-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Sports Science
p-ISSN: 2169-8759 e-ISSN: 2169-8791
2023; 13(1): 1-7
doi:10.5923/j.sports.20231301.01
Received: Jan. 29, 2023; Accepted: Feb. 10, 2023; Published: Feb. 14, 2023

Motivation for Exercise Among Active Seniors
Joshua Astle , Mark DeBeliso
Southern Utah University, Department of Kinesiology and Outdoor Recreation, Cedar City, UT, USA
Correspondence to: Mark DeBeliso , Southern Utah University, Department of Kinesiology and Outdoor Recreation, Cedar City, UT, USA.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

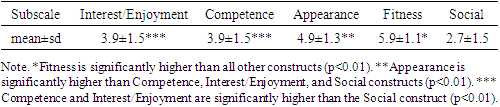
It is well established that physical activity is necessary for long term health and well-being. Despite this fact, many seniors (age 65+) remain inactive. Self Determination theory, a psychological model of human motivation and behaviour, has been utilized by health professionals to understand reasons for exercise engagement and adherence. However, minimal evidence exists on the motives for exercise participation of active seniors. Purpose: Therefore, the study herein assesses personal incentives for exercise habits among active seniors using the Motives for Physical Activities Measure- Revised (MPAM-R) scale. Methods: The MPAM-R scale consists of 30 questions that measure the interest/enjoyment, competence, appearance, fitness, and social constructs for engaging in physical activity. A convenience sample of forty-seven seniors (age 65+), who met the criteria of 150 minutes of moderate or 75 minutes of vigorous weekly activity, completed the survey online by way of surveymonkey.com and social media platforms. Results: The construct scores were as follows: Fitness (5.9±1.1), followed by Appearance (4.9±1.3), Competence (3.9±1.5) Interest/Enjoyment (3.5±1.5), and Social constructs (2.7±1.5). Fitness was significantly higher than all other constructs (p<0.01). Appearance was significantly higher than Competence, Interest/Enjoyment, and Social constructs (p<0.01). Competence and Interest/Enjoyment were significantly higher than the Social construct (p<0.01). Conclusion: Within the parameters of this study: extrinsic factors appear to be highly desirable and primary motivators for participation in exercise among aging adults.
Keywords: Motivation for exercise participation, Active seniors, Motives for Physical Activities
Cite this paper: Joshua Astle , Mark DeBeliso , Motivation for Exercise Among Active Seniors, International Journal of Sports Science, Vol. 13 No. 1, 2023, pp. 1-7. doi: 10.5923/j.sports.20231301.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- It is well established that consistent exercise mitigates many of the negative health effects of aging. Physical activity has been shown to improve balance, improve sleep, enhance muscle strength, alleviate depressive symptoms, maintain healthy body composition, improve cholesterol levels, improve insulin sensitivity, reduce blood pressure, improve circulation, and improve overall cardiac function [2,10,36]. To optimize the positive effects of exercise, the United States (U. S.) Department of Health and Human Services [39] advises a minimum of 150 minutes moderate intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous intensity exercise per week, with elderly individuals encouraged to emphasize, “multicomponent physical activity that includes balance training as well as aerobic and muscle-strengthening activities” [39]. Notwithstanding the widely accepted health benefits, research indicates that one third of the global adult population are physically inactive [17]. Furthermore, approximately 40-50% of older adults report no engagement in physical activity [23].The sedentary behavior of older adults has been attributed to a lack of social support, lack of information on suitable exercises, lack of understanding of benefits, negative prior experience, underlying health conditions, retirement, fear of injury, lack of energy, knee pain, and changes in social roles [15,20,26,28,34,38,41]. Furthermore, elderly individuals are at greater risk of dropping out of an exercise program when compared to their younger counterparts [16]. Despite these issues, seniors show a general positive attitude towards physical activity [25]. Clearly, there is a need for intervention to encourage senior groups to engage in more physical activity.Encouragingly, coaching and guidance have a positive effect in modifying behavior towards exercise [1]. Grove & Spier [18] reports that leadership by health professionals, caretakers, and peer support positively influence participation in exercise among elderly groups. Furthermore, Self Determination Theory (SDT), a psychological model of human motivation and behavior, has been successfully adapted by health professionals to improve adherence to exercise programs [18,23,24,29,37].SDT bases human behavior around three essential needs; 1) autonomy, defined as the need to engage in, “behaviors congruent with one’s authentic interests and values” [29, pg. 10]; 2) competence, defined as, “our basic need to feel effectance and mastery” [29, pg.11]; and 3) relatedness, defined as the need for, “belonging and feeling significant among others” [29, pg.11]. SDT espouses that when autonomy, competence, and relatedness needs are met, one experiences a strong sense of well-being which reinforces behavior. Moreover, satisfying these needs will positively influence exercise behaviors [11,32,42].SDT places motivation on a continuum of; extrinsic, intrinsic, and amotivation. Ryan et al., [31] explains these terms; intrinsic motivation, defined as, “engagement in an activity because of the inherent pleasures and satisfactions it provides” [pg. 109]; extrinsic motivation, defined as, “activities that are performed in order to obtain some separable outcome, whether that be a tangible reward, an avoidance of punishment, or the attainment of recognition, or approval” [pg. 109]; and amotivation, defined as, “when a person has no intention to act” [pg.114].The continuum of extrinsic to intrinsic is further broken down into: external regulation, defined as, “when a person’s actions are compelled or driven by externally controlled rewards or punishments” [pg. 112]; introjected regulation, defined as, “engagement in behaviors to feel better about self-worth or avoid self-esteem blows or self-disapproval” [pg. 112]; identified regulation; defined as when, “the person ‘identifies with’ or personally values the behaviors they engage in” [pg. 112]; and integrated regulation, defined as, “when identifications are well synthesized and coordinated with the persons values” [pg. 112]. As one moves from extrinsic to intrinsic motives, the behavior becomes self-determined, or part of one’s autonomous functioning. The applicability of SDT to exercise behavior has been well established in the literature. Teixeira et al. [37] conducted a meta-analysis of 66 studies related to SDT and exercise behaviors finding that overall, intrinsic motives positively predicted exercise behaviors across a wide range of variables. Although identified regulation predicted initial adoption of exercise behavior more strongly than intrinsic motivation, intrinsic motivation predicted long term exercise adherence. According to research, exercise behaviors often result from a mixture of intrinsic and extrinsic motives for engagement [29]. Additionally, motives for exercise differ across age groups, and thus motives reported by younger subjects may not apply to senior subjects [27].The aim of this project was to assess the motives for exercise participation among senior groups who meet the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services [39] guidelines for physical activity. The hope in this endeavor was to uncover motivational trends particular to elderly subjects that may be useful for health professionals in their pursuit of promoting exercise behaviors in these groups. In accordance with the literature on SDT, it was hypothesized that senior groups would report a mixture of extrinsic and intrinsic reasons for participating in regular exercise, with the scale overall favouring intrinsic motives.
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
- The sample population for this study were individuals who met the age requirement of 65 or older and met the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services recommendations of 75 minutes vigorous or 150 minutes moderate physical activity per week [39]. Participants were recruited by way of social media platforms (Instagram, Facebook, etc.) and email. All participation was voluntary and subjects were required to give informed consent before accessing the questionnaire.
2.2. Instruments and Apparatus
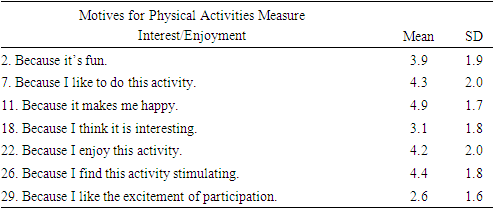
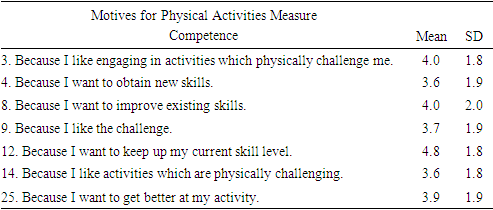
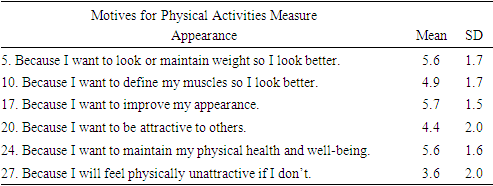
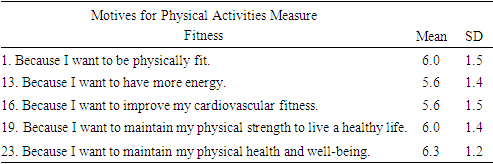
- This project utilized the Motives for Physical Activities Measure Revised (MPAM-R) scale designed to measure the strength of various intrinsic and extrinsic motives for participation in physical activity. The MPAM-R scale has been confirmed as a valid and reliable means to measure motivation for both individuals and groups [19,40]. The scale is composed of 30 items designed to measure the strength of 5 motivational constructs to engage in physical activity; an interest/enjoyment construct composed of 7 items, a competence construct composed of 7 items, an appearance construct composed of 6 items, a fitness construct composed of 5 items, and a social construct composed of 5 items. Motives for physical activity such as “because I want to be physically fit”, or “because it makes me happy” are rated on a 1-7 Likert scale, with 1 representing ‘not at all true for me’ and 7 representing ‘very true for me.’ The project utilized Surveymonkey, the web-based software, to distribute the questionnaire.
2.3. Procedures for Assessments
- This project was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Southern Utah University for the protection of the rights of human subjects in research studies, in accordance with federal and state regulations. All subjects were required to provide informed consent by clicking an ‘agree’ tab before accessing the survey. All responses were anonymous. Links to the survey were sent out to individuals by way of email or social media. Before accessing the survey, clear instructions were provided as to what the age and activity requirements were to complete the survey. It is assumed all participants followed these guidelines and all data is accurately represented.
2.4. Design and Analysis
- The 5 MPAM-R motivational constructs to engage in physical activity were compared with dependent t-tests with significance achieved at α≤0.05. Data management and statistical analysis were conducted in a MS Excel spreadsheet.
3. Results
- Forty-seven subjects, aged sixty-five or older, who self reportedly met the minimum requirement of 150 minutes of moderate or 75 min vigorous weekly activity, filled out the questionnaire online. Descriptive statistics were calculated for the motivational constructs: Interest/enjoyment, Competence, Appearance, Fitness, and Social constructs.
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. Discussion
- The purpose of this study was to examine motivation for daily exercise habits among senior population groups that meet the United States Department of Health and Human Services [39] guidelines of 150 minutes of moderate or 75 minutes of vigorous weekly physical activity. In accordance with SDT, it was expected that active seniors would report a mixture of extrinsic and intrinsic reasons for participating in routine exercise, with the scale overall favoring intrinsic motives. Present findings demonstrated aging adult exercisers are primarily driven by motives of fitness (5.9±1.1) and appearance (4.9±1.3), secondarily by interest/enjoyment (3.9±1.5) and competence (3.9±1.5), while social motives scored lowest of all (2.7±1.5). Results of the analysis support an indication of extrinsic motives being primary among aging adult exercisers, and thus failing to support the research hypothesis.The high value placed on fitness and appearance among those who engage in physical activity was supported in the review of the literature. For example, Caudwell & Keatley [6] examined the implicit and explicit exercise motives of 99 male subjects (age 18-68) who regularly attended a public gym. Results revealed that attitudes towards body fat and muscularity significantly predicted gym attendance. Further, the preponderance of the sample reported [6] health and fitness as their primary motive for gym attendance (57.3%), followed by appearance (16.7%), amateur body building (16.7%), training or competing (8.3%), and other (1%) [6]. Similarly, Costa et al. [7] demonstrated that among a sample of 33 individuals of various ages, dissatisfaction with appearance predicts engagement in frequent physical activity even among the elderly.Research by Garrido et al. [14] demonstrates that body image satisfaction among 90 elderly women who participated in water aerobics did not significantly differ in perceived body satisfaction from their sedentary counterparts, despite reporting a significant enhancement in quality of life. Conversely, a similar study by Mazo et al. [22] comprised of 60 elderly subjects, 75% of which being female, reported high levels of self-esteem and self-image among water exercise program participants. Initiation of the water aerobics program was motivated by a desire to improve physical and mental health, while continuation was driven by a feeling of well-being and enjoyment in the water activity itself. The modest levels of enjoyment were expected, and consistent with the review of literature. It’s been reported that exercisers that do not enjoy their activity are less likely to persevere in it [58]. Furthermore, Dacey [9] demonstrates that enjoyment contributes more to differentiating activity levels among elderly individuals when compared to health/fitness, social benefits, weight management, stress management, and appearance. Furthermore, intrinsic factors, such as the pleasure of the exercise and the prospect of improved sleep have been indicated to be powerful motivators for seniors to engage in exercise [33].Using the same MPAM-R survey, Stelzer et al. [35] indicated that United States students manifest higher scores of fitness and appearance compared to students from Czechia. Despite the US students reporting higher motivation to participate in physical activity, the group reported a significantly higher BMI. Moreover, US students reported fewer steps measured by pedometers and scored higher on extrinsically motivated questions. Thus, higher self-reported motivation to engage in physical activity ostensibly does not always correspond to higher levels of activity. While the Stelzer et al. [35] study is not directly comparable to the current study in terms of population (aging adults vs. students), culture may be a relevant variable to explore in future research.Many studies support the assumption that motivation measures vary according to the type of physical activity. For example, Gavin & Myers [15] demonstrated that participants in a line-dancing class reported social interaction as a primary motive for participation, whereas health and fitness was the top motivating factor among participants with similar characteristics in a Tai-Chi class. Additional research supports recreational exercisers being driven by desires of health and fitness, while competitiveness and personal achievement serve as stronger motivators among sport participants [4,13,17]. One limitation of the present study is not accounting for the mode of activity. Activities common in public gymnasiums or fitness centers (e.g., weightlifting or jogging on a treadmill) do not require intense social interaction. It is possible that the sample herein was comprised of individuals who exercised by way of health or fitness-oriented activities, rather than competitive sports or dancing classes.The low social construct scores exhibited in the current study were unexpected, given the abundance of literature emphasizing social incentive for exercise among older groups. For instance, Cousins et al. [8] demonstrated that social context and self-referent belief variables predicted the efficacy of walking blocks or climbing stairs in a group of 447 adults aged over 50. Fougner et al. [12] reported that the most important positive impact of group exercise was related to social belonging and well-being, as well as physical ability being a more important motive than appearance in group exercise participation among aging women. Additionally, it’s been shown that people aged 50 or older show more autonomous motivation when they have a peer to exercise with, and are more likely to persist in higher levels of physical activity for extended periods of time [5].There is a growing body of research examining competitive Masters athletes by Walsh and colleagues [43-58]. Research specific to motivations for Masters athletes to compete by Walsh and colleagues [58] suggesting that the primary motivation of this population is “to socialize with other participants.” One of the assessments included the Motivations of Marathoners Scale. While participants in the current study were chronic exercising aging adults and not competitive athletes, a direct comparison between the current study and the Walsh et al. [58] is warranted given the conflicting results.Differing modes of physical activity could likely account for the aforementioned dissimilarity. For example, Ball et al. [3] found that recreational exercisers show more extrinsic motivation when compared to those who participate in sport. This notion is further supported by Frederick and Ryan [13] who reported that sport participants scored higher in competence and enjoyment factors as primary motivators as opposed to fitness group participants who scored higher in body related factors. Furthermore, women scored high in social and appearance motives while men scored high in competition-related motives [13]. Therefore, both sex and type of activity are relevant when considering motives for physical activity (exercise and/or competition) and may explain the differing results between the current study and that of Walsh et al. [58].Data results of the current study suggests social factors are minimally motivating when sustaining long term exercise habits for aging adults. It should be noted that the data was collected during the Covid-19 pandemic lockdown, and as such, social motives may have been altered accordingly. Fitness facilities across the country closed down during the pandemic prompting a choice by individual to participate in home workouts providing minimal social contact [21]. Additional research addressing mode of exercise, gender, and other additional variables is desired to build upon the results of the current study.This study relied on honest participation from its subjects. Participants were sought out by various social media platforms and email, therefore, there was no regulation on part of the researchers to enforce the criteria prescribed in the study. Furthermore, the participants in the current study were self-selected, not randomly selected. In addition, the survey was further limited in that it did not specify which type of exercise modality each subject participated in or the gender of the subjects. While gender, age, and mode of activity manifest differing motives for engagement, the findings herein illuminate that routine exercising seniors generally perceive fitness and appearance are the primary motivating factors. Therefore, health and fitness professionals should not discount the value of extrinsic motivating factors on exercise adherence among elderly subjects.
5. Conclusions
- Within the parameters of this study, it was demonstrated that extrinsic factors such as fitness and appearance are powerful motives for engagement in routine exercise, even among the elderly. Furthermore, social factors may not be as influential among self-determined active seniors as one might expect, despite the abundance of support in the literature. Additionally, mode of activity is relevant to understanding motives for exercise. Health professionals should not discount the potential influence of extrinsic factors on aging adults.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML