Sultan Mansour Bediri
Al-Baha University Department of Physical Education, Saudi Arabia
Correspondence to: Sultan Mansour Bediri, Al-Baha University Department of Physical Education, Saudi Arabia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Abstract
The study of some aspect's for team preparation in futsal were studied with the aim to knowthe main reasons for the poor preparation of futsal players at Al-Baha University. A sample survey was applied to (12) players and (12) coaches. The survey was based on four axes for team preparation which were player's affairs, administrative side, plans and programs, and Equipment and possibilities. The results indicate the most disables to preparing futsal players were statements were provides a dedicated and equipped dressing room for players, availability of legal training grounds, and availability of all assistive training devices. The goals of the participants are commensurate with the available capabilities. Have interest in applying a special method for incentives. There are exceptions in universities for athletic students. Have full dedication to the required administrative tasks. The results also show that there were differencessignificance between coaches and players in many statements at (p<0.05). However, the main reasons for the poor preparation of futsal players at Al-Baha University wereinstatements the goals of the participants are commensurate with the available capabilities; there is a breakdown of roles and tasks Administrative side, and Regularity of players in training on a daily basis.
Keywords:
Some aspect's, Team preparation, Futsal
Cite this paper: Sultan Mansour Bediri, Study of Some Aspect's for Team Preparation in Futsal, International Journal of Sports Science, Vol. 11 No. 1, 2021, pp. 1-5. doi: 10.5923/j.sports.20211101.01.
1. Introduction
It is clear that futsal continues to grow as a sport. This growth has lead to an increased demand for futsal related information, to allow people to better understand the sport and its qualities and intricacies. Particularly, there is a desire for coaches, players, sport scientists, and administrators to improve their depth of knowledge, to help them contribute to the development of the sport in their respective countries. [8] Most researchers in organizational behavior argue for stability in teams. According to Hackman, “Teams with stable membership perform better than those that constantly have to deal with the arrival of new members and the departure of old ones. Stable membership comes with shared experience that helps not only players on the field but also in training, getting health care services and other routine aspects. [3]Therefore, Team members need to understand that everyone is doing a small part of work that leads to a victory in individual games. Each player's individual performance, collectively, is what determines success for the team. To win, a head-coach needs players to perform well while players need a head-coach to develop tactics and training sessions because players don't have all necessary information to develop a game day plan. [3] However, while most studies have focused on coaches' behaviour during training sessions and during competitions [4], there is still a lack of studies examining the importance given by coaches to training and drill items. [4]
2. Details Experimental
2.1. Materials and Procedures
In this study, the researcher used the descriptive method (Survey) witch is very appropriate with the Study objective, and that is managed through the description of current existents, their analysis and the drawn conclusions.The study restricted society is composed of player of Al-Baha university team and coaches who have an experience with this field.
2.2. Sample
Sample was selected by player of Al-Baha university team for number of (12) players and (12) coaches. - used the following implements in date collection:• Documents' analysis• interview
2.3. Validity
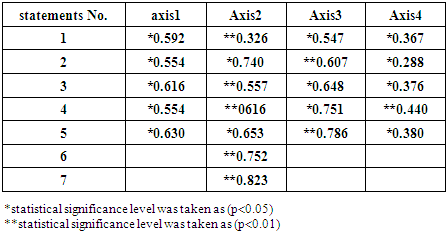
Initially, the questionnaire, immediately after the design, was submitted to five professors and experts in university sport to determine whether the questions were clear, understandable and valid. The result was 100%. Following, they conducted the survey on a sample composed of 10 players to ensure that questions are suitable for the time allowed is enough, and the statements are clear. The findings proved that there is a statistical correlation between the mark given to each statement and the total mark. This proves the intrinsic validity of the questionnaire. Table (1). Values of correlation co-efficient each statement and the overall score
 |
| |
|
As the table (1) shows, all Pearson's correlation co- efficient results fall between 0.288 and 0.823 at the point of 0.01-0.05. This means that each question is consistent whit the overall questionnaire.
2.4. Reliability
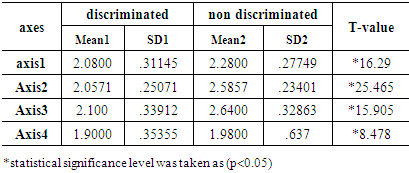
The internal consistency and the reliability of questionnaire were tested using discriminated test. In particular, 20 players were used in order to assess the reliability of the questionnaire. First group were discriminated and second group were none discriminated. Table (2). Difference Significance between discriminated and non discriminated
 |
| |
|
As the table (2) shows, that there are statistically significant differences at level 0.05 between the discriminated and none discriminated of the sample in the axes of study, also the t-test were ranged between 8.47 - 25.46.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1 Results
3.1.1. The Most Important Aspects to Preparing Futsal Players at Al-Baha University
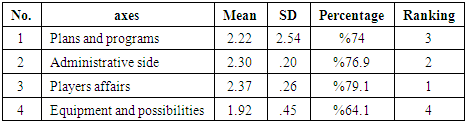
Table (3). The percentage of axes under study
 |
| |
|
As the table (3) shows, the most important aspects to preparing futsal players were players affairs in the first ranking with rate %79.1. The Second ranking was in administrative side with rate %76.9. The third ranking was in plans and programs with rate %74. The forth ranking was in Equipment and possibilities with rate %64.1.
3.1.2. The Most Disables to Preparing Futsal Players at Al-Baha University
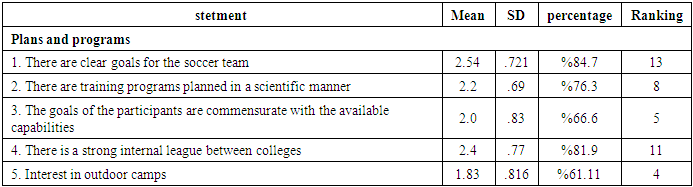
Table (4). The percentage of statements under study
 |
| |
|
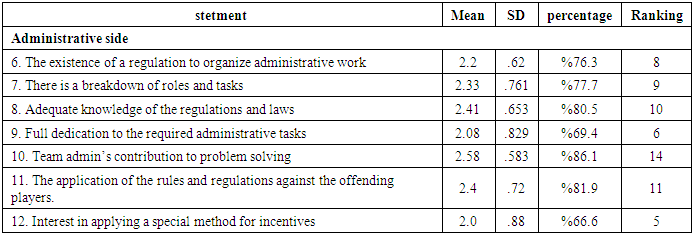
Table (5). The percentage of statements under study
 |
| |
|
Table (6). The percentage of statements under study
 |
| |
|
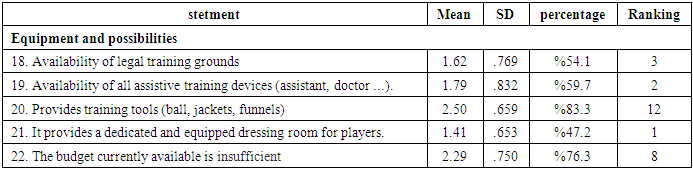
Table (7). The percentage of statements under study
 |
| |
|
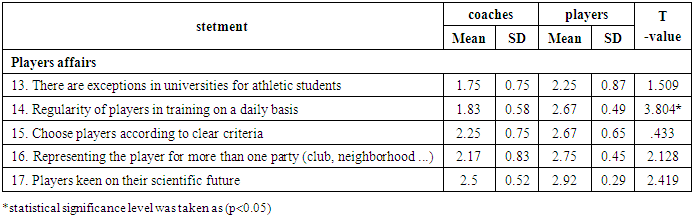
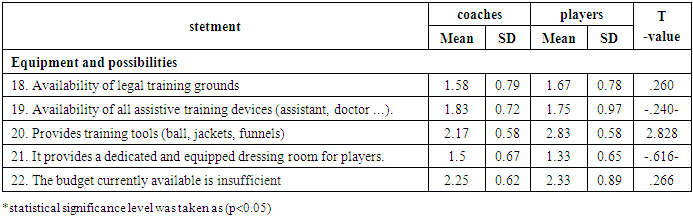
As the table (4), (5), (6), (7) shows, the most disables to preparing futsal players were statements (21, 19, 18, 3, 12, 13, 9, 14) with rate between (%47.2-%75).
3.1.3. The Main Reasons for the Poor Preparation of Futsal Players at Al-Baha University
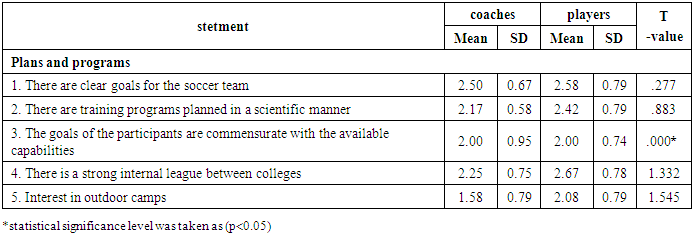
Table (8). Difference significance between Coaches and players
 |
| |
|
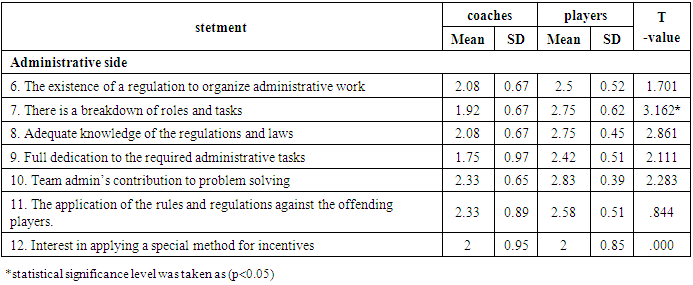
Table (9). Difference significance between Coaches and players
 |
| |
|
Table (10). Difference significance between Coaches and players
 |
| |
|
Table (11). Difference significance between Coaches and players
 |
| |
|
As the table (8), (9), (10), (11) shows, there were differences significance between coaches and players in many statements at (p<0.05). However, the main reasons for the poor preparation of futsal players at Al-Baha University were in statements (3, 7, 14).
3.2. Discussion
This study aimed to know the most important aspects to preparing futsal players, the most disables to preparing futsal players, and the main reasons for the poor preparation of futsal players at Al-Baha University. Results indicate that the most disables to preparing futsal players were player's affairs, administrative side, plans and programs, and Equipment and possibilities. In line with the present study, study [4] included that have analysed various factors that influence acquisition and expression of high levels of sports performance. They have presented primary factors (genetic, psychological and sport preparation that is related to the quantity and quality of training) and secondary factors (context, socio-cultural - which includes family support and its influence on continued involvement in the sport, relative age and population density). [4] Also, study [3] indicates that the world of sports, and particularly Futsal, can be subject to a great volatility, which has wide impacts ranging from fans to players, coaches, and ownership. "Gazprom-Ugra" must be able to build goals on a long-term strategic vision in order to enjoy continued success. Taking these much-needed steps would help to change the short-sighted practice to the practice of long-term continue incremental improvement that would allow development of foundations that would bring new names in the world of futsal. Success of individual clubs will eventually lead to proliferation of this sport around the globe and recognition as Olympic sport. [3] In Bediri Sultan (2013) stated that, the implementation of the preparation plans requires capabilities with special specifications, as the provision of regular or traditional capabilities prevents the player or team from reaching the best levels, as the first Saudi team suffered from a lack of financial resources as a result of the low material return from sponsorship contracts and commercial advertisements, and accordingly the capabilities must be studied. A good study is available so that the objectives to be achieved are formulated in a suitable manner for the capabilities to be used during the various preparation periods and stages. [7] Also, Results indicate that the most disables to preparing futsal players were (provides a dedicated and equipped dressing room for players. availability of legal training grounds. availability of all assistive training devices. The goals of the participants are commensurate with the available capabilities. Have interest in applying a special method for incentives. There are exceptions in universities for athletic students. Have full dedication to the required administrative tasks). This consistent with the finding of (Andrey Berezin, et al, 2016) who reported that application of Vroom’s Expectancy theory to the club reveals lack of motivation due to an absence of instrumentality criteria. The team doesn’t have shared experience that supports trust among the team members. Compensation plans are designed in a way that ensures motivation of only the starting team. To ensure the long-term improvement of the club, all the members need to have high motivation because members with low motivation would resist to positive changes. [3] Also, Results indicate that main reasons for the poor preparation of futsal players at Al-Baha University were the goals of the participants are commensurate with the available capabilities; there is a breakdown of roles and tasks Administrative side, and Regularity of players in training on a daily basis. In line with the present study, [7] stated that, The implementation of the preparation plans requires capabilities with special specifications, as the provision of regular or traditional capabilities prevents the player or team from reaching the best levels, and accordingly the available capabilities must be well studied so that the objectives to be achieved are formulated in an appropriate manner for the capabilities to be used during the various preparation periods and stages. [7]
4. Conclusions
The main objectives of this study know the main reasons for the poor preparation of futsal players at Al-Baha University. The researcher noticed through training futsal at Al-Baha University for several years that there was no scientific basis for preparing futsal players in order to actively participate in the futsal competitions organized by the Saudi Universities Sports Federation, and also noted that Al-Baha University Futsal team did not achieve positive results in the Federation championship in Saudi University Athletic, which drew the researcher's attention to find out aspects of preparing futsal players at Al-Baha University.A Solution was made by the survey based on four axes for team preparation which were player's affairs, administrative side, plans and programs, and Equipment and possibilities. The results demonstrate that were the goals of the participants are commensurate with the available capabilities, there is a breakdown of roles and tasks Administrative side, and Regularity of players in training on a daily basis.
References
| [1] | Coskun, A., Dinc, M.S., & Tetik, S. (2020). Strategic performance management for soccer clubs: A quantitative model proposal. Journal of Human Sport and Exercise, in press. doi:https://doi.org/10.14198/jhse.2021.164.08. |
| [2] | Amirmasoud Mohamadi Shamsabadi, Nima Majedi, Zahra Nobakht Ramezani. Analysis of the Factors Affecting Brand Value of Iranian Futsal Premier League Clubs. Submitted 09 October 2019; Accepted in final form 01 January 2020. |
| [3] | Andrey Berezin, Prof. Natalia Gorodnova, Prof. Vladimir Matyushok, Sergey Chernov, Dmitriy Skipin. case on team management in futsal. 3rd International Multidisciplinary Scientific Conference on Social Sciences & Arts SGEM 2016. |
| [4] | João Serrano, Shakib Shahidian, Nuno Leite, Long-term Sport Development in Portuguese Futsal Players. International Journal of Sports Science 2014, 4(6A): 19-27. DOI: 10.5923/s.sports.201401.03. |
| [5] | João Serrano, Shakib Shahidian, Jaime Sampaio, Nuno Leite. The Importance of Sports Performance Factors and Training Contents From the Perspective of Futsal Coaches. |
| [6] | Ricardo Augusto Barbieri, Alessandro Moura Zagatto, Fabio Milioni, Fabio Augusto Barbieri. Specific futsal training program can improve the physical performance of futsal players. Sport Sci Health (2016) 12: 247–253. DOI 10.1007/s11332-016-0283-z. |
| [7] | Bediri Sultan Mansour, Study of strategy for preparation the first Saudi soccer national team to world cup finales 2010, the requirement ph.D Degree in Physical Education in coaching department at Helwan university. Med 2013, 125-143. |
| [8] | R. Moore, S. Bullough, S. Goldsmith, L. Edmondson. A Systematic Review of Futsal Literature. American Journal of Sports Science and Medicine, 2014, Vol. 2, No. 3, 108-116 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajssm/2/3/8. |



 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML









