-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Stroke Research
2013; 1(1): 1-6
doi:10.5923/j.stroke.20130101.01
Hyperglycemia and Stroke
Sharan Badiger1, Prema T. Akkasaligar2, Utkarsha Narone1
1Department of Medicine, BLDE University's Sri. B.M.Patil Medical College, Bijapur, 586103, Karnataka, India
2Department of Computer Science, B.L.D.E.A’s Dr. P.G.H.Engineering College, Bijapur, 586103, Karnataka, India
Correspondence to: Sharan Badiger, Department of Medicine, BLDE University's Sri. B.M.Patil Medical College, Bijapur, 586103, Karnataka, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Cerebrovascular accident is the third most common leading cause of death worldwide, after coronary heart disease and cancer. The World Health Organisation defines stroke as “rapidly developing clinical signs of focal (or global) disturbance of cerebral function, with symptoms lasting for 24 hours or longer, or leading to death with no apparent cause other than of vascular origin”. Among 80% of all cerebrovascular accidents are ischemic, rest being due to haemorrhage. There are many factors which alter the outcome of stroke. Acute hyperglycemic response to stress has been recognized since Claude Bernard’s observations more than a century ago. This “diabetes of injury” exemplifies the obligatory metabolic rearrangements required to cope with critical stress. The concept evolved as glucose became identified as metabolic mirror of the severity and outcome of critical illness.
Keywords: Acute Ischemic Stroke, Endothelial Dysfunction, Stress Hyperglycemia
Cite this paper: Sharan Badiger, Prema T. Akkasaligar, Utkarsha Narone, Hyperglycemia and Stroke, International Journal of Stroke Research, Vol. 1 No. 1, 2013, pp. 1-6. doi: 10.5923/j.stroke.20130101.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Stress hyperglycemia has been defined as hyperglycemia in previously euglycemic patients that corrects once the acute process resolves. Hyperglycemia occurs in 60% of the cases with acute stroke and in 12- 53% cases without the prior diagnosis of diabetes. It imposes a range of adverse effects like abnormal immune function[1], hemodynamic and electromyocardial disturbances and increased infection rate[2]. Various studies have shown a direct relationship between the extent of stress hyperglycemia and severity and outcome of stroke, including mortality. Hyperglycemia in both diabetic and non- diabetic (i.e., stress hyperglycemia) patients is associated with poor prognosis both in terms of mortality and functional recovery, irrespective of patient’s age, severity of condition or stroke sub- type[3].
2. Pathophysiology of Hyperglycemia and Acute Ischemic Stroke
- Hyperglycemia is common in patients with acute stroke, occurring in up to 60% of patients overall[4, 5] and approximately 12- 53% of acute stroke patients without a prior diagnosis of diabetes[6]. Hyperglycaemia predicts higher mortality and morbidity after acute stroke independently of other adverse prognostic factors, such as older age, type and severity of stroke, and non-reversibility of the neurological deficit[7].Several explanations may account for the observed association between hyperglycemia and poor prognosis after ischemic stroke.Hyperglycemia may be directly toxic to the ischemic brain. Accumulation of lactate and intracellular acidosis in the ischemic brain (produced through anaerobic cerebral glucose metabolism)[8] promotes and accelerates ischemic injury by enhancing lipid peroxidation and free radical formation[9], and impairing mitochondrial function[10]. These neurotoxic effects may be particularly important in the ischemic penumbra where neurons are injured but still viable[11]. Hyperglycemia facilitates the development of cellular acidosis in the ischemic penumbra and results in a greater infarct volume, thus promoting the recruitment of potentially salvageable neurons into the infarction.Hyperglycemic patients are relatively deficient in insulin. This leads to both reduced peripheral uptake of glucose (increasing the amount of glucose available to diffuse into brain) and increased circulating free fatty acids. Free fatty acids may impair endothelium-dependent vasodilation[12].Stress hyperglycemia patients are likely to have dysglycemia (ie, blood glucose level above the normal range but below the threshold for diabetes[13] or undiagnosed diabetes when not stressed. These patients have a higher risk of vascular disease than patients with normal blood glucose level[14]. These patients could sustain more ischemic damage at the time of infarction as a result of more extensive underlying cerebral vasculopathy compared with those who do not develop stress hyperglycemia. Hyperglycemia is an important determinant of the widespread changes in both small cerebral blood vessels[15] and large extracranial vessels[16] seen in diabetic patients.Hyperglycemia may disrupt the blood-brain barrier[17] and promote hemorrhagic infarct conversion[18]. Higher admission serum glucose level is associated with a higher risk of hemorrhagic conversion of the infarct, with a substantial rise in risk with levels >8.4 mmol/L[19].Stress hyperglycemia may be a marker of the extent of ischemic damage in patients with stroke. Patients with severe or fatal strokes might develop hyperglycemia because of greater release of "stress hormones" such as cortisol and norepinephrine. Strength of the positive association between hyperglycemia and mortality lessened after accounting for the severity of stroke (as indicated by decreased level of consciousness and weakness score at the onset of stroke)[20]. Stress hyperglycemia is of pathophysiological significance in patients with stroke and is not simply an epiphenomenon of the stress response to stroke.
2.1. Hyperglycemia-Associated Reduction in Perfusion
- Hyperglycemia causes 24% reduction in regional blood flow, reduction in blood circulation to the marginal ischemic areas and converts ischemic penumbra to infarct[21]. CO2-induced increase in cerebral blood flow is decreased in diabetics[22]. CO2-induced cerebral vasodilatation is mediated through NO, and diabetics are known to have decreased endothelial NO production.
2.2. Hyperglycemia-Associated Impaired Calcium Homeostasis
- Excitatory amino acids, notably glutamate, play a central role in neuronal death by activation of postsynaptic glutamate receptors, particularly NMDA receptors. This leads to an excessive influx of calcium through ion channels, mitochondrial injury, and eventual cell death. Thus, hyperglycemia, by increasing the availability of glutamate, may induce calcium-mediated neuronal cell death. Hyperglycemia may also be harmful to calcium recovery during the early perfusion period after focal cerebral ischemia, thereby increasing intracellular calcium for a longer time[23].
2.3. Inflammation and Free Radical–Associated Injury
- Hyperglycemia is known to be associated with inflammation and oxidative stress. Glucose intake results in comprehensive inflammation as reflected in an increase in nuclear factor kB (NF- kB) binding and a decrease in inhibitor kappa B (I kB) expression[24]. NF-kB is a nuclear transcription factor that normally stays in the cytoplasm in association with I kB[25].In response to an inflammatory stimulus, there is an increase in I kB kinase-α and I kB kinase-ß, which phosphorylate I kB and result in its ubiquitination and proteosomal degradation. Degradation of I kB results in release of NF- kB and in its translocation from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, where it stimulates the transcription of proinflammatory cytokines. Activation of NF- kB and superoxide generation has been shown to be involved in tissue injury after occlusion of middle cerebral artery. NF- kB activation leads to increased production of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines such as tumor necrosis factor- and monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP-1). This attracts leukocytes to the ischemic area. Superoxide radicals can cause direct cell damage through lipid peroxidation, protein carbonylation, and DNA damage. Superoxide also neutralizes NO produced by endothelium by converting NO to peroxinitrite. NO is critical in maintenance of blood flow to the ischemic brain tissue by causing vasodilatation of arteries.Glucose intake also causes an increase in the other proinflammatory transcription factors. Activator protein-1 (AP-1) and early growth response-1 (Egr-1). AP-1 regulates the transcription of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), whereas Egr-1 modulates the transcription of tissue factor (TF). Thus, glucose intake increases the expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 as well as that of TF.MMP-9, also involved in the process of central spreading depression after an acute stroke, plays a significant role in brain damage by increasing brain edema. Central spreading depression is characterized by neuronal and glial depolarization, which is followed 3 to 6 hours later by an increase in the expression of MMP-9 initially in the cortical blood vessels, spreading later to neuronal layers and finally to the pia and the arachnoid[26,27].The increase in MMP-9 results in a reduction of laminin, endothelial barrier antigen, and the zona occludens.[27] These 3 proteins are important in the maintenance of blood–brain barrier. The decrease in their concentration affects the integrity of the blood–brain barrier and an increase in the permeability of the barrier, resulting in edema with the leakage of plasma proteins and inflammatory cells. Stroke patients with hyperglycemia indeed develop more pronounced cerebral edema[28]. (Figure 1.)
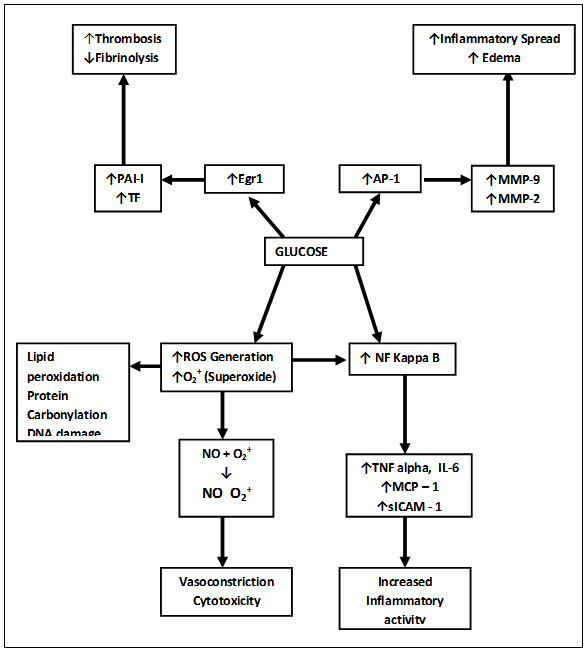 | Figure 1. Glucose Mediated Pro-inflammatory and Pro-Coagulant Effects |
2.4. Hyperglycemia and Thrombosis
- Multiple studies have identified a variety ofhyperglycemia-related abnormalities in hemostasis, favoring thrombosis [29]. Human studies in patients with type 2 diabetes have shown platelet hyperactivity indicated by increasedthromboxane biosynthesis Hyperglycemia-induced elevations of interleukin (IL)-6 levels have been linked to elevated plasma fibrinogen concentrations and fibrinogen mRNA[30,31].Increased platelet activation as shown by shear-induced platelet adhesion and aggregation on extracellular matrix has been demonstrated in patients with diabetes[29].In the healthy state, the vascular endothelium maintains the vasculature in a quiescent, relaxant, antithrombotic, antioxidant, and antiadhesive state. Acute hyperglycemia may directly alter endothelial cell function by promoting chemical inactivation of nitric oxide[32], triggering production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) or activating other pathways.
3. Insulin Treatment in Acute Ischemic Stroke
- Insulin therapy reduces ischemic brain damage and can be neuroprotective. Insulin reduced neuronal necrosis regardless of its effect on glucose levels[33]. In addition, insulin, and to a lesser extent insulin-like growth factor-1, reduced ischemic damage when injected directly into the brain ventricles.[34].Insulin has recently been shown to possess a potent anti-inflammatory effect in vitro and in vivo. It suppresses several proinflammatory transcription factors, such as NF- κB, Egr-1, and AP-1, and the corresponding genes regulated by them that mediate inflammation. Insulin suppresses ROS generation[35]. In addition to its inhibitory effect on AP-1 and Egr-1, insulin suppresses their regulated gene products as indicated by a fall in plasma concentration of MMP-9, TF, and PAI-1[36], an effect diametrically opposite to that of glucose. MMP-9 is a cardinal mediator and a reduction in its activity or expression by insulin could be a rational therapeutic approach in the prevention or the limitation of ischemia-related damage to the brain.Insulin causes reduction in the plasma concentration of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), a cytokine that induces an increase in the expression of MMP-9[37]. It has also been shown that VEGF can cause the loss of endothelial cell tight junctions. It is possible that VEGF and MMP-9 may act in a synergistic fashion to cause a disruption of the blood–brain barrier during ischemia because hypoxia is the major factor inducing an increase in the expression of VEGF. The fact that insulin suppresses MMP-9 and VEGF, both of which are mediators of ischemic damage, suggests strongly that it may have a beneficial role in the treatment of an acute stroke. Moreover, insulin-mediated suppression of TF and PAI-1 can produce an anticoagulant effect.High catecholamine levels in the circulation during acute stroke can increase the production of free fatty acids. Free fatty acids decrease the generation and the stability of Prostacyclin[38], which is important for not only vasodilatation but also for preventing platelet aggregation. Insulin inhibits lipolysis, leading to a decrease in plasma-free fatty acids and thus may exert an antiplatelet and anticoagulant effect. Insulin increases endothelial NO release and the expression of NO synthase (NOS) expression in the endothelial cells[39]. Generation of NO would potentially help in vasodilatation and improved blood flow to the penumbra but also result in decreased production of ICAM-1. In addition, insulin has a direct inhibitory effect on platelet aggregation, mediated through the NO– guanylate cyclase-c GMP pathway activated by NO generated by NOS in platelets[40]. The antiplatelet effect of insulin may also potentially mediate further anti-inflammatory activity because platelet aggregation leads to the release of CD40 ligand (also called CD 154) contained in alfa-granules of platelets. CD40 ligand is a major mediator of inflammation (Figure 2.).
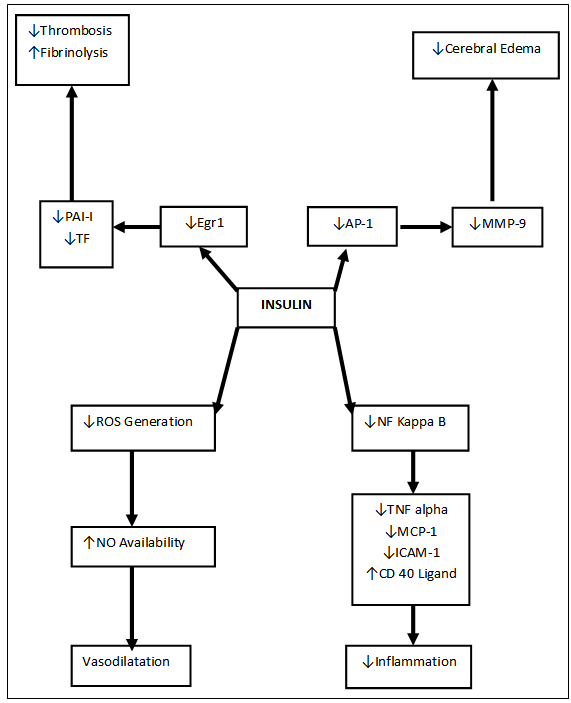 | Figure 2. Anti Inflammatory, Anti Coagulant and Vasodilatory Effects of Insulin |
4. Molecular Mechanisms of Stroke and Hyperglycemia
- Stroke is the main cause of disability and mortality among the aging population, and about 75% of all cases are ischemic stroke while 15% are hemorrhagic stroke[41]. The free radicals arising from sources such as xanthine oxidase, cyclooxygenase, inflammatory cells and mitochondria are associated with stroke[42], and leading to neuronal death[43]. During ischemia and reperfusion the mitochondrial electron transport chain is altered and is a likely source of free radicals[44], which leads to an increased formation of superoxide radical anions as supported by the fact that knockout mice for mitochondrial superoxide dismutase (mSOD) genes display larger brain lesions after focal ischemia[45]. During reperfusion the accumulation of blood borne inflammatory cells such as neutrophils and monocytes/macrophages, can promote further oxidative stress. In ischemic stroke patients increased levels of oxidative damage to DNA and lipid peroxidation has been demonstrated[41]. The increased levels of ROS can make the brain more susceptible to oxidative stress due to a variety of reasons like: the brain consumes a significant amount of the body oxygen, relatively poor antioxidant defense system, enriched in pro-oxidant molecules and contains high concentration of readily peroxidizable lipids[46].
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- Authors acknowledge the immense co-operation and the help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The author is also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML