-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Statistics and Applications
p-ISSN: 2168-5193 e-ISSN: 2168-5215
2015; 5(5): 181-195
doi:10.5923/j.statistics.20150505.02
Fisher Effect, Structural Breaks and Outliers Detection in ECOWAS Countries
Omorogbe J. Asemota1, Dahiru A. Bala2, Yahaya Haruna3
1Department of Statistics, University of Abuja, Nigeria
2Dept of Econ Engineering, Kyushu University, Japan
3Department of Statistics, University of Abuja
Correspondence to: Omorogbe J. Asemota, Department of Statistics, University of Abuja, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This paper empirically investigates the Fisher effect in selected ECOWAS countries by employing annual data from 1961 to 2011. The inflation and interest rates for Burkina Faso, Cȏte d’Ivoire, Gambia, Ghana, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal and Togo are used in the study. Firstly, we investigate the order of integration of the 16 time series using the augmented Dickey-Fuller (ADF), Phillips-Perron (PP) and the Kwiatkowski-Phillips-Schmidt-Shin (KPSS) unit root tests as a confirmatory test. Our empirical results indicate that inference based on the ADF and the Phillips-Perron test displays a considerable degree of robustness to the method of lag selection and the correction for heteroskedasticity and autocorrelation adopted, however, the robustness of the KPSS test to the method of computation of the long-run variance seems to be weak. On allowing for structural breaks, we found more evidence against the unit root hypothesis. Secondly, the Fisher equation is cast in the state space framework and the Kalman filter is applied to estimate the slope parameter. Our state space model results indicate that the strength of the Fisher effect does vary over time. For the ECOWAS countries; in some periods there appears to be a full Fisher effect, while in other periods, the relationship seems to be partial and non-existing at some other periods. The Harvey-Koopman procedure is also employed to detect the time of structural breaks and outliers in the state space model. We recommend that monetary authorities in the ECOWAS countries should aimed at making effective monetary policies and demonstrate strong commitments to monetary targets in order to strengthen the Fisher relation.
Keywords: Fisher effect, Inflation rates, Interest rates, Kalman filter, Outliers, Structural break
Cite this paper: Omorogbe J. Asemota, Dahiru A. Bala, Yahaya Haruna, Fisher Effect, Structural Breaks and Outliers Detection in ECOWAS Countries, International Journal of Statistics and Applications, Vol. 5 No. 5, 2015, pp. 181-195. doi: 10.5923/j.statistics.20150505.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The Fisher hypothesis postulated by Fisher [1] suggests that when expected inflation rises, nominal interest rate will rise with an equal amount without affecting the real interest rate. This implies that a one-for-one relationship exist between the nominal interest rate and the inflation rate. Asemota and Bala [2] noted that this hypothesis has important policy implications for the behavior of interest rates, efficiency of financial markets and the conduct of monetary policy. The Fisher effect is usually tested by imposing rational expectations on inflation forecasts. This is empirically tested by a regression of the nominal interest rate on a constant and the realized inflation. The closer the coefficient of the inflation rate is to one, the stronger the Fisher effect, if the coefficient is substantially different from one, any change in the nominal interest rates will also change the interest rate and may consequently spread to other macroeconomic variables. Given the important policy implications of the Fisher hypothesis, a large body of research has been devoted to studying the Fisher relation; howbeit, there is no general consensus among researchers on the Fisher hypothesis. Asemota and Bala [2] using the cointegration and Kalman filter approaches could not find evidence of a full Fisher effect for the nominal interest and inflation rates in Nigeria. Also, Engsted [3] and Hatemi-J [4] could not find evidence of the Fisher hypothesis. However, Mishkin [5], Evans and Lewis [6], Wallace and Warner [7], and Crowder and Hoffman [8] found evidence in favour of long-run Fisher effect. Badillo et al. [9] used the panel cointegration approach to analyze the Fisher hypothesis for 15 European Union (EU) countries. The empirical results showed that the coefficient of inflation rate is significantly less than one, which implies the existence of a Partial Fisher effect. Gul and Acikalin [10] using monthly time series could only find evidence of a partial Fisher effect for Turkey. There are several reasons behind the inability to find evidence of a full Fisher effect. Tobin [11] noted that investors re-balance their portfolios in favour of real assets during high inflationary periods. In addition, the different types of interest rates and sample periods used in the empirical analysis may also affect the results. It may also be due to structural changes in the co-integrating vector. Mishkin [5] noted that the relationship between interest rate and inflation, shift with changes in monetary policy regimes. Chuderewics [12] argued that the Central Bank behavior plays an important role in understanding the varying strengths and weakness associated with the Fisher relation. He developed a theoretical model that incorporates Central Bank behavior and demonstrated that the strength of the Fisher relation depends explicitly on its behavior. Recently, more attention has been given to investigations of possible structural breaks in macroeconomic time series. Hatemi-J [4] argued that the inability to find a full Fisher effect may be due to parameter instability. Structural breaks may occur due to financial crises, policy changes, changes in consumers’ preferences and behavior, technological changes and political instability, among others. The aim of this paper is to empirically investigate the Fisher effect in selected ECOWAS1 countries by employing annual data from 1961 to 2011. The inflation and interest rates for Burkina Faso, Cȏte d’Ivoire, Gambia, Ghana, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal and Togo are used in the study. First, we investigate the order of integration of the 16 time series using the augmented Dickey-Fuller (ADF), Phillips-Perron (PP) and the Kwiatkowski-Phillips- Schmidt-Shin (KPSS) unit root tests. We apply different lag selection criteria for the ADF tests and different methods are used for the computation of the long-run variance for PP and KPSS tests. These were conducted to ascertain if inferences based on unit root tests are affected by the method of lag selection and method of constructing heteroskedasticity and autocorrelation consistent (HAC) estimators. In addition, we also conducted unit root tests allowing for one and two endogenous structural breaks. To examine the dynamic relationship between inflation and nominal interest rate, the time varying parameter model is constructed and the Kalman filter estimation method is utilized to estimate and show the varying strength of the response of the interest rates to changes in inflation. Finally, the Harvey-Koopman technique is employed to detect the time of structural breaks and outliers in the constructed models. This is the first attempt in the literature to examine the Fisher effect using Kalman filter methodology in the ECOWAS region and it is aimed at filling an important gap in the empirical literature on developing countries. In addition, the paper is one of the few studies that empirically compare and provide evidence on the performance of the PP and KPSS test when different methods are used in the computation of the long-run variance. The rest of the paper is organized as follows: section 2 describes the methodology. Section 3 presents the data and the empirical findings, and the last section concludes.
2. Econometric Methodology
2.1. Unit Root Tests without Structural Breaks
- It is now a tradition in the field of econometrics to investigate the order of integration of macroeconomic variables prior to modeling the series. This is necessary in order to avoid the problem of spurious regression as first pointed out by Granger and Newbold [13]. Mishkin [5] argued that both inflation and interest rates contain unit roots, hence, the “traditional” forecasting equation suffers from the spurious regression problem, except, if the variables are cointegrated. The augmented Dickey-Fuller (ADF), the Philips-Perron (PP) and the Kwiatkowski– Phillips–Schmidt–Shin (KPSS) tests will be used in this study to examine the order of integration of the 16 macroeconomic variables. The augmented Dickey–Fuller (ADF) test (Dickey and Fuller 1979 [14]) is based on the following model:
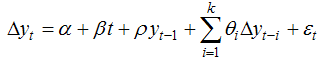 | (1) |
 is a well behaved error tem2;
is a well behaved error tem2;  is the lagged first difference added to correct for serial correlation in the error and the maximum lag
is the lagged first difference added to correct for serial correlation in the error and the maximum lag 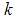 is selected using the Schwartz information criterion (SIC) and the ‘t sig’ approach proposed by Hall [15] and
is selected using the Schwartz information criterion (SIC) and the ‘t sig’ approach proposed by Hall [15] and 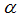 ,
, 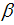 ,
, 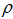 and
and 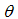 are the parameters to be estimated. Equation (1) tests the null hypothesis of a unit root against a trend stationary alternative. The Philips–Perron [16] method estimates the test equation below:
are the parameters to be estimated. Equation (1) tests the null hypothesis of a unit root against a trend stationary alternative. The Philips–Perron [16] method estimates the test equation below: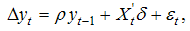 | (2) |
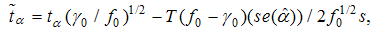 which modifies the Dickey–Fuller test. Where
which modifies the Dickey–Fuller test. Where 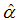 is the estimate,
is the estimate, 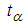 the t–ratio,
the t–ratio, 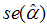 is coefficient standard error, and
is coefficient standard error, and 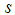 is the standard error of the test regression. Further,
is the standard error of the test regression. Further, 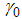 is a consistent estimate of the error variance in (2), while
is a consistent estimate of the error variance in (2), while 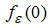 is an estimator of the residual spectrum at frequency zero. The lag window or bandwidth use in the study is estimated by two criteria; the Newey-West criterion (Newey and West, [17]) using the Bartlett kernel and the Andrews criterion (Andrews [18]) using the quadratic spectral kernel. However, Kwiatkowski et al. [19] argued that the classical method of hypothesis testing is biased towards the null hypothesis. Hence, it ensures that the null hypothesis is accepted unless there is strong evidence against it. They pointed out that the standard unit root tests are not very powerful against relevant alternatives; see (Kwiatkowski et al. [19], pg. 160). To circumvent this problem, KPSS [19] proposed a test of the null hypothesis that a series is stationary around a deterministic trend. They concluded that by testing both the unit root null hypothesis and the stationarity null hypothesis, researchers can distinguish series that appear to be stationary, those that appear to have a unit root, and those that the data (or the tests) are not sufficiently informative to decide whether they are stationary or integrated. The KPSS test is given by the following equations:
is an estimator of the residual spectrum at frequency zero. The lag window or bandwidth use in the study is estimated by two criteria; the Newey-West criterion (Newey and West, [17]) using the Bartlett kernel and the Andrews criterion (Andrews [18]) using the quadratic spectral kernel. However, Kwiatkowski et al. [19] argued that the classical method of hypothesis testing is biased towards the null hypothesis. Hence, it ensures that the null hypothesis is accepted unless there is strong evidence against it. They pointed out that the standard unit root tests are not very powerful against relevant alternatives; see (Kwiatkowski et al. [19], pg. 160). To circumvent this problem, KPSS [19] proposed a test of the null hypothesis that a series is stationary around a deterministic trend. They concluded that by testing both the unit root null hypothesis and the stationarity null hypothesis, researchers can distinguish series that appear to be stationary, those that appear to have a unit root, and those that the data (or the tests) are not sufficiently informative to decide whether they are stationary or integrated. The KPSS test is given by the following equations: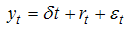 | (3) |
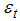 is a stationary error and
is a stationary error and 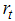 is a random walk given by:
is a random walk given by: | (4) |
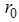 is treated as fixed and serves as the intercept in the model and the null hypothesis of stationarity is formulated as
is treated as fixed and serves as the intercept in the model and the null hypothesis of stationarity is formulated as 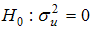 or
or 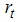 is constant. The LM statistic is given by:
is constant. The LM statistic is given by: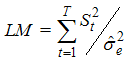 | (5) |
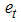 are residuals from the regression of
are residuals from the regression of 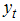 on an intercept and time trend,
on an intercept and time trend, 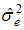 is the estimate of the error variance of the regression and
is the estimate of the error variance of the regression and 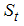 is the partial sum of
is the partial sum of 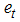 defined by:
defined by: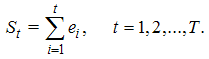 | (6) |
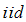 the estimator
the estimator 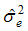 converges to
converges to 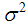 , however, when the errors are not
, however, when the errors are not 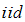 , a consistent estimator of the long-run variance
, a consistent estimator of the long-run variance 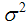 is given by:
is given by: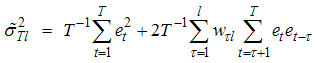 | (7) |
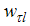 is an optimal weighting function that corresponds to the choice of a spectral window. KPSS use the Bartlett window suggested by Newey and West [17]. The modification is given by:
is an optimal weighting function that corresponds to the choice of a spectral window. KPSS use the Bartlett window suggested by Newey and West [17]. The modification is given by: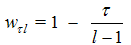 | (8) |
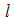 that is used in the computation of the
that is used in the computation of the 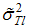 . Hence, in this paper, we also consider Andrews’ [18] quadratic spectral kernel in the computation of the long-run variance to ascertain the degree of sensitivity of the KPSS test to the different method of computation of heteroskedasticity and autocorrelation consistent long-run variance.
. Hence, in this paper, we also consider Andrews’ [18] quadratic spectral kernel in the computation of the long-run variance to ascertain the degree of sensitivity of the KPSS test to the different method of computation of heteroskedasticity and autocorrelation consistent long-run variance. 2.2. Unit Root Tests with Structural Break
2.2.1. Zivot-Andrews Unit Root with one Structural Break Test
- Starting with the pioneer work of Perron [21], it has been proved that conventional unit root tests are biased towards the non-rejection of the unit root null hypothesis even if the data are stationary with structural break(s). Perron [21] incorporated dummy variables in the ADF test to account for one exogenous structural break. However, this exogenous imposition of break date has been criticized by Christiano [22] and Zivot-Andrews [23]. Zivot-Andrews [23] proposed a data dependent algorithm to determine the breakpoint. The Zivot-Andrews test is carried out using the following regression equations:Model A (Crash Model):
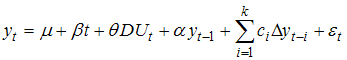 | (9) |
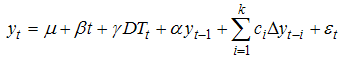 | (10) |
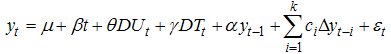 | (11) |
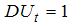 if
if 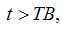 0 otherwise;
0 otherwise; 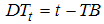 if
if 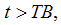 0 otherwise,
0 otherwise, 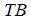 is the date of the endogenously determined break. Model A, referred to as the “crash model” allows for a one-time change in the intercept of the trend function, model B, referred to as the “changing growth model” allows for a single change in the slope of the trend function without any change in the level; and model C, the “mixed model” allows for both effects to take place simultaneously, i.e., a sudden change in the level followed by a different growth path. 3 The null hypothesis for the three models is that the series is integrated (unit root) without structural breaks (α = 1). The test statistic is the minimum “
is the date of the endogenously determined break. Model A, referred to as the “crash model” allows for a one-time change in the intercept of the trend function, model B, referred to as the “changing growth model” allows for a single change in the slope of the trend function without any change in the level; and model C, the “mixed model” allows for both effects to take place simultaneously, i.e., a sudden change in the level followed by a different growth path. 3 The null hypothesis for the three models is that the series is integrated (unit root) without structural breaks (α = 1). The test statistic is the minimum “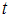 ” over all possible break dates in the sample. Zivot-Andrews [23] suggested using a trimming region of (0.10T, 0.90T) to eliminate endpoints.
” over all possible break dates in the sample. Zivot-Andrews [23] suggested using a trimming region of (0.10T, 0.90T) to eliminate endpoints. 2.2.2. Lagrange Multiplier (LM) unit Root Test with Structural Breaks
- Lee and Strazicich [25] argued that the Zivot-Andrews test omit the possibility of unit root with break. Hence, researchers may incorrectly conclude that a time series is stationary with breaks when in fact the series is nonstationary with break(s). To circumvent this problem, they proposed the minimum LM unit root test in which the alternative hypothesis unambiguously implies trend stationarity. The LM unit root test can be explained using the following data-generating process (DGP):
 | (12) |
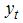 is the observed time series,
is the observed time series, 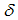 is a vector of coefficients,
is a vector of coefficients, 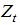 is a vector of exogenous variables and
is a vector of exogenous variables and 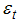 is a well-behaved error term. Corresponding to the two-break equivalent of Perron’s [21] Model C, with two changes in the level and the trend,
is a well-behaved error term. Corresponding to the two-break equivalent of Perron’s [21] Model C, with two changes in the level and the trend, 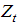 is defined by
is defined by 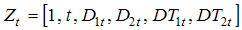 to allow for a constant term, linear time trend, and two structural breaks in level and trend.4 Under the alternative hypothesis, the
to allow for a constant term, linear time trend, and two structural breaks in level and trend.4 Under the alternative hypothesis, the 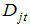 terms describe an intercept shift in the deterministic trend, where
terms describe an intercept shift in the deterministic trend, where 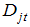 = 1 for
= 1 for 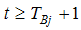 ,
, 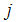 = 1, 2, and 0 otherwise;
= 1, 2, and 0 otherwise; 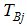 denotes the time period when a break occurs and
denotes the time period when a break occurs and 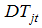 describes a change in slope of the deterministic trend, where
describes a change in slope of the deterministic trend, where 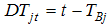 for
for 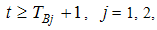 and 0 otherwise. Note that the DGP includes breaks under the null
and 0 otherwise. Note that the DGP includes breaks under the null 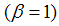 and alternative
and alternative 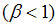 hypothesis in a consistent manner. Lee and Strazicich [25] used the following regression to obtain the LM unit root test statistic:
hypothesis in a consistent manner. Lee and Strazicich [25] used the following regression to obtain the LM unit root test statistic: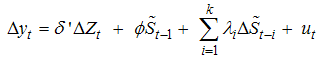 | (13) |
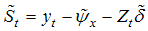 ,
, 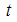 = 2, … ,
= 2, … , 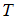 is a de-trended series;
is a de-trended series; 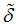 are coefficients in the regression of
are coefficients in the regression of 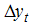 on
on 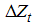 ;
; 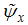 is given by
is given by 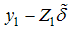 ;
; 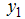 and
and 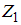 denote the first observations of
denote the first observations of 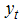 and
and 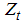 respectively. Vougas [27] has shown that the LM type test using the above optimal de-trending device is more powerful and finds more evidence in favor of trend stationary than the ADF type test.
respectively. Vougas [27] has shown that the LM type test using the above optimal de-trending device is more powerful and finds more evidence in favor of trend stationary than the ADF type test. 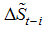 ,
, 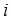 = 1, …,
= 1, …, 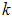 terms are included as necessary to correct for serial correction. Note that the test regression (12) involves
terms are included as necessary to correct for serial correction. Note that the test regression (12) involves 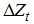 instead of
instead of 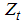 so that
so that 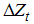 becomes
becomes 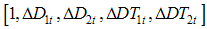 . The unit root null hypothesis is described by
. The unit root null hypothesis is described by 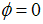 , and the LM test statistics are given by:
, and the LM test statistics are given by: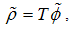 | (13a) |
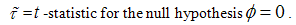 | (13b) |
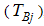 , the minimum LM unit root test uses a grid search as follows:
, the minimum LM unit root test uses a grid search as follows: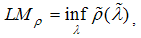 | (14a) |
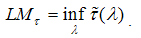 | (14b) |
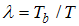 , and
, and 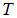 is the sample size. Vougas [27] indicated that in the application of LM test, the studentized version
is the sample size. Vougas [27] indicated that in the application of LM test, the studentized version 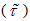 takes into account the variability of the estimated coefficients and is more powerful than the coefficient test
takes into account the variability of the estimated coefficients and is more powerful than the coefficient test 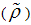 . The breakpoints are determined to be where the test statistic is minimized. As is typical in endogenous break test, we use a trimming region of (0.15T, 0.85T) to eliminate endpoints. Critical values are tabulated in Lee and Strazicich [25].
. The breakpoints are determined to be where the test statistic is minimized. As is typical in endogenous break test, we use a trimming region of (0.15T, 0.85T) to eliminate endpoints. Critical values are tabulated in Lee and Strazicich [25].2.3. The State Space Model
- The Fisher effect is usually investigated by regressing the nominal interest rate on a constant and the realized inflation rate. The value of the coefficient on the inflation rate provides a measure of the Fisher effect. The closer the value of the coefficient is to one, the stronger the Fisher effect. The Fisher effect is usually represented by the following equation:
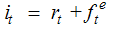 | (15) |
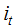 is the nominal interest rate,
is the nominal interest rate, 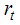 is the ex-ante real rate of interest and
is the ex-ante real rate of interest and 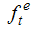 is the expected inflation rate. Assuming rational expectations on the inflation forecasts implies that;
is the expected inflation rate. Assuming rational expectations on the inflation forecasts implies that;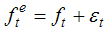 | (16) |
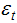 the forecast error is white noise. Hence, the regression equation for Fisher effect is:
the forecast error is white noise. Hence, the regression equation for Fisher effect is: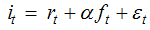 | (17) |
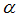 to one. If
to one. If 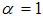 in equation (17), we have the full Fisher effect, however, if
in equation (17), we have the full Fisher effect, however, if 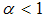 it is known as the partial Fisher effect. The specification in (17) above assumes that the
it is known as the partial Fisher effect. The specification in (17) above assumes that the 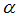 coefficient is constant throughout the time under investigation. This specification may be spurious especially in economic and business applications where the level of randomness is high, and also where the constancy of patterns or parameters cannot be guaranteed. In addition, the monetary policy behavior of the central banks is not constant through time. Thus, to capture the dynamic economic environment and the evolving policy behavior, a more flexible model that allows the parameter to vary randomly over time is adopted. This flexible model is popularly referred to as the time varying parameter model. The state space representation of (17) as a time varying parameter model is given as:
coefficient is constant throughout the time under investigation. This specification may be spurious especially in economic and business applications where the level of randomness is high, and also where the constancy of patterns or parameters cannot be guaranteed. In addition, the monetary policy behavior of the central banks is not constant through time. Thus, to capture the dynamic economic environment and the evolving policy behavior, a more flexible model that allows the parameter to vary randomly over time is adopted. This flexible model is popularly referred to as the time varying parameter model. The state space representation of (17) as a time varying parameter model is given as: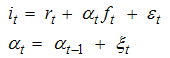 | (18) |
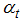 ), while the transition equation describes the evolution of the state variable. The observation error
), while the transition equation describes the evolution of the state variable. The observation error 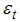 and state error
and state error 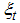 are assumed to be Gaussian white noise (GWN) sequences. The overall objective of state space analysis is to study the evolution of the state (
are assumed to be Gaussian white noise (GWN) sequences. The overall objective of state space analysis is to study the evolution of the state (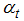 ) over time using observed data. When a model is cast in a state space form, the Kalman filter is applied to make statistical inference about the model. The Kalman filter (hereafter, KF) is simply a recursive statistical algorithm for carrying out computations in a state space model. A more accurate estimate of the state vector or slope coefficient can be obtained via Kalman Smoothing (K.S). The unknown variance parameters (
) over time using observed data. When a model is cast in a state space form, the Kalman filter is applied to make statistical inference about the model. The Kalman filter (hereafter, KF) is simply a recursive statistical algorithm for carrying out computations in a state space model. A more accurate estimate of the state vector or slope coefficient can be obtained via Kalman Smoothing (K.S). The unknown variance parameters (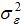 and
and 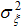 ) in model 12 are estimated by the maximum likelihood estimation via the Kalman filter prediction error decomposition initialized with the exact initial Kalman filter. Harvey and Koopman [28] demonstrated that the auxiliary residuals in the state space model can be very informative in detecting outliers and structural change in the model. For a complete exposition of the state space model and Kalman filter, see Durbin and Koopman [29] and Hamilton [30].
) in model 12 are estimated by the maximum likelihood estimation via the Kalman filter prediction error decomposition initialized with the exact initial Kalman filter. Harvey and Koopman [28] demonstrated that the auxiliary residuals in the state space model can be very informative in detecting outliers and structural change in the model. For a complete exposition of the state space model and Kalman filter, see Durbin and Koopman [29] and Hamilton [30].3. Data, Results and Discussion
3.1. The Data
- The data used in this study are obtained from the International Financial Statistics (IFS) database CD-ROM (June, 2012). We utilize annual inflation and nominal interest rates data of ECOWAS countries over the time period of 1961-2011 depending on data availability.5 A time series plot of the series for the different countries is depicted in figure 1.
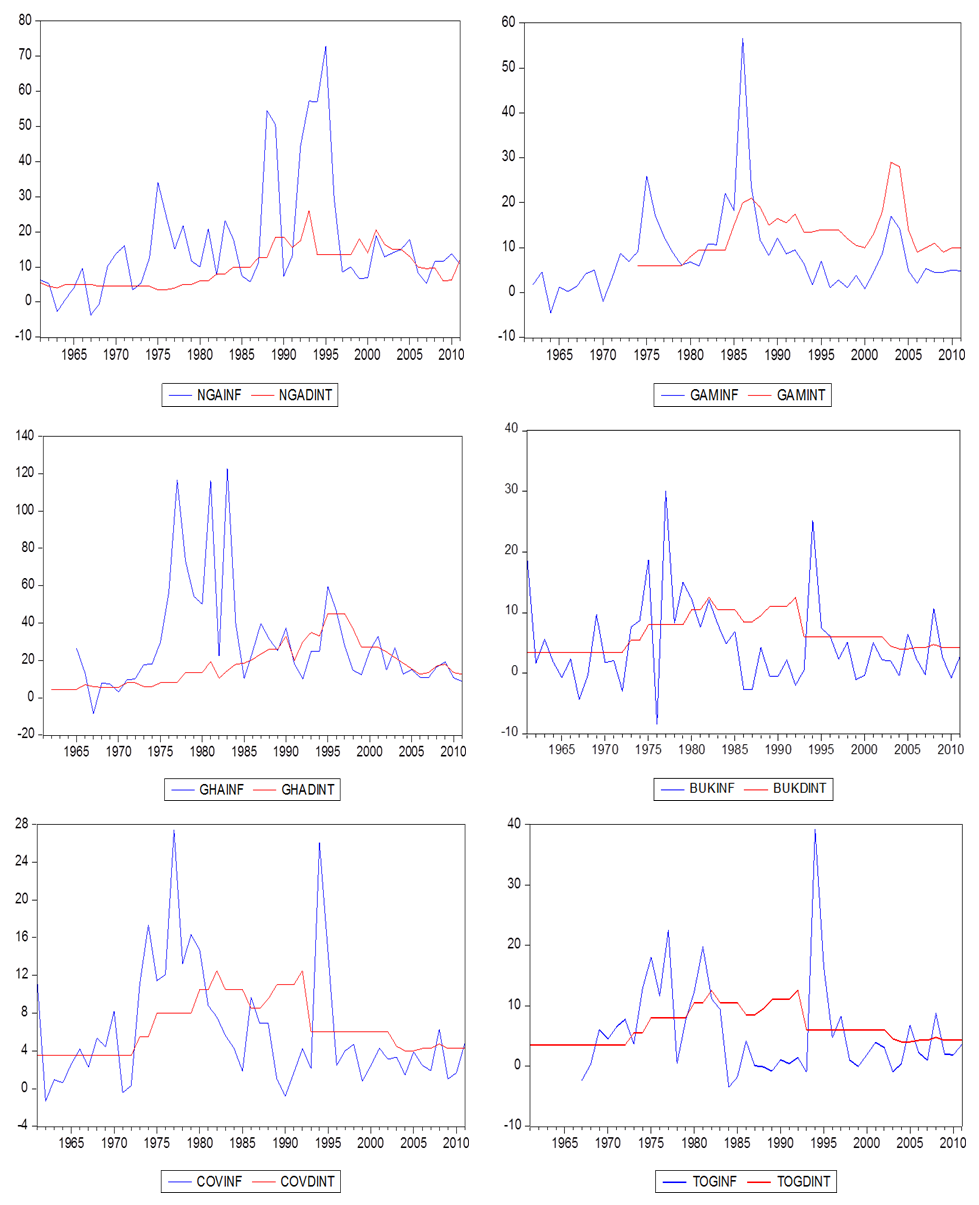 | Figure 1. Time Series Plots of Inflation and Interest Rates for the ECOWAS countries |
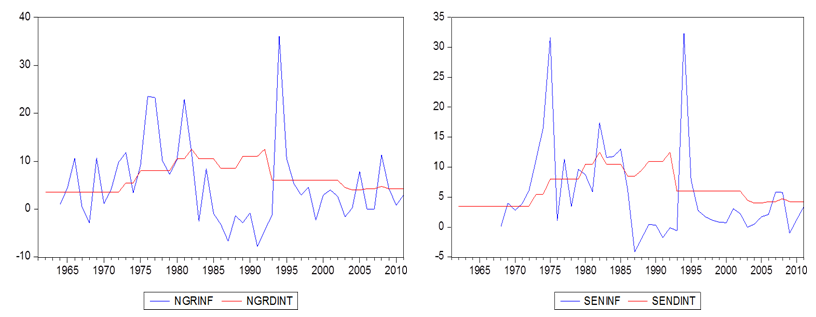 | Figure 1. Continued |
3.2. Unit Root with and without Structural Breaks Tests Results
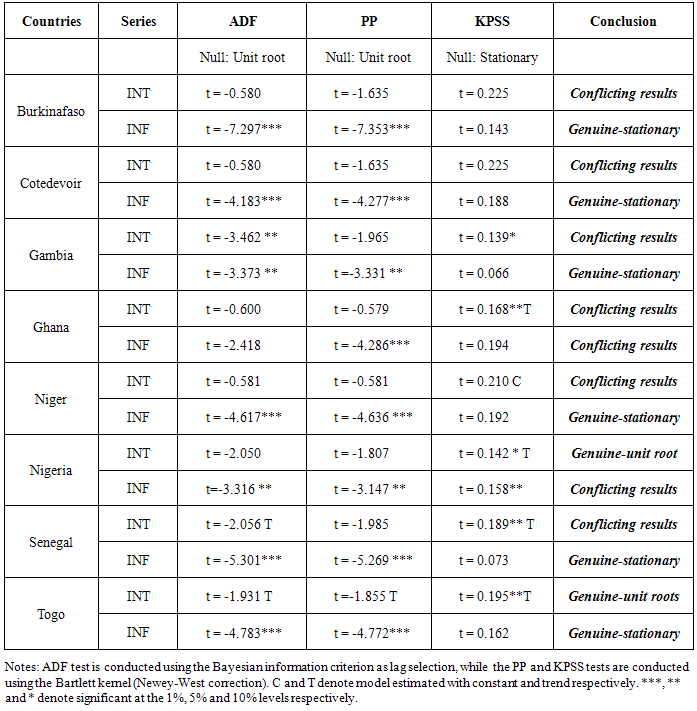
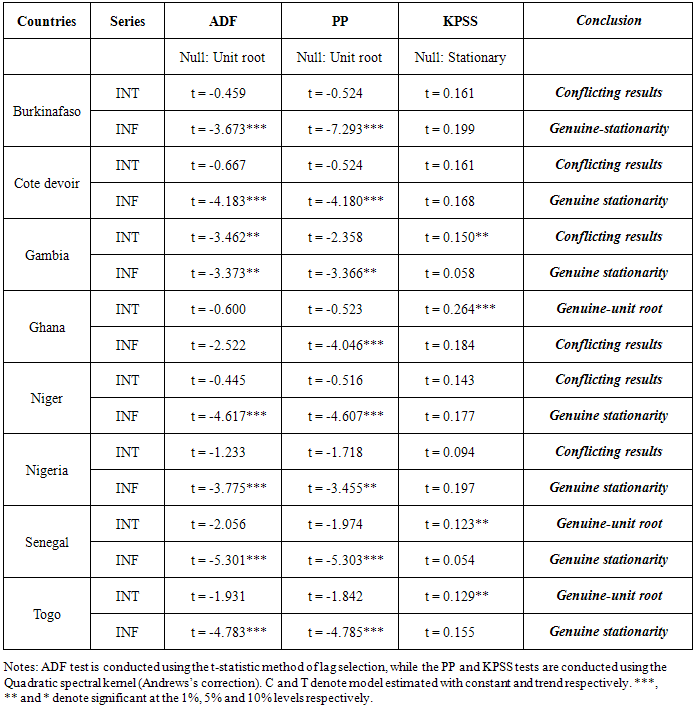
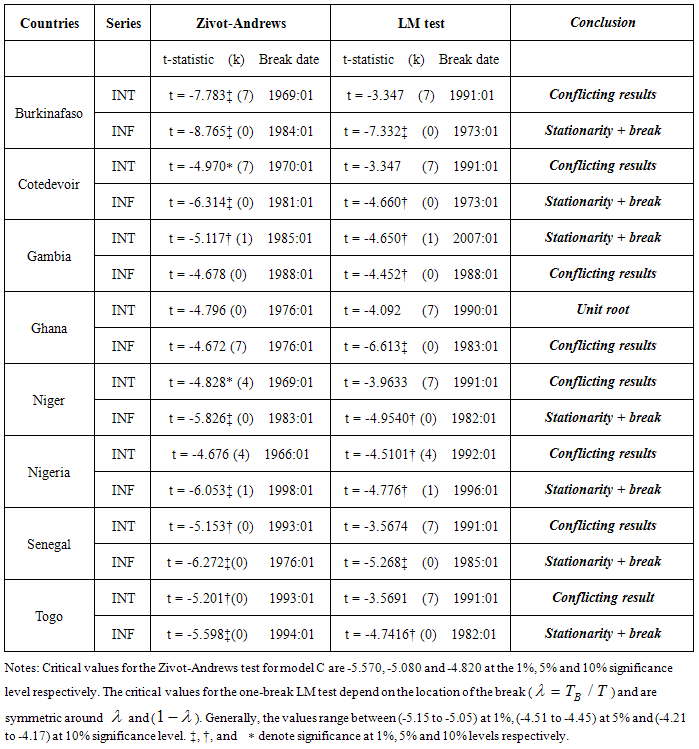
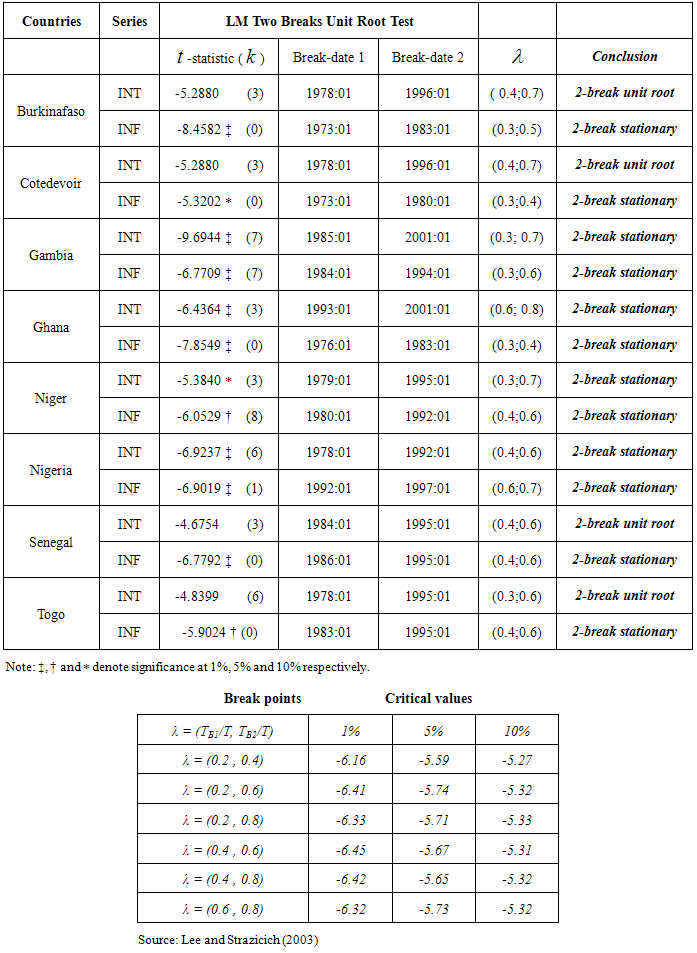
- It has now become standard practice in time series analysis to investigate the order of integration of the series prior to its statistical modeling. In the econometric literature, the augmented Dickey-Fuller test is most commonly used to ascertain the order of integration of the time series data. In addition, we also apply the Phillips-Perron [16] and the Kwaitkowski et al. [19] tests to the series while varying the method of lag selection (for the ADF test) and the method of correction for autocorrelation and heteroskedasticity (PP and KPSS tests). The conventional unit root tests (ADF, PP and KPSS) that do not allow for the possibility of structural breaks have been proven to be biased towards the non-rejection of the null hypothesis. Hence, we also apply the one-break and two-break unit root tests. The results are provided in the table 1.
|
|
|
|
3.3. The State Space Model Estimation Results
- We employed the time varying parameter techniques to capture the behavior of interest rates to changes in the inflation rates over time. The relationship is examined in the state space framework and the Kalman algorithm is apply to assess if this relationship is stable through time. Prior to Kalman filtering and smoothing, we estimate the unknown variance parameter of the model using the maximum likelihood method maximized by the BFGS (Broyden-Fletcher-Goldfarb-Shannon) method. After estimating the unknown variances, the Kalman filter technique is applied to estimate the time path of the parameter of interest (Fisher coefficient). The Kalman filter estimate of the behavior of the parameter is depicted in figure 2.
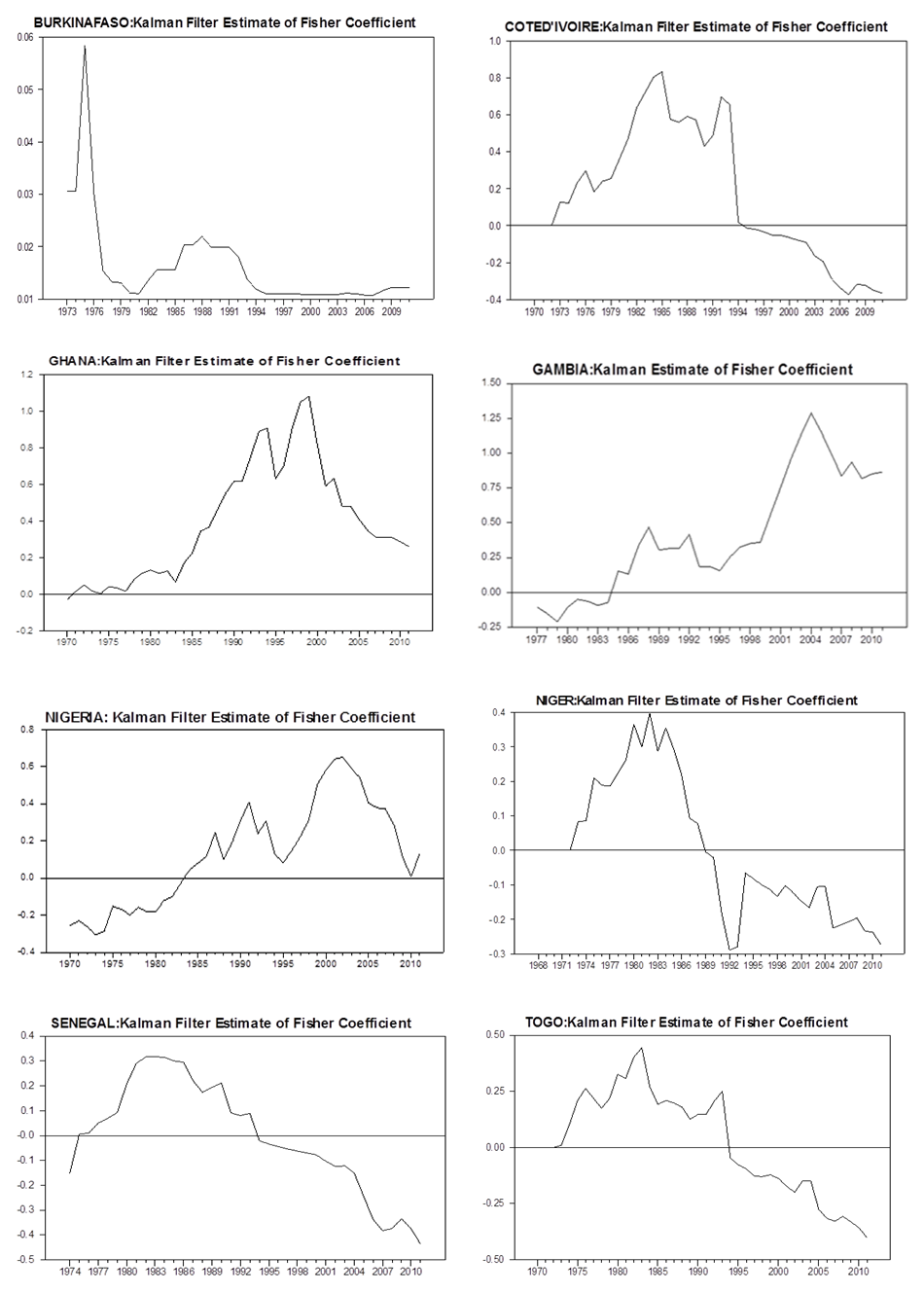 | Figure 2. Kalman Filter Estimate of the Fisher Coefficient for the ECOWAS Countries |
3.4. Structural Breaks and Outliers Detection Results
- We exploit the capability of the state space model in detecting the time of structural breaks and outliers. Harvey and Koopman [28] demonstrated that auxiliary residuals in state space models are potentially useful not only for detecting outliers and structural breaks but for distinguishing between them. The auxiliary residuals are estimators of the disturbances associated with the unobserved components. The detection strategy is to plot the standardized residuals. In a Gaussian model, indicators of outliers and structural breaks arise for values greater than 2 in absolute value. We apply this procedure to the standardized observation equation residuals and the state equation residuals in (18) to detect outliers and time of structural breaks respectively. The plots are presented in Figure 3.
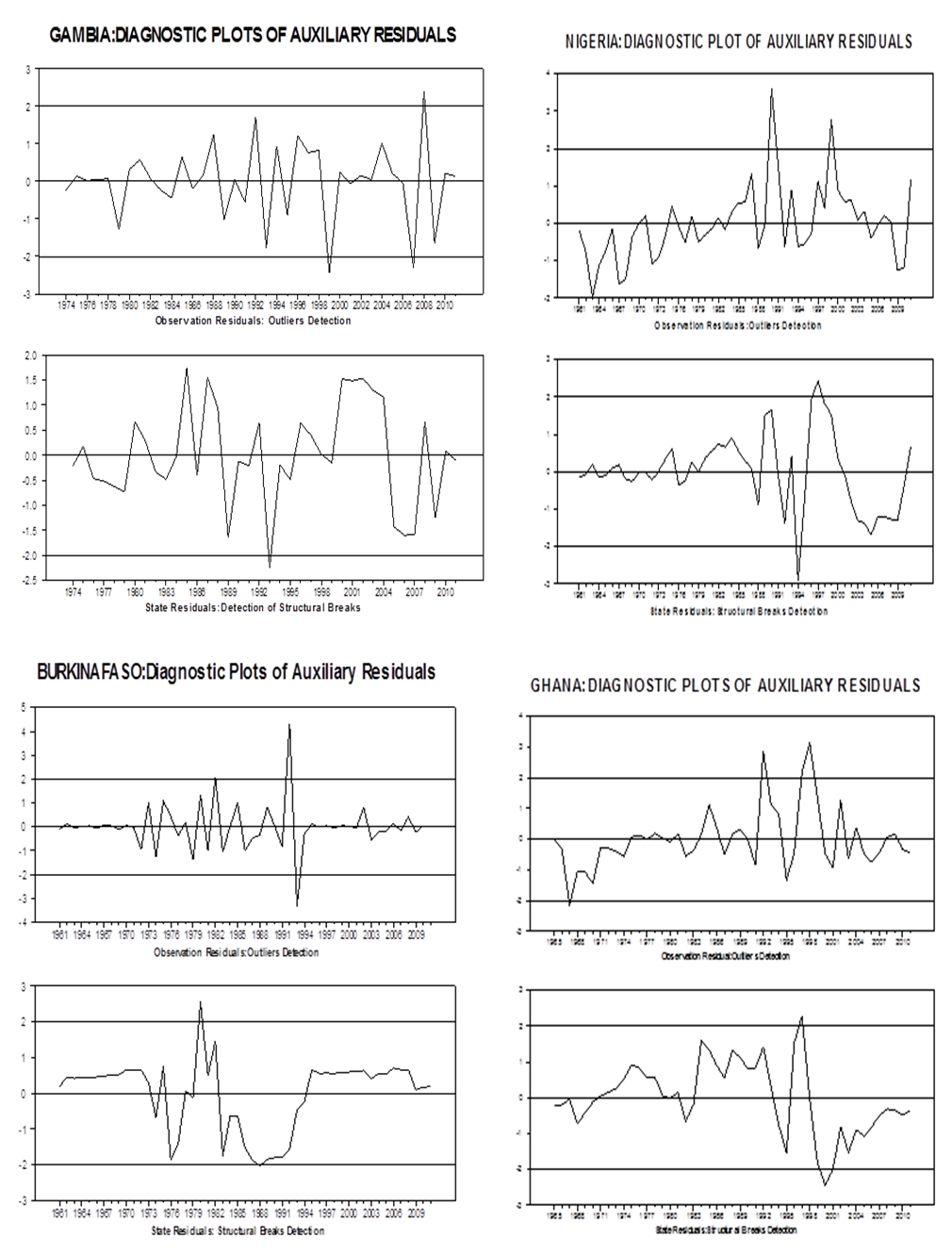 | Figure 3. Detecting Outliers and Structural Breaks |
4. Conclusions
- This paper empirically investigates a fundamental relationship in macroeconomics: the relationship between interest and inflation rates. The fundamental issue addressed in this paper is whether this relationship is stable over time for ECOWAS countries. The inflation and interest rates for Burkina Faso, Cȏte d’Ivoire, Gambia, Ghana, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal and Togo are used in the study. First, we investigate the order of integration of the 16 time series using the augmented Dickey-Fuller (ADF), Phillips-Perron (PP) and the Kwiatkowski-Phillips-Schmidt-Shin (KPSS) unit root tests as a confirmatory test. Using the BIC as the lag selection criteria for the ADF test and the Bartlett kernel for the computation of the covariance matrix for both the PP and KPSS, the results yield 8 cases of conflicting results, 6 cases of genuine-stationarity and 2 cases of genuine-unit roots. When the
 -statistic is used for the selection of the lag order for the ADF test and the Quadratic Spectral kernel is used for the PP and KPSS, the test results indicate 6 cases of conflicting results, 7 cases of genuine-stationarity and 3 cases of genuine-unit roots. This indicates that inference based on unit root tests may be affected by the method of lag selection and method of constructing heteroskedasticity and autocorrelation consistent (HAC) estimators. We also conduct unit root tests allowing for one and two structural breaks. On allowing for structural breaks, the unit root hypothesis is rejected for 12 out of the 16 series considered in the study. Secondly, the Fisher equation is cast in the state space form and the Kalman filter is apply to estimate the slope parameter. Our results indicate that the strength of the Fisher effect does vary over time. Specifically, for the ECOWAS countries; in some periods there appears to be a strong relationship between the interest and inflation rates (full Fisher effect), while in other periods, the relationship seems to be weak (partial Fisher effect) and non-existing at some other periods. Using the Harvey-Koopman procedure, we detect the time of structural breaks and outliers in our model. Finally, we recommend that monetary authorities in the ECOWAS countries should aimed at making effective monetary policies and demonstrate strong commitments to monetary targets in order to strengthen the Fisher relation.
-statistic is used for the selection of the lag order for the ADF test and the Quadratic Spectral kernel is used for the PP and KPSS, the test results indicate 6 cases of conflicting results, 7 cases of genuine-stationarity and 3 cases of genuine-unit roots. This indicates that inference based on unit root tests may be affected by the method of lag selection and method of constructing heteroskedasticity and autocorrelation consistent (HAC) estimators. We also conduct unit root tests allowing for one and two structural breaks. On allowing for structural breaks, the unit root hypothesis is rejected for 12 out of the 16 series considered in the study. Secondly, the Fisher equation is cast in the state space form and the Kalman filter is apply to estimate the slope parameter. Our results indicate that the strength of the Fisher effect does vary over time. Specifically, for the ECOWAS countries; in some periods there appears to be a strong relationship between the interest and inflation rates (full Fisher effect), while in other periods, the relationship seems to be weak (partial Fisher effect) and non-existing at some other periods. Using the Harvey-Koopman procedure, we detect the time of structural breaks and outliers in our model. Finally, we recommend that monetary authorities in the ECOWAS countries should aimed at making effective monetary policies and demonstrate strong commitments to monetary targets in order to strengthen the Fisher relation.ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- We thank Professor Peter C. B. Phillips, Felix Chan and other participants at the New Zealand Econometric Study Group Meeting 2013 for their helpful comments when this paper was first presented at the New Zealand Econometric Society Conference. The usual disclaimer applies.
Notes
- 1. ECOWAS is an acronym for Economic Community of West African States. It is a regional group of fifteen countries founded in May 28, 1975 to promote cooperation and integration, with a view to establishing an economic and monetary union as a means of stimulating economic growth and development in West Africa. 2. The error term is said to be well–behaved if it is independently and identically normally distributed.3. Perron [21] suggest that most macroeconomic time series can be adequately modeled using either model A or model C. In addition, Sen [24] argued that if one assumes that the location of the break is unknown, it is most likely that the form of the break will be unknown as well. Sen [24] demonstrated that the loss in power is quite negligible if the mixed model specification is used when in fact that the break occurs according to the crash model or changing growth model, and concluded that practitioners should specify the mixed model in empirical applications. Hence, we used model C in our empirical analysis. 4. Lee et al. [26] noted that there are technical difficulties in obtaining relevant asymptotic distributions and the corresponding critical values of endogenous test with three or more breaks.5. The inflation and interest rates for Burkina Faso, Cȏte d’Ivoire, Gambia, Ghana, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal and Togo are used in the study. The other ECOWAS countries are omitted from the study because the data available on their inflation and interest rates are too scanty to be included in the analysis.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML