-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Sports Science
p-ISSN: 2169-8759 e-ISSN: 2169-8791
2017; 7(2): 87-93
doi:10.5923/j.sports.20170702.10

Protein Overfeeding is Associated with Improved Lipid and Anthropometric Profile thus Lower Malondialdehyde Levels in Resistance-Trained Athletes
Wilson Max Almeida Monteiro de Moraes1, Ana Erbênia Pereira Mendes1, Marcela Mota Moreira Lopes2, Fernanda Maria Machado Maia1
1Functional Nutrition Laboratory, Ceará State University, CE, Brazil
2Physical Education and Sports Institute, Ceará Federal University, CE, Brazil
Correspondence to: Wilson Max Almeida Monteiro de Moraes, Functional Nutrition Laboratory, Ceará State University, CE, Brazil.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

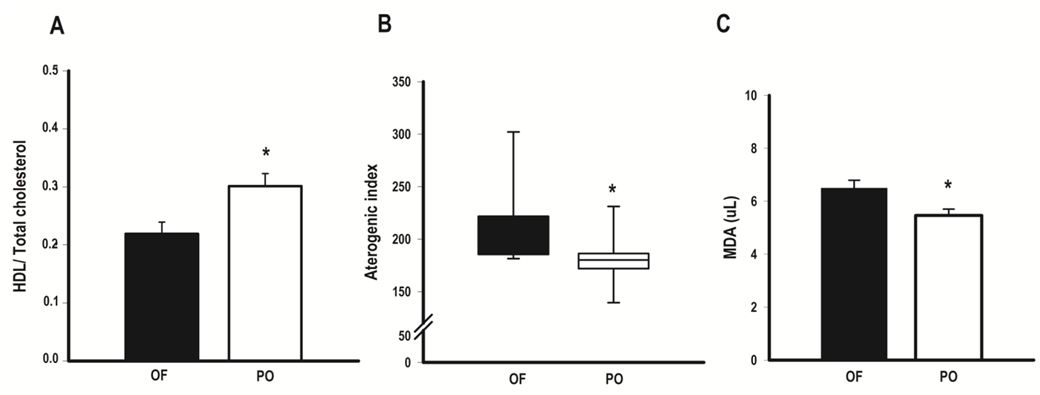
Background: Overfeeding is the most common nutritional strategy to promote weight gain in athletes. Some studies suggest that protein intake exceeding can prevent deleterious effects of overfeeding, as an increased body fat, worsening lipid profile and oxidative stress. Objective: To examine if bodybuilders with high protein intake (>1.7g/kg) had better quantitative lipid profile, less malondialdehyde (MDA) on plasma and body fat following overfeeding. Method: Of 33 bodybuilders interviewed, 19 who practice overfeeding were selected and divided into two groups according to reported protein intake: overfeeding group (OF, n=10) and protein overfeeding (PO, n=9). The waist circumference and body fat (skinfold thickness) were evaluated and plasma lipoproteins determined by colorimetric enzymatic techniques and MDA as a biomarker of oxidative stress. Results: The mean protein intake in OF and PO were 1.6 and 3.1g/kg/day, respectively. The PO showed lower body weight (82.9 vs. 89.9kg; p<0.05), waist circumference (83.5 vs 90.8cm; p<0.05), body fat (11.8 vs 18.9%, p<0.05), MDA levels (5.5 vs 6.6uL, p<0.05), total cholesterol (186.1 vs 193.8mg/dl; p<0.05), triglycerides (141.6 vs 155.1mg/dl); p<0.05), VLDL (28.3 vs 31.0mg/dl; p<0.05), cholesterol non-HDL (127.0 vs 165mg/dl; p<0.05), atherogenic index (180.8 vs 209.4, p<0.05), a higher HDL/ total cholesterol ratio (0.31 vs 0.21; p<0.05), and trend towards higher HDL (54.2 vs 44.6mg/dl; p=0.07). The frequency of adequacy according to current recommendations proved to be superior in all lipoproteins, except VLDL, in PO group. Conclusion: Resistance-trained athletes with high protein intake had better quantitative lipid and anthropometric profiles and lower MDA levels following overfeeding.
Keywords: Energy Intake, Lipoproteins, Cholesterol, Triglycerides, Resistance training
Cite this paper: Wilson Max Almeida Monteiro de Moraes, Ana Erbênia Pereira Mendes, Marcela Mota Moreira Lopes, Fernanda Maria Machado Maia, Protein Overfeeding is Associated with Improved Lipid and Anthropometric Profile thus Lower Malondialdehyde Levels in Resistance-Trained Athletes, International Journal of Sports Science, Vol. 7 No. 2, 2017, pp. 87-93. doi: 10.5923/j.sports.20170702.10.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Aerobic and resistance training (RT) exercise are non-pharmacological approaches for prevention of dyslipidemia and cardiovascular disease risk decrease [1, 2, 3]. Regarding RT, meta-analysis of clinical trials have shown beneficial effects as reduction in total cholesterol (TC), TC/HDL ratio, non-HDL cholesterol, triglycerides and LDL levels [4]. Previous studies involving bodybuilders as representative of “resistance-trained athletes”, have shown a favorable lipid profile and within the reference values for age/gender [5-7]. However, some of these studies were conducted with athletes in pre-competitive phase [6, 7], when bodybuilders lose weight to achieve weight class limit for competition through energy restriction, an increase in training volume and aerobic exercise [7, 8], which are well known practices for efficacy in improving lipid profile [1-3] and may explain the findings in above studies. Bodybuilders devote most of their preparation in a non-competitive phase, characterized by low training volume and, frequently, an overfeeding practice [8, 9], which are associated with an unfavorable lipid profile and body adiposity gain [9-11]. Overfeeding usually takes place through the addition of 500-2000kcal/day [9-11] and although it promotes weight gain and fat-free mass [9, 10], it has been criticized [9, 12] because may increase body weight to about 60% in body fat [9, 10]. Thus, overfeeding may also increase total cholesterol and triglycerides levels [10, 11], as well as oxidative stress markers, which can lead to systemic inflammation, a condition marked in obesity and insulin resistance [13]. Beneficial effects on body composition and blood lipids after periods of hypocaloric diets with high protein intake have been reported [14], but it remains controversial whether high protein intake (potentially above 1.7g/kg/day for athletes) when extra calories are consumed may reduce adverse effects of overfeeding. Antonio et al. [15] demonstrated that high protein consuming (~4.4g/kg/day) on a hypercaloric diet (increase~800kcal/day for 8-weeks) does not result gains on fat mass in resistance-trained individuals. In a study crossover, resistance-trained man consuming a high protein diet (3.3 versus 2.6g/kg/day, increase ~400kcal/day for 4-months) had no effect on blood lipids [16]. More recently, overfeeding with consumption of 96g additional supplement protein during 56 days did not preferentially improve body composition versus iso-energetic carbohydrate supplement in resistance-trained men [17]. The purpose of present study was to investigate if high protein intake is associated with improved of blood lipid profile, anthropometrics markers and lower malondialdehyde (MDA) (oxidative stress marker) levels on plasma in resistance-trained men following overfeeding.
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
- Initially, the President and Vice President of Brazilian Confederation of Bodybuilding and Fitness were contacted and helped to disclose the study and contact athletes. Thirty three male bodybuilders were interviewed and nineteen of them selected (aged 20-35 years). The inclusion criteria were: have participated in at least one championship; be in preparation for any competition in non-competitive period; and report excessive caloric intake. Were excluded individuals who did some aerobic exercise regularly or use any medication that could interfere with lipid profile including anabolic steroids for at least eight months. When there was doubt about nutritional composition with interfering potential, the label was requested for verification. This research was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Ceará State University (process 04463980-5) in accordance to Helsinki Declaration and all participants signed an informed consent form.
2.2. Dietary Data
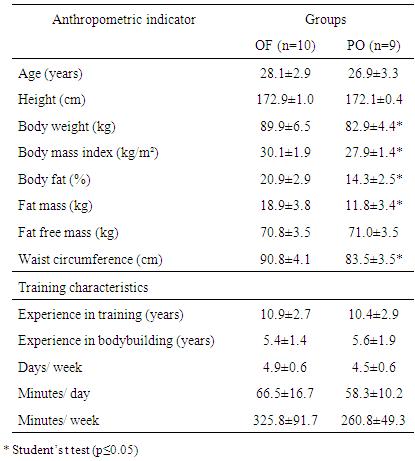
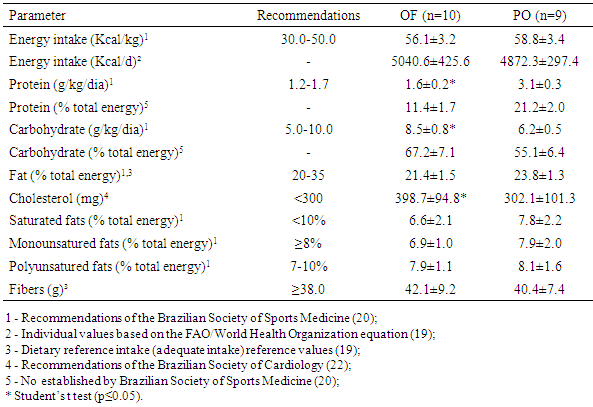
- It was used a three-day dietary food record (two weekdays and one corresponding to weekend day), in order to evaluate caloric and nutrient ingestion. Food amounts were recorded in household measures to assist in the conversion of the food for grams. Data were processed with DietWin® software [18]. When it was reported food intake, which was absent in software, nutritional information was inserted according to labels description.The energy intake was based on the Estimated Energy Requirement (EER) [19] and Brazilian Society of Sports Medicine Guidelines [20]. For the first, calculation was based on the EER = 662 formula - (9.53 x age) + [NAF x (15.91 x weight + 539.6 x height)], where EER: Estimated energy demand; NAF: physical activity level, assessed using International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) short version [21]. For Brazilian Society of Sports Medicine Guidelines [20], it was used caloric intake relative to body mass and considered overfeeding when athlete met both two requirements: higher calorie intake to two standard deviations of estimated total calorie need [19] and a daily calorie intake more than 50kcal/ kg [20]. For macronutrients intake, cholesterol and monounsaturated fats, polyunsaturated and saturated Brazilian Society of Sports Medicine Guidelines [20] and Brazilian Society of Cardiology [22] were used. Nineteen bodybuilders classified as “overfeeding” were divided into two groups according to protein intake reported: overfeeding group (OF), composed by those with protein intake in accordance to Recommendations (≤1.7 grams/kg/day) and protein overfeeding group (PO) with high protein intake (>1.7 grams/kg/day).
2.3. Anthropometric Measures
- The measurements of weight, height, circumferences and skinfold thickness were taken. During the measures subjects remained with least clothing possible. For height measurement, it was used a stadiometer brand (exata, Brazil) with precision of 1mm; for body weight a scale Plenna®, with precision of 100 grams. Waist circumference was measured using a circumference measuring tape (WCS, Brazil) at umbilical and skinfolds with scientific skinfold (Lange, EUA) with precision of 1mm and constant pressure of 10g/mm². Each fold was measured three times and the mean of each anatomical point adopted as benchmark for calculations. The measurements were performed on the right side of the individual, with marking performed at 1cm deep, after two seconds of impingement. To calculate body density (BD) was used the Petroski method [23] second equation: BD = 1.10726862 - 0.00081201 (SI+SE+TR+MC) + 0.00000212 (SI+SE+TR+MC)2 - 0.00041761 (age, in years) and for the percentage of body fat (% BF), the Siri equation [24] described as: % BF = [(4.95 / BD) - 4 5] x 100, where body BD: body density in g/ml, and skinfold SI: suprailiac, SE: subscapular, TR: triceps (TR), medial calf (MC). The measurements were performed by a single evaluator, with test-retest coefficient exceeding 0.95 for each of the anatomical points.
2.4. Blood Collection and Biochemical Analysis
- After at least 48 hours prior to the last exercise session, and fasted for at least 12 hours, 5ml of venous blood was collected in vacuntainer tubes containing ethylene diaminoacetic-EDTA (1mg/mL), kept on ice and protected from light to obtain the plasma.The creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB), a muscle injury marker well-known, and total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) were determined by enzymatic methods using commercially available reagents (Bioclin®, Belo Horizonte, MG, Brazil). The very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) and low density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol was estimated according to Friedewald equation [2].After lipoproteins values concentrations were determinated, HDL/ total cholesterol ratio and non-HDL cholesterol were calculated by the equation: cholesterol non-HDL=TC - HDL and the atherogenic index (AI) by AI = total cholesterol - HDL/ Cholesterol total [2]. Lipid peroxidation was utilized as oxidative stress marker and measured for thiobarbituric acid reactive substances adapted [25], utilizing a standard curve made from malondialdehyde (MDA) at 4.00µM as previously descript [26].Biochemical tests were conducted in Laboratory of Functional Nutrition at Ceará State University.
2.5. Psychological Measurements
- Mood states were measured with Profile of Mood States (POMS), a questionnaire which assesses Tension, Depression, Anger, Vigour, Fatigue and Confusion items. The choice of this instrument was to reflect training loads with sensitivity and low cost, and have been previously validated with Brazilian athletes [27] and thus, POMS provide additional information beside those obtained by creatine kinase essays and self-reported training.
2.6. Statistic Analysis
- The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test was used to verify if continuous variables were Gaussian distribution. If affirmative, Student T test for independent samples was used in order to compare data between OF and PO groups and data presented with means and standard error (SE). When data did not show Gaussian distribution, it was used Wilcoxon Signaled Rank Test and presented as median and interquartile intervals. Categorical variables were presented for absolute numbers and percentages. Differences were considered significant when p≤0.05.
3. Results
- As it can be seen in Table 1, there was a significant difference in all anthropometric indicators between the groups, except of height. Increased body mass in OF group may be assigned to larger stores of body fat since this group showed higher adiposity and fat mass values in contrast to fat free mass, which were similar between groups.
|
|
|
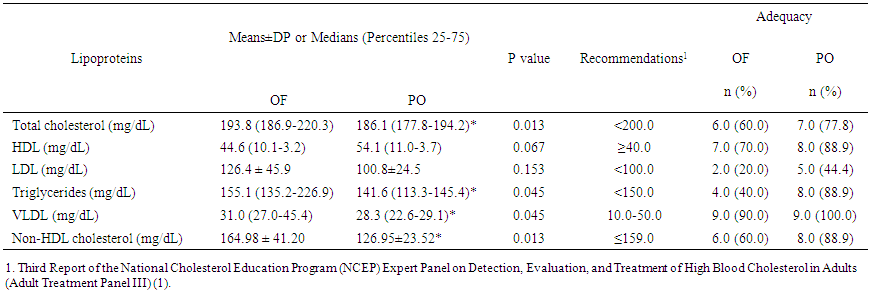 | Table 4. Lipoprotein profile in overfeeding (OF) and protein overfeeding (PO) groups. Values are presented as mean±SD or medians (percentiles 25-75) |
4. Discussion
- At present study, it was demonstrated that bodybuilders in non-competitive period and similar RT volumes, consuming high calorie diet, presented better quantitative lipoprotein profile and body composition; thus less oxidative stress on plasma when consumed higher protein intake. The better lipid profile was evidenced by lower levels of cholesterol, triglycerides, VLDL and non-HDL cholesterol, a tendency to lower HDL levels, lower total cholesterol/ HDL and atherogenic index. In addition, frequencies of adequacy in accordance to current recommendations [1, 2], demonstrated to be superior in all lipoproteins with the exception of VLDL levels, accompanied by lower values of MDA. Moreover, athletes under protein overfeeding shown body fat levels 30% lower, regardless of differences in fat free mass levels.Overfeeding is the most common nutritional strategy among strength athletes to promote weight gain in non-competitive periods, which usually takes place through the addition up to 2000 calories daily [9-11]. However, when the excess of consumed calories is provided by carbohydrate, it promotes substantial gain in fat mass and increases total cholesterol and triglycerides levels [8-10, 28]. Here, overfeeding observed in OF group seems to be mainly caused by an increase in carbohydrates, since OF consumed ~25% more carbohydrates than PO group. It has been shown that carbohydrate overfeeding results in gain of adiposity by elevating lipogenesis di novo [10, 28].For other land, our findings support the notion that protein intake within more than three times of recommended daily allowance values [19] and almost two times current recommendations for strength athletes [20] during overfeeding periods, can not only prevent a gain in body fat, as observed previously in longitudinal studies [15, 16, 29], but may have contributed to reduction in body fat.In this sense, it has been proposed that higher protein intake may affect energy expenditure, as shown in a previous investigation [29], in which protein intake (25% of total energy) increased 24h sleep and resting energy expenditure versus 15% and 5% in subjects consuming 40% excess energy for 56 days. Moreover, protein’s high thermic effect may increase postprandial energy expenditure impairing gain weight during overfeeding, especially leaners, such as present study athletes [30]. Bodybuilding athletes use resistance exercises to contemplate their main objectives and training sessions have high intensity and predominant use of energy from anaerobic sources [8]. The particular fact that athletes on this study do not practice aerobic exercise suggests that adaptations promoted by training in lipoprotein profile are derived exclusively from RT. In this context, it has been shown that decreases in body mass were associated with greater improvements in TC, HDL, and non-HDL cholesterol [4]; and increases in HDL associated with increases in lean body mass after RT protocols [4] suggests a relation between body composition and blood lipids. Yke-Jarvinen et al. [31] demonstrated that a combination of lower body fat and higher proportion of muscle mass is strongly correlated with lower VLDL and LDL serum levels in bodybuilders, more than body fat itself. Our results corroborate these findings, since OF group, with higher adiposity, showed to higher non-HDL cholesterol and lower HDL/ total cholesterol ratio. Of interest, waist circumference, which was higher in OF group, can also influence HDL levels. Our data are suggestive that central adiposity impact negatively in HDL levels during overfeeding and increased protein intake can attenuate this effect. In fact, data from NHANES [32] showed that protein intake exceeding RDA (~1.5g/kg/day) is associated with lower waist circumference and higher HDL cholesterol compared to RDA levels (~0.8g/kg/day). The reason why central adiposity is lower on higher-protein diets consumers is not fully understood, but probably is related to an inhibition of lipogenesis in the liver [33].It is well known the relation between higher body fat (particularly abdominal fat), and dyslipidemias, thus waist circumference is the anthropometric variable most used in clinical approaches for its correlation with visceral adiposity. The higher waist circumference was positively correlated with higher triglycerides, VLDL and MDA in OF group, suggesting that fat distribution may have greater impact on blood biochemistry of athletes than total fat distribution during carbohydrate overfeeding. Bamman et al. [34] showed that waist circumference comes to be ~6.9cm greater in non-competitive period, probably due to adipose tissue accumulation which occurs in this training period. In addition, Spliter et al. [35] showed a greater adipose tissue accumulation in central region, especially back and abdomen, when compared with those of the limbs, suggesting that central adiposity increase is a remarkable feature in non-competitive period and overfeeding probably has a role pivot. Besides that, adiposity accumulation in central region has been positively correlated with lipid peroxidation markers including MDA, probably due adipocytes in this region have more resident macrophages and cytokines, showing a great propensity to oxidative stress [13]. Concerning the relation between macronutrients intake and lipoproteins, lower blood triglycerides and VLDL observed in PO group might be a result of lower carbohydrate, higher protein content or both. A decrease in plasma triglycerides induced by lower carbohydrate intake may be caused by inhibition of hepatic de novo lipogenesis and/ or a decreased clearance of VLDL-triglycerides (28). Hyper protein diet too inhibit lipogenesis through a decrease into enzymes expression involved in hepatic lipogenesis, but also a poor utilization of amino acids-derived carbon skeleton in lipogenic pathways since amino acids are "diverted" to transaminations and gluconeogenic pathways as part of the regulation process of protein homeostasis [33].Limitations of our study should be acknowledged. The extension of changes observed during all non-competitive period reflects data collection time, since athletes do not necessarily maintain same training regimen and dietary habits during whole non-competitive period. Additionally, future studies might consider including a control group without overfeeding, as well as the utilization of more than one oxidative stress marker.In spite sample size was relatively small, our findings suggests protein overfeeding may contribute to prevent excessive gain in adipose tissue and improve blood lipids. Future studies comparing protein overfeeding with other proposals to establish weight gains protocols are desirable. For example, Garthe et al. [14] proposes diets with lower caloric density (~300kcal additional) than those observed in overfeeding studies, which added extra energy corresponding to 1000-2000 kcal/day [9, 10], since athletes with considerable time in RT are generally less responsive to gains in fat-free mass and are more prone to accumulate body fat than athletes with lower training level [14]. Moreover, studies addressing renal parameters measurements in order to provide a better understood of putative adverse effects of protein overfeeding. In conclusion, our data show high protein intake is associated with improved profile lipid and body fat, reinforcing that protein overfeeding may favor lipid and anthropometric profile, and reduces oxidative stress in comparison to carbohydrate overfeeding in resistance-trained athletes.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors are grateful to Alexandre Pagnani (in memorian) and José da Páscoa Neto, President and Vice-president of Brazilian Confederation of Bodybuilding and Fitness, respectively, for assistance during the study.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML