-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Stroke Research
2017; 5(1): 1-9
doi:10.5923/j.stroke.20170501.01

Effects of Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation and Balance Training on Activities of Daily Living (ADL) of Stroke Survivors with and without Cognitive Impairment
Okonkwo U. Prosper1, Okoye G. Chuba2, Ibeneme S. C.2, Ihegihu Y. E.1, Egwuonwu V. Afam3, Nwankwo M. J.3, Ummuna J. Onuwa3
1Department of Physiotherapy, Nnamdi Azikiwe University Teaching Hospital, Nnewi, Nigeria
2Department of Medical Rehabilitation, Faculty of Health Sciences and Technology, University of Nigeria, Enugu Campus, Nigeria
3Department of Medical Rehabilitation, Faculty of Health Sciences and Technology, Nnamdi Azikiwe University, Awka, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Okonkwo U. Prosper, Department of Physiotherapy, Nnamdi Azikiwe University Teaching Hospital, Nnewi, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Background: Motor training after stroke should be targeted to goals that are relevant to the functional needs of the patient in order to facilitate functional recovery. Therefore, combining Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF) and Task-specific Balance Training to facilitate Activities of Daily Living (ADL) on stroke survivors with and without cognitive impairment was intentioned in this study. Activities of Daily Living are those activities that people must be able to do routinely to be considered fully independent. Barthel Index is one of the instruments used in measuring ADL. This study evaluated the effect of 12 months Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF) and Task Specific Balance Training on Activities of Daily Living in cognitive impaired and cognitive normal stroke survivors. Methods: One hundred of 143 available stroke survivors were recruited using convenience sampling technique in a quasi-experimental study. Those with and without cognitive deficits were assigned into a cognitive impaired group (CIG) and non-cognitive impaired group (NCIG) group, respectively. The patients were grouped into cognitive impaired mean age 55.36±10.2 and cognitive normal mean age 50.20± 13.23 after neuropsychiatric test. Ethical approval was obtained at Nnamdi Azikiwe University Ethical Committee (NAUTHEC), Nnewi. The Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation comprising rhythmic initiation, repeated contraction, slow reversal and rhythmic stabilization and Task-specific Balance Training TSBT comprising repetitive rising from a chair (10 repetitions), cycle ergometer (10 mins), stepping over obstacle (10 repetitions), backward and forward progression (10 repetitions), turning task (10 repetitions) and standing balance training (10 repetitions). TSBT was applied three times a week, 30mins per session, for 12 months. Four research assistants were trained to assist in each treatment session. The outcome measures applied were mini-mental state examination for determining the neuropsychiatric status of participants at baseline and Berthal index for activities of daily living. Result: The mean Berthel Index (BI) scores was significantly greater than the baseline values for the both CIG (F (1.729, 84.709) = 158.575, p < 0.001, with large effect size (partial eta squared) of .764), and NCIG (F(2.478, 121.409) = 5.787, p < 0.001 with large effect size (partial eta squared) of 0.549). Conclusion: There was improvement in Activities of Daily Living (ADL) of the subacute stroke survivors with and without cognitive impairments after 12 months PNF and Task Specific Balance Training protocol adapted in this study.
Keywords: Stroke, Cognitive Impairment, ADL, PNF, Task Specific Balance Training
Cite this paper: Okonkwo U. Prosper, Okoye G. Chuba, Ibeneme S. C., Ihegihu Y. E., Egwuonwu V. Afam, Nwankwo M. J., Ummuna J. Onuwa, Effects of Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation and Balance Training on Activities of Daily Living (ADL) of Stroke Survivors with and without Cognitive Impairment, International Journal of Stroke Research, Vol. 5 No. 1, 2017, pp. 1-9. doi: 10.5923/j.stroke.20170501.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Activities of daily living (ADLs) are basic self-care tasks, akin to the kinds of skills that people usually learn in early childhood. They include feeding, toileting, selecting proper attire, grooming, maintaining continence, putting on clothes, Bathing, walking and transferring (such as moving from bed to wheelchair). To effectively carry out ADL an individual needs to be physically fit, so as to maintain upright posture which is essential to maintain balance and balance is negatively affected by postural control [1] Additionally, ADL demands from an individual that he/she must be mentally sound and coordinated in other to prioritize and process information which is essential for daily living. The ability to be physically and mentally sound is challenged among stroke survivors, due to the loss of brain function resulting from focal disturbances in the blood supply or oxygen to the brain, previously suffered by this group of individuals. Stroke survivors are people that had stroke at one point or the other suffered from cerebrovascular accident or stroke and might be left with residual deformities. The residual deformity could be resulting from loss of function from the affected area of the brain which might cause inability to move one or more limbs on one side [2]. Residual deformities are the major cause of morbidity in the elderly, resulting not only in physical disability but also significant cognitive impairment. Stroke survivors often have deficit in motor control which contributes to balance impairment [3, 4], postural control and mobility [5], and reduced proprioception [6]. These deficits also known as post-stroke syndrome negatively impact activities of daily living and social participation [7]. Moreover, reduced static and dynamic balance associated with post-stroke residual deformities are major risk factors of fall and fear of falling [8, 9] and limit the ability to perform activities of daily living [12]. Any health challenge capable of influencing the Barthel index scores of stroke survivors can alter the performance of ADL by either increasing dependence or enhancing independence. Cognitive impairment occurs in 35.2%–43.9% of the patients three months after stroke and may continue for a longer time in approximately 1/3 of the patients [11-13]. Post-stroke residual deficits or impairments may lead to decrease in functional abilities of stroke survivors; thereby affecting their rehabilitation outcomes [14, 6]. Because of the negative impact of residual impairment on stroke survivors’ ADL [15-18] especially those with cognitive impairment, a more robust rehabilitation approach needs to be integrated into the conventional management plan in order to reduce their dependence in performance of activities of daily living and better their reintegration into the community especially in Nigerian environment. There were scientific evidences from literature reviews that PNF as well as Task Specific Balance Training (TSBT) when used as a standalone therapeutic intervention technique was beneficial in stroke rehabilitation [19, 20]. This study sorts to explore the beneficial effect of using the two in combination in order to maximize the potential bolstering effects in recovery of activity of daily living of cognitive impaired and non-cognitive impaired stroke survivors.
2. Methodology
- A multi-center quasi-experimental study of 143 stroke survivors, who were selected using convenience sampling, was conducted at four hospitals: Nnamdi Azikwe University Teaching Hospital, Myles Specialist Hospital, Hope Specialist Hospital and Mercy Specialist Hospital. The patients recruited were treated at facilities with the required equipment: Landmark Physiotherapy Services, Nnewi and Department of Physiotherapy, Nnamdi Azikiwe University Teaching Hospital, Nnewi. The sample size was determined using a mathematical relationship recommended by a previous author [21]:
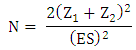 ES = standardized difference of variable with the least possible change = mean difference
ES = standardized difference of variable with the least possible change = mean difference  Standard deviation= 1.8/3.0= 0.60; N= sample size for a group; Z1 = percentage point of normal distribution for statistical significance level at 95% confidence Interval = 1.96; Z2 = percentage point of normal distribution for statistical power at 80% = 0.8416; N = 2 (1.96 + 0.84)2/ (0.60)2 = 15.68/0.36 = 43.56 = 44; N = 2x44 = 88. About 70% of the population was expected to be compliant, and therefore an attrition rate of 30% of the calculated sample size i.e. 30/100 x 88 = 26), was added to the sample size. Therefore, N (total sample size) = 88 + 26 = 114. However, 143 participants were available, and were recruited, but only 100 (comprising 85 and 58 participants with and without cognitive impairments, respectively) of them completed the study.The inclusion criteria were (i) adults of between 30-65years of age, (ii) diagnosis of Ischemic stroke by a physician, (iii) adjudged cognitively impaired and non-cognitively impaired by neurologist and a psychiatrist using the mini mental state examination, (iv) stroke duration ≥ 3 months but ≤ 6 months, (v) participants at high risk ambulatory status, (vi) no history of other neurological, metabolic or orthopedics conditions and (x) domiciled within Nnewi and its environs (Ichi, Amichi, Orifite, Utuh, Ozubulu), and (xi) must be literate.Ethical Approval: Ethical Consideration. Ethical approval from the Nnamdi Azikiwe University Teaching Hospital Ethical Committee (NAUTHEC), Nnewi, was obtained alongside a supervision approval from a Consultant Neurologist. All the participants gave their informed consent to participate in the study after the purpose was explained to them. They were also assured of the confidentiality of the information they provide. It was made clear to the participants that they have the right to refuse to participate or to withdraw at any stage of the project, and these rights were respected all through the research procedure.
Standard deviation= 1.8/3.0= 0.60; N= sample size for a group; Z1 = percentage point of normal distribution for statistical significance level at 95% confidence Interval = 1.96; Z2 = percentage point of normal distribution for statistical power at 80% = 0.8416; N = 2 (1.96 + 0.84)2/ (0.60)2 = 15.68/0.36 = 43.56 = 44; N = 2x44 = 88. About 70% of the population was expected to be compliant, and therefore an attrition rate of 30% of the calculated sample size i.e. 30/100 x 88 = 26), was added to the sample size. Therefore, N (total sample size) = 88 + 26 = 114. However, 143 participants were available, and were recruited, but only 100 (comprising 85 and 58 participants with and without cognitive impairments, respectively) of them completed the study.The inclusion criteria were (i) adults of between 30-65years of age, (ii) diagnosis of Ischemic stroke by a physician, (iii) adjudged cognitively impaired and non-cognitively impaired by neurologist and a psychiatrist using the mini mental state examination, (iv) stroke duration ≥ 3 months but ≤ 6 months, (v) participants at high risk ambulatory status, (vi) no history of other neurological, metabolic or orthopedics conditions and (x) domiciled within Nnewi and its environs (Ichi, Amichi, Orifite, Utuh, Ozubulu), and (xi) must be literate.Ethical Approval: Ethical Consideration. Ethical approval from the Nnamdi Azikiwe University Teaching Hospital Ethical Committee (NAUTHEC), Nnewi, was obtained alongside a supervision approval from a Consultant Neurologist. All the participants gave their informed consent to participate in the study after the purpose was explained to them. They were also assured of the confidentiality of the information they provide. It was made clear to the participants that they have the right to refuse to participate or to withdraw at any stage of the project, and these rights were respected all through the research procedure.2.1. Intervention Procedures
- 2.1.1. Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF)The PNF technique/ strengthening program that was applied comprised rhythmic initiation, repeated contraction, slow reversal and rhythmic stabilization,1. Rhythmic initiation- the participants were made to progress from passive to active resistance, then followed by active movements. It was applied for those participants to teach movement to the participants.2. Repeated contraction. Here the participants were allowed to move their limb isotonically through resistance just before fatigue was present.3. Slow reversal. Participants were made to contract the agonist and immediately after the antagonist. It was intended for developing active range of motion and coordination between agonist and antagonist. It was also used to increase strength of a specific Range of motion4. Rhythmic stabilization. This technique was used to elicit isometric contraction of agonist followed by isometric contraction of antagonist. It was also used to achieve the holding power of a targeted range of motion.Ten repetitions of each pattern were done before proceeding to the next pattern, in line with what obtains in previous PNF studies [22, 23]. After the set of pattern were completed, it was repeated twice in each treatment session making 3 sets per session. This usually lasted about 30 minutes per participant per session. However, the PNF training were applied equally in terms of intensity, frequency and duration, irrespective of laterality of stroke and the set used in the study were as described by Knott and Voss [24] for the following:1. Lower extremity:1. abduction-external rotation (knee flexed and knee extended)2. Extension-adduction –internal rotation (knee flexed and knee extended)3. Flexion-adduction-internal rotation (knee flexed and knee extended)4. Extension –abduction-external rotation (knee flexed and knee extended)2. Upper extremity:1. Flexion-abduction-external rotation (elbow flexed and elbow extended).2. Extension-adduction-internal rotation (elbow flexed and elbow extended).3. Flexion-adduction-internal rotation (elbow flexed and elbow extended).4. Extension-abduction-external rotation (elbow flexed and elbow extended)A pamphlet containing the described patterns also served as treatment guide during training. [25].2.1.2. Task Specific Balance Training (TSBT)The Tasks specific activities that were initiated to train balance include;1. Graded strengthening (repetitive rising from a chair) – 10 repetition2. Aerobic training (cycle ergometer) - 5 repetitions3. Walking tasks (stepping over obstacle) - 10 repetitions4. Standing balance-10 repetitions5. Forward and backward and forward progression - 5 repetitions6. Turning task - 10 repetitionsThese tasks were participants’ specific (made flexible according to the need of the individual patient) and lasted for an average of 30 minutes to reduce the chance of their getting fatigued. However, the same intensity, frequency and duration of treatment were administered on the participants irrespective of laterality- left or right sided of the cerebral lesion. Patients were dressed in a pair of shorts vest so as to make them comfortable for the exercise. They were also allowed to wear appropriate sized flat-heeled shoes or bare footed as the case may be. An interval of 10 minutes rest was allowed for the participants and deep breathing exercises performed during rest period to enhance recovery. Patients were closely monitored to prevent any adverse cardiovascular or respiratory reactions as a result of the training. The training was timed with a stop watch (diamond model, made in China) and scheduled between 9 am -1pm on the appointment days. Data were collected at baseline, 4th, 8th and 12th months, respectively to build a profile and track the trend of change.
2.2. Outcome Measures
- 2.2.1. Mini-mental State Examination (MMSE) was used by the researchers to assess global cognition which comprised items concerning orientation, registration and recall, attention, language, following commands and figure copying for those stroke cases that had minimum of 3months duration. The cut off score was 23/24. Those below the cut off were deemed to be cognitively impaired while those above the cut off were deemed to be cognitively normal. MMSE is brief, inexpensive, and simple to administer. Its widespread use and accepted cut off scores increases its interpretability. However, it has low sensitivity with people with mild cognitive impairment [26].
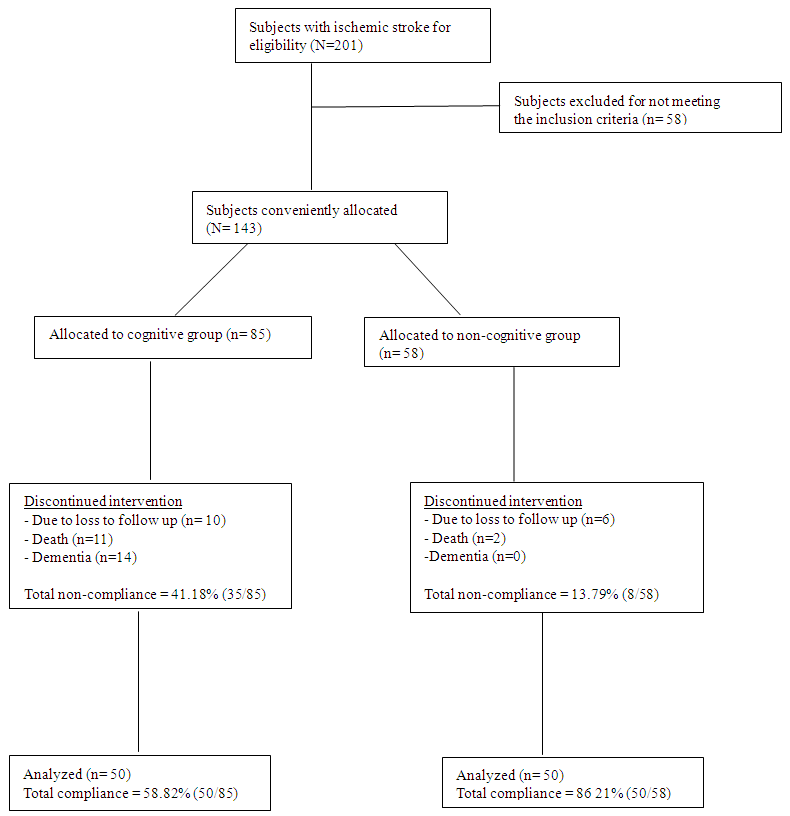 | Figure 1. Subject Selection Flow Chart |
2.3. Statistical Analysis
- Statistical Analysis was performed by using SPSS version 20: Descriptive statistic of Mean ± SD was used in the analysis of demographic and baseline characteristics. The raw data was tested for normality using Shapiro-wilks test, while Log Transformation was utilized to normalize the data. Repeated Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) was adopted to compare variations within each group; independent t-test was applied to compare variations between the two treatment groups. Probability value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
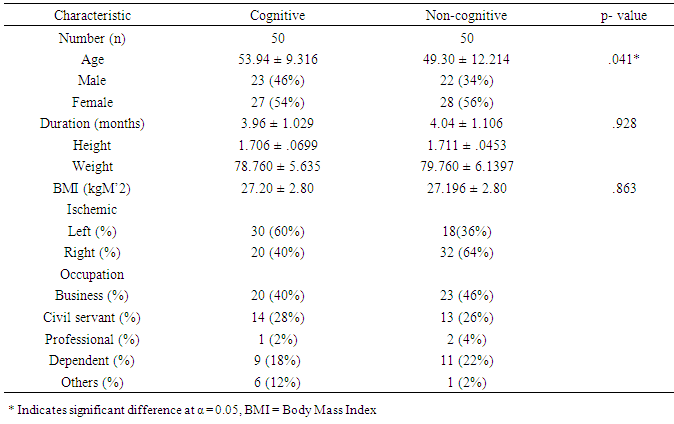
- A total of 143 participants that commenced the treatment 43 dropped out before the 6th month of the study for various reasons. Meanwhile, in the cognitive group, 10 participants missed their follow-up appointments, 11 deaths were recorded as serious adverse events; while 14 others tended towards dementia. The non-cognitive group had 6 participants that missed their follow up appointments, 2 deaths which were reported had a serious adverse event. However, only 100 participants completed the entire study. In the cognitive group, the compliance level was 58.82% while the non-compliance level was 41.18%. The high level non-compliance recorded in the cognitive group may be explained by the greater number of loss in follow up associated with death and loss of memory. The baseline characteristics in table 1 showed the number of male and female participants were 23(46%) and 27(54%), respectively, for the cognitive group, while the non-cognitive had 22(34%) and 28(56%) for the males and females, respectively. Their mean age differed significantly (p<0.05) and was recorded as 53.94±9.316 years and 49.30±12.214 years for the cognitive and non-cognitive groups, respectively. However, the duration of stroke and body mass index were not significantly different (p>0.05) for the both groups. The both types of stroke were common among the traders (business men) and civil servants with professional workers having the least incidence of stroke. The other physical characteristics of the participants are presented in Table 1.
|
|
|
4. Discussions
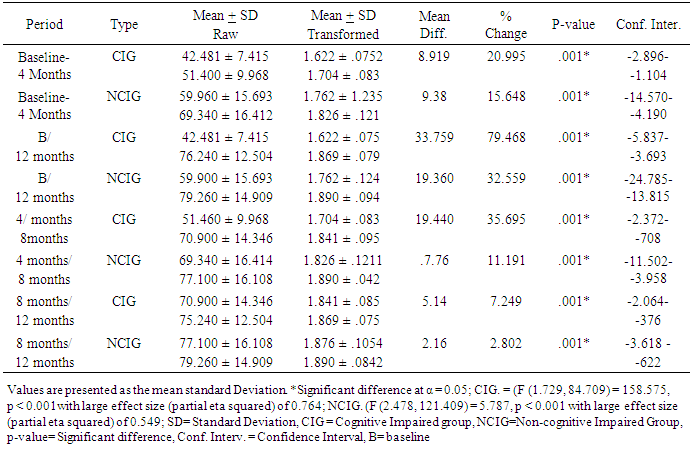
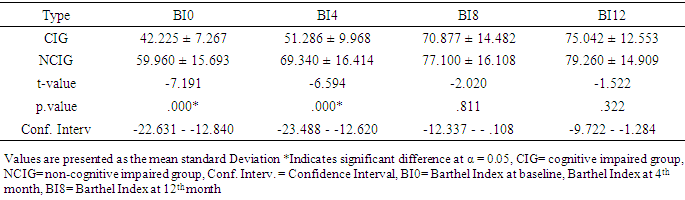
- The baseline characteristics revealed that a total of 100 stroke survivors (50 cognitive and 50 non-cognitive) completed the study. The ratio of the male to female was matched in the two groups; therefore, the differences in sex were consistent and indicate the similarity of the samples to rule out gender effect in this context. It was further revealed that both the duration of stroke and the body mass index were not significantly different between the two groups. It appears that traders and civil servants were vulnerable to stroke than other professionals, which may be induced by work related stress increasing the activities of reactive oxygen species leading to degenerative changes of the vasculature. Therefore, the high incidence of stroke in the two occupations may be attributed to the preponderance of this group of participants in the general population hence increasing the possibility of stroke.Strength and limitations of studyThis work was limited by the high level of noncompliance from the cognitive group and by the limited number of participants. However, there were significant age differences between the two groups which were not unexpected considering that the subjects were not randomly selected. This may be a weakness for the study design, as age is an important confounding variable for balance function, Perhaps, this difference between the groups may add to the explanations that up to the 4th month of the intervention study, there were significant differences in the outcome measures across both groups. However, this was no longer evident at the 8th – 12th month of the TSBT intervention. This could be an indication that age-related differences and cognitive dysfunction may not suppress gains in ADL function when PNF /TSBT is given beyond the 8th month. It is also possible that PNF/TSBT may have a dose-response curve which, might shift to the right towards the 3rd quartile of the 12-month intervention program.This finding agrees with the results of a previous study which found that old and even very old patients with stroke benefit from specialized inpatient neuro rehabilitation and high amounts of therapy in the same degree as younger patients. [28]. The above finding contradicted the earlier views of the American Heart Association [29] that the younger stroke patients benefited more by stroke unit rehabilitation compared with older patients. What is however strikingly different from the two studies above was that they were short term studies, unlike this study that was a long-term study.The Activities of Daily Living (ADL) in within group analysis for cognitive impaired stroke survivors showed a statistical significant improvement (p < 0.05) as well as that for the non-cognitive group. This outcome showed that both categories of stroke survivors had improvement after the first four months of exercise intervention. We also noted that between 4 months and 8 months there was also statistical significant increases p <. 0.05 in the activities of daily living for the two groups; however, the percentage change in the ADL was higher in the CIG than NCIG. Similarly we noted that the trend of improvement continued between 8 and 12 months of intervention though with an inclination towards a plateau. The outcome of this analysis revealed that for CIG that the highest mean change resulting from the exercise intervention was recorded between 4 and 8 months of intervention while the NCIG was between baseline and 4 months. However, there is paucity of literature to explicitly explain the improvement pattern as regards response to exercise noticed above however it may be postulated that because of the presenting cognitive status at baseline that it took the cognitive impaired group longer time to adapt to the exercise training compared to the cognitive normal group. We interestingly noted that the least mean difference was recorded between 8 and 12 months post intervention for the two groups. This could be attributed to the improvement plateaus (exercise intervention was not bringing about much improvement in the ADL status of the stroke survivors subjected to PNF and TSBT) in the two groups likely because of the minimal effects of neuroplasticity. The BI scores at baseline and 12 months were significantly different (p < .0.05) for the two groups (CIG and NCIG) with large effect size (partial eta) of .793 and .500 respectively. Moreover the independent t-test as shown in table 3 shows significant (p < 0.5) at baseline and 4th month while between the 8th month and 12th month there was no significant different (p > 0.5) between the two groups. This pattern of improvement was in tandem with the findings of Gbiri and Akinpelu, 2011 [30] which stated that the recovery in stroke survivors witnessed clinically significant but statistically insignificant improvement to 12-month. Also a number of researches showed significant recoveries in ADL after intensive physical therapy intervention; Kwakkel and Wagenaar, were able to show that a rehabilitation program comprising mainly the PNF technique led to improvement in voluntary movement of the hemiplegic lower limb, in arm functions and Activities of Daily Living (ADL) [31]; Zinn concluded that improvement rate of more complex life activities as measured by Lawton instrumental ADL score was lower among the stroke patients with cognitive impairment but cognitive impairment did not have negative effect on recovery of ADL [19]. Another study showed that acute stroke patients with cognitive impairment had significant functional gain after rehabilitation intervention and that cognitive impairment did not completely block the efficacy of rehabilitation [20]. It has been found that cognitive impairment did not lead to decrease in the efficacy of outpatient rehabilitation, and has no effect on the treatment duration and functional recovery in the elderly [32]. The long term management adopted in this study was in line with the finding that because cognitive impairment was associated with decreased ADL and independent ADL functions that patient with impaired cognition will require prolonged rehabilitation. The outcomes of some studies were however at conflicts with the improvement recorded in this research work this may be explained by short-term management approach adopted in those studies [19, 20]. Reduced cognition had been associated with a decreased ability to perform ADLs, with poorer physical functioning at discharge and with a greater likelihood of mortality within 1 year of discharge [33]; also the reason according to Diamond et al for the poor functional outcome among the cognitive impaired geriatric patients compared with non-cognitive impaired was the low functional status at admission to rehabilitation unit. The same study also noted that although rehabilitation intervention was successful in patients with cognitive impairment, functional capacity was low at discharge when compared to non-cognitive impaired post stroke survivors [14]. However, the review of previous studies conducted during planning of the present study, the findings were contradictory on the subjects with cognitive impairment having negative effect on rehabilitation intervention and functional outcome in stroke. This may be due to the different features of participants such as age, duration of disease on admission to rehabilitation as well as severity of the cognitive impairment. [34]. The intervention approach adopted which applied the principle of enhanced neuroplasticity and cortical reorganization in the present study may have impacted positively on the ADL improvement noted in the two groups. Additionally, the present study also revealed that the rate and extent of recovery post stroke depends largely upon the initial degree of impairment, on an intact cortex adjacent to the lesion, and on the timing and intensity of the rehabilitation. [33, 15]. Meanwhile, improvement of motor activity was noted post stroke due to marginal recovery of functional neurons and lastly reorganization of neural functions (neuroplasticity) [15, 35]. The initial finding from previous studies by [33, 34] revealed that stroke deficits were permanent after 3 to 6 months making further intervention unnecessary, but the outcome of this research work support the findings that subjects with stroke improve their motor function even in the chronic state (longer than 6 months) due to neuroplasticity [36].It is believed that since PNF achieves its maximal effects by cumulative effect [37], the duration, length and intensity of exercise intervention employed in this study may have aided the full manifestation of vital cumulative effects that made significant impact on the ADL status of both groups of stroke survivors. The PNF/TSBT intervention employed in this study may have influenced the enriched environments coupled with the repetitive nature of the exercises that excited the interest of the participants, consequently stimulating participation of subjects in the training inducing long-lasting motor learning and associated cortical reorganization [38, 39]. This may be associated with the finding that task-specific training emphasizes the repetitive practice of skilled motor performance thereby improving individual functional abilities [40, 41] and that repetitive task-specific training was found to elicit better functional improvements compared to non-repetitive training [42, 43]. Therefore, task-specific training may be said to effectively recover a wide array of motor behaviors involving the upper limbs, lower limbs, sit-to-stand movements, and gait after stroke [44-47]. Significantly, the outcome of this study showed that there was strong evidence to explain that adaptive neural plasticity induced by PNF and task-specific training enhanced functional motor recovery [48, 30, 38, 49] in both groups.
5. Conclusions
- The findings of this study made the authors to conclude that ADL status of sub-acute stokes survivors improved significantly in both groups, irrespective of cognitive status of the subjects due to long term PNF/TSBT intervention approach utilized in this research. Specifically, because participants in this study were not very old and had mostly mild to moderate cognitive impairment, prolonged rehabilitation utilized in this study had positive impact in the outcome. In essence age and mild or moderate cognitive impairment in long term PNF/balance training does not significantly impede activities of daily living (ADL) and recovery during rehabilitation. The authors speculated that similarities in outcomes between the two groups were influenced by interplay of factors thus highlighted: participants not being very old; mild or moderate cognitive impairment; enriched environment created by the intervention protocol; intensity of the exercise; and neuroplasticity.
6. Recommendations
- A long term task specific balance training that is multi-level in approach should be adopted in stroke rehabilitation program. Age and mild or moderate cognitive impairment should not be seen as a hindrance to effective rehabilitation program. More studies are necessary which will involve more sample size to enhance generalizability.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- This work was part of a Thesis submitted to the School of Postgraduate Studies, University of Nigeria, Nsukka, Nigeria in part fulfillment of the requirements for the award of the Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in Neuro Rehabilitation.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML