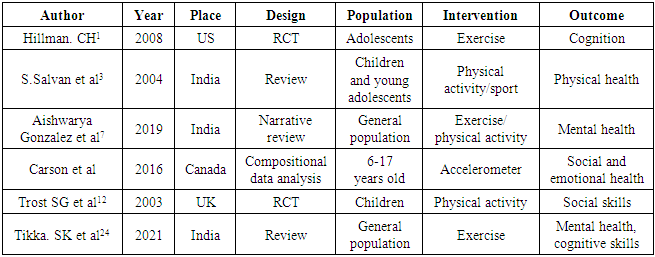
-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Sports Science
p-ISSN: 2169-8759 e-ISSN: 2169-8791
2023; 13(2): 29-35
doi:10.5923/j.sports.20231302.02
Received: May 2, 2023; Accepted: May 22, 2023; Published: May 27, 2023

Sports Participation, Physical Activity and Their Correlation with Sports Development Theories in Adolescents: A Systematic Review
Zeinia Samar
Sports Science, Olympic Gold Quest, New Delhi, India (IAP)
Correspondence to: Zeinia Samar, Sports Science, Olympic Gold Quest, New Delhi, India (IAP).
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Physical activity and Sports in adolescents is an integral part of incorporating a healthy lifestyle and promote sports participation. In this study, we have analysed cultural, social and political nuances and present evidence-based case studies from local context as well as from global perspective in the capacity of this topic and demonstrate initiative in exploring the global Sports-development policies and strategies and to explore alternative approaches to the issues. This article have established various challenges in awareness and implementation of physical activity in adolescents, barriers in sports participation and have also proposed measures to promote physical activity and sports participation in Adolescents. Author have also co-related various Sports-development theories and SD Models related to these issues and their applicability to National/International context within the scope of this subject.
Keywords: Physical activity, Sports, Exercise, Health, Adolescents, Lifestyle, Sport development models, Sports participation, Sports policy
Cite this paper: Zeinia Samar, Sports Participation, Physical Activity and Their Correlation with Sports Development Theories in Adolescents: A Systematic Review, International Journal of Sports Science, Vol. 13 No. 2, 2023, pp. 29-35. doi: 10.5923/j.sports.20231302.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- A growing number of studies support the idea that physical exercise is a lifestyle factor that might lead to increased physical and mental health throughout life. As per WHO, globally, 81% of adolescents aged 11-17 years were insufficiently physically active in 2016. Adolescent girls were less active than adolescent boys, with 85% vs. 78% not meeting WHO recommendations of at least 60 minutes of moderate to vigorous intensity physical activity per day. Bergeron et al [1] suggests that engaging in regular physical activity can help prevent chronic disease and enhance quality of life. Hillman et al [2] studied that lack of physical activity, particularly among children in the developed world, is one of the major causes of obesity. They also suggested that exercise might not only help to improve their physical health, but might also improve their academic performance.Selvan et al [3] suggests that a focus on children and young adolescents in the primary prevention of health risks and disorders such as cancer, hypertension and other cardiovascular diseases, HIV/AIDS, and obesity has been suggested in many reports published throughout the world. WHO suggests that increased levels of physical inactivity have negative impacts on health systems, the environment, economic development, community well-being and quality of life. As per Australian Sports Commission, between the ages of 13 to 17 years a significant number of young people stop playing organised sport. This includes in secondary schools.
 | Figure 1. Importance of physical activity in 15-18yrs old: WHO recommendation |
2. Methods
- The author has done a literature review on the subject. The research objective is to identify the importance of physical activity and sports in adolescents.
2.1. Source of Data
- For this review, a search was carried out in the PubMed/Medline, Google Scholar, Embase, Scielo, and Cochrane databases, of studies published between August 2013 and October 2022. The bibliographic search strategy was based on the combination of the independent variable (physical activity/physical exercise/sports), dependent variable (weight–height growth) and the population of interest (schoolchildren, adolescents). The combination of Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) was used to generate the list of terms for the search. The following keywords were used: “physical activity” OR “physical exercise” OR “resistance training” OR “strength training” OR “sports” OR “athlete” AND “physical growth” OR “children” OR “school children” OR “preschool children” OR “teenage” OR “adolescent”.Articles that presented a study with some type of physical activity and its corelation with health, fitness and lifestyle involving the adolescents were included. Studies with different designs (cross-sectional, case–control, cohort, clinical trials, and review studies) were included in the review. Searches were performed in 2022 and the inclusion criteria specified review articles reporting physical activity or sport and health or lifestyle outcomes that included cognitive abilities, school achievements, mental health, decreased rate of illness etc. The exclusion criteria were: studies in which the intervention with physical activity was associated with another intervention (diet, medication or other types) or with a population of children or adolescents with some type of disease. The methodological quality of the selected studies was assessed by the author using the CONSORT, STROBE, and PRISMA guidelines for clinical trials, observational studies, and systematic reviews, respectively. Articles were sourced from online databases including PubMed, ScienceDirect, Cochrane Database, PsycINFO and Google Scholar.
2.2. Synthesis of Data
- A total of 1134 studies retrieved after the search carried out using the search terms were screened by reading the summary. After excluding the duplicate studies and applying the inclusion criteria, a total of 73 studies were selected, which were read in full and analysed. Of these, 41 were excluded because physical activity was associated with another intervention or the population had some disease; thus, 32 studies were analysed in this review, of which 18 were review articles.
|
3. Results
- Eighteen articles reported an evidence of a corelation between physical inactivity and increase in health issues, loss of interest at school, poor cognitive functions, and poor self-esteem. Seven articles suggested a positive co-relation between sports and academic excellence. A substantial body of literature suggests a causal relationship between increased levels of physical activity in adolescent years and cognitive function, school achievement, decrease in risk of obesity and other illnesses in later part of life. Emerging research has considered how physical activity parameters may interact to influence health outcomes. However, there is a paucity of good quality research. Primary studies also show consistent negative co-relation with mental health, obesity, low self-esteem and sedentary lifestyle.
3.1. Review of Literature
3.1.1. From National Context
- Mohan. V [4] suggested that several of the factors associated with diabetes are potentially modifiable, this epidemic of diabetes can be curbed if proper measures are taken to increase physical activity and reduce obesity rates in adults, and most importantly, in children. Existing literature from India has also shown promising results towards the impact of physical activity in mental health disorders. Rajeev. A et al [5] concluded that in India, more than 135 million individuals were affected by obesity. The prevalence of obesity in India varies due to age, gender, geographical environment, socio-economic status, physical activity etc.
3.1.2. From Western & Worldwide Thinkers
- Canada has an established track record in the development of 24-h movement guidelines having previously released guidelines for Children and Youth (aged 5 to 17 years) in 2016 (Tremblay et al. 2016) and for the Early Years (aged 0–4 years) in 2017 (Tremblay et al. 2017b) [6]. Following Canada’s lead, several jurisdictions including Australia (Okely et al. 2017), New Zealand (Ministry of Health 2017), South Africa (Draper et al. 2020), and the World Health Organization (2019) [7] have since released 24-h movement guidelines for the early years and/or children and youth, embracing the concept that the mixture of movement behaviours across the whole day is important when health enhancement is the desired objective (Tremblay 2020). [6]An analysis of population data of children aged five to 19 years estimated that in 2016 obesity was identified in 50 million girls and 74 million boys worldwide (NCD Risk Factor Collaboration 2017). In the USA in 2014, the prevalence of child and adolescent obesity (BMI > 95th centile) was 9.4% (two to five years), 17.4% (six to 11 years), and 20.6% (12 to 19 years) (Ogden 2016). In Europe, obesity prevalence was on average 4.0% in adolescents, with vast differences between countries (Inchley 2017). For example, in Scotland the prevalence was 15% in adolescents aged 12 to 15 years (SHeS 2016). Childhood obesity prevalence is increasing in middle- and low-income countries (NCD Risk Factor Collaboration 2017), for example, up to 40% of children in Mexico were living with obesity or overweight, 32% in Lebanon and 28% in Argentina (Gupta 2012). Low levels of physical fitness (Chaddock 2011; Davis 2011a; Raine 2013) and moderate-to-vigorous intensity physical activity have also been linked to impaired cognitive functions in children (Haapala 2017). In addition to the observational evidence, a substantial body of literature suggests a causal relationship between increased levels of physical activity and cognitive function or school achievement or both. For example, a meta-analysis of 44 experimental and cross-sectional studies (in participants aged four to 18 years) indicates that increased physical activity caused significant overall improvement in cognitive function and school performance (Hedge’s g = 0.32; standard deviation (SD) 0.27) (Sibley 2003). Physical activity may affect cognitive function and school achievement through physiological mechanisms (elevated blood circulation, increased levels of neurotrophins and neurotransmitters) (Dishman 2006), learning and motor developmental mechanisms (Pesce 2016a). Kejal R. et al [8] studied that in Croatia, 35.8% of the population are physically inactive. As for age distribution, physical inactivity is most prevalent (74.8%) in the youngest age group (18-34 years).
4. Discussion
4.1. Theoretical Concepts & Models
- (i) Functionalist social theory-SD Model: Views society as a system of interrelated parts (Coakley, 2001). The kids are interrelated part of society and as sport helps to maintain social order (Kent, 2007), and each part of society is functional for stability of the whole society (Crossman, 2014). It’s important for kids to indulge in a sport. It helps in learning team-building skills, promotes socialising, share common goals and build confidence. (ii) Community development-driven SD model (CSD): CSD is a form of provision which addresses social & political concerns about nature and extent of inequality, especially as its professional management and practice emerged at the same time and in the spirit of ‘sport for all’ in the early 1970s (Hylton & Totten 2008). Promoting community engagement and participation in voluntary work across all groups in society through the games (Thornton, 2012) and will contribute to improved school attendance/educational performance. (iii) Thompson’s (2003) PCS model (personal, cultural and structural): The use of the PCS model to illustrate how discrimination and oppression function demonstrates that not only does discrimination operate at personal, cultural and structural levels but they also work with, across and against each other. Thompson’s use of the term ‘cultural’ rather than ‘institutional’ emphasises that, though it is important to consider formal organisations as significant social entities, we should not forget that most people experience sport and recreation in less formal spaces too. These spaces may be after-school clubs, recreational work settings, local gyms, on the street or with friends and family.
4.2. Complex Issues
- A. Barriers in Sport participation: B. Provision of Sport opportunities and facilities These can be further categorised as physical, economic, motivational, cultural and political.
4.2.1. Sociocultural Barriers
- Inequality: Persistent barriers to participation can be understood as ‘social exclusion’. Social exclusion is more than exclusion from sport. Dept for Culture, Media and Sport and Cabinet office strategy Unit, 2002. Inequality based on the factors like age of participants, gender, social class, occupation, level of educational attainment, wealth, ethnicity, access to car use and others. According to EPPI/Matrix indicators of higher participation are likely if someone is male, with a higher income and higher education and not in social housing.Insufficient resources: Physical barriers to participation include the location of facilities, activities and services, and physical access into and within those facilities, activities and services. Economic barriers relate to affordability, cost and perceived value at that cost. Motivational barriers to participation relate to the perceived absence of value in activity, or towards a conflict with self-image when viewed in the light of the perceived image of an activity. Cultural barriers to participation include direct conflicts with codes, customs and conventions or values inherent in an activity, or perhaps, less directly, with a discomfort associated with the perceived cultural image of an activity. Political barriers to participation relate to feelings of alienation from, or lack of ownership over, the existing choice of provision.
4.2.2. Practical Barriers
- Refer to the physical, medical and economic obstacles to activity that individuals encounter in their daily lives. Polly Hardy et al [9] studied that issues such as cost, safety, access, time pressures and health issues were significant for each group (although different groups were impacted in different ways).
4.2.3. Knowledge Barriers
- Include the correlation between higher educational achievement and higher levels of physical activity. Knowledge gaps also appear to be linked with socio-cultural factors, self-perceptions and the perceptions of others. Evidence suggests that individuals in specific groups (particularly people from ethnic minority communities and older people) might not be fully aware of all the benefits of physical activity (Polly H, 2021).In India, Ambika et al coded transcriptions using a combination of inductive and deductive approaches, guided by the "youth physical activity promotion model." They identified various personal, social, and environmental barriers and enablers (Ulka B, 2021) [10]. Personal barriers: Private school girls cited body image-related negative consequences of PA participation. Social barriers: Girls from both schools faced more social censure for participating in PA. Environmental barriers: Reduced opportunity for PA in schools was commonly reported across all participants.
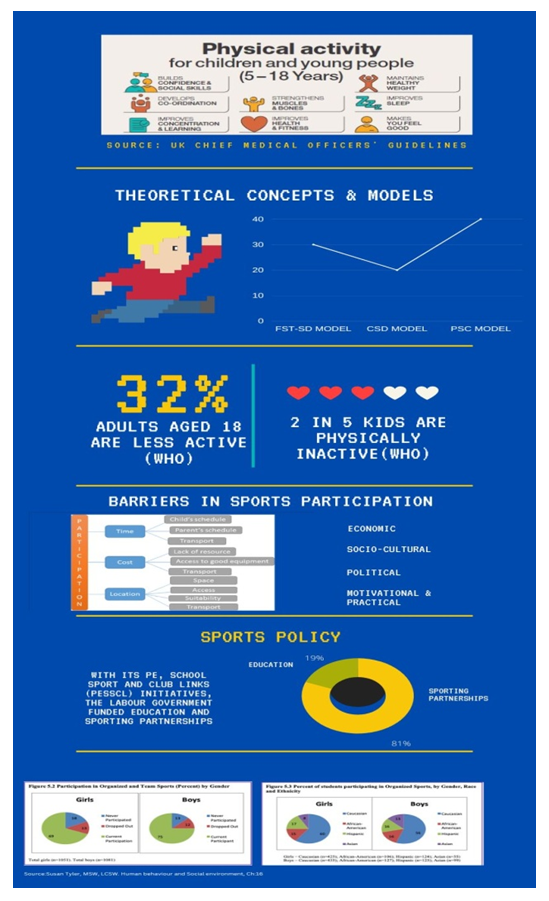 | Figure 2. Theoretical concepts and SD models, Barriers in Sports participation, Sports Policy |
4.3. Possible Solutions
- (i) Increased and equal participation: Biological-psychological-social development influences talent identification decisions and the efficacy of such decisions (Johnston and Baker, 2019). Whilst paediatric exercise science has a large evidence base, the translation and application of such knowledge within coach and practitioner education programs may be limited (Eisenmann, 2017), although this has increased in recent years (e.g., Football Associations Youth Qualifications; Football Associations [FA], 2018). Whilst increasing knowledge may be one solution, policy decisions at the macro level of the sport system may be a further solution. Similarly, it appears that a cultural change is needed. Sport and physical activity appear to be dominated by notions of elitism and masculinity which are exclusive. Personal enablers: All participants reported perceived health benefits of PA. Social enablers: Several participants mentioned active parents and sports role models as motivators for increasing PA. Few environmental enablers were identified.(ii) Efficient Use of Resources in the System: Encourage greater evaluation of program effectiveness and efficiency (e.g., in developing performance without compromising health) of TIDS (Talent identification and development system) by national sport governing bodies and professional clubs including questions about the effectiveness of the program (Robert Ross, 2020) [11].In the era of social media, near-constant connectivity and access to big data, traditional approaches to coach education may need to be updated. These emerging platforms emphasize the value of developing stronger communities of practice for coaches and could facilitate sharing information across contexts (Robert Ross, 2020) [11]. (iii) Good education to develop good coaches: Improving educational coaching system can ensure correct knowledge awareness amongst the youth. The need to provide positive role models is evident for almost every group examined.(iv) Paradigm shift of knowledge and understanding of multiple benefits of regular physical activity.
4.4. Policy and Strategy
- Sports Policy: The establishment of the Sports Council in 1972 was a response to successful lobbying by voluntary governing bodies organising sport (NGBs), orchestrated by the Central Council for Physical Recreation (CCPR). From the 1990s New Labour pursued similar sports objectives to those of New Right administrations, but it is a complicated narrative.With its PE, School Sport and Club Links (PESSCL) initiatives, the Labour government also funded education and sporting partnerships between specialist sports colleges and NGBs, both to increase mass participation and to identify talent and gifted young athletes.There are three ideologies or major traditions of conservatism, liberalism and social reformism on which Sport policy was based.Satyajit et al [12] suggests that Physical activity promotion seems to be lacking in the policy perspective and currently physical inactivity as a risk factor is not considered seriously. The structure of the NCD-care model should be detailed and strengthened by incorporating lessons from other successful NCD models from across the globe. Indian NCD model must provide sufficient scope of interfacing individual care to that of population-based risk factor strategies like physical activity promotion.In a globalised world in which transnational economic, environmental, security and cultural forces reign supreme, even transcending nation state boundaries, sports policies continue to offer national governments the tempting illusion that ideologically based interventions can make a difference.Sports Policy Interventions: • Policy interventions may consider the role of the wider community, neighbourhoods and infrastructure and how these elements might be (re)designed/utilised to facilitate activity.• Policy interventions and promotional campaigns might benefit from addressing these knowledge gaps.• Policy intervention could address the link between socio-cultural factors and knowledge gaps.• In addition to providing positive role models, service providers could be better equipped, both practically and attitudinally, to meet the needs of the groups examined.WHO recommendation for Children and adolescents aged 5-17 years• should do at least an average of 60 minutes per day of moderate-to-vigorous intensity, mostly aerobic, physical activity, across the week.• should incorporate vigorous-intensity aerobic activities, as well as those that strengthen muscle and bone, at least 3 days a week.• should limit the amount of time spent being sedentary, particularly the amount of recreational screen time.WHO also formulates Global Strategy for Women’s, Children and Adolescents’ Health 2016–2030 [13].Partnerships for action are: member states, development agencies, intergovernmental organisations, International organisations, professional associations, philanthropic foundations, academic and research institutions, Industry leaders and private sector, City leaders and local government, community, and WHO at all levels, headquarters, regional and country offices.
4.5. Strategies
4.5.1. Parental Support Behaviour
- There are a number of parent behaviours that have been found to be associated with increasing child physical activity. Parents’ own physical activity levels as observed by their children—often referred to as parental modelling—have been shown to be positively associated with children’s physical activity levels. Trost and colleagues [14] have suggested that children’s physical activity may instead be more strongly determined by parents’ support behaviours across a variety of strategies. Positive reinforcement (e.g., encouragement) has been found to be significantly related to child and adolescent physical activity, perhaps by increasing children’s feelings of competency and behavioural intentions.
4.5.2. Sports Development Theory, Practice and Management
- There are several theoretical policy frameworks for SD:• The Stages model• Institutional Rational Choice• Multiple-streams framework• Punctuated-equilibrium framework• Advocacy coalition framework
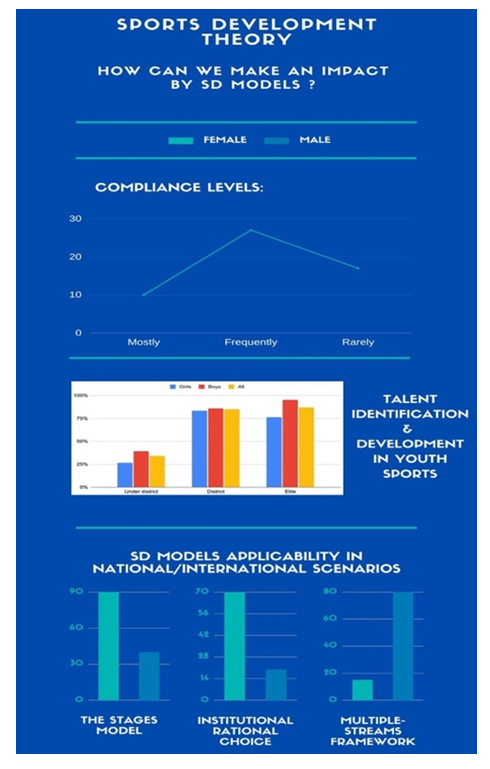 | Figure 3. SD Models applicability in National/International scenarios |
5. Conclusions
- Evidence shows a co-relation between physical activity and sports with overall improved mental and physical health of an adolescent. In children and adolescents, physical activity improves:• physical fitness (cardiorespiratory and muscular fitness)• cardiometabolic health (blood pressure, dyslipidaemia, glucose, and insulin resistance)• bone health• cognitive outcomes (academic performance, executive function)• mental health (reduced symptoms of depression)• reduced adiposityExercise might not only help to improve the physical health, but might also improve the academic performance. However, if we overcome the barriers, enable a correct knowledge paradigm to reach the communities and a strong Sports Policy to ensure active participation and physical activity, good resources and facilities will definitely help us achieve the goal of optimum physical activity in youth.LimitationsThis study reviewed the current literature in this area and suggested a few measures to be taken for addressing the issue. Limitation of this study is one-sided review process which has been conducted by one author only. Future research can focus on a practical scenarios of involvement in physical activity or sports on the basis of area/region.Conflict of InterestAuthor declare no conflicts of interest.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML