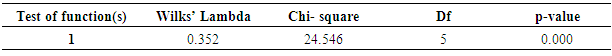-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Statistics and Applications
p-ISSN: 2168-5193 e-ISSN: 2168-5215
2017; 7(1): 1-11
doi:10.5923/j.statistics.20170701.01

Insolvency Prediction Model of Some Selected Nigerian Banks
Yahaya H. U., Nasiru M. O., Ebgejiogu O. N.
Department of Statistics, University of Abuja, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Yahaya H. U., Department of Statistics, University of Abuja, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

There is a great interest to know if a financial institution will be able to survive or not. Models of insolvency are important for managers who may appreciate how serious the financial health of their company is becoming, not until it is too late to take effective action. Discriminant analysis is used in this study to evaluate the predictor variable used to predict insolvency. Financial ratios obtained from corporate balance sheet are used as independent variables while failed and non-failed company is the dependent variable. Result shows that the most significant factor in bank insolvency evaluation are: Retained Earning to Total Asset, Earning before interest tax to total asset and the market Value of Equity to total Liability. The result also indicates that the failed companies were also less profitable and less liquid and lower quality assets. The feed- forward back propagation neural network is used to predict the insolvency in this study. The result of applying feed-forward back propagation neural network methodology to predict financial distress based upon selected financial ratios shows the abilities of neural network to be a very useful tool to model the company’s survival capability due its ability to model a nonlinear process without a prior knowledge about the nature of process. The percentage correctly classified by the feed-forward back propagation network is approximately 89 percent. Artificial neural networks show significant signs for providing early warning signals and solvency monitoring.
Keywords: ANN, NN, NDIC, MDA, DA, Insolvency, Banks, Prediction
Cite this paper: Yahaya H. U., Nasiru M. O., Ebgejiogu O. N., Insolvency Prediction Model of Some Selected Nigerian Banks, International Journal of Statistics and Applications, Vol. 7 No. 1, 2017, pp. 1-11. doi: 10.5923/j.statistics.20170701.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- There are more than one thousand financial companies in Nigeria offering a wide variety option to investors. Given this wide of choice and increasing bad publicity around failed investment companies, financial advisors are facing a daunting task of prudently investing their client’s hard earn money. Thus, models of insolvency prediction that help identify future business failures or financial distress is important tools for advisors. The model may not specifically tell the manager what is wrong, but it should encourage them to identify problems actions to minimize the incidence of failure. A predictor model may warn an auditor of company vulnerability and help protect them against charge of neglect of duties in not disclosing the possibility of insolvency.In this research, “failure” is define as a registered company being liquidated. One of the most significant threats for many businesses today despite their size and the nature of their operations is insolvency. Between 2008 and 2009, large numbers of financial institution failed over the world with devastating economy, social and political consequences. In Nigeria, almost half of the banks have one of distress or the other. Leading causes of corporate failure can be into economic, financial neglect, fraud or disaster (Anderson, 2006) Economic factors including industrial weakness and poor location while financial factors include excessive debt and cash flow problems. One widely accepted method of assessing financial statement is ratio analysis which uses data from the balance sheet and income statement to produce values that have easily interpreted financial meanings. The financial statement analysis and financial ratio believe to have originated in the United States (Horrigan, 2001). The major development that create data are the emergence of the corporation as main organizational form of business enterprise, resulting in the separation of management from ownership and the fast increasing role of financial institution (e.g. banks, investment and insurance companies) as the major suppliers of capital for business expansion requiring formal evaluation of borrowers, credit worthiness, consequently analyzing corporate financial data.The objectives of this study include:a. To construct a neural network for predicting companies’ insolvency and to compare its forecasting capability to that of parametric models.b. To test the reliability of ratio analysis and the application of multiple discriminant analysis.c. To use neural network as a tool for predicting insolvency in the Nigerian financial institutions.The financial service industry in general and the foreign exchange market in particular were severely affected over the years by the unstable environment created by the high and accelerating inflation rapidly growing liquidity, sharply rising market interest rates and the political environment under these condition, financial weak institution proved unable to cope and the ensuring wave of default eroded confidence in the banking sector.According to Agenor et al (2004) an excess liquidity demand function of the excess reserves requirement was a function where bank’s holding of excess liquidity over and above requirement was a function of the excess reserved to deposits lagged by one year. Using patterns of excess liquidity in sub-Saharan Africa, Saxegaard (2006) extended Agenor et al (2004) model by proposing a framework for how a decomposition of excess liquidity can be achieved. Bordo et al (2001) also asserts that crises are an intrinsic part of business cycles and results from shocks to economic fundamentals when the economy goes into recession or depression, asset return are expected to fall.Unegbu and Tasie (2011) tested the efficacy of ‘CPT’ cash flow statement and percentage trend analysis model to identify false financial statement and examined further some relevant literature in an attempt to develop analytical tools for detecting false statement. Henebry (1997) used both cash flow proportional hazard model to test for stability of the model over time. The result indicates that none of the specific formation were stable across different horizon for the same starting date.Martkanen et al (1991) used a time series approach with transformation analysis to predict financial failure. Theodossious (1993) applied sequential procedure to predict a business tendency towards failure, Kumar and Ganeslingam (2001) applied principal component analysis and cluster analysis to predict the financial distress of major companies.Amadasu (2012) in his work bank failure prediction showed the ratio retained earning/total assets are most significant in a failing firm, he also found that working/total assets among others should be closely taken care of.Ibiwoye et al (2012) propose that the insurance industry serves as a medium for fund mobilization. An insolvency prediction model was constructed based on ANN approach which can be used to evaluate the financial capability of insurance companies. Onyeiwu and Alimeke (2012) applied MDA techniques to Nigerian organization to ascertain it ability to effectively discriminate unhealthy organization in Nigeria manufacturing industry. Financial statement was used as instrument for prediction of corporate heath, there was 70% right classification of healthy organization and 80% correct classification of unhealthy organization. Okezie (2011) examined the relationship between capital ratios and bank distress and also compare the efficacy of three ratios as prediction of distress. Ani and Ugbawka (2012) in their study detecting early warning Bank distress signal in Nigerian applied multivariate discriminant analysis model as proposed by Altman in 1968 to group of failed and healthy banks in Nigeria to ascertain if MDA is a veritable tool to predict business failure. The study showed that MDA not only predicts business failure but revealed most important that the warning signals of impending failure become manifested one to two years before the study banks actually failed.Neophyton et al (2000) developed and validate a failure classification model for UK industrial companies using logit analysis and neural network in predicting corporate failure, the result indicates that a parsimonious model that includes three financial variable can yield an overall correct classification accuracy of 83% one year prior to failure.Goss and Vozikis (2010) used neural network on a non-parametric model alternative to past techniques and showed how this methodology more effectively predicts insurer insolvency than parametric models. Chung at; al, (2008) in insolvency prediction model using Multivariate Discriminant Analysis and Artificial Neural network for the financial industry in New Zealand utilized MDA and ANN in their study to create an insolvency prediction model that can effectively predict any future o a finance company in New Zealand. The result indicates that the financial ratios of a field company differs significantly from non-failed companies and that failed company were also less profitable and less liquid and had higher leverage ratio and lower quality assets.
2. Methodology
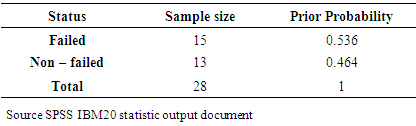
- This study uses secondary data and hypothesis testing to assess the relationships in a pattern of financial ratios of failed and non-failed companies. Data were collected from companies that filed for receivership or failed from (1996-2012) extracted from the Nigerian company financial statements over the accounting period of one year 2012. The various corporate financial statements were collected from their respective website/brochures. Overall data were collected from 15 unknown failed companies and 13 non-failed companies. Data was analyzed using the SPSS statistical software package, R consul and C#.
2.1. Multivariate Discriminant Analysis (MDA)
- Discriminant analysis is a statistical procedure which allows us to classify cases in separate categories to which they belong on the basis of a set of characteristic independent variables called predictors or discriminant variables. The target variable (the one determining allocation into groups) is a qualitative (nominal or ordinal) one, while the characteristics are measured by quantitative variables.For each respondent a score is computed using the estimated linear combination of the predictors (the discriminant function), when the discriminant score is standardized to have zero mean and unity variance it is called Z score.Discriminant analysis characterizes an individual, or a phenomenon, by a vector of variables which constitute a multivariate density function. The discriminant function maps the multidimensional characteristics of the density function of the populations variables into a one-dimensional measure, by forming linear combination (Zavgren 1983). The linear discrimination functions is as follows:
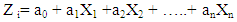 | (1) |
2.2. Artificial Neural Network (ANN)
- An artificial Neural network is a computer algorithm which can be “trained” to imitate the cellular connections in the human brain (Hwertz, Krogh & Palmer 1991). It consist of a large number of interconnected elementary processing units to compute data. The network’s processing results are derived from the collective behavior of its units and are dependent on how the unit interacts with each other (Altman, Marco & Varetto 1994). By processing and evaluating the interactions in a complex set of prior data, a neural network attempts to assign proper weights to the respective input to allow for correct deduction.According to Nelson and Illingworth (1990), there are infinitely many ways to organize a neural network although perhaps only two dozens models are in common usage. A neural network organization can be described in terms of its neurodynamics and architecture. Neuridynamics refers to the properties of an individual artificial neuron that consist of the following:a. Combination of input(s)b. Production of output(s)c. Type of transfer (activation) functions; and d. Weighting schemes, i.e. weight initiation and weight learning algorithm (synapses)Figure 2.1 presents an artificial perception neuron model with n inputs {x1, x2, …., xn} in which each input x1 has an associate synapse wi, and an output y.
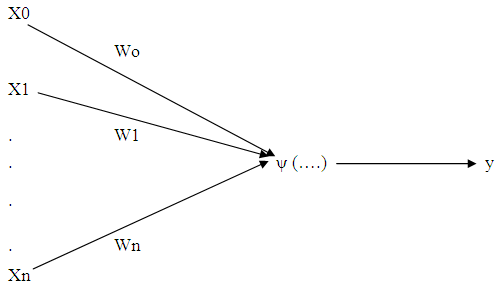 | Figure 2.1. Artificial perception neuron model |
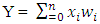 | (2) |
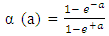 | (3) |
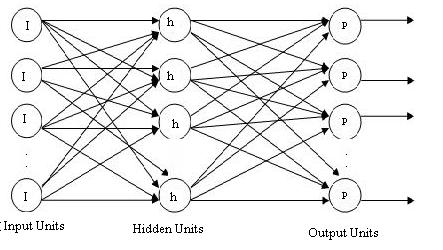 | Figure 2.2. Back propagation model |
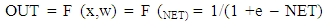 | (4) |
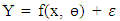 | (5) |
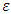 is the random error component. Equation is the known function for estimating and predicting from the available data. As such, the model can be formulated as:
is the random error component. Equation is the known function for estimating and predicting from the available data. As such, the model can be formulated as: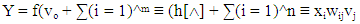 | (6) |
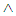 = hidden unit bias (j = i,…..,m)n = number of input unitxi = input vectorwij = weight from input I to hidden unit jvj = weight from hidden j to output (j = 1, ….,m)Learning by gradient descent error minimizationThe perception learning rule is an algorithm that adjusts the network weights Wmn to minimize the difference between the actual outputs yki and the target tki. We can quantify this difference by defining the sum squared error function, summed overall output unit i and all training patterns m:
= hidden unit bias (j = i,…..,m)n = number of input unitxi = input vectorwij = weight from input I to hidden unit jvj = weight from hidden j to output (j = 1, ….,m)Learning by gradient descent error minimizationThe perception learning rule is an algorithm that adjusts the network weights Wmn to minimize the difference between the actual outputs yki and the target tki. We can quantify this difference by defining the sum squared error function, summed overall output unit i and all training patterns m: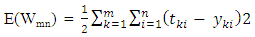 | (7) |
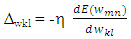 | (8) |
2.3. DA approach Versus ANN as Predictor of Insolvency
- Statisticians are being encouraged to apply and test neural networks (Cheng and Titterrington 1994), Warner as Misra (1996). The neural network used in this paper are artificial in that they are algorithm rather than real neural network, DA is one of the most popular techniques used for analyzing insolvency (Perez 2006). The main advantage of the DA approach to predict corporate failure is its ability to reduce a multidimensional problem to a single score with a high level of accuracy. However, DA is subject to a number of restrictive assumptions. First DA requires the decision set which is used for distinguishing between failed and non failed companies be linearly separable. Second, DA does not allow a ration’s signal to vacillate depending on its relationship with another ratio, or set of ratios (Ticehurst & Veal 2000). In practice, a ratio may signal financial distress if it is higher or lower than normal. These problems together with issues such as, bias of extreme data points, the multivariate assumption of normality and equal group variance, may ensure DA is unsuited to the complex nature, boundaries and interrelationships of financial ratios (Coats & Fant 1993). The advantage of Artificial Neural Network is that they do not require the pre-specification of a functional form, or the adoption of restrictive assumptions about the characteristics of statistical distributions of the variables and errors in the model. By their nature, ANN systems are able to work with imprecise variables and with model changes over time. They are also able to adapt to the appearance of new cases which represent changes in the situation (Altman et al, 1993). However, reviews on the accuracy of neural network are mixed. Nag (1991) observed that while the ANN’s prediction error was less than with multiple regression model, the residual autocorrelations of the neural network were higher, indicating that performance may not necessarily be superior. However, Odom & Sharda (1990), Wilson and Sharda (1994), Atman (1993) and Trippi and Turban (1996) all found ANN to be superior to DA.
3. Analysis and Results
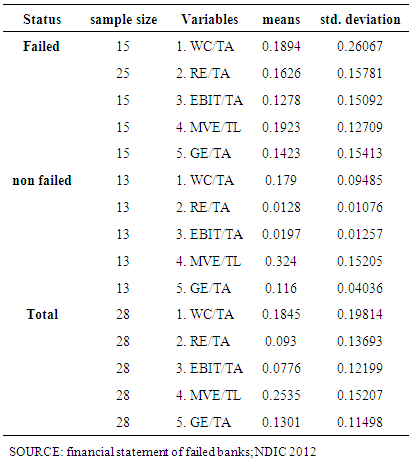
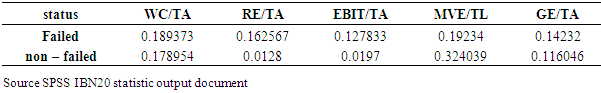
- A basic step for the analysis of the data is the identification of any significant difference between the two groups of the companies (i.e failed and non-failed). This statistics points out some basic characteristics of each group. In this section, we discuss descriptive statistics, discriminant analysis, neural network results and comparison of all results.
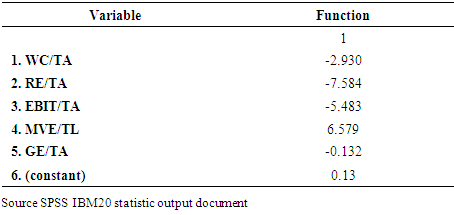
3.1. Discriminant Analysis Output
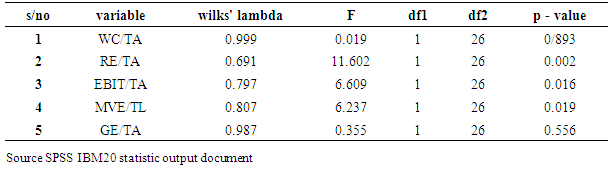
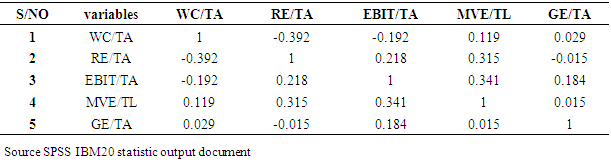
- In discriminant analysis, we try to predict a group membership by examining whether there are any significant differences between groups on each of the independent variables using group means data.
|
|
|
|
|
|
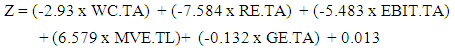 | (9) |
|
|
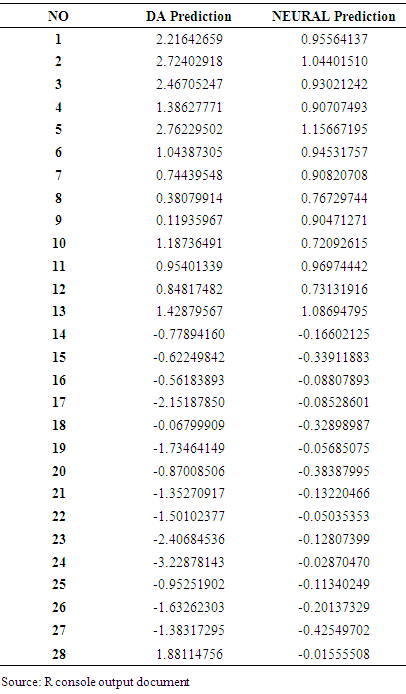
3.2. Neural Network Output (One Hidden Layer)
- The networks considered in this paper are commonly referred to as multi-layer perception, in that they are organized hierarchically into layers of neurons or nodes.Goals is to predict output based on 5 inputsFirst few rows of raw data file are:
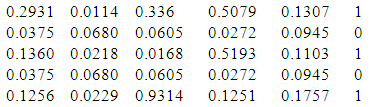 Train and test matrices using a 64.3% 35.7% splitFirst few rows of training matrix are:
Train and test matrices using a 64.3% 35.7% splitFirst few rows of training matrix are: Creating 5 – input 3- hidden 2-output neural networkBest neural network weighs using PSO with cross entropy error final best (smallest) cross entropy error = 0.424Best weights found:
Creating 5 – input 3- hidden 2-output neural networkBest neural network weighs using PSO with cross entropy error final best (smallest) cross entropy error = 0.424Best weights found: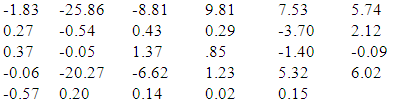
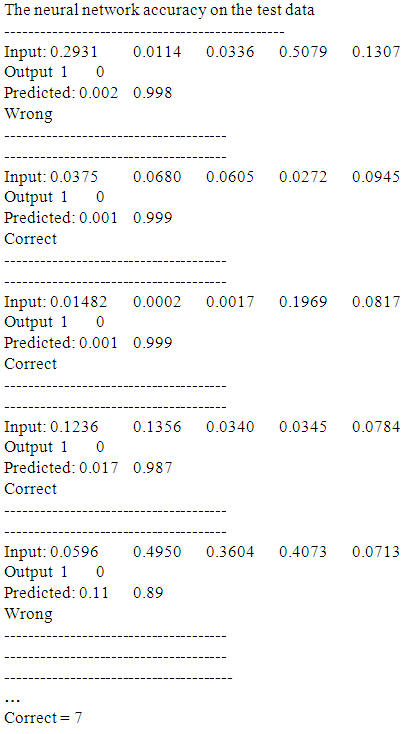

|
|
|
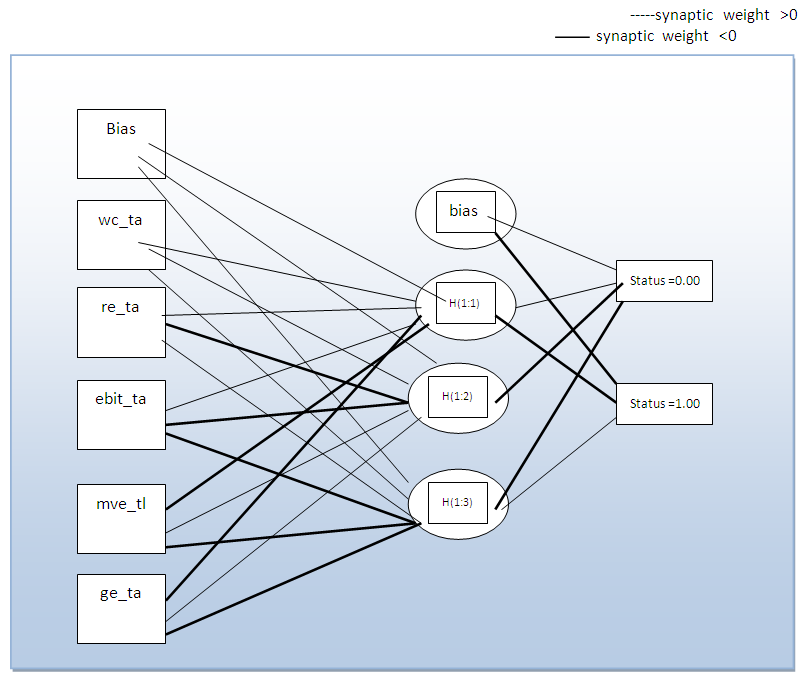 | Figure 2.3. Output layers activation function |
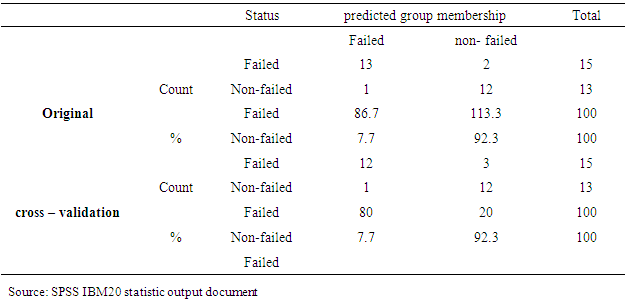
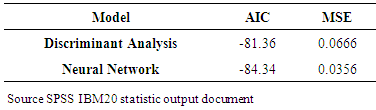
3.3. Comparison of Neural Network and Discriminant Analysis
- This section compares the testing results derived from failure prediction models developed in this study. Table 12 summarizes the results of these methods. As far as the overall correct classification is concerned, NNs were proved to be superior as the highest prediction results to insolvency.
|
|
4. Conclusions
- This study employed financial ratios for differentiating between failed and non-failed financial companies (banks) in Nigeria. These financial variables were derived from the financial statements of failed and non – failed companies. Methodologies adopted include univariate tests, DA and ANN (back propagation algorithm). The univariate test indicates that failed companies’ financial ratios differ significantly from non – failed companies. Failed companies were less profitable and less liquid.The aim of this study is to adopt a model that will accurately predict failure of financial companies; twenty – eight banks constitute the sample of which fifteen have been indicated as failed and thirteen as non – failed. However, using discriminant analysis. It is observed that the banks can be disaggregated into two distinct classes i.e. those with positive predicting score which rightly fall into category of banks that has not been filed for receivership and those with negative score which fall into category of banks that has been indicated by Central Bank of Nigeria. Following categorization, it can be concluded that the predicting score is a useful toll to identify banks with deteriorating conditions in Nigeria.Neural network with their flexible non linear modeling capability without the prior knowledge about the nature of the process do provide more accurate estimates, leading to higher classification rates than other traditional statistical methods. Preliminary findings suggest that satisfactory results (85.7%) accuracy of classification) were achieved with a DA model using those five financial ratios which were found earlier to be effective in predicting insolvency in Nigeria, namely: working capital/total assets retained earnings/total assets, EBIT/total assets and market value of equity/total.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML