-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Sports Science
p-ISSN: 2169-8759 e-ISSN: 2169-8791
2020; 10(6): 131-144
doi:10.5923/j.sports.20201006.02
Received: Nov. 16, 2020; Accepted: Dec. 4, 2020; Published: Dec. 15, 2020

Hypohydration Impairs Cognition, Technical Ability and Physical Performance in Team Sports: A Review
Mariana A. Matos1, João A. Lopes2, Leonor S. Loureiro2, Rute Borrego1, Lino Mendes1, 3
1Dietetics and Nutrition, Escola Superior de Tecnologia da Saúde de Lisboa, Instituto Politécnico de Lisboa, Lisbon, Portugal
2Dietetics and Nutrition Department, Sporting Clube de Portugal, Lisbon, Portugal
3H&TRC- Health & Technology Research Centre, Escola Superior de Tecnologia da Saúde de Lisboa, Instituto Politécnico de Lisboa, Lisbon, Portugal
Correspondence to: Mariana A. Matos, Dietetics and Nutrition, Escola Superior de Tecnologia da Saúde de Lisboa, Instituto Politécnico de Lisboa, Lisbon, Portugal.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The aims of this literature review is to characterize the impact and mechanisms of hypohydration on cognitive, technical and physical performance in team sports; Performance in many team sports depends on cognitive function (e.g., attention, decision-making, memory and reaction time), execution of sport-specific technical skills (e.g., shooting, passing and dribbling) and high-intensity physical skills (e.g., running, lateral movement, jumping, intermittent high-intensity running). The influence of hydration status has been studied mostly in soccer, basketball and field hockey, with mixed results. Regarding cognitive performance, vigilance, decision-making time, reaction time of working memory or reactive agility were hindered by hypohydration. Regarding technical and physical performance, the results seems to be inconsistent. Studies suggest that 2-4% of hypohydration can impair the performance during basketball shots but has minimum effects in soccer and field hockey. However, it appears that hypohydration impairs cognition, technical ability and physical performance at higher levels of body mass loss (3 to 4%). Impaired performance is also more likely when the dehydration method involves heat stress. The increased subjective classifications of fatigue and perceived exertion consistently accompanied hypohydration and could explain, in part, the performance impairments reported in some studies. Further research is needed to develop valid, reliable and sensitive sport-specific protocols to be used in future studies.
Keywords: Athletic performance, Dehydration, Athletes
Cite this paper: Mariana A. Matos, João A. Lopes, Leonor S. Loureiro, Rute Borrego, Lino Mendes, Hypohydration Impairs Cognition, Technical Ability and Physical Performance in Team Sports: A Review, International Journal of Sports Science, Vol. 10 No. 6, 2020, pp. 131-144. doi: 10.5923/j.sports.20201006.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Total Body Water (TBW) balance depends on the difference between water consumption and loss. “Euhydration” (EUH) reflects a normal and average fluctuation in TBW content, while “hypohydration” and “hyperhydration” refer to a generalized deficit or excess of TBW beyond the normal range, respectively. Finally, "dehydration" (DEH) describes the process of water loss in the body, while "rehydration" describes the process of obtaining water in the body [1,2].The benefits of an optimal hydration status include maintaining athletic performance [3], maximizing metabolic heat transfer [4], maintaining mood [5] and facilitating recovery from exercise [1,6]. Hypohydration is classified as acute or chronic. Acute refers to exercise-induced hypohydration, while chronic is when water intake is insufficient over time [7]. A TBW deficit > 2% of body mass (BM) is the DEH threshold that has been found to adversely affect sports performance [8].Exercise can cause a sharp interruption in fluid balance, challenging the athlete to maintain optimal performance and safety during exercise [2]. Team sports, which are characterized by intermittent efforts of high intensity for prolonged periods, can cause higher sweating rates [9,10]. There are other factors that are associated with increased sweating such as hot/humid environments and the use of protective equipment that is present in many team sports [10–12]. However, individual sweating rates vary considerably [13], as do athletes’ fluid intake habits and opportunities for fluid replacement during sports play [10,14].Dehydration can negatively affect different physiological systems, such as nervous, cardiovascular, thermoregulatory and endocrine systems, and metabolism [15], which can lead to negative health consequences, affect athletic performance and increase the risk of heat stress injury in sports [1,15]. In addition, DEH affects short-term memory, while reducing alertness and the ability to concentrate [1,5,16]. Performance in many team sports depends on cognitive function (e.g., attention, decision-making, memory and reaction time), execution of sport-specific technical skills [e.g., shooting, passing and dribbling] and high-intensity physical skills (e.g., running, lateral movement, jumping and intermittent high-intensity running) [10]. Results of several studies suggest that dehydration negatively affects cognitive function, muscle strength, power and endurance [7,17–19].Given the potential impact of hydration status on athletic performance, the assessment of hydro electrolytic balance in athletes has been reported in a large number of studies [20]. However, few presented its effects on exercise performance and a comprehensive literature summary.The aim of this paper is to characterize the impact and mechanisms of hypohydration on cognitive, technical and physical performance in team sports.
2. Methods
- On May 7, 2020, a search was made in the online databases PubMed and Web of Science. Since they are platforms with different search systems, the keywords used were adjusted to the specific platforms.Thus, the terms "athletic performance", "performance", "athletes", "physical performance", "cognition", "attention”, “exercise", "anaerobic threshold", "Task performance", "task performance and analysis", "resistance performance", "balance, water electrolyte", "fluid balance", "hypohydration", "dehydration" and "water deprivation" were used as keywords (MeSH Terms). The keywords also included as terms only appearing in the title and summary of articles, the terms "team sports", "basketball", "volleyball", "handball", "field hockey", "soccer", "football". The terms and keywords were organized into three lines of research divided by themes that were later arranged into a single line of research with the boolean operator “AND”. That is, all concepts related to athletic performance were inserted with the boolean operator “OR”, creating two more different themes, namely for concepts related to hydration and concepts related to team sport, all inserted with the boolean operator “OR”. As inclusion criteria, we chose to use only articles available in English and Portuguese, whose sample was only comprised of humans, with a time limit of 15 years. Through the search in the PubMed database, 58 results were obtained which, together with the 134 results obtained in the Web of Science, made a total of 192 articles. The selection process is shown in Figure 1, following the steps of PRISMA [21].
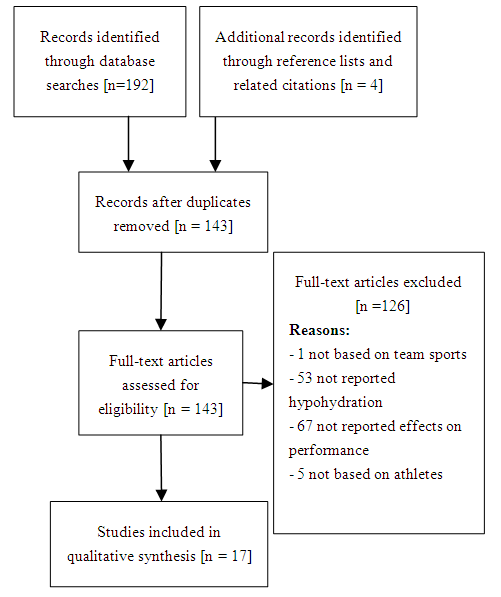 | Figure 1. PRISMA flow diagram of study selection and inclusion |
3. Results
- At the end of the selection process, 17 articles were selected for analyses (see table 1 for analysis of the studies).
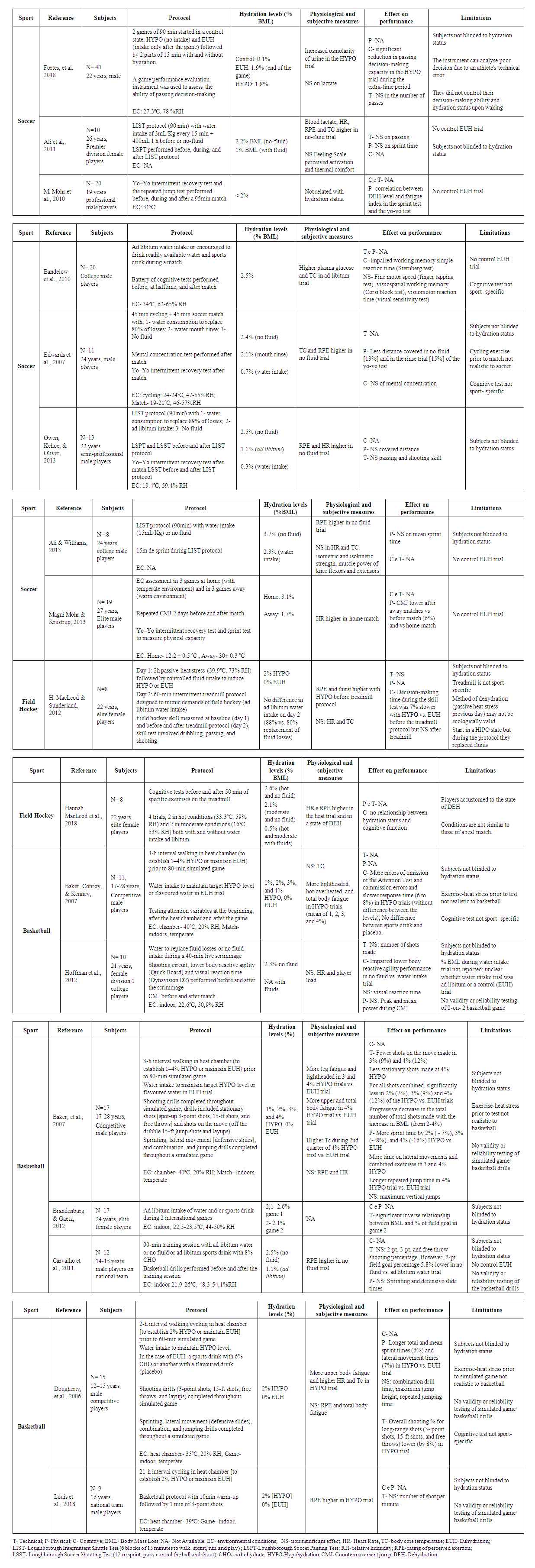 | Table 1. Summary of studies measuring effects of hypohydration on athletic performance during team sports |
3.1. Cognitive Performance
- Decision-making refers to the ability of the human brain to extract information from the visual scene, considered essential for good performance in unpredictable sports [22]. According to Murgia et al. [23], decision-making is based on cognitive processes such as visual perception, attention, anticipation and memory.
3.1.1. Soccer
- Specifically, in soccer, decision-making becomes important as a good pass can reach a team member who is not directly or indirectly scored and therefore create a chance for a goal [24].Three studies have investigated hypohydration and cognitive performance in soccer [22,25,26]. Overall, these studies suggest that water restriction has minimal effects on cognition, at least up to a 2.5% of Body Mass Loss (BML). Bandelow et al. and Fortes et al. [22,25] found significant effects on reaction time and decision-making ability. However, Edwards et al. didn’t report differences in mental concentration.Bandelow et al. [25] used a field study approach and complex data modelling to determine the relative contribution of several factors to cognitive performance. In this study, players drank water ad libitum in the first game and were encouraged to drink in the second game. Before, during half time and after each game, players performed cognitive tests which included fine motor speed, visuomotor reaction time, visuospatial working memory and working memory simple reaction time. Bandelow et al. [25] reported that >2.5% BML impaired working memory reaction time but had no effect on any other measure of cognitive performance. Instead, the maintenance of blood glucose and changes in core temperature were more important in determining speed and accuracy during the cognitive tests.Fortes et al. [22] used a soccer performance test through video analysis. The main findings indicated a reduction in decision-making capacity only in the DEH trial at compensation time. In addition, a ~2% BML was revealed after 90 minutes in the DEH and EUH conditions, with BM returning to baseline values in the EUH condition after athletes ingested water in the proportion of 1.5 L/kg of BML. The deprivation of water ingestion resulted in the attenuation of decision-making performance during the extra-time. Results of the present study demonstrated that water intake is an efficient strategy for maintaining decision-making performance in the EUH condition [22]. These results corroborate the findings of the systematic review by Lieberman (2007) [27], but contrast with the findings of the systematic review by Pross (2017) [28].
3.1.2. Basketball
- Two studies in basketball tested the impact of hypohydration on cognitive performance, reporting mixed results [29,30]. Hoffman et al. [30] found no differences in visual reaction time during a reaction test when players drank water versus restricted fluid intake (2.3% BML). On the other hand, the number of successful attempts during a lower body reactive agility test was significantly lower in the no-fluid trial.In addition, Baker, Conroy, et al. [29] found that hypohydration was associated with impaired vigilance. In this study, subjects performed the test of attention variables at the baseline, after stress from physical exercise to induce 1-4% hypohydration or maintain EUH and after a simulated basketball game (where target hydration levels were maintained). Players made significantly more errors of omission and commission and had slower response times (6-8%) in the 1-4% hypohydration trials. In this study, there were no differences between levels of hypohydration.In conclusion, the basketball-specific relevance of the findings from this study were [29]: 1) the slower response time and the lack of attention to relevant suggestions would likely lead to costly mistakes during a basketball game; 2) conservative decision-making is the process by which DEH harms the attention of basketball players; and 3) the basketball game is an example of a frequent stimulus situation; thus, the results of this study are directly applicable to the performance of basketball.The results of this study are in agreement with Moran's theory [31]. Moran suggests that fatigue can impair attention, increasing distraction and depleting information processing resources. The signal detection model of vigilance performance [32] predicts that, in conditions of low excitation, the most common type of error is failure to respond to target stimuli (i.e., an increase in the number of omission errors).
3.1.3. Field Hockey
- The effect of hypohydration on cognitive performance in field hockey was tested in 2 studies [3,33]. H. MacLeod & Sunderland [3] subjected the field hockey players to 2 hours of passive heat to stimulate fluid loss. After this, fluid intake was controlled so that, in the next morning, they were either euhydrated or 2% dehydrated. On day 2, players completed a field hockey skill test before and after an intermittent 1-hour protocol in which players drank water ad libitum. The decision-making time during the skill test was 7% slower in the 2% DEH, but only before the intermittent exercise since during the game they could consume fluids. The main conclusions [3] were that the performance of field hockey skills and the decision-making time were hindered by 2% hypohydration. The response to dehydration induced by exposure to heat, water restriction or treadmill exercise, is a decline in task accuracy and response speed in tests such as short-term memory, visuo-motor tasks, attention related to vigilance or arithmetic skills [29]. It is possible that the increased sensation of thirst, discomfort and fatigue and reduced levels of alertness, commonly associated with fluid restriction, are responsible for part of the observed decline in performance [18].H. MacLeod et al. [33], used the same cognitive tests as the previous study, with the difference that they did 4 trials. Two in a hot environment and 2 in a moderate environment, each with ad libitum consumption and without fluids. The BML was 2.6% in the warm and no-fluid environment, 2.1% in the moderate and no-fluid environment and 0.5% in both environments with ad libitum consumption. The study didn’t detect significant changes between the trials except in the greater perception of the effort. In this study [33], the range of dehydration was 1.6-2.8%, demonstrating the inter-individual variability. This is mainly related to ad libitum consumption in the study design, which reflects field practices. The participants in this study were elite, familiar with the demands of exercise and highly motivated individuals. As such, it seems plausible that increased motivation and attention have maintained or improved performance on various tasks and thermal stress has increased arousal to help overcome any possible decreases in performance as a result of dehydration [34].
3.2. Technical Performance
3.2.1. Soccer
- Three studies have tested the impact of water restriction on specific soccer skills [22,35,36]. Ali et al. and Owen et al. [35,36] tested before, during and after a Loughborow intermittent run test [LIST]. Ali et al. reported no impact of fluid restriction (2.2% BML) versus water intake (1.0% BML) on passing performance in first division players.Likewise, Owen et al. [36] found that passing and shooting skills of semi-professional players were unaffected by water restriction (2.5% BML) compared to ad libitum (1.1% BML) or prescribed water intake (0.3% BML). Fluid intake compensated for the small levels of DEH observed in the group without fluids and led to reduced central temperature and cardiovascular tension and perceptual responses during and after exercise. Fortes [22] concluded that the number of passes made during the game wasn’t affected by the hydration status.Taken together, these results suggest that the effect of hypohydration on soccer performance may depend on the type of skill examined. However, they show that shooting and passing ability in football was similar after drinking fluids, although more research is needed to corroborate these observations [36].
3.2.2. Basketball
- The potential impact of hypohydration on basketball shooting performance has been assessed in six studies [30,37–41]. Results from these studies were mixed. For example, Hoffman et al. [30] found no impact of fluid restriction on the number of shots. Despite a significant loss of BML during DEH, individuals were able to maintain jump strength during the game, but shooting performance and reaction time were significantly impaired [30].Similar results were found in a study by Carvalho et al. [39] which compared the effects of no-fluid intake [2.5% BML] versus ad libitum (1.1% BML). In this study [39], didn’t find significant differences in the number of shots between conditions, but reported a reduction of 5.8% in shot accuracy (i.e., lowest number of goals) in a two-point field without fluid consumption. The main results of this study were that fluid restriction during exercise was associated with a higher level of dehydration and increased perceived exertion but had no significant impact on basketball performance. In the current research, athletes in the no-fluid group hypohydrated by 2.5% of their BM. Thus, although it didn’t achieve statistically significant differences, players in the condition without fluids underperformed in all exercises and took more time to complete them [39].Dougherty et al. reported that 2% hypohydration was associated with a significantly lower shooting percentage (8%). Brandenburg and Gaetz [40] allowed elite players to have unlimited access to drinks of their choice during two international games. In both games, players accumulated >2.6% BML. The authors reported a significant inverse relationship between BML and the percentage of shots with goals on the field in the second game, but no relationship in the first game. Although measuring the impact of hydration status on performance during the actual game increases the ecological validity of this study, the interpretation of these results is limited due to the potential impact of confounding factors (e.g., concomitant carbohydrate intake or additional eating behaviours) and the defensive ability of the opposing team.The effects of hypohydration levels on performance in basketball courts were tested in a study with male players. Baker, Dougherty, et al. [37] found that compared to EUH, increasing levels of DEH (2-4%) led to a progressive decrease of 7-12% in the total number of shots during a simulated game. In this study, players were given a standardized time to make as many throws as possible during each exercise. Thus, there was a progressive decrease in the number of shots due to the degree of hypohydration, which was probably the result of lower running speed and dribbling between them.Louis et al. [41], studied professional male athletes through a basketball protocol that players initiated after being subjected to thermal and exercise stress to establish 2% DEH or EUH. The main results indicated a slight but not significant decrease in performance in 3 points with a DEH status of 2%, accompanied by small changes in body kinematics and in the ball release variables. Taken together, the results of the six studies in basketball suggest that 2% hypohydration can potentially affect shooting performance, perhaps due to less accuracy and/or slowness in the frequency of shots attempts. Both factors can affect the total number of points scored, which is crucial in determining the outcome of a basketball game.
3.2.3. Field Hockey
- H. MacLeod & Sunderland [3] investigated the potential effects of hypohydration induced by passive thermal stress the day before field hockey skills. MacLeod and Sunderland assessed skills using a test that involves dribbling, passing and shooting after a treadmill protocol with ad libitum drink and found no impact of 2% DEH versus EUH on specific hockey skills on the field in elite players.
3.3. Physical Performance
3.3.1. Soccer
- Six studies have studied the impact of hypohydration on physical performance in soccer athletes [26,35,36,42–44].Four studies tested the impact of hypohydration on the performance of the 15 m sprint during the LIST protocol [35,36,42,43]. Ali et al. reported that although sprint performance deteriorated by 2.7% over the 90-minute protocol, there was no difference between trials in which soccer players drank water (1.0% BML) or no-fluid intake [2.2% BML]. Mohr and Krustrup and Owen et al. [36,42] had similar results. Mohr and Krustrup [42] also studied the effect of temperature and dehydration on height and repetition of counter-movement jumps. After a game at normal ambient temperatures, there was no decline in the jumping ability. However, in a heat-induce environment, there were a correlation between decrease repeated jumping performance and fluid loss [42].M. Mohr et al [44]. reported that as the match was played at relatively high ambient temperatures, very high muscle temperatures were recorded, and significant dehydration occurred during the game and the degree of dehydration was correlated with the fatigue index of the sprint test after the game.Ali & Williams [45] reported that after 90 min of simulated soccer exercise, knee isokinetic strength was reduced by 8.8% and 7.9% at fast and slow contraction speeds, respectively. The isometric strength of the knee extensors was also reduced by 16.5% after exercise, but there was only a tendency for a decrease in the performance of the knee flexors (9.1%). However, fluid intake didn’t affect muscle function or sprint speed during or after the simulated soccer exercise. This was combined with a reduction in sprint performance as well. In addition, research suggests that when thermal stress accompanies DEH, greater losses in muscle function can be expected [43].Four studies used the YO-YO intermittent recovery test to determine the effect of hypohydration on intermittent running ability in soccer [26,36,42,44]. Owen et al. reported no differences between trials in which players did not drink fluids (2.5% BML), water ad libitum (1.1% BML) or drank water to replace 89% of fluids losses (0.3% BML). On the other hand, Edward et al. reported that the physical fitness test was significantly impaired in both experimental conditions in which fluid intake was restricted. This resulted in decreases of 13 to 15% in the total distance covered when male soccer players mouth rinsed water (2.1% BML), didn’t consume fluids (2.4% BML) versus when water was ingested (0.7% BML) [26].The evaluations of perceived effort and order of classification of thirst showed that individuals considered the no-fluid condition to be the most challenging. The relatively small but significant increases in urine osmolarity and central temperature in the no-fluid condition may have stimulated intrinsic anticipatory mechanisms in the brain, recognizing that heat storage occurred quickly and invoked performance limitations to prevent future physical damage [46].
3.3.2. Basketball
- The impact of hypohydration on sprint and lateral movements performance was assessed in 3 basketball studies [37–39]. Baker, Dougherty, et al. [37] assessed male players during a simulated basketball game with different DEH levels. Increasing levels of hypohydration (2, 3 and 4% BML) were associated with progressively longer total sprint times by 7, 8 and 16%, respectively. The lateral movements were not affected by 1-2% hypohydration but was significantly increased from 3-4% DEH versus EUH. In another study, the hypohydration (2% BML) led to a total and average 6% longer sprint and 7% in the lateral movements during a simulated game [38]. Carvalho P. et al. reported that there was no effect of water restriction (2.5% BML) versus water intake ad libitum (1.1% BML) on sprint performance and lateral movements after training.Three basketball studies investigated the effects of hypohydration on jumping performance, including maximum jump height, time to complete a set number of jumps, and maximum or average anaerobic power during repeated jump tests [30,37,38]. These studies reported no impact of hypohydration (1–4% BML) on the maximum jump height. However, Baker, Dougherty, et al. [37] reported a significantly longer repeated jump time with 4% DEH versus EUH.The impaired performance of basketball in the Baker, Dougherty, et al. [37] study can be partially explained by the subjective measures of physical well-being; that is, increased feeling of fatigue in the legs and dizziness associated with DEH. The deleterious effect of water restriction on subjective feelings of fatigue and physical well-being is consistent with previous researches. For example, in the study by Dougherty et al., basketball players reported higher feelings of dizziness and fatigue in the upper body during the 2% DEH condition.
4. Discussion
- There are many difficulties in assessing performance during the sport itself and this is undoubtedly a factor that contributes to the inconsistency of the findings in the literature. Given the methodological constraints on data collection during the competition, many of these researches have evaluated performance in laboratories or other controlled locations. In addition, other issues, contribute to inconsistencies in the literature and may limit the applicability of these studies to real life performance.Regarding cognitive performance, based on the results of seven studies published to date, the impact of hypohydration (~1-2.5% BML) on team sports athletes is ambiguous. In five studies, vigilance, decision-making time, reaction time of working memory or reactive agility were hindered by hypohydration. However, no other measure of cognition (e.g., mental concentration, fine motor speed, visual perception, visual-motor reaction time or mathematics) was affected. This inconsistency is probably due in part to the measured aspects of cognition, the types of cognitive tests used, the reliability and sensitivity of these tests and other factors related to the study design [35]. Impaired cognitive performance is difficult to measure, particularly in the context of sport and can be partly explained by the increased feeling of fatigue associated with DEH compared to EUH [3,29].In addition, McCartney, Desbrow, & Irwin [47] demonstrated through a systematic review with a meta-analysis that the speed of information processing and memory, which are components of decision-making performance, were reduced after dehydration. On the other hand, the results of the systematic review carried out by Pross [28] indicate that performance is often impaired when dehydration is achieved by combining fluid restriction with heat or exercise. When dehydration is induced only by fluid deprivation, healthy adults seem capable of maintaining performance. Therefore, players should be advised to maintain EUH in order to obtain optimal concentration and attention skills during competition [29].Regarding technical performance, the effect of hypohydration on technical skills in sports seems to be inconsistent. Studies suggest that ~2-4% of hypohydration can impair the performance during basketball shots. On the other hand, the balance of studies suggests a minimum impact of ~2–3% hypohydration on the performance of skills in soccer and field hockey. Like cognition, technical skills are difficult to measure. Therefore, more work is needed to develop specific, reliable, valid and sensitive tests to use in future studies [10].Regarding physical performance in soccer, the research suggests that ~2–4% hypohydration is unlikely to affect the average 15 m running performance but may prolong the running time in extra time. Results are more consistent in basketball, with most studies reporting more time to complete races when athletes are hypohydrated by ~2-4%.The ability to make quick lateral movements is important for performance in many sports but has only been tested in basketball and the effects of DEH are currently unclear [10].Studies suggest that hypohydration is unlikely to have a negative impact on vertical jump height. However, anaerobic power can be impaired by hypohydration, especially at higher levels of hypohydration (~4% BML). In general, these results are in line with recent reviews and meta-analyses on the effect of hypohydration on jumping ability and anaerobic power [10,19,48].In basketball, there was a decrease in performance in a range of 1% DEH (suicide running), 2% DEH (throwing around the world), 3% DEH (zigzag dribbling, wide sprints, lay-out footage and full court combination) and four exercises at 4% DEH (repeated vertical jumps, key combination, track slides and baseline shots) [37]. The performance of the remaining four individual exercises (maximum vertical jump, three-point throw, free throws and missing line throws] were not affected. When the performance results were divided into two main categories [timed exercises and throwing exercises), the critical water deficit causing a decrease in the performance of basketball skills, was 2% of BM [37].In the case of soccer, in the LIST skills test, the intensities of repeated efforts are manipulated to reflect the different types of activities experienced during a game (i.e., high and low intensity running and walking). A well-controlled test-retest reliability study confirmed that variables such as heart rate are highly reproducible in the LIST protocol [49]. Although several soccer simulations protocols, such as those discussed briefly here, are sensibly constructed, their direct validity to the game is obviously limited by factors such as absence of the ball, direct competition, straight running and minimal opportunities for self-regulation of physical effort [50]. It should also be considered that most studies are conducted in indoor conditions, imposing a different physical stress on outdoor play [51].However, although several hypotheses have been proposed, the mechanisms of these effects are still not well studied. Hypohydration appears to impair endurance performance through a combination of mechanisms, mainly driven by hypovolemia. This hypovolemia and the resulting hyperosmolarity precipitate a cascade of physiological and perceptual responses that apparently act together to reduce endurance performance. From a physiological point of view, these responses include reductions in brain and muscle blood flow, increased body temperature, increased heart rate/cardiovascular tension and increased muscle glycogenolysis, possibly limiting peak oxygen uptake [52,53].Consistent with previous studies that examined physiological responses to prolonged intermittent exercise, no-fluid trials during 90-minute intermittent exercise were associated with increased perceived exertion and cardiovascular stress [26,45]. Finally, these physiological and perceptual responses are likely to work together to increase the perceived effort at a given intensity, thus compromising performance [52–54].Alternative mechanisms include decreased muscle creatine phosphate and increased muscle acidosis [reduced pH and increased lactate], which were demonstrated after the same high-intensity intermittent running test [55,56]. The degree to which these cardiovascular changes affect strength and power, however, is unclear. Experimental evidence, although limited, refutes the possibility that hypohydration fundamentally changes intramuscular reserves of ATP and CP or circulating blood glucose concentrations [57]. The increase in muscle acidosis is associated with reduced soccer performance through mechanisms of central and peripheral fatigue [36].The results of this review should be evaluated and interpreted with the following limitations in mind. Firstly, since oral fluid replacement cannot be blinded, it is conceivable that the placebo effect may be responsible for a small amount of the benefits seen with rehydration. Attempts should be made to blind the experimental conditions. For example, small volumes of fluid must be provided during dehydration tests and BM, fluid intake and urine volumes of individuals must be hidden [58]. Secondly, not all studies have a control group and therefore it is not possible to properly compare the effect of dehydration. Thirdly, there is great methodological variability in studies that assess performance and some information reported is limited. The protocols and tests used to measure performance in team sports must be sport-specific and individuals must be familiar with the methods before starting experimental tests [51]. The tests must also be valid, reliable and sensitive [59]. Of the studies reviewed, most tests were sport-specific for skill, running, jumping/strength, lateral movements and intermittent running ability, but not for cognition (with the exception of a field hockey study by Baker, Conroy, et al.). Future research must recognize the 3 vital components of the appropriate research design: [1] dehydration technique; [2] subject population; and [3] performance measures. Scientists should avoid dehydration methods using diuretics to reduce TBW (including the physiological stresses of diuretic-induced hypohydration). However, exercise and exposure to heat are useful methods for dehydrating individuals.
5. Conclusions
- Studies regarding the impact of hydration status on team sports performance reported mixed findings. However, it appears that hypohydration impairs cognition, technical ability and physical performance at higher levels of BML (3 to 4%). Impaired performance is also more likely when the dehydration method involves heat stress. Although in some studies there was no effect on performance, most studies reported a decrease in perceived effort with no fluid intake. This information is critical to help providing practical recommendations on fluid balance and team sports performance.Conclusively, water intake is vital to optimize exercise performance. It helps to delay fatigue and prevent injuries that occur with dehydration, decrease submaximal heart rate, heat stress, heat exhaustion and potential heat stroke. However, more research is needed to develop valid, reliable and sensitive sports specific protocols to be used in future studies.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- No sources of funding were used to assist in the preparation of this review. The authors have no conflicts of interest that are directly relevant to this review.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML