-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Sports Science
p-ISSN: 2169-8759 e-ISSN: 2169-8791
2020; 10(3): 68-72
doi:10.5923/j.sports.20201003.03

Comparison of Treadmill and Simultaneous Arm and Leg Ergometry in VO2MAX Analysis
Jacob A. Kostuck, Corey A. Selland, Jeremy M. Frost
Department of Human Performance, Minnesota State University, Mankato, 1400 Highland Center, Mankato, MN, USA
Correspondence to: Jeremy M. Frost, Department of Human Performance, Minnesota State University, Mankato, 1400 Highland Center, Mankato, MN, USA.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

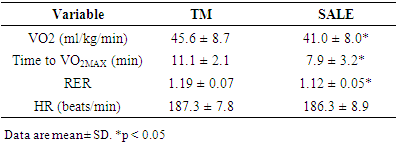
Maximal oxygen consumption (VO2MAX) testing can be performed on a variety of modalities ranging from treadmills to rowing ergometers. The purpose of VO2MAX testing is to determine a person's aerobic capacity and has been shown to elicit the highest response in treadmill (TM) testing. Very few studies have examined the idea of incorporating arm cycling combined with leg cycling in VO2MAX testing. The purpose of this study was to compare a simultaneous arm and leg ergometry (SALE) testing protocol to a TM VO2MAX test. Forty-seven college-aged individuals (female: n=27) volunteered for this study, completing both TM and SALE VO2MAX tests. VO2MAX was higher for TM than SALE (45.6 ± 8.7 vs. 41.0 ± 8.0 ml/kg/min, respectively; p < 0.05), and total length of VO2MAX test was longer for TM than SALE (11.1 ± 2.1 vs 7.9 ± 3.2 min, respectively; p < 0.05); however, the tests were highly correlated (r = 0.92). Heart rate at VO2MAX (p = 0.31), was not different between tests. The ratio of SALE/TM results ranged from 68.9-104.6%. VO2MAX values were more similar for females than males (F(1, 45) = 5.08, p = 0.03). The main finding is the addition of arm-ergometry to leg-ergometry produced lower VO2MAX and test length compared to a treadmill test. Future research should look into modifying the resistances of the SALE protocol to be adapted to the subject's body weight and fitness level to determine if this elicits a higher VO2MAX.
Keywords: VO2MAX, Treadmill, Simultaneous Arm and Leg Ergometry
Cite this paper: Jacob A. Kostuck, Corey A. Selland, Jeremy M. Frost, Comparison of Treadmill and Simultaneous Arm and Leg Ergometry in VO2MAX Analysis, International Journal of Sports Science, Vol. 10 No. 3, 2020, pp. 68-72. doi: 10.5923/j.sports.20201003.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Maximal oxygen consumption (VO2MAX) is an objective measurement of the human body’s ability to perform aerobically [1]. The concept of measuring VO2MAX has been researched extensively with evidence of articles from the early 1920s discussing this idea. Assessment of VO2MAX can be performed on a variety of modalities and can be considered valid if the subject reaches the researcher's inclusion criteria (Heart rate (HR) within 10 beats per minute (beats/min) of age-predicted max (220-age), respiratory exchange ratio (RER) > 1.1, rating of perceived exertion (RPE) ≥ 18 on the Borg scale, and a plateau in VO2) [1,2,3,4]. These tests can be performed to assess baseline cardiorespiratory fitness, predict race results, or to monitor progress over time [5,6]. Arguments have been made in the past stating that specificity of the testing protocol will maximize the relative VO2MAX achieved during testing, meaning cyclists should test on a cycle ergometer, and runners should test on a treadmill [7]. However, little research exists that shows this relationship [7]. Typically, individuals of any training status performing a VO2MAX test on a treadmill will achieve a higher relative VO2MAX than on any other modality [7,8,9,10].The selection of the testing modality may vary based on the availability of equipment or the comfortability or capability of the subject being tested. The option of using a cycle ergometer could be appealing to those who may not be comfortable testing on a treadmill, but has been shown to yield a lower VO2MAX than a treadmill test [7,10]. This may be due in part to an increased amount of muscle mass being recruited while ambulating when compared to cycling while seated. The addition of arm cycling while peddling on a cycle ergometer has been glossed over in past research [11,12,13] but could theoretically increase the amount of muscle mass being recruited and lead to a higher relative VO2MAX.The purpose of this study was to investigate whether simultaneous arm and leg ergometry (SALE) could be used as a valid VO2MAX testing modality when compared to a treadmill (TM) VO2MAX test. It was hypothesized that simultaneous arm and leg ergometry would yield a higher relative VO2MAX than the TM VO2MAX test due to the increased amount of muscle mass being recruited. The possibility of exceeding the VO2MAX attained during a TM test while in a seated position would allow more populations to perform a VO2MAX test, and to decrease impact stress on the lower extremities.
2. Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
- Subjects completed two VO2MAX tests allowing 7-14 days between each test. The tests were conducted on a treadmill (TM), requiring the subject to be standing while walking and/or running, and simultaneous arm and leg ergometry (SALE), requiring the subjects to be in a seated position (Figure 1). The testing order was randomly assigned when each subject arrived at the testing site.
 | Figure 1. Setup for simultaneous arm and leg ergometry (SALE) |
2.2. Subjects
- Forty-seven subjects: twenty males and twenty-seven females (Mean ± SD: age 21.2 ± 1.9, weight: 159.8 ± 30 lb) participated in this study. Subjects did not need to be physically active to participate in this study but were excluded if they had any conditions that would prevent them from performing a VO2MAX test. Subjects were instructed not to deviate from their normal exercise routines but were asked not to exercise before their VO2MAX test. Data collection was performed between September-March. All subjects completed an informed consent and health history questionnaire before testing. This study and all its testing procedures were approved by the university's institutional review board.
2.3. Procedures
- Subjects signed up for testing times online allowing at least seven (7) days between each test but no more than 14 days between each test. On the first day of testing, subjects completed the informed consent and health history questionnaire which included age and activity level, then resting blood pressure, height, and weight was collected and recorded. The testing order was randomly assigned when each subject arrived at the testing site. Subjects were briefed on testing procedures and expectations before starting the test. Breath by breath data collection was performed using a Parvo Medics metabolic analyzer (TrueOne 2400, Sandy, Utah) calibrated before each test using 3-liter calibration syringe (Hans-Rudolph, Kansas City, Missouri) and a gas calibration tank (4.001% carbon dioxide, 16% oxygen, and 79.999% nitrogen). This data was displayed using the associated TrueOne 32 (Version 4.3.4) computer software which displays the VO2 in 15-second intervals. Before each test, subjects were fitted with the associated mouthpiece headgear and nose plug as well as a polar H6 HR monitor (Kempele, Finland). Subjects were given a three (3) minute warm-up period (2.5 MPH at 5% grade for TM and 40 Watts at a self-selected cadence for SALE) and the test began immediately afterward. Heart rate (HR), rating of perceived exertion (RPE), and respiratory exchange ratio (RER) were collected every minute until the subject could no longer continue the test. Subjects performing the SALE test who could not maintain 50 ± 5 RPMs on the arm ergometer were considered to have reached their point of exhaustion. To be considered a valid VO2MAX test, two of the following criteria need to be achieved: a RER of at least 1.1, a HR within 10 beats per minute (beats/min) of age-predicted max heart rate (220-age), a plateau in VO2, and an RPE of ≥ 18 [1,2,3,4]. Blood pressure was also taken at the end of each test.
2.4. Heart Rate
- Heart rate was collected using a Polar H6 heart rate monitor (Kempele, Finland) and its associated mobile app for display. The heart rate monitor was on during the entire duration of the test but was only collected once every minute. A final heart rate was collected after each test. Similar heart rate monitors have been used in similar studies and are considered valid [14,15].
2.5. Rating of Perceived Exertion
- Rating of perceived exertion (RPE) was collected every minute, and at the end of the test, using the BORG 6-20 scale which has been used throughout the literature in similar studies [8,16,17].
2.6. Treadmill
- A Cosmed T170DE treadmill (Rome, Italy) was used for the treadmill VO2MAX test. Speed and inclination were automatically adjusted by the treadmill every three minutes to ensure the accuracy of the protocol and consistency across subjects.
2.7. Arm Ergometry
- A Monark 891 E (Vansbro, Sweden) arm cycle ergometer with a 0.5kp basket was during the SALE VO2MAX testing to assess upper-body power output. Calibrated weights are used in conjunction with the basket to further increase the resistance on the flywheel of the arm ergometer.
2.8. Leg ergometry
- A Monark LC7 electromagnetically braked ergometer (Vansbro, Sweden) was used during the SALE VO2MAX testing to assess lower body power output.
2.9. TM Protocol
- The Bruce protocol is a treadmill-based test that increases in speed and grade through three-minute stages. Stage 1 is set at a speed of 1.7MPH and a grade of 10%. Stage 2 is set at a speed of 2.5MPH and a grade of 12%. Stage 3 is set at a speed of 3.4MPH and a grade of 14%. Stage 4 is set at a speed of 4.2MPH and a grade of 16%. Stage 5 is set at a speed of 5MPH and a grade of 18%. Stage 6 is set at a speed of 5.5MPH and a grade of 20%. The Bruce protocol has often been used as a valid TM protocol for determining VO2MAX [18,19,20].
2.10. SALE Protocol
- The arm ergometer started with a 0.5 kp basket for resistance while the subject pedaled at a cadence of 50 ± 5RPM. A metronome was used to help maintain this cadence throughout the test. Resistance for the arm ergometer was increased every two minutes by 0.1kp, while the resistance of the leg ergometer was increased by 30 watts every two minutes, starting at 50 watts. The cadence for the leg ergometer was self-selected, and the resistance continued to be added until a pace of 50 ± 5 RPM on the arm ergometer could no longer be maintained.
2.11. Statistical Analysis
- A paired t-test was performed to determine differences in VO2MAX, HR at VO2MAX, and test time between TM and SALE. The level of significance was set at α = 0.05. Correlations between TM and SALE VO2MAX, as well as between TM and SALE time, were assessed using Pearson’s correlation coefficient (r). A repeated-measures ANOVA was performed to compare testing modality and fitness level, as well as testing modality and gender.
3. Results
- The VO2MAX was significantly higher (p < 0.05) for TM than SALE (45.6 ± 8.7 vs. 41.0 ± 8.0 ml/kg/min, respectively (Table 1). Figure 2 shows the range of individual differences in VO2MAX between testing modalities, expressed as TM VO2MAX - SALE VO2MAX (a higher TM score results in a positive number whereas a higher SALE score results in a negative number). TM VO2MAX and SALE VO2MAX had a strong correlation (r= .91 p < 0.05). The correlation was slightly lower when comparing by gender (Male = 0.89 p < 0.05; Female = 0.89 p < 0.05) and when categorized by fitness (High = 0.90 p < 0.05, Low = 0.80 p < 0.05). The total duration of the TM VO2MAX test was significantly greater (p < 0.05) than that of the SALE VO2MAX test (11.1 ± 2.1 vs 7.9 ± 3.2 min, respectively) There was not a statistical difference in HR recorded at the end of each test (p = 0.31). The ratio of SALE/TM VO2MAX ranged from 68.9-104.6% (M = 90%).
|
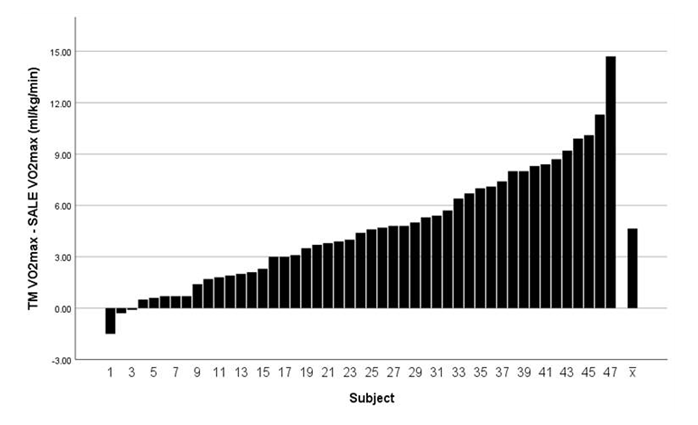 | Figure 2. Individual difference in VO2MAX (ml/kg/min) between testing modalities (TM VO2MAX - SALE VO2MAX) |
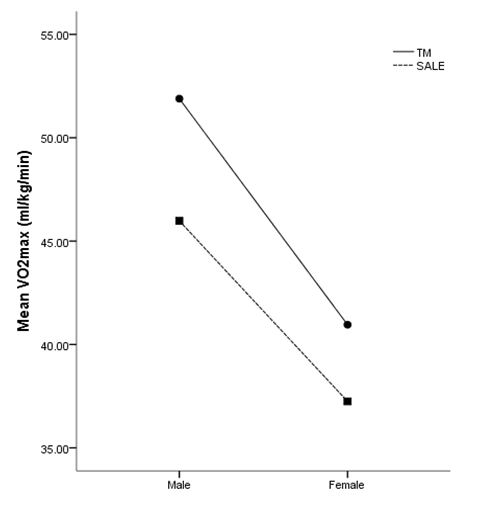 | Figure 3. Repeated measures ANOVA comparing VO2max between testing modality and gender |
4. Discussion
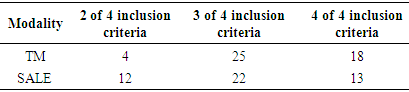
- The main purpose of this study was to investigate whether SALE would yield a higher relative VO2MAX when compared to the results of a TM VO2MAX test. The results showed that the subjects achieved a higher relative VO2MAX on the TM than SALE. This is the first study that compares TM and SALE VO2MAX testing on such a large scale. The present study included 47 subjects completing both VO2MAX tests compared to Secher et al., [13] study which had 16 total subjects, but only seven of them completed both TM and SALE VO2MAX tests. Secher, et al [13] investigated SALE using two Monark cycle ergometers as resistance for the arms. The study included VO2MAX results from arms only, legs only, SALE, and TM across a spectrum of sport disciplines. Results showed SALE to yield a higher VO2MAX than arms only, and legs only, but was only able to achieve a higher VO2MAX in 3 out of the 7 TM comparisons. Brown, Kueffner, O’Mahony, & Lockard [8] compared the results of TM and arm-leg elliptical ergometry. They concluded that the results from both tests were not statistically significant, showing that the arm-leg elliptical is a modality that can incorporate arm movement to match the results seen on a treadmill while also reducing lower body stress and impact. Basset & Boulay [7] studied the results of trained cyclists, runners, and triathletes comparing their VO2MAX tests between TM and leg ergometry. Their results indicated VO2MAX was greater for TM than leg ergometry for all groups [7]. Eston & Brodie [12], investigated submaximal exercise VO2, HR, and RPE responses using a Schwinn Air-Dyne ergometer at three specific work rates using only arms, only legs, and SALE. VO2, while not statistically greater when comparing only legs to SALE was greater at each submaximal workrate. This study, however, only measured submaximal responses at a fixed workrate instead of VO2MAX using a graded exercise protocol. The Schwinn Air-Dyne does share a flywheel between the arms and legs but it does not allow for incremental increases to resistance via external weight but rather uses a flywheel fan to generate resistance. Results from these studies indicate the possibility of achieving similar VO2MAX results witnessed on a TM by incorporation of arm ergometry [8,12,13].Despite a statistical difference in VO2MAX results, there was a strong correlation (r = .92) when comparing the sample as a whole. When comparing the data with the subjects split into a high fitness group and a low fitness group, defined as below the 60th percentile for their respective age and gender [21], the correlations dropped slightly (r = .90 and r = .80 respectively). Although such a strong correlation exists between these two modalities, the difference in relative VO2MAX shows that SALE may not be the ideal method for achieving a higher VO2MAX. While not a means to exclude test results, test times for TM were statically longer than SALE tests (11.1 ± 2.1; 7.9 ± 3.2; respectfully). Given these shorter test times, all subjects were still able to achieve inclusion at least 2 of the 4 inclusion criteria used for validation of testing (Table 2).
|
5. Conclusions
- The current study observed higher VO2MAX, RER, and time to VO2MAX using TM than SALE. However, both options appear to be valid for assessing VO2MAX. The SALE protocol offers an additional testing modality that may be utilized with groups that are more whole-body focused or prefer to be seated during testing.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML