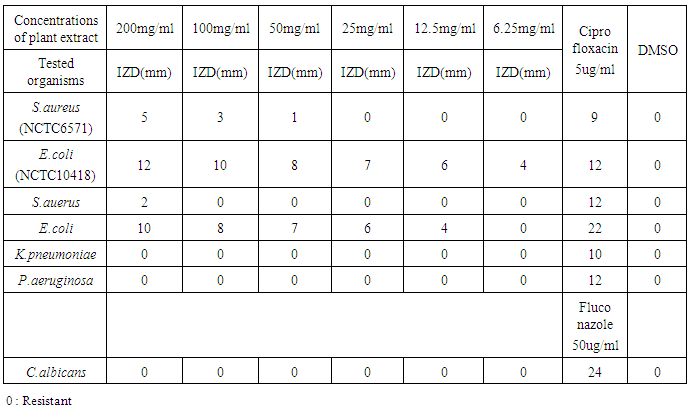
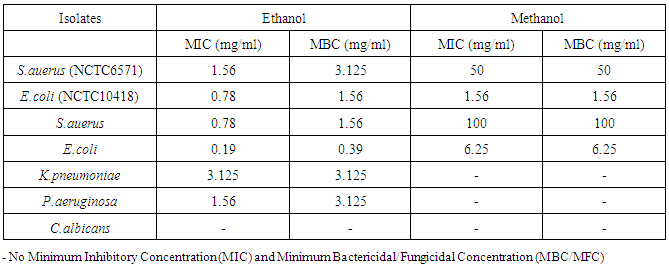
- Wound infection is a major cause of morbidity and mortality and a major source of worry to both the patients, doctors, hospitals and the community as a whole. Increasing multidrug resistance of pathogens has renewed the research for alternative compounds for the treatment of infectious diseases. Qualitative phytochemical analysis of this study, detected the presence of tannins, reducing sugar and saponins in all plant extracts. Secondary metabolites of plants such as tannins, reducing sugar and saponins and all other active principles of plants have been shown to be responsible for the antimicrobial activities shown by these extract. For instance, the sensitivity of Escherichia coli to V. amygdalina may be due to the presence of active saponins and essential oils [34]. The study also showed that the clinical isolate of Escherichia coli was found to be the most susceptible to ethanol crude extract of Vernonia amygdalina with an inhibition zone diameter range of 24mm at 200mg/ml concentrations followed by Staphylococcus auerus with an inhibition zone diameter range of 18mm while Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, while Candida alblicans was only found to be resistant at 200mg/ml concentrations of ethanol extract of Vernonia amygdalina leaves. The susceptibility of E. coli to the crude leaf extract of V. amygdalina agreed with the findings of [35] that demonstrated the antimicrobial activity of some medicinal plants against bacteria by using the extract of V. amygdalina as one of the samples. Generally the ethanol extract showed greater antimicrobial activity compared to its corresponding extract of methanol and commercial antibiotics used. The ethanol extract showed the highest bacteriostatic and bactericidal activities against clinical isolate of E.coli then, S.auerus followed by P.aeruginosa and K.pneumoniae. The methanolic extract was both bacteriostatic and bacteriocidal at a concentration of 50mg/ml, 1.56mg/ml, 100mg/ml and 6.25mg/ml on the typed isolate of S.auerus, typed isolate of E.coli, clinical isolate of S.auerus and clinical isolate of E.coli respectively while the ethanolic extract was both bacteriostatic and bacteriocidal at a concentration of 3.125mg/ml on the clinical isolate of K.pneumoniae. The minimum Inhibitory Concentration and Minimum Bactericidal Concentration of the extracts on the test organisms also increased in the following order; methanol < ethanol. The bacteriostatic activity of crude extract of V. amygdalina in study agreed with the results of [36]. This research showed methanol and ethanol were used for extract preparations as [37] has reported that the ethanolic extracts showed more antimicrobial activities than methanol extracts.
5. Conclusions
- Wound infection still remained the major cause of morbidity and mortality. Increasing emergence of multiple antibiotics resistance of wound isolates pose enormous public health concerns thus making the need for exploring possible alternatives a necessity. Secondary metabolites of this plant has been shown to be responsible for the antimicrobial activities shown by this extract. Consequently, the present study investigated the in-vitro antimicrobial activities of Vernonia amygdalina extracts. This leaf extracts could be used as broad spectrum antibiotics in the treatment of wound infections since it has antimicrobial effects on these pathogens.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML