-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Sports Science
p-ISSN: 2169-8759 e-ISSN: 2169-8791
2020; 10(6): 145-163
doi:10.5923/j.sports.20201006.03
Received: Dec. 13, 2020; Accepted: Dec. 26, 2020; Published: Dec. 31, 2020

The Influence of Biological Sex and Fitness Status on Markers of Recovery Optimisation in Response to Prolonged High Intensity Interval Exercise
Isabella Russo1, Paul A. Della Gatta2, Andrew Garnham1, Judi Porter1, 2, Louise M. Burke3, Ricardo J. S. Costa1
1Department of Nutrition Dietetics & Food, Monash University, Notting Hill, Australia
2Institute for Physical Activity & Nutrition, Deakin University, Geelong, Australia
3Mary MacKillop Institute for Health Research, Australian Catholic University, Melbourne, Australia
Correspondence to: Ricardo J. S. Costa, Department of Nutrition Dietetics & Food, Monash University, Notting Hill, Australia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This study aimed to characterise recovery outcomes and repeated performance following 2h high-intensity interval training (HIIT) exercise, followed by consumption of 1.2g/kg body mass (BM) and 0.4g/kgBM of carbohydrate and protein, respectively, between biological sex and fitness status categories. Venous blood samples, muscle biopsies, BM, body water, and breath samples were collected, and gastrointestinal symptoms (GIS) were measured, pre-exercise, and throughout 4h recovery. The following morning, participants returned to assess performance outcomes. Significantly greater body water losses were experienced by high (BM loss: 2.3%) vs. moderate fitness athletes (1.8%; P=0.009), but there were no differences between sexes (1.9%). Intestinal injury, carbohydrate malabsorption, and GIS occurred amongst all groups, with no differences. Phosphorylation of mTOR (P<0.001) and Akt (P=0.031), but not rpS6, increased from 0-2 h recovery in both fitness groups. Greater overall phosphorylation of GSK-3β was observed amongst high fitness (P=0.033). There were no group differences for glucose, insulin, cortisol, leukocyte or cytokine markers. A decline in neutrophil functional responses (36%) occurred for all groups. The following day, rates of carbohydrate oxidation were greater amongst males at all intensities. Rates of fat oxidation rates were greater at 50% and 60% V̇O2max, and carbohydrate oxidation were greater at 70% and 80% V̇O2max amongst high compared to moderate fitness athletes. Absolute performance was greater amongst high vs. moderate fitness; however, there were no differences in relative performance between groups. Recovery optimisation markers following a 2h HIIT exercise protocol and consumption of carbohydrate and protein at 1.2g/kgBM and 0.4g/kgBM, respectively, are similarly achieved by male and female athletes of moderate and high fitness status. Registration: This sub-group analysis was part of a larger study that was prospectively registered with ANZCTR (reference number 375090).
Keywords: Muscle glycogen, Protein synthesis, Hydration, Immune, Gastrointestinal, Performance
Cite this paper: Isabella Russo, Paul A. Della Gatta, Andrew Garnham, Judi Porter, Louise M. Burke, Ricardo J. S. Costa, The Influence of Biological Sex and Fitness Status on Markers of Recovery Optimisation in Response to Prolonged High Intensity Interval Exercise, International Journal of Sports Science, Vol. 10 No. 6, 2020, pp. 145-163. doi: 10.5923/j.sports.20201006.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The implementation of recovery nutrition strategies to support training adaptations and performance outcomes is common practice amongst athletes at all levels of competition [1]. Generally, these strategies focus on replacement of substrate and body water losses, and repair of damaged tissues (e.g., skeletal muscle). Indeed, over several decades, an extensive body of literature has developed to determine the ideal intake of carbohydrate, protein, and water to support muscle and liver glycogen replenishment, skeletal muscle protein synthesis, and rehydration, respectively [2,3]. To date, however, few studies have considered nutritional support for restoring immunocompetency in response to immunodepressive exercise, and (or) the impact of exercise-induced gastrointestinal syndrome on nutrient assimilation in the post-exercise recovery period [4-7]. Moreover, these guidelines acknowledge that fitness status and biological sex may influence individual nutrient requirements, but currently lack data to provide definitive and (or) quantitative recommendations. It is well established that the extent of physiological (i.e., thermoregulatory and immune stress) and biochemical (i.e., substrate depletion, local and systemic inflammatory responses, and accumulation of metabolic by-products) disturbances induced by the specific exercise stress are major determinants of recovery nutrition requirements [3]. Prolonged strenuous exercise is known to reduce muscle glycogen and body water content, and induce skeletal muscle damage. For example, steady state treadmill running (i.e., 90-120 min at 70-75% V̇O2max) in thermoneutral conditions has been reported to deplete muscle glycogen content below 250 mmol/kg dry weight (dw) and induce body mass (BM) loss >2.5% [8-12]. Likewise, skeletal muscle damage, as indicated by biochemical (i.e., increased creatine kinase and (or) myoglobin) and functional (i.e., reduced isometric maximal voluntary contraction, increased muscle soreness) markers, is induced by prolonged intermittent running (i.e., 90 min Loughborough Intermittent Shuttle Test) and eccentric and (or) plyometric type contractions (e.g., 5 x 20 plyometric drop jumps) exercise protocols [13,14]. However, characterisation of these exercise-induced perturbations is bias towards young well-trained male athletic populations, with a scarcity in female athlete population recovery research. Prolonged strenuous exercise is proposed to induce an acute immune alteration, characteristics of: 1) an ‘open window’ that may lead to increased risk of microorganism-borne infectious episode as a result of pathogenic exposure, and 2) an acute systemic inflammatory response [15,16]. Steady state running (i.e., 70-75% V̇O2max) for 2 h in thermoneutral conditions has consistently been shown to decrease innate immune system responses, including depressed in-vitro bacterially challenged (E.coli lipopolysaccharide) neutrophil elastase release by >30%, despite the post-exercise neutrophilia, and also increasing the systemic inflammatory cytokine profile (SIR profile) [4,5,17-19]. Moreover, skeletal muscle (i.e., ultrastructural myofibrillar disruption, swelling, efflux of myocellular proteins) and gastrointestinal tissue damage (i.e., ischemic epithelial cell death, disruption to function and regulation of tight-junction proteins) occur following prolonged and muscle-damaging exercise, and launch local and systemic inflammatory responses, that further disrupts regulation of gastrointestinal and sarcolemma barriers, respectively [6,20]. Impaired functionality of epithelial tissue and sarcolemma may interfere with assimilation of recovery nutrition, from the lumen into circulation, and form circulation into intracellular compartment, respectively. A functional and coordinated immune response is required for removal of damaged skeletal muscle tissue for subsequent growth and adaptation, and to repair gastrointestinal-associated lymphoid tissue structure and function. There is mounting evidence to describe the interrelated nature of the targeted systems and (or) organs of recovery nutrition (i.e., skeletal muscle glycogen repletion and tissue repair, hydration status, immune and gastrointestinal function), and the importance of timely and adequate nutritional interventions. The concept of ‘exercise recovery optimisation’ integrates recovery strategies that maximise desired outcomes while minimising those that cause detrimental outcomes within the complex and interrelated responses to exercise [21]. Studies to date investigating post-exercise nutritional strategies to support immune and gastrointestinal function have predominantly employed well-trained (i.e., V̇O2max >60 ml/kgBM/min) male athletes [4,5,17,22], while the effects of fitness status and biological sex on the responsiveness to recovery optimisation nutrition interventions have not been systematically and comprehensively researched. Although it is well established that differences in fluid dynamics, substrate oxidation, and relative performance intensities exist between male and female athlete populations (i.e., biological sex differences), and well-trained (elite or high competitive) and moderately-trained athletes (recreationally active), the implications of these differences on post-exercise recovery nutrient bioavailability and assimilation, and subsequent nutritional requirements, between these subgroups remain poorly characterised [23-30]. With this in mind, the current study aimed to characterise differences in recovery outcomes following 2 h high-intensity interval training (HIIT) exercise protocol and consumption of a recovery beverage, and subsequent performance the following day, between 1) male and female athletes, and 2) moderate and high fitness athletes. The influence of biological sex and fitness status on assimilation and integration of recovery nutrition was assessed using global markers of recovery optimisation including exercise-induced gastrointestinal syndrome, immune function response previously confirmed to depress after exercise and respond to recovery nutrition (e.g., in-vitro bacterially-stimulated neutrophil elastase release), muscle glycogen resynthesis, protein synthesis, rehydration, and performance outcomes. It was hypothesised male athletes and high fitness status athletes would experience greater exercise-induced perturbations in response to 2 h HIIT exercise. It was further hypothesised that following the exercise stress, greater exercise induced perturbations amongst male and high fitness athletes would result in suboptimal delivery, absorption and assimilation of recovery nutrition leading to impaired recovery outcomes and diminished subsequent performance.
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
- Thirty-five (n= 27 male, n= 8 female) endurance trained athletes volunteered to participate in the study. Participants were grouped according to their V̇O2max (i.e., <55 ml/kg BM/min or >60 ml/kg BM/min) for fitness status, and in accordance with their biological sex. Baseline characteristics are summarised in Table 1. All participants gave written informed consent. This sub-group analysis was part of a larger study that was prospectively registered with ANZCTR (reference number 375090), received approval from the local ethics committee (MUHREC: 12799) and conformed to the Helsinki Declaration for Human Research Ethics. Inclusion and exclusion criteria has been previously reported in Russo et al [31].
|
2.2. Preliminary Measures
- Baseline measurements were recorded one to three weeks prior to the first experimental trial. Height (stadiometer, Holtain Limited, United Kingdom) and BM (Seca 515 MBCA, Seca Group, Germany) were recorded. V̇O2max (Vmax Encore Metabolic Cart, Carefusion, USA) was estimated using a continuous incremental exercise test to volitional exhaustion on a motorised treadmill (MyRun Technogym; Technogym, Italy) as previously reported [4]. To determine running speeds for the exercise trials, the speed at approximately 50%, 60%, 70%, and 80% V̇O2max and 1% gradient was determined and verified from the V̇O2 work rate relationship.
2.3. Experimental Protocol
- Participants were required to consume a standardised low FODMAP (<2 g/meal) diet during the 24 h prior to, and throughout the experimental trial. Daily intake met current nutrition guidelines for endurance athletes (overall mean (SD):, energy 10.3 (2.5) MJ/day, protein 99 (29) g/day, fat 58 (29) g/day, carbohydrate 358 (84) g/day, fibre 44 (11) g/day, and water 2717 (1187) ml/day) [3,32]. Participants were asked to refrain from consuming alcohol, and performing strenuous exercise during the 48 h before the experimental trial, and from consuming caffeinated beverages during the 24 h before the experimental trial. Compliance to these instructions was checked via the completion of a 24 h pre-trial food and exercise diary. Participants reported to the laboratory at 0800h after consuming the standardised low FODMAP mixed carbohydrate breakfast (energy 2.8 (0.9) MJ, protein 25 (10) g, fat 20 (6) g, carbohydrate 92 (32) g, fibre 12 (4) g, and 357 (243) ml water). Trials for female athletes were scheduled during the follicular phase of their menstrual cycle (n= 7) or when taking the active medication of the oral contraceptive pill (n= 1). Resting estrogen levels (DKO003/RUO; DiaMetra, Italy) were measured for verification (7.0 (3.4) pg/ml). Before commencing exercise, participants were asked to void, and pre-exercise nude BM and total body water (TBW) (Seca 515 MBCA, Seca Group, Germany) were recorded. Participants inserted a thermocouple 12 cm beyond the external anal sphincter to record pre- and post-exercise rectal temperature (Precision Temperature 4600 Thermometer, Alpha Technics, USA). Participants provided a breath sample into a 250 ml breath collection bag (Wagner Analysen Technick, Germany), and completed an exercise-specific modified visual analogue scale GIS assessment tool [33]. Blood was collected by venepuncture from an antecubital vein into three separate vacutainers (6 ml 1.5 IU/ml lithium heparin, 4 ml 1.6 mg/ml K3EDTA, and 5 ml SST; BD, UK). The exercise protocol consisted of a 2 h (initiated at 0900h) HIIT session in 23.4 (0.7) °C ambient temperature and 42 (8) % relative humidity on a motorised treadmill, as described in Figure 1. Immediately post-exercise, nude BM and rectal temperature were recorded. The recovery period commenced 30 min after the end of the exercise protocol to prepare for muscle biopsy sampling. Participants rested in a supine position in a sterile phlebotomy room for venous blood sampling followed by the first muscle biopsy thereafter. TBW was measured immediately after muscle biopsy sampling. After sample collection and measurement recording, participants were provided with a commercially available chocolate flavoured dairy milk beverage. The beverage was served in opaque bottles at ~7°C beverage temperature [34], in 3 equal boluses every 10 min, from 0.5 h of recovery. The volume of the beverage was calculated to provide 1.2 g/kg BM of carbohydrate and 0.4 g/kg BM of protein (energy 2.5 (0.3) MJ, protein 28 (4) g, fat 16 (2) g, and carbohydrate 84 (12) g). Additional water calculated to provide a total fluid intake of 35 ml/kg BM was provided at hourly intervals. Participants were instructed to drink as much as tolerable. Total fluid intake was recorded hourly. The percentage of fluid retained was calculated from the difference between ingested fluid and urine output, as a fraction of total fluid intake [35]. An additional muscle biopsy samples was taken at 2 h into the recovery period. Blood samples, nude BM and TBW were collected again at 2 h and 4 h of recovery. Breath samples were collected and GIS recorded every 30 min throughout the recovery period. Total urine output was collected throughout the total recovery period. Weight of urine output was recorded at 2 h and 4 h of recovery. After sample collection and measurement recording at 2 h of recovery, participants received a standardised recovery meal (energy 2.8 (0.6) MJ, protein 31 (7) g, fat 4 (1) g, carbohydrate 130 (29) g, fibre 9 (2) g, and water 409 (90) ml), and were instructed to consume as much as tolerable. The total weight of the meal consumed was recorded. In addition, participants were provided with a standardised low FODMAP evening meal to consume after leaving the laboratory (energy 3.0 (1.4) MJ, protein 29 (14) g, fat 17 (16) g, carbohydrate 98 (50) g, fibre18 (7) g, and water 897 (712) ml).
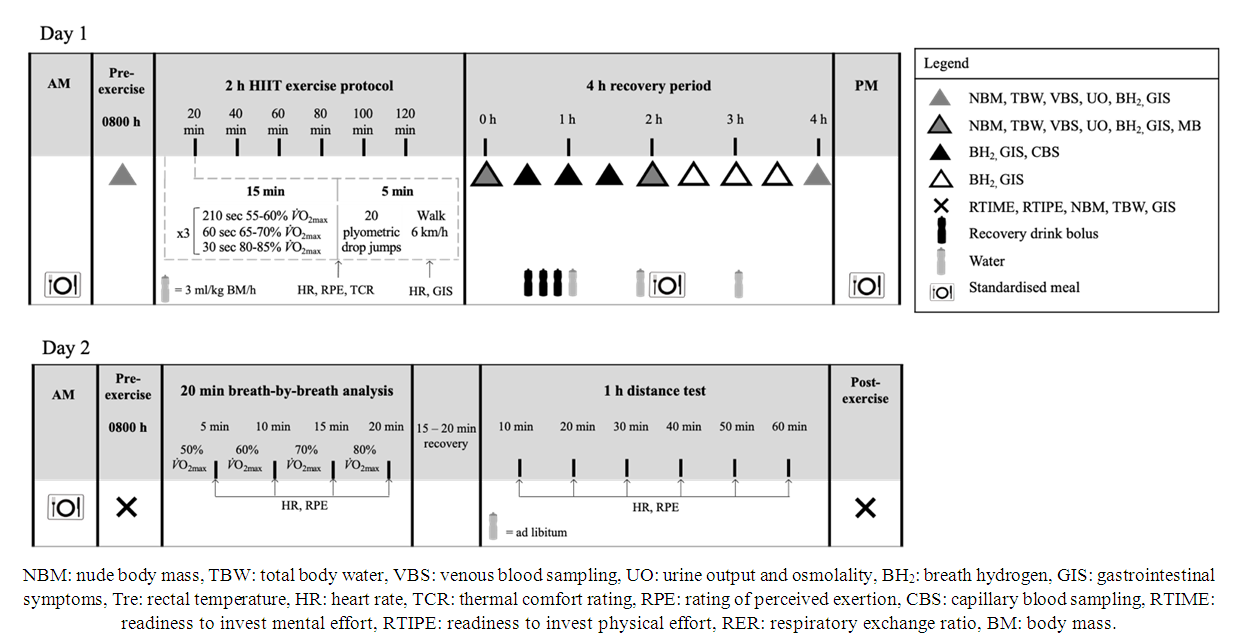 | Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the experimental design |
2.4. Muscle Biopsy Procedure
- Nineteen male and three female participants consented to providing muscle samples. Muscle biopsies were performed using a modified 5 mm Bergstrom biopsy needle. Samples were obtained from the vastus lateralis of the ipsilateral leg for the first trial, and contralateral leg for the second. The skin of the lateral aspect of the mid-thigh was washed well (10% Povidone – Iodine solution) then 2-3 ml of local anaesthetic (lidocaine 1%) was infiltrated subcutaneously over vastus lateralis to anaesthetise the skin and superficial fascia. After the anaesthetic had taken effect, two 5mm stab incisions ~15 mm apart were made through skin and fascia, with one incision made for each muscle biopsy sample. Samples were then extracted, immediately submerged in liquid nitrogen and stored at -80°C prior to further analysis.
2.5. Sample Analysis
- Blood glucose concentration, hemoglobin, haematocrit, total and differential leukocyte counts, were determined as previously described [17,32]. Coefficient of variation (CV) for blood glucose concentration, hemoglobin, haematocrit, and leukocyte counts were 5.5%, 2.3%, 0.6% and 11.8%, respectively. Hemoglobin and hematocrit values were used to estimate changes in plasma volume (PV) relative to baseline, and used to correct plasma variables. To determine the blood glucose response to the recovery beverage, immediately before and every 30 min thereafter for 2 h, blood glucose concentration was measured from capillary blood samples (CV 3.7%). To determine in-vitro bacterially-stimulated elastase release, 1 ml of whole blood was pipetted into a microcentrifuge tube containing 50 μg of 1 mg/ml bacterial stimulant (lipopolysaccharide from E.coli, Sigma, Poole, UK) within 5 min of collection and gently vortex-mixed. Samples were incubated in a water bath (Labline, Thermo Fisher Scientific Australia, Scoresby, Victoria, Australia) at 37°C for 1 h, and further mixed by gentle inversion at 30 min. Bacterially challenged samples were then centrifuged at 4000 rpm (1500 g) for 10 min, and supernatant was aspirated into 1.5 ml micro-storage tubes and stored at -80°C for further analysis. PMN elastase (BMS269; Affymetrix EBioscience, Vienna, Austria) was determined by ELISA. The remaining whole blood processing and analysis (i.e., insulin, cortisol, aldosterone, I-FABP, and sCD14 ELISA, and multiplex system for systemic inflammatory profile) were performed, as previously reported [17,22]. Plasma osmolality (POsmol) was determined by freezepoint osmometry (Osmomat 030, Gonotec, Germany) (CV 0.6%). The CVs for ELISAs were ≤10.0% and for cytokine profile multiplex was 17.5%. Breath samples (20 ml) were analysed (CV 2.0%) for hydrogen (H2) content using a gas-sensitive analyser (Breathtracker Digital Microlyzer, Quintron, USA). Plasma sodium, potassium and calcium concentrations were determined using ion selective electrodes (Cobas c 501, Roche Diagnostics, Switzerland) and analysed by local pathology services (Cabrini Pathology, Australia).
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
- Approximately 30 mg of skeletal muscle was solubilized in radioimmunoprecipitation buffer (Millipore, Bayswater, Victoria, Australia) with 1 μl/ml protease inhibitor cocktail (Sigma- Aldrich, Castle Hill, New South Wales, Australia) and 10 μl/ml Halt Phosphatase Inhibitor Single-Use Cocktail (Thermo Scientific, Australia, North Ryde, New South Wales, Australia). The concentration of protein per sample was determined by the bicinchoninic acid assay (BCA Protein Assay Kit#23225, Thermo Scientific). 20 μg of skeletal muscle protein lysate was loaded onto into either Bio-Rad precast Criterion TGX Stain-Free 4-12% gels (Bio-Rad, Gladesville, New South Wales, Australia). SDS-PAGE was conducted following manufacturer’s instructions. Protein was then transferred to PVDF membranes and blocked for 1 h in 5% bovine serum albumin (BSA) solution in Tris-buffered saline-Tween, (pH 7.6, 20 mmol/L Tris and 150 mmol/L NaCl, 0.1% Tween) (TBST) at room temperature. Membranes were then incubated in primary antibodies diluted in 5% BSA/TBST overnight at 4°C. Following washing in TBST, membranes were incubated for 1 h with fluorescent secondary antibodies (phospho-mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)Ser2448, phospho-protein kinase B (Akt)Ser473, phospho-ribosomal protein S6 (rpS6)Ser235/236, and phosphor-glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK-3β)Ser9) (Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) DylightTM 800 Conjugate; Anti-mouse IgG (H+L) DylightTM 680 Conjugate) (Cell Signalling Technologies®, Danvers, Massachusetts, USA) diluted 1:10,000 in TBST. Following 2 further washes in TBST and 1 wash in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) membranes were scanned using the LiCOR® Odyssey CLx® Imaging System (Millennium Science, Mulgrave, Victoria, Australia). All targets were normalized to total protein using either the Bio-Rad stain-free system.
2.7. Muscle Glycogen Analysis
- One fraction of muscle sample (approx. 20-25 mg (ww)) was freeze-dried, after which collagen, blood and other non-muscle material were removed from the muscle fibres. Samples were then pulverized and powdered. Samples were extracted with 0.5 M perchloric acid (HClO4) containing 1 nmol EDTA and neutralised using 2.2 M KHCO3. Adenosine triphosphate, phosphocreatine, and creatine was determined from the supernatant by enzymatic spectrophotometric assays [37,38]. Muscle glycogen content was determined from 2 aliquots of freeze-dried muscle (2–3 mg) as previously reported [37].
2.8. Statistical Analysis
- Confirmation of adequate statistical power was determined from the applied statistical test, mean, standard deviation, and effect size of original research data extracted from a systematic literature review process on markers of recovery optimisation a priori [21]. Using a standard alpha (0.05) and beta value (0.80), the current participant sample size, within an independent cohort design, is estimated to provide adequate statistical power (power* 0.80-0.99) for detecting significant group differences (G*Power 3.1, Kiel, Germany). Data in the text and tables are presented as mean (SD) for experimental descriptive method, and mean and 95% confidence interval (CI) for primary variable, as indicated. For clarity, data in figures are presented as mean and standard error of the mean (SEM), and/or mean and individual responses, as indicated. Systemic inflammatory cytokine responses are presented as raw values and systemic inflammatory response profile (SIR-profile), as previously reported [39]. Only participants with full data sets within each specific variable were included in the data analysis. Due to low rates of consent to muscle biopsy procedures amongst female participants, intramuscular markers are limited to analysis by fitness status only. All data were checked for normal distribution (Shapiro-Wilks test of normality) by calculating skewness and kurtosis coefficients. Variables with singular data points were examined using independent sample t-tests, or non-parametric Mann-Whitney U test, when appropriate. Variables with multiple data points were examined using a two-way repeated-measures ANOVA, with fitness status and biological sex as between-subject factors. Assumptions of homogeneity and sphericity were checked, and when appropriate adjustments to the degrees of freedom were made using the Greenhouse- Geisser correction method. Main effects were analysed by Tukey’s post hoc HSD. Statistics were analysed using SPSS statistical software (V.26.0, IBM Corp, Armonk, NY) with significance accepted at P≤ 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
- V̇O2max relative to BM and fat free mass (FFM) did not differ between male and female athletes (Table 1). TBW was significantly greater (Table 2), and body fat percentage lower (Table 1) amongst male and high fitness athletes, compared to female and moderate fitness athletes, respectively. As intended, there was a significant difference in V̇O2max between high and moderate fitness athletes (Table 1). High fitness athletes were younger than their counterparts (P= 0.034).
3.2. Exertional Strain
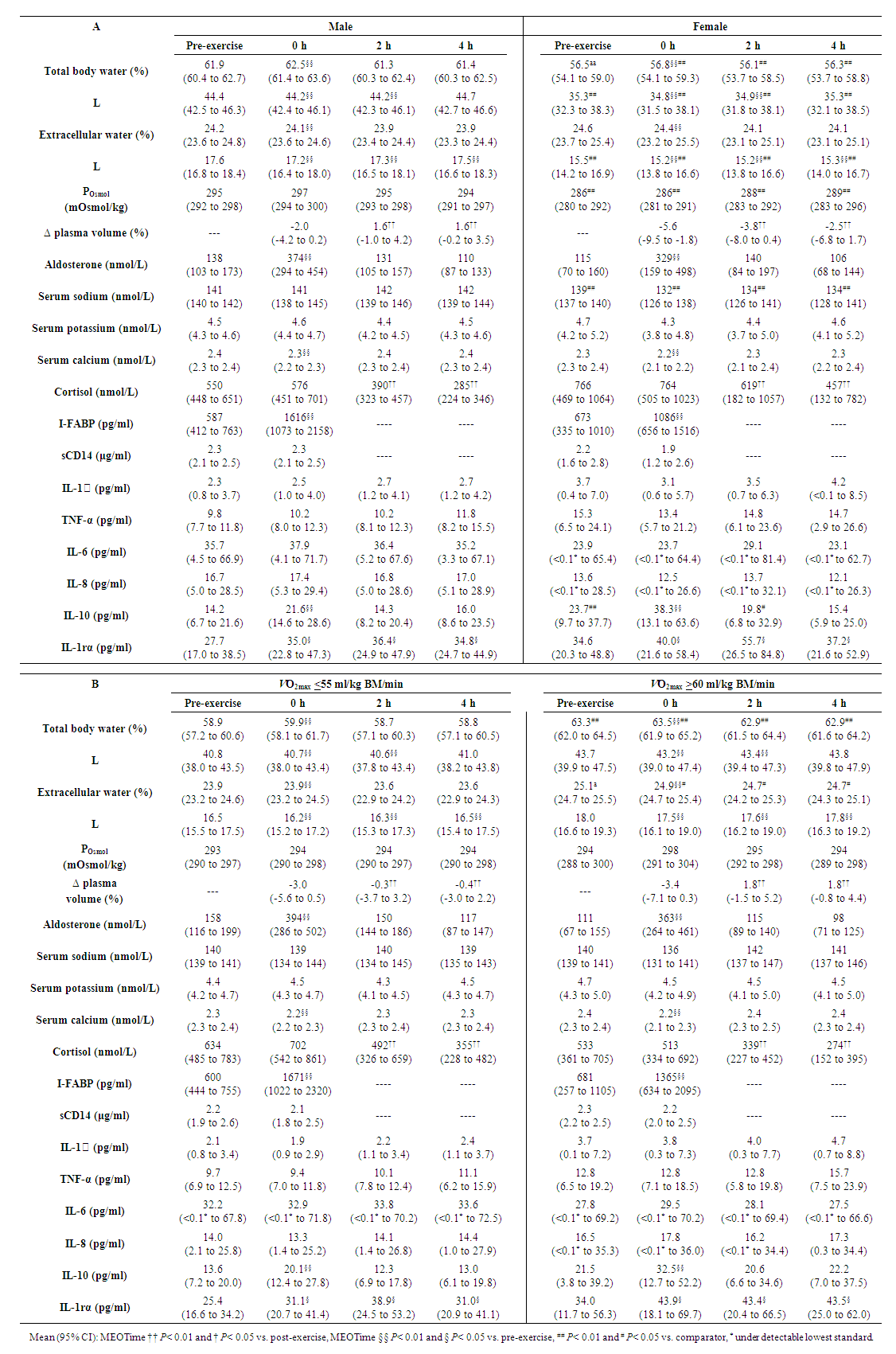
- During exercise, a main effect of time (MEOTime) was observed for peak (overall mean and 95% CI otherwise specified: 158 (156 to 160) bpm; P< 0.001) and recovered HR (122 (120 to 124) bpm; P< 0.001), RPE (13 (12 to 13); P< 0.001) and TCR (9 (8 to 9); P< 0.001); whereby HR, RPE and TCR increased as exercise progressed for all groups. A trend towards a fitness*time interaction (P= 0.053) was observed for recovered HR, such that values were lower amongst high fitness athletes as the exercise progressed. Rectal temperature increased pre- (36.6 (36.3 to 36.9) °C) to post-exercise (37.8 (37.5 to 38.1) °C) for all groups (P< 0.001). Plasma cortisol concentration decreased significantly from 0 h to 2 h and 4 h recovery (P< 0.01), with no group differences (Table 2).
3.3. Gastrointestinal Integrity and Symptoms
- There were no differences in exercise-associated increases in plasma I-FABP concentration between groups (Table 2). There were no significant group differences in severity of GIS during exercise and recovery period (Table 3). There was a MEOTime for breath H2 (P< 0.001), with all groups reaching a peak of clinical significance (male: 22 (15 to 29) ppm, and female: 15 (5 to 25) ppm), high fitness: 21 (13 to 28) ppm, moderate fitness: 22 (13 to 32) ppm at 3.5 h post exercise (Figure 2). No significant main effects or interaction were observed for plasma sCD14 concentration (Table 2).
3.4. Blood Glucose Availability and Serum Insulin Response
- A MEOTime occurred for blood glucose and serum insulin, imposed by feeding during the recovery period (Figure 3). Blood glucose concentration was significantly greater 1 h and 1.5 h into recovery, compared to pre-exercise values (P< 0.01). Serum insulin was significantly lower at 0 h recovery compared to all other time points (P< 0.01). No group differences were observed.
3.5. Immune Responses
- An exercise-induced leukocytosis (10.2 (9.3 to 11.1) x109/L; P< 0.001), neutrophilia (6.9 (6.2 to 7.7) x109/L; P< 0.001), monocytosis (0.6 (0.6 to 0.7) x109/L; P= 0.004), and increased neutrophil: lymphocyte ratio (2.9 (2.6 to 3.3); P< 0.001) were observed in the recovery period in all groups. No main effects or interaction were observed for unstimulated plasma elastase concentration (178 (116 to 239) ng/ml). A MEOTime was observed for total bacterially-stimulated plasma elastase concentration such that values increased from pre-exercise (3.3 (2.0 to 4.7) μg/ml) to 2 h recovery (5.3 (3.7 to 6.8) μg/ml) (P< 0.01). Neutrophil function decreased during the recovery period (36%); however no main effects or interaction were observed for bacterially-stimulated elastase release per neutrophil (544 (428 to 660) fg/cell). A biological sex*time effect was observed for IL-10 concentrations, whereby values were significantly greater amongst females pre-exercise and 0 h recovery, and 2 h recovery. A MEOTime occurred for plasma IL-1ra concentrations, whereby IL-1ra values increased at 0 h recovery and remained elevated throughout the remainder of the recovery period (P< 0.05). No main effects or interaction were observed for plasma IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-8 concentrations (Table 2). No difference in exercise-induced SIR-profile (male: 32 (21 to 43) arb.unit, and female: 45 (11 to 78) arb.unit, high fitness: 37 (17 to 57) arb.unit, moderate fitness: 40 (13 to 66) arb.unit) and recovery beverage post-prandial SIR-profile (male: 8 (-1 to 17) and female: 11 (-28 to 50) arb.unit, high fitness: -1 (-13 to 10) arb.unit, moderate fitness: 13 (-11 to 37)) was observed between groups.
3.6. Intramuscular Markers
- Post-exercise muscle glycogen content was 264 (232 to 297) mmol/kg dw and did not differ by fitness status (Figure 4). The early rate of muscle glycogen formation did not differ between trials (-15.3 (-27.3 to -3.3) mmol/kg dw/h). A group effect was observed for the ratio of phosphorylated GSK-3β to total GSK-3β such that values were greater amongst high fitness athletes (P= 0.033); however there was no effect of time for either group. A MEOTime occurred for the ratio of phosphorylated mTOR (P< 0.001) and Akt (P= 0.031) to total protein, such that values increased following consumption of the recovery beverage. No main effects or interaction was observed for phosphorylation of rpS6.
3.7. Hydration and Plasma Electrolyte Status
- Baseline POsmol was significantly higher amongst male compared to female athletes (P= 0.006), and remained higher throughout the experimental trial (P= 0.004); however, values remained within range of euhydration for all groups throughout the experimental trial (Table 2). An effect of biological sex was observed for plasma sodium concentration, as values were lower amongst female athletes (P= 0.004). Body water losses were greater amongst high compared to moderate fitness athletes (P= 0.009), and a significant correlation was observed between V̇O2max and BM loss (rs= 0.412, n= 35, P= 0.014). Total fluid intake during the recovery period did not differ between groups (male: 24 (22 to 26) ml/kgBM, female: 22 (18 to 26) ml/kgBM, high: 24 (22 to 27) ml/kgBM, moderate: 23 (21 to 25) ml/kgBM), and fluid retention at the end of the recovery period did not differ between groups (79 (76 to 83) %). A MEOTime occurred for TBW (P< 0.001) including extracellular (P< 0.001) water, with values returning to near baseline values 2 h into the recovery period. Plasma volume increased significantly at 2 and 4 h, compared to 0 h recovery for all groups (P< 0.01); however values were more negative amongst female compared to male athletes (P= 0.037). Plasma calcium and aldosterone concentrations decreased from pre- to post-exercise, before returning to resting values (P< 0.01).
3.8. Psychophysiological Parameters & Performance Outcomes
- There was a group effect for mental readiness to invest effort (P= 0.021), whereby male athletes reported greater readiness to perform (7 (6 to 8)) compared to female athletes 5 (3 to 6)). TBW was significantly greater amongst male (61 (60 to 62) %) and high fitness athletes (62 (61 to 64) %), compared to female (56 (53 to 59) %) and moderate fitness athletes (59 (57 to 61) %), respectively (P< 0.01). During the breath-by-breath test, rates of carbohydrate oxidation were greater at all intensities amongst male compared to female athletes (P= 0.008; Table 4). V̇O2 values were greater amongst high compared to moderate fitness athletes (P< 0.001). Rates of fat oxidation rates were significantly greater at 50% (P= 0.044) and 60% V̇O2max (P= 0.024) and carbohydrate oxidation were significantly greater at 70% (P= 0.030) and 80% V̇O2max (P= 0.031) amongst high fitness athletes compared to moderate fitness athletes. Mean HR (169 (167 to 171), RPE (15 (15 to 16)) and water intake (514 (297 to 731) ml) did not differ across the distance test. Relative (75 (73 to 78) % V̇O2max) and absolute (11.4 (10.8 to 11.9) km) performance was not different between male and female athletes. Total distance covered over 1 h was significantly greater amongst high fitness (12.6 (11.8 to 13.5) km) compared to moderate fitness athletes (10.6 (9.9 to 11.3) km; P= 0.001), however relative intensity did not differ (75 (72 to 78) % V̇O2max).
4. Discussion
- The current study aimed to characterise differences in recovery outcomes following 2 h high-intensity interval training (HIIT) exercise protocol and consumption of a recovery beverage, and subsequent performance the following day, between 1) male and female athletes, and 2) moderate and high fitness athletes. Contrary to our hypothesis, exercise-induced increases in plasma I-FABP, carbohydrate malabsorption, GIS and decline in neutrophil function did not differ between biological sexes. Total body water, plasma sodium and plasma osmolality were greater, and plasma volume change was lesser amongst male compared to female athletes. Carbohydrate oxidation rates were greater amongst male athletes at all intensities the following morning, but no differences in fat oxidation rates were observed. In accordance with our hypothesis, the 2 h HIIT exercise stress model used in the current study induced greater BM loss amongst high level fitness athletes compared to moderate fitness athletes. Plasma I-FABP concentration, carbohydrate malabsorption and associated GIS did not differ between fitness groups. Decline in neutrophil function occurred amongst both fitness status groups, with no differences. Fitness status did not influence post-exercise glycogen concentration or glycogen resynthesis in the acute timeframe, but a greater phosphorylation of GSK-3β was observed amongst high compared with moderate fitness athletes. Increased phosphorylation of mTOR and Akt protein signalling was observed in response to consumption of the recovery beverage amongst both fitness groups. Total body water was greater amongst high fitness athletes at all time points, but no other differences in fluid-electrolyte status were observed. The following day, rates of carbohydrate oxidation were greater at 50% and 60% V̇O2max, and fat oxidation were greater at 70% and 80% V̇O2max amongst high compared to moderate fitness athletes. Absolute performance was greater amongst high fitness athletes, however there were no differences in relative performance between groups. Findings from the current study suggest that recovery optimisation following a 2 h HIIT exercise protocol and consumption of 1.2 g/kg BM carbohydrate and 0.4 g/kg BM protein, using a dairy milk recovery beverage, is similarly achieved by male and female athletes of moderate and high fitness status.
4.1. Gastrointestinal Response to Recovery Nutrition
- Exercise-induced gastrointestinal syndrome is a recently recognised term used to describe the gastrointestinal disturbances caused by exercise stress, including intestinal epithelial injury, impair gastrointestinal function, and associated GIS, mediated by neuroendocrine and circulatory pathways [6]. Exercise-induced gastrointestinal syndrome may impair nutrient availability via impaired tolerance and (or) nutrient losses (i.e., vomiting, malabsorption, or diarrhoea), thereby impacting overall recovery optimisation outcomes [6,31,40-43]. In response to the 2 h HIIT exercise, there were no differences between biological sexes in plasma I-FABP or plasma cortisol concentrations. Subsequently, there were no differences in carbohydrate malabsorption and (or) GIS incidence or severity between sexes. In line with the current findings, previous literature has shown comparable responses in intestinal injury and symptomology amongst male and female athletes, following prolonged strenuous exercise (i.e., 2 h running at 60% and 70% V̇O2max) and adhering to the same dietary control [17,19].To our knowledge, this is the first study to explore the effect of training status on EIGS with post-exercise nutrition. Contrary to our hypothesis, the present findings suggest that circulatory- and (or) neuroendocrine-mediated gastrointestinal responses are unaffected by fitness status, as evidenced by no differences in intestinal injury (i.e., I-FABP), or stress (i.e., cortisol) and blood glucose responses, respectively. Consequently, it appears that assimilation of recovery nutrition does not differ by fitness status in response to a 2 h HIIT at the same relative intensity. Indeed, breath H2 concentration reached clinical significance (e.g., >10 ppm breath H2) amongst all groups (i.e., male, female, high fitness and moderate fitness athletes) following the exercise stress and consumption of the dairy milk beverage. These values are consistent with those seen amongst healthy individuals after consuming a solution containing 50 g lactose at rest [44], and are possibly related to the dosage and timing of nutrient intake and gastrointestinal presence. Similarly, the present findings show wide individual variation with regards to epithelial injury (Table 2) and carbohydrate malabsorption (Figure 2) that does not appear to be attributed to biological sex, nor fitness status, within the current cohort. Possible underlying physiological mechanisms include a) intestinal enterocyte carbohydrate transporter saturation capacity; and (or) b) exercise associated impairment of carbohydrate transporter translocation and activity effectiveness at the enterocyte brush border, secondary to increased enterocyte damage (i.e., circulatory gastrointestinal pathway of exercise-induced gastrointestinal syndrome) and (or) sympathetic activation (i.e., neuroendocrine gastrointestinal pathway of exercise-induced gastrointestinal syndrome). Transporter capacity and (or) individual capacity to curb circulatory and neuroendocrine strain on gastrointestinal integrity and function may be influenced by gut training [6], usual fibre and FODMAP intake [32], microbiota composition [39], or stress responses [45].
4.2. Immune Responses to Recovery Nutrition
- Exercise-associated immune perturbations, characterised by, circulatory leukocytosis and neutrophilia, with an adjunct reduction in neutrophil function, and inflammatory cytokine responses occurs during the acute post-exercise period, proportional to the intensity and duration of the exercise stress [15,16]. In the current exercise protocol, these immune perturbations were observed amongst all groups, with no group differences observed for all immune markers measures. An interesting observation was that, in all groups, the recovery beverage ingested after exercise failed to prevent the decline in in-vitro bacterially-stimulated neutrophil elastase release (i.e., indicative of neutrophil degranulation function); an immune marker repeatedly shown to be sensitive to recovery nutrition responses compared with other immune response markers [4,5,7,15-17,46], and an immune functional response essential for coping with exercise-associated luminal originated bacterial pathogenic endotoxins (e.g., lipopolysaccharide) [6,47,48]. This effect was likely attributed to the delay (i.e., 60 min) in provision of the recovery beverage [4], considering immediate feeding has consistently been shown to prevent this immune functional decline [4,5,17]. We have recently provided evidence to show that following 2 h running at 70% V̇O2max in thermoneutral conditions, immediate consumption of a dairy milk beverage (i.e., 1.2 g carbohydrate and 0.4 g protein/kg BM) increased bacterially-stimulated elastase release 3 h post-exercise [22]. It is hypothesised that the hyperinsulinemic and hypercalcemic effect on increased neutrophil chemotaxis, phagocytosis, and bactericidal capacity, and the effectiveness of neutrophil phagocytosis and degranulation processes, respectively, are possible contributing mechanisms [48-51]; whereas, delaying feeding may suppress the full activation of these mechanisms. Accordingly, no groups differences in serum insulin or plasma calcium concentrations were observed in response to consumption of the recovery beverage. To date, studies investigating nutritional interventions to support immune function following prolonged, strenuous exercise have been conducted exclusively amongst well-trained, male athletes [4,5,17,46]. In response to an acute exercise stress, research suggests that circulating leukocyte populations and cytokines amongst females during the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle, are comparable to their male counterparts [53]. In the present study, authors observed minor differences in cytokine profiles between sexes characterised by a greater pro-inflammatory (i.e., IL-1β) response amongst male athletes, while a greater anti-inflammatory (i.e., IL-10) response was observed amongst female athletes. In the current body of literature, sex-based differences in cytokine responses to prolonged exercise are mixed, likely due to lack of controlling for menstrual cycle and (or) oral contraceptive use; however, in accordance with the present findings, it is generally accepted that responses are not markedly different between trained male and female athletes and of clinical irrelevance [53]. Resting and exercise-induced leukocyte and inflammatory markers are reportedly unaffected by training status [54-56]. Consistent with this consensus, there were no differences in resting or exercise-induced leukocytosis, neutrophil activity or inflammatory profiles between high and moderate fitness athletes. Findings from the current study builds on previous evidence to show that innate immune markers are not affected by training or biological sex, following an acute bout of HIIT exercise and 1 h delayed nutritional intervention.
4.3. Muscle Glycogen and Recovery Nutrition
- Restoration of skeletal muscle glycogen stores is a primary focus of recovery nutrition following prolonged, glycogen depleting exercise [57]. In the current study, following 2 h HIIT, muscle glycogen stores were reduced to <300 mmol/kg dw. High fitness athletes showed greater phosphorylation of GSK-3β, suggestive of greater cellular activity towards skeletal muscle glycogen disposal. These results align with previous studies that have shown enhanced muscle glycogen restoration following continuous concentric exercise (i.e., 2 h cycling at 75% V̇O2max) amongst well-trained endurance athletes [58]. Indeed, consumption of 1.4 g carbohydrate/kg BM/h resulted in ~2-fold greater muscle glycogen concentrations amongst well-trained (i.e., >59 ml/kg/min) compared to sedentary (i.e., V̇O2max <40 ml/kg/min) adults, and that these rates correlated to sarcolemma glucose-transporter 4 (GLUT-4) concentration [58]. Authors also observed a more pronounced blood glucose and insulin response amongst sedentary adults. In the current study, despite a training effect of phosphorylation of GSK-3β, there were no group differences in the magnitude of change of GSK-3β phosphorylation, and all groups failed to achieve muscle glycogen disposal towards repletion of muscle glycogen stores within 90 min of consumption of 1.2 g carbohydrate/kg BM. Previous research has shown compromised muscle glycogen resynthesis >24 h after eccentric exercise, likely associated with reduced translocation of the GLUT-4 transporter and (or) insulin sensitivity of the damaged muscle sarcolemma [59-61]. Indices of muscle damage (i.e., creatine kinase or myoglobin) were not collected in the current study, as they are known to peak >24 h after muscle damaging exercise [62]. Potential limitations within the current protocol include the inability to quantify the extent of muscle damage between groups and metabolic activity towards muscle glycogen resynthesis beyond the 4 h acute recovery period. Moreover, due to low rates of consent to muscle biopsies, it was not possible to compare male and female muscle glycogen responses. Differences in GLUT-4 concentration, exercise-induced muscle damage and potential recovery nutrition requirements to mediate damaging effects amongst different athletic populations warrants further investigation.
4.4. Muscle Protein and Recovery Nutrition
- It is well established that the male phenotype is characterised by greater skeletal muscle mass and a greater relative contribution of protein, in particular leucine, to substrate oxidation [63,64]. In light of these phenotypic and metabolic differences, has been suggested that female daily protein requirements relative to BM are 15-20% less than their male counterparts [65]. Current recovery nutrition guidelines, however, do not differentiate male and female protein requirements [3]. As previously noted, analysis of differences in intramuscular signalling proteins between males and females was not possible. Quantification of fractional synthetics rates is necessary to establish sex-based differences in muscle protein synthesis.Phosphorylation of mTOR and Akt has consistently been observed following endurance exercise in endurance trained and untrained adults [66-68]. Indeed, in the current study, the exercise stress and subsequent intake of 0.4 g protein/kg BM increased phosphorylation of mTOR and Akt in both high and moderate fitness athletes. The current body of literature investigating protein requirements to support skeletal muscle protein synthesis following endurance exercise has employed athletes with V̇O2max ranging from 45-66 ml/kg/min [68]. Although research is limited, the current findings support the notion that there do not appear to be any training-associated differences in the acute anabolic responses to a standardised relative intensity endurance exercise stress and (or) protein feeding.
4.5. Hydration and Recovery Nutrition
- Total body water and fluid dynamics are known to differ between sexes and fitness groups, owing to differences in body composition (i.e., fat free mass vs. fat mass) [69]. TBW and ECW differed between all groups throughout the experimental trial, corresponding to differences in skeletal muscle mass and fat mass (Table 1, 2). Although resting POsmol was significantly different between male and female athletes, all participants commenced exercise within range of euhydration [17]. Likewise, all groups achieved euhydration at the end of the recovery period as indicated by body water, BM, PV, and POsmol, with no group differences in fluid retention. It has previously been reported that women typically experience lower sweat rates compared to men [25,26]. In the current study, however, no differences in BM loss were observed. Greater decreases in PV and sodium concentrations were observed amongst female athletes, however there were no groups differences in aldosterone concentrations. No other differences in hydration status after exercise or throughout the recovery period were observed between sexes. In the current study, all women completed trials during the follicular phase of their menstrual cycle, or when taking the active oral contraceptive pill. Maughan, McArthur & Shirreffs, have previously reported that menstrual phase did not influence fluid retention, net fluid balance, urine or plasma electrolyte losses following 1.8% exercise-induced BM loss, and provided 150% fluid replacement [70]. Consistent with current exercise and fluid replacement guidelines, sex-based differences in fluid-electrolyte balance during exercise are inconsequential, and as such there do not appear any differences in rehydration requirements [2].Endurance-training is known to refine thermoregulatory responses, characterised by a more rapid onset of sweating and (or) greater overall sweat rates [23,24]. Accordingly, a significantly greater change in BM occurred amongst high fitness athletes in the current study. However, PV, POsmol, TBW, electrolyte status, absolute and relative fluid intake, and fluid retention did not differ between groups. These findings support the notion that water losses <2.5% BM loss are mild in nature and do not significantly perturb fluid-electrolyte status. As such, aggressive hydration strategies are unnecessary, as adequate water intake can be achieved by drinking to thirst and consuming sodium-containing meals [71].
4.6. Performance Outcomes
- It has previously been reported that female athletes are more reliant on fats as an energy substrate [28,29], and reach their fat max at a greater relative intensity compared to age and fitness matched males [30]. Due to greater energy requirements, absolute carbohydrate oxidation rates were significantly greater amongst males in the current study; however, relative contributions of carbohydrates and fats did not differ between sexes at any intensity (Table 4). It is generally accepted that at the elite level, female performance in endurance events is 7-12% slower than their male counterparts [72,73]. In the current study, however, absolute and relative intensities maintained during the performance trial were the same between males and females. Indeed, sex-based differences in the progression of recovery from muscle damaging exercise appear to be minor or inconsequential. Collectively, these findings suggest that the recovery nutrition provided (i.e., recovery beverage and meals), supported recovery optimisation similarly between male and female athletes.Endurance trained athletes display enhanced respiratory capacity of the muscle and increase propensity for fat oxidation during submaximal exercise [74-76]. In the current study, high fitness athletes demonstrated greater rates of fat oxidation rates at 70% V̇O2max. In addition, although greater distances were covered by high fitness athletes, there were no differences between groups in the relative intensity during the performance test. This conflicts with previous literature that has shown trained athletes reach their lactate threshold at a higher percentage of their V̇O2max, and maintain a higher percentage of their V̇O2max during endurance events [27]. It is possible that differences in fitness status were insufficient to detect significant differences.
4.7. Strengths and Limitations
- This is the first study to comprehensively compare markers of recovery optimisation between male and female, and moderate and high fitness athletes. Moreover, this is the first study to comprehensively examine the effect of post-exercise nutrition on multiple markers of innate immune function amongst female athletes. Although preceding studies have been indispensable in formulating current recovery nutrition guidelines, such studies have examined recovery outcomes in isolation amongst limited participant cohorts. The present findings highlight the inter-related nature of recovery optimisation outcomes, as well as the wide individual variation in exercise induced perturbations and recovery outcomes, particularly those associated with EIGS and nutrient assimilation. This reinforces the importance of recovery nutrition requirements being provided on an individual basis. A noted limitation within the current study is the imbalance between male and female participant numbers. The authors experienced difficulty recruiting female athletes to take part in the current study to completion, presumably due to the high burden and invasive nature of the experimental protocol. Despite lower female participant numbers, power calculations indicated n= 8 was sufficient to detect differences of a magnitude of practical and clinical relevance for the investigated markers.
5. Conclusions
- The current 2 h HIIT exercise protocol resulted in comparable exercise-induced increases in plasma I-FABP, carbohydrate malabsorption, GIS and decline in neutrophil function amongst male and female athletes of moderate at high fitness. Total body water, plasma sodium and plasma osmolality were greater, and plasma volume change was lesser amongst male compared to female athletes. The following morning, carbohydrate oxidation rates were greater amongst male athletes at all intensities, but no differences in fat oxidation rates were observed. In response to the 2 h HIIT, body water losses were significantly greater amongst high fitness athletes compared to moderate fitness athletes, but there were no differences in post-exercise muscle glycogen. The recovery beverage containing 0.4 g protein/kg BM resulted in increased phosphorylation of mTOR and Akt protein signalling amongst high and moderate fitness groups. Greater phosphorylation of GSK-3β was observed amongst high fitness athletes, but there were no group differences in early-phase muscle glycogen resynthesis. The following day, rates of carbohydrate oxidation were greater at 50% and 60% V̇O2max, and fat oxidation were greater at 70% and 80% V̇O2max amongst high compared to moderate fitness athletes. Findings from the current study suggest that recovery optimisation following a 2 h HIIT exercise protocol and consumption of 1.2 g/kg BM carbohydrate and 0.4 g/kg BM protein, using a dairy milk recovery beverage, is similarly achieved by male and female athletes of moderate and high fitness status. Considering the professional practice implications of the present findings, individual assessment of body composition, fluid dynamics, and gastrointestinal response to exercise and subsequent absorptive capacity, should be primary considerations for post-exercise nutritional recommendations, before biological sex and fitness status.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- Ricardo Costa (RC) was the chief investigator of this research. Isabella Russo (IR), Judi Porter (JP), and Louise Burke (LB) contributed towards development of the experimental design. All other authors contributed towards various aspects of data collection, and sample collection and analysis. IR and RC contributed to the analysis of the raw data. IR and RC prepared the original draft manuscript. All authors contributed to the review and final preparation of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Firstly, the authors would like to thank all the participants that volunteered to take part in this study, as well as Stephanie Gaskell, Alan McCubbin, Christopher Rauch, Alexandra Parr and Jamie Whitfield for their assistance in the laboratory during data and sample collection, and (or) sample analysis. The author would also like to thank industry collaborators Greg Holden and Katrina Strazdins for their support and industry input along the course of the Monash University Graduate Research Industry Partnership- Food and Dairy program.
Disclosure
- The current study was supported by Lion Dairy & Drink Australia Pty Ltd. The funder was not involved in the development of the experimental protocol, data collection, analysis or interpretation of results. No restrictions were placed on the reporting of findings.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML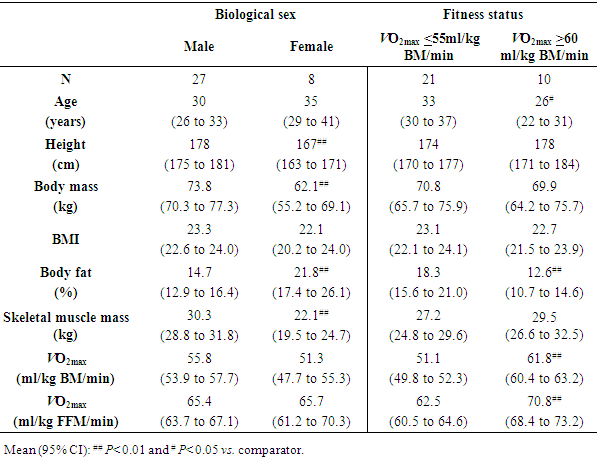
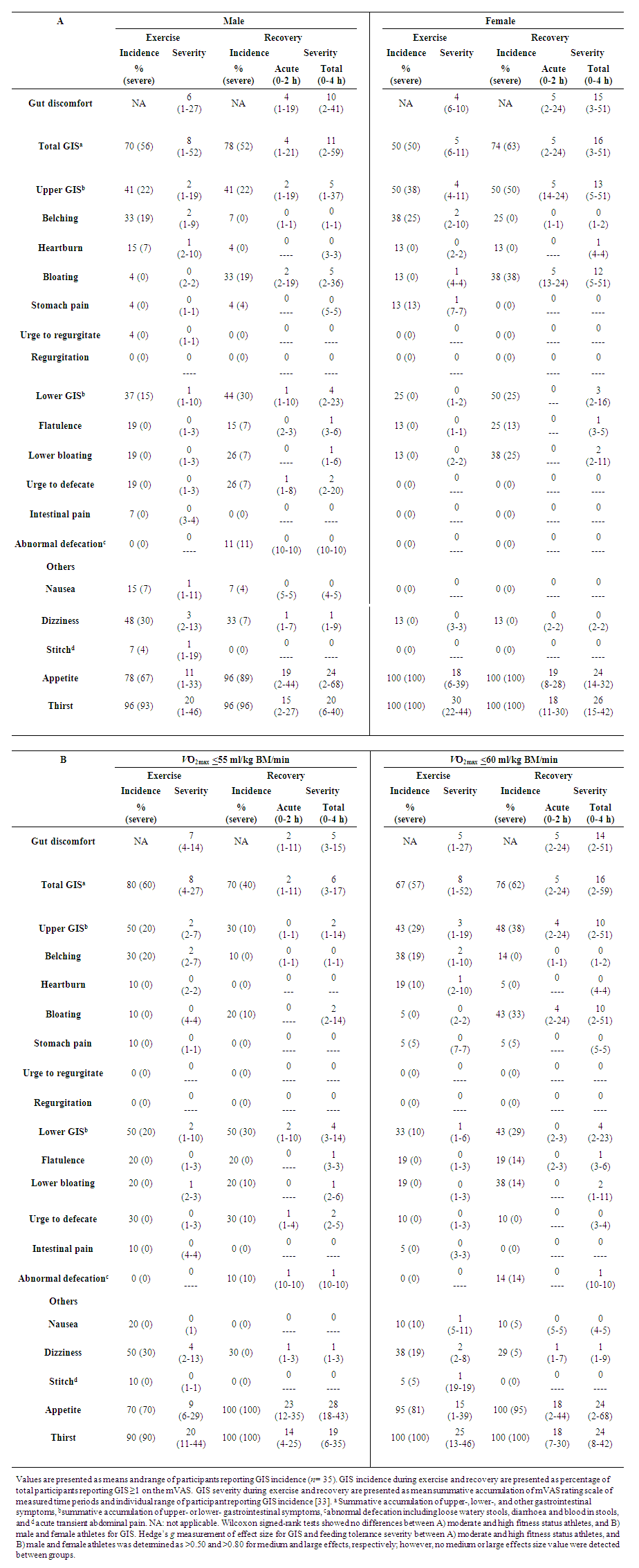
 vs. female athletes
vs. female athletes  , B) high fitness athletes
, B) high fitness athletes  vs. moderate fitness athletes
vs. moderate fitness athletes  , and C) and individual peak breath hydrogen responses after 2 h HIIT exercise in temperate ambient conditions and consumption of a dairy milk beverage
, and C) and individual peak breath hydrogen responses after 2 h HIIT exercise in temperate ambient conditions and consumption of a dairy milk beverage
 vs. female athletes
vs. female athletes  , and high fitness athletes
, and high fitness athletes  vs. moderate fitness athletes
vs. moderate fitness athletes 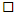 )
)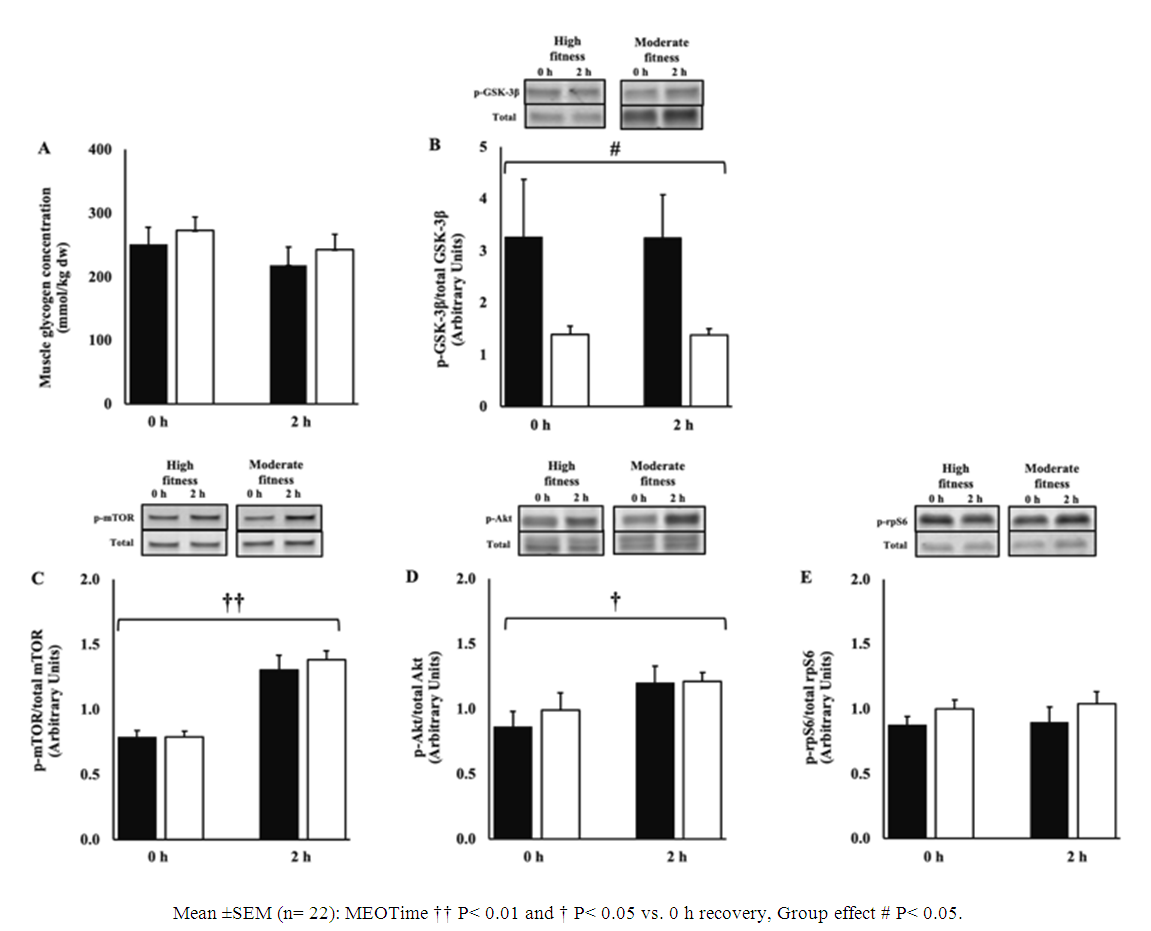
 to total GSK3-
to total GSK3- (B), ratio of phosphorylated mTOR to total mTOR (C), phosphorylated Akt to total Akt (D), and phosphorylated rpS6 to total rpS6 (E) after 2 h HIIT exercise in temperate ambient conditions and consumption of a dairy milk beverage for high fitness
(B), ratio of phosphorylated mTOR to total mTOR (C), phosphorylated Akt to total Akt (D), and phosphorylated rpS6 to total rpS6 (E) after 2 h HIIT exercise in temperate ambient conditions and consumption of a dairy milk beverage for high fitness  vs. moderate fitness athletes
vs. moderate fitness athletes