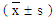-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Sports Science
p-ISSN: 2169-8759 e-ISSN: 2169-8791
2022; 12(1): 1-7
doi:10.5923/j.sports.20221201.01
Received: Jan. 11, 2022; Accepted: Jan. 21, 2022; Published: Jan. 27, 2022

Influence of IMB Education Model on the Improvement of Teenagers' Comprehensive Sports Literacy
Lin Huai
School of Public Management, Tianjin University of Commerce, Tianjin, China
Correspondence to: Lin Huai, School of Public Management, Tianjin University of Commerce, Tianjin, China.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Since 2021, China's relevant government and departments have focused on a series of rectification actions for the education and training industry. The most typical file is the Opinions on Further Reducing the Burden of Students' Homework and Off-class Training at the Compulsory Education Stage. Double Reduction largely restricts the behavior of educators in providing services. But the most important thing is to actively promote the transformation of educational concepts. It can be predicted that the future trend of youth education industry will be interest-oriented, while sports are regarded by many scholars as one of the main activities to promote physical and mental development. on the one hand, as a beneficial sport to physical and mental development, youth groups do not fully recognize the cultural impact of sports; On the other hand, base on the score-only society, Chinese students and their parents do not attach importance to the positive existence of sports. This study takes the normative literature of physical education as a reference, applies the IMB education model, and highlights the endogenous dynamic formation of the implementation of educational behavior in the IMB link. In this study, adolescents were divided into intervention group and control group. Systematic physical education based on IMB was implemented in the intervention group, while the control group only relied on its environment to exert influence. After 4 months of follow-up, the physical literacy of the intervention group and the control group has improved compared with 4 months ago. The physical literacy of the intervention group who implemented the IMB education model was significantly higher than that of the control group in the same period, and significantly higher than that of the same group four months ago. The implementation of physical education system has achieved remarkable results, especially in personality and gender cognition. Boys are more able to shape male behavior and reduce feminization based on male phenomenon and gender contrast behavior. The research shows that IMB education model can be applied to physical education, and can effectively promote the formation and improvement of sports literacy. The results of the research provide a strong power for the progress of social education concept and the shaping of young people's physical fitness and mind.
Keywords: Sports, IMB, Double Reduction, NSCA, Education
Cite this paper: Lin Huai, Influence of IMB Education Model on the Improvement of Teenagers' Comprehensive Sports Literacy, International Journal of Sports Science, Vol. 12 No. 1, 2022, pp. 1-7. doi: 10.5923/j.sports.20221201.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Background
- In July 2021, the General Office of the State Council of China issued the Opinions on Further Reducing the Burden of Students' Homework and Off-class Training in Compulsory Education Stage (hereinafter referred to as "Double Reduction"). It can be predicted that the introduction of the "Double Reduction" policy will restrain the momentum of blind growth of discipline training to a certain extent. However, the Notice of the General Office of the Ministry of Education on Further Clarifying the Scope of Subjects and Non-Subjects in off-class Training at the Compulsory Education Stage clearly states that schools are encouraged to provide students with after-class service activities of interest in their spare time for students to choose to participate independently. After-class service can not meet the special needs of some students to develop their interests and special needs. Non-disciplinary training institutions can be appropriately introduced to participate in after-class services. The Notice of the General Office of the Ministry of Education on Further Clarifying the Scope of Disciplines and Non-disciplines in off-class Training at the Compulsory Education Stage clearly stipulates that sports (or sport health) should be managed according to non-disciplines when conducting off-class training. "Double Reduction" encourages interest and sports training to intervene. Under the regulation of policy and market, some smaller "workshop-style" discipline training institutions will have the opportunity to transform their operation to the direction of national policy support. The sports training market for primary and secondary school students is expected to flourish. The cognitive level of primary and secondary school students is still in the learning stage. They are unable to fully understand the development history of sports, research materials, sports theory and so on. In addition, the number of obese children continues to increase worldwide, and the physical activity levels of most boys and girls are declining [1] [2] [3] [4]. These overweight children face a greater risk of cardiovascular disease than other normal-weight children of the same age [5] [6]. The problem of childhood obesity has also become more acute than ever because of our Internet environment. With the popularity of the Internet and mobile phones, children spend more time in the media, and long-term inactivity can also lead to obesity [7].
1.2. Question Raising
- At present, China's training market is in the stage of transformation from "static" to "dynamic", and parents' educational concept will also usher in the transition period. They are thinking of what is the real education. Traditional Chinese parents always confine education to the fixed mode of "subject + achievement", and this educational liberalism revolution has broken the educational paradox of subject dominance. Studies have shown that regular participation in sports and extracurricular physical activities can help improve academic performance. Sports have so many advantages that many social organizations involved in health. Fitness business are promoting children to participate in activities appropriate to their needs and physical strength [8] [9] [10] [11]. Unfortunately, at present, parents' awareness of sports is far less attractive than that of subject education. Lack of awareness of physical education makes it impossible for parents to guide their children scientifically. This results in a gap between physical education and its recipients, which makes it impossible to obtain sustainable educational experience.In addition, in September 2021, the General Office of the State Administration of Radio and Television of China issued the Notice on Further Strengthening the Management of Literary and Art Programs and Their Personnel, pointing out that abnormal aesthetics such as "feminization based on male" should be resolutely eliminated. This statement reflects that the governance of feminized gender contrast behavior based on men is imminent. This also gives research expectations for physical education to play a role in this field.Information-motivation-behavior skills (IMB) model emphasizes the comprehensive intervention of information, motivation and behavior of the audience. In the aspect of physical education and health education, it takes behavior change as the purpose orientation and emphasizes how motivation and behavior skills play a role in the process of this change. It can be widely used in sports behavior, ideological intervention and health education. In this study, IMB intervention will be carried out on the physical exercise of primary and secondary school students in a municipality directly before and after summer vacation, which will provide a scientific basis for promoting the physical health of primary and secondary school students, improving the level of sports theory, and continuously promoting the implementation of the "Double Reduction" reform results.
2. Object and Method of Study
- Studies have shown that the positive or negative behavioral tendency to participate in physical activity formed in childhood will continue into adulthood, so children should be helped to form healthy social behavior habits [12] [13]. Developing the habit of regular participation in physical activity in children aged 6 years and older is considered the most important step in improving their health [9]. To sum up, Physical education for children should form a systematic concept as comprehensively as possible to contribute to their physical development and personality formation.
2.1. Object of Study
- One month before the summer vacation in 2021 (June), the research team selected 102 students from senior primary and secondary schools who participated in systematic sports training during the summer vacation. The 102 students were randomly divided into two groups, 51 students in the intervention group and 51 students in the control group. The overall study time spans one month before and one month after the summer vacation, that is, from June to September. The selection criteria of research objects are as follows:• Conform to the requirements of the National Standards for Students' Physical Health; • Good understanding ability, fluent and barrier-free communication; • Conditional use of mobile technology (such as e-mail, WeChat, etc.) and operational capabilities; • Students and their parents participated in the study voluntarily; • Parents do not over-explain the educational content involved in the study. It only gives guiding explanations to the content that students can't understand, and does not mix personal subjective opinions. • There is no interference in the form of sports training, but qualified training institutions must be selected. Exclusion criteria were as follows: • Patients with acute and chronic diseases and permanent disability; • Cognitive impairment; • Withdraw from the study.
2.2. Research Methods
2.2.1. Physical Education and Health Education
- The interveners in the control group were parents of students and instructors of training institutions, who provided guidance including sports movements and diet. The forms of intervention were oral guidance, answering questions or providing books and materials related to sports. The intervention group will receive physical health education based on the IMB model, and the interveners are project researchers with IMB theoretical knowledge. Intervention forms include telephone, e-mail and Wechat follow-up through network media, including sports theory guidance, nutrition and diet health guidance, sports skills guidance, injury prevention and rehabilitation guidance, psychological counseling and so on.
2.2.2. Specific Contents of IMB Mode
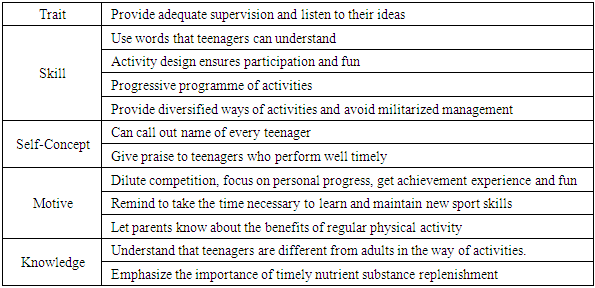
- NSCA (National Physical Fitness Association of the United States) believes that coaches should provide the following recommendations for teenagers (hereinafter referred to as NSCA recommendations). This study classifies the guidance items according to the elements of competence, highlighting scientific guidance. Guidance items are shown in Table 1.
|
3. Index Selection and Data Analysis
3.1. Basic Background Questionnaire
- Before receiving educational intervention, a general questionnaire was used to collect and analyze the data of the participants in physical exercise. The questionnaire involved gender, age, educational level, family economic situation, etc.Physical management ability: effectively follow-up was carried out for 4 months while receiving physical training, and evaluate according to NSCA training standards, including effective training (3 items), training norms (7 items), nutrition intake (5 items), injury identification (5 items) and physical monitoring (10 items). The above five dimensions total 30 items. Each item is scored by 5 grades (0-4 points). Higher score means stronger physical management ability. After statistical test, the Cronbach's of the scale is 0. 827. Data have good internal consistency.Control of bad habits: effectively follow-up was carried out for 4 months while receiving physical training, and evaluate according to the relevant statements of NSCA on the identification of bad habits. The assessment included the restriction of bad habits on life, the influence of bad habits on sleep, the control assessment of bad habits, interventional therapy and the representation of physiological morbidity. For the above 5 items, the maximum score for each item is 5. If fully controlled, the total score is 25 points; For good control, take 4 points for each item, totaling 20 points (i.e. 20-24 points); The uncontrolled score is less than 15 points.Quality of life: effectively follow-up was carried out for 4 months while receiving physical training. The quality of life scale is used to evaluate the psychological situation (5 items), concern for physical health (4 items), scientific attitude (4 items), conceptual response (10 items) and demand (5 items). The total number of items involved in five dimensions was 28. Each item adopts a five-level scoring method (1-5 points). Higher score means higher quality of life. The Cronbach's of the scale is 0. 831 by statistical test. Data had good consistency.The items listed in the questionnaire are the responsibility of the coaches and parents of students who have received training and explanation in the same group. Before receiving comprehensive sports training, the coaches and parents fill in the questionnaire according to the real situation of the students who have received training. Four months later, the students and their parents in the same group are surveyed and fed back, and the statistical data are filled in according to their real feedback.
3.2. Statistical Analysis and Result Feedback
- SPSS 22 software is used for statistical analysis and test. The statistical results of the scale were means
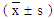 . Paired t test was used for comparison between groups, and group t test was used for comparison within groups. The occurrence frequency or degree probability was used to count the statistical data, and the chi-square test showed that the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05).
. Paired t test was used for comparison between groups, and group t test was used for comparison within groups. The occurrence frequency or degree probability was used to count the statistical data, and the chi-square test showed that the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05).4. Statistical Results and Interpretation
4.1. Conditions of Experimental Subjects
- The intervention group consisted of 51 people, including 35 males (68.62%) and 16 females (31.4%). Average age is (12.27 ± (2.12) years; There are 29 cases of education level ≤ Primary school (56.9%), 22 cases > primary school (43.1%); Based on the average annual wage of 97379 yuan for urban non-private employees in China in 2020, the average monthly wage is 8114.92 yuan. Considering the possible impact of single-parent families, the monthly income of families is 8114.92 yuan. As a result, there are 9 cases of household income ≤ 8114.92 monthly (17.6%), and 42 cases > 8114.92 yuan (82.4%).The control group consisted of 51 people, and 7 people dropped out during the experiment, 44 people participated in the whole process of the experiment. Of the 44, 28 people (63.6%) are males and 14 people(31.8%) are females; Mean age is (13.55 ± 3.07) year-old; Education level: ≤ 27 cases (61.4%) in primary school, 17 cases (38.6%) in primary school; There are 5 cases of household income ≤ 814.92 monthly (11.4%), and 39 cases > 814.92 yuan (88.6%). There is no significant difference between the two groups (P > 0.05).It can be seen that in terms of subjective initiative in physical education, the participation of male students is higher than that of female students. With the increase of academic and examination pressure, the number of junior high school students participating in physical education has decreased relative to primary school students. With the development of China's economy and the progress of educational concepts, the number of junior high school students participating in physical education has decreased. Parents' interest in promoting pupils' participation in sports training (such as ice hockey, Taekwondo, basketball, football and other sports) is increasing. Through statistical analysis and research, family income is one of the factors that determine children's objective and systematic physical exercise. The relatively high cost of physical education is one of the obstacles for children to participate in physical exercise systematically.
4.2. Comparison of Physical Management Ability Before and After Physical Education
- After four months of effective follow-up, the five dimensions of physical management ability of adolescents in both groups increased significantly compared with those before physical education, and the total score was higher than that before physical education (P < 0.05). Through data analysis, the scores of other items in the intervention group were higher than those in the control group (P < 0.05) except for the item of "injury identification". Data are shown in Table 2.
|
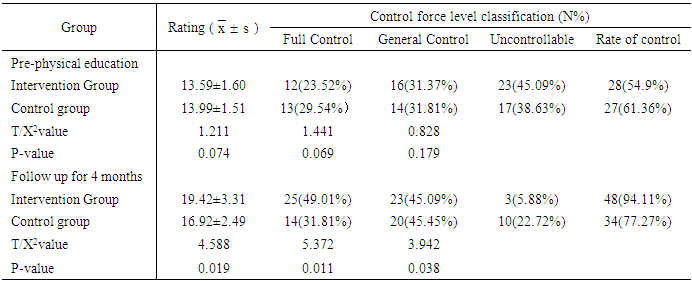
4.3. Comparison of Bad Habit Control Before and After Physical Education
- After 4 months of effective follow-up, the control score of bad habits and vacancy rate of adolescents in both groups were better than those before physical education (P < 0.05). The score and control rate of the intervention group after follow-up were better than those of the control group (P < 0.05). Data are shown in Table 3.
|
4.4. Comparison of Quality of Life Before and After Physical Education
- After 4 months of effective follow-up, the five dimensions of quality of life of adolescents in both groups were better than those before physical education (P < 0.05). After follow-up, the scores of other dimensions in the intervention group were better than those in the control group except for the dimension of "demand" (P < 0.05). Data are shown in Table 4.
|
5. Discussion and Conclusions
- Through data analysis, it is feasible to apply the IMB model to physical education for adolescents. Debate RD et al. found that in the IMB model, information is a necessary condition for changing behavior, while the most important factor for changing behavior is motivation, and the key to objective skills and self-efficacy of implementing behavior lies in behavioral skills. The combined effect of information, motivation and skills is reflected in behavior change, and behavior change will produce feedback, and then optimize information, motivation and skills more in line with expectations. The IMB education model is highly consistent with the expectation of policy promotion in sports, and the educational effect is better than that of traditional physical education.The basis and premise of forming motivation and behavioral skills lies in information support. Based on the concept of "Internet +", the study disseminates sports culture, sports skills, scientific concepts and health knowledge in the form of electronic text, video demonstration, micro class and MOOC interaction. The dissemination of knowledge and information can be effectively transmitted through the media. Media includes platforms such as email and web groups. The results show that the scores of the intervention group are significantly higher than those of the control group in terms of physical management ability, bad habit control and quality of life. After systematic physical education, different items in various aspects have also been significantly improved. This shows that the application of IMB model in physical education can effectively promote teenagers' scientific cognition of sports.Lack of sports outlook is not conducive to the physical and mental development of young people. It may affect the individual's outlook on life and values to a certain extent. Lack of sports and culture in Long term will lead to the systematic lack of physical fitness in the group, and may also contribute to the prevalence of "feminization based on male" culture, which is more concerned by Chinese society today. Objective environment is a part of the impetus to enhance the concept of sports. But the main driving force comes from endogenous power. This study shows that from the perspective of sports science of physical exercise, the integration of physical education and IMB education concept under the platform of composite media will effectively improve physical fitness and training effectiveness, understand training and diet from a scientific point of view. To a certain extent, recognize how to avoid sports injuries. Compared with the external performance brought by physical education, the optimization of internal thought will greatly improve the quality of individual life. Through physical education, teenagers can acquire scientific attitudes and correct concepts. After forming endogenous motivation, they begin to pay attention to their physical and mental health. In the end, they are more inclined to spiritual pursuit. All internal expressions can be explained by external expressions. Because the experimental results are better than the pre-education data, this makes the control force as an endogenous dynamic performance well interpreted.To sum up, based on IMB education model, it is helpful for teenagers to cultivate and improve their own sports concept, and then achieve the purpose of managing their body and literacy. With the development of wearable equipment technology, data collection, analysis and feedback will become feasible. The study still has possibility for further standardization and supplementary research, and will increase knowledge convergence with cloud computing, perception technology and other fields.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML