-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Sports Science
p-ISSN: 2169-8759 e-ISSN: 2169-8791
2016; 6(2): 32-35
doi:10.5923/j.sports.20160602.03

A Comparative Analysis of Physical and Tactical Variables with Play Positions in Final Match FIFA World Cup 2014
Sultan Mansour Bediri
Al-Baha University, Department of Physical Education, Saudi Arabia
Correspondence to: Sultan Mansour Bediri, Al-Baha University, Department of Physical Education, Saudi Arabia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The final match of fifa world cup 2014 were analysis with the aim of this study which was to identify the difference between physical and tactical variables with play positions for national soccer teams in final match. The analysis was based on final match fifa world cup 2014 played between Germany and Argentina. Four physical and tactical variables were studies each one included group of variables. They were: distance covered (meters) – total distance covered, distance covered with and without possession of ball; time spent – in opposing half, in attaching third and in penalty area; speed – sprints and top speed; activity time spent– low, medium and high. Result analysis of this match revealed the following: (a) the most discriminate analysis related to defender players were distance covered– total distance covered, distance covered and distance covered with possession of ball; time spent– in opposing half, (b) the most discriminate analysis related to midfielder players were distance covered without possession of ball, (c) the most discriminate analysis related to forward players were time spent– in opposing half, in attaching third and in penalty area.
Keywords: FIFA world cup 2014, Analysis, Physical and tactical, Play positions, National soccer teams
Cite this paper: Sultan Mansour Bediri, A Comparative Analysis of Physical and Tactical Variables with Play Positions in Final Match FIFA World Cup 2014, International Journal of Sports Science, Vol. 6 No. 2, 2016, pp. 32-35. doi: 10.5923/j.sports.20160602.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The aim of this study was to identify the difference between physical and tactical variables with position play in competition national soccer teams in final match fifa world cup 2014 that identify points of strength in performance competition national soccer teams in final match. In this context, the study is the first to have applied a multivariate analysis to physical and tactical variables of final match world cup. Notational analysis is essentially a means of recording events so that there is an accurate and objective record of what actually took place. Spectators view matches differently, often disagree about what happened and my be completely mistaken. Each individual brings his or her bias to the game and may see it from a partisan viewpoint. Even the best coaches are often unable to recall sequences of events correctly and fail to appreciate where successful plays originated or mistakes began. Notational analysis provides a factual record which does not lie – as long as the data collection methods used are reliable and objective and the system is adapted to the level of play (Carling et al., 2005).To analyze the collective of the notational analysis of the game includes optimizing feedback to the performer and coach to improve the performance (Liebermann, et al., 2002). Therefore the information given to the coach need to be an important and relevant information to understand the reality. A well- designed system provides the coach with accurate and reliable information that is easily gathered and has an impact on subsequent practice and performance (carling, et al., 2005). The main aim of match analysis is to identify the strengths and weaknesses of one's own team, thereby enabling the former to be further developed and the latter to be worked upon. Similarly, a coach analyzing the performance of an opposing side will use the data to identify ways of countering that team's strengths and exploiting its weaknesses (Carling et al., 2008).Observing how strengths and weaknesses of teams happen can help to design better training program, also can benefit of physical and tactical variables as strengths and weaknesses of teams. From this viewpoint, the information analysis aspects of the game results in terms of coaching whereas knowledge about position play for other teams.
2. Details Experimental
2.1. Materials and Procedures
- The date used in study was obtained through official website of World Cup 2014 (http://resources.fifa.com/ mm/document/ footballdevelopment/ technicalsupport/ 02/42/15/40/2014fwc_tsg_report_15082014web _neutral.pdf). On official website Fifa technical report and statistics, stated that "A virtual platform enabled the 64 matches to be recorded and incidents to be selected and immediately analyzed by instructors and viewed by the referees.During the practical training, a virtual refereeing programmer enabled the referees and assistant referees to analyze their decisions immediately after they had taken them on the field of play by viewing them on a monitor providing replays at different speeds.The experts on technical matters, fitness, psychology, energy and medicine prepared extensive theoretical and practical preparation programmers. The training sessions took place with the assistance of a team of footballers in order to carry out exercises using match situations.After the matches, meetings were held to analyses the major incidents. All the matches were recorded and the instructors selected all the incidents that were to be analyzed with the referees. The aim was to analyze these situations with a view to improving performance in the next matches".More specifically, the date obtained of final match for national soccer teams Germany and Argentina over the competition for some tactical Variables. Sample was also classified into three tactical lines: defenders, midfielders and forwards.ProcedureFour physical and tactical variables were studies each one included group of Variables. They were: distance covered (meters) – total distance covered, distance covered with and without possession of the ball; time spent – in opposing half, in attaching third and in penalty area; speed – sprints and top speed; activity time spent – low, medium and high.Statistical analysisA descriptive analysis was first carried out. The homogeneity of variances was examined by means by (T- test) to determine which variables revealed differences between physical and tactical Variables of team play positions; this was done for each of three tactical lines (defenders, midfielders and forwards). Sample was excluded goalkeepers from it. They were (4) defenders player, (4) midfielders players and (2) forwards player. All the statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 16.0 for windows, with significance being set at p<0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Results
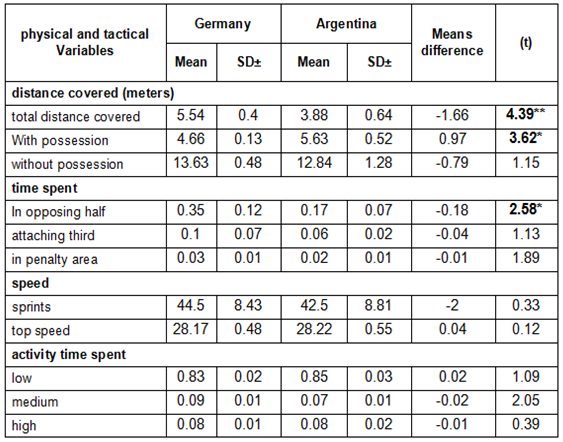
- 3.1.1. Difference Significance for Defender Players at Final Match on all Physical and Tactical Variables under Investigation Table 1. Shows the descriptive results derived from final match statistics for physical and tactical Variables in defender line. There were differences between Germany defender players and Argentina defender players in the average for the first group of variables distance covered– total distance covered was significantly higher for Germany defender players than Argentina defender players at (p<0.05 - p<0.01).However, the average for the first group of variables distance covered– distance covered with possession of ball was significantly higher for Argentina defender players than Germany defender players at (p<0.05 - p<0.01). There were, also, differences between Germany defender players and Argentina defender players in the second group of variables time spent– in opposing half was significantly higher for Germany defender players than Argentina defender players at (p<0.05 - p<0.01). However, there were no differences between defender players in others group of variables.
|
|
|
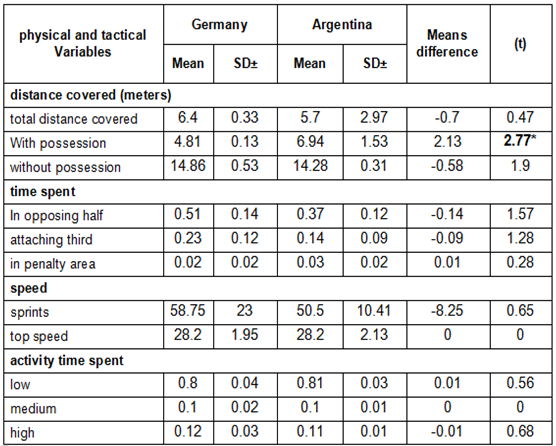
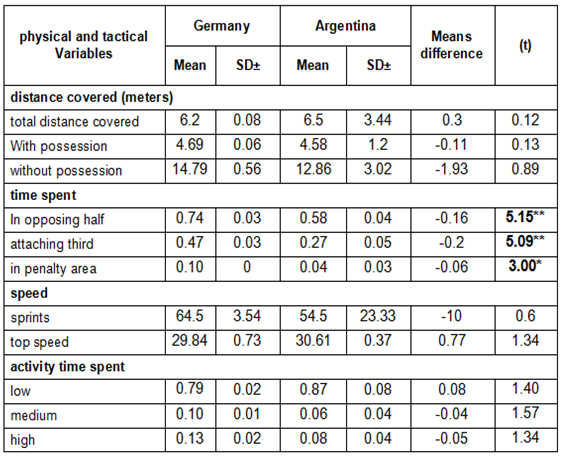
3.2. Discussion
- Analyzing the final match world cup 2014 as a whole the variables with the greatest discriminatory were distance covered – total distance covered and distance covered with possession of the ball; time spent– in opposing half, in attaching third and in penalty area. Because of that the present study shows slight differences in the variables with position play that discriminate between competition national Soccer teams in final match fifa world cup 2014.In line with the present study, Alexander Dellal et al. (2011) also found that the variables total distance covered had the greatest discriminatory with regard to matches played in the Spanish and English league and found no difference across individual playing positions (Alexander Dellal et al., 2011).Distance covered with possession is one of the most widely-studied performance indicators (Lego and Martin, 2007), it would seem, and therefore, that what best discriminates physical and tactical variables between competition national soccer teams in final match performance is the distance covered with possession. In Julen Castellano, et al. (2012) ball possession was a variable that discriminated winning and other teams in the 2006 world cup, the values for the side that won that tournament, Italy, were not significantly different from those of their rivals (Balyan et al., 2007).This not consistent with the finding of (Christian Collet, 2012) who reported that while possession time and passing predicted aggregated team success in domestic play, both variables were poor predictors at the individual level once team quality and home advantage were accounted for. In league play, the effect of greater possession was consistently negative; in the champions' league, it had virtually no impact. In national team tournaments, possession failed to reach significance when offensive factors were accounted for.However, time spent has been shown one of the best discriminating between physical and tactical variables. In addition, weighted mean percentage time spent in different zone of the pitch (defensive third, middle third, and attacking third) was influenced by match status and match location. A combination of these variables and their interactions can be used to develop a model to predict future possession in football (Carlos Lago, 2009).On the other hand, the present study found significant differences between physical and tactical variables and position play in competition national soccer teams at final match fifa world cup 2014 (table 1, 2 and 3). It did show discriminate power in defender, midfielder player and forward player when these analyzed separately. Carlos Lago, (2009) found emphasize the need for match analysts and coaches to consider independent and interactive potential effects of match location, quality of opposition, and match status during assessments technical and tactical components of football performance. Actually, defender players have been shown one of the best at discriminating between physical and tactical variables distance covered; total distance covered and distance covered with possession, time spent; in opposing half. This is consistent with Melih Balyan, et al. (2007), who stated that the Italian national soccer team possessed superiority in the defensive actions, which had brought considerable achievements in wining the world cup. More specifically, (Daniel Barreira, et al. 2014), the teams tended to recover the ball directly in the central mid-defensive zone, and less frequently in the defensive and mid-offensive zone.Regarding the midfielder players, they have been shown one of the best at discriminating between physical and tactical variables distance covered with possession. This consist with the finding of, Alexander Dellal et al. (2011), who stated that FAPL wide midfielders had ̴ 20% more ball touches per possession than their La Liga counterparts.Finally, forward players have been shown one of the best at discriminating between physical and tactical variables time spent; in opposing half, in attaching third and in penalty area. This is consistent with RoboCorp. (2012), who stated that the most successful teams scored most goals inside of penalty area than other team, these results show the relevance of achieve the penalty area in order to improve the opportunity to score. Therefore possession with a high degree of ball control inside penalty area has the potential for producing quality shots (Clemente, et al., 2012). However, Linear regression analysis showed that possession of the ball was greater when losing than when winning (p<0.01) or drawing (p<0.05), and playing strong opposition was associated with a decrease in time spent in possession (p<0.01) (Carlos Lago, 2009).
4. Conclusions
- The main objective of this study was analyzing physical and tactical variables with play positions in final match FIFA world cup 2014. The results demonstrate that team's strengths in performance national soccer teams in final match. The study has applied a multivariate analysis to physical and tactical variables of final match world cup such as distance covered (meters) – total distance covered, distance covered with and without possession of the ball; time spent – in opposing half, in attaching third and in penalty area; speed – sprints; top speed; activity time spent – low, medium, high. It has also sought to identify the performance indicators that best discriminate between physical and tactical variables with position play.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML