-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Sports Science
p-ISSN: 2169-8759 e-ISSN: 2169-8791
2016; 6(2): 23-26
doi:10.5923/j.sports.20160602.01

Perception of Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness in Children and Adults Trained, Submitted to a Training Session of Force Eccentric
Renan Renato Cruz dos Santos, Remo Rodrigues Rossi, Erica Carine Campos Caldas Rosa
Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Brasília, Brasília, Brazil
Correspondence to: Renan Renato Cruz dos Santos, Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Brasília, Brasília, Brazil.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

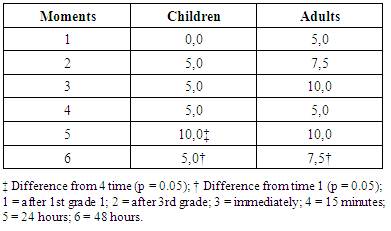
This study aimed to investigate the influence of an eccentric ST session on the DOMS in children and adults. The sample comprised 10 children / pre-teens (age: 11.3 ± 0.82) and 10 adults (age: 24.5 ± 5.58 years) of both sexes. The 10 maximum repetitions test was applied (10MR) in the bench press (BP) on different days separated by 72 hours. After testing 10MR was calculated 10MR 110%, load at which the subjects performed five sets of 15 repeats spaced by 3 minutes of recovery. It was analysed in individuals the sense of discomfort through the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS), where they were questioned about the presence of localized pain in the pectoral / deltoid and upper limb triceps. Thus, for the children were found differences between the five and four moments (p = 0.004) and six one (p = 0.0016). For adults, the time difference was found six for the moment one (P = 0.0014) and no difference between children and adults was found (P> 0.05). It was concluded that in this study children and adults have similar responses from LOMS perception peaking at up to 24 hours after an eccentric training.
Keywords: Eccentric Strength Training, Visual analogue scale of pain (VAS), Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness (DOMS)
Cite this paper: Renan Renato Cruz dos Santos, Remo Rodrigues Rossi, Erica Carine Campos Caldas Rosa, Perception of Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness in Children and Adults Trained, Submitted to a Training Session of Force Eccentric, International Journal of Sports Science, Vol. 6 No. 2, 2016, pp. 23-26. doi: 10.5923/j.sports.20160602.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Strength Training (ST) is regarded as an important type of exercise and has been recommended by leading health organizations [1-3]. The ST provides several benefits in children and adolescents as increased muscle strength, improvement in motor activity, reduction and injury rehabilitation and of course, the improvement in sports performance [4-7]. This modality has also been shown effective in several health indicators as improved body composition, bone mineral density, blood lipid profile and cognitive health [8, 9].The various methodologies that can be employed for the ST, there is the Eccentric Strength Training (EST), which occurs when an external force is greater than that exerted by the muscle, leading to muscle stretching while the voltage is generated [10, 11]. Although strength gains prove specific to this method, it has presented more efficiency gains in muscle mass and improved glucose uptake [12]. Nevertheless, the EST is also responsible for further damage in muscle tissue [13, 14] and possibly more Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness (DOMS).That said, according Tricoli (2001) DOMS occurs eight hours after the effort reaching its peak between 24 and 72 hours after the completion of physical activity [15]. The DOMS manifests itself in response to mechanical stimuli to which the muscle is not used and its magnitude in ST depend on the intensity and effort volume, as well as the type of exercise performed and the type of contraction, for example, emphasizing the eccentric muscle actions [16]. The relative DOMS may preclude a new ST session for several days, as well as disrupt the training sequence of the practitioner, delaying your workout plan, so the present study aims to assist professionals of Physical Education in prescribing this method. In addition, studies involving children and ST are still scarce in the literature, so that little is known about the effects of EST on DOMS in children. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the effects of a single session of EST on the perception of DOMS in children and adults trained.
2. Matherial & Methods
2.1. Sample
- The sample consisted of 10 children (11.3 ± 0.82 years) and 10 adults (24.5 ± 5.58 years), of both sexes, with regular practice of strength training for at least two months. They excluded those with musculoskeletal disabilities or illnesses that prevented the execution of the exercise, drug users or medications that could affect the outcome of research and children who had already reached sexual maturity 1 and 2 according to the Tanner scale [17]. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the University. After being informed about the purpose of this research and the procedures adopted for evaluations and tests, those responsible for the teenagers signed a free informed consent form authorizing their participation in the study. Each stage of the research was carried out in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
2.2. Procedures
- The exercise was performed bench press sitting on the machine (Technogym©). A 10 maximum repetitions (10MR) test was applied for determining the load following protocol Monteiro (2005) [18]. After 72 hours the first test, was performed eccentric strength training session, which consisted of a brief warm 5-10 repetitions with low subjective burden, followed by 5 sets of 15 repetitions at 110% of 10MR - so that the evaluated only performed the eccentric action, with the help of the teacher / researcher for the concentric action during the repetitions - each set had a range of 3 minutes of recovery.To measure the perception of DOMS, the visual analogue scale (VAS) of pain was used (Figure 1). The volunteers were questioned about the presence of localized pain in the pectoral / deltoid and triceps, following procedure previously described [19]. The scale was shown as suggested by Jonhagen (2009) over the following times: immediately after the series 1, 3 and 5; 15 minutes; 24 hours; 48 hours [20].
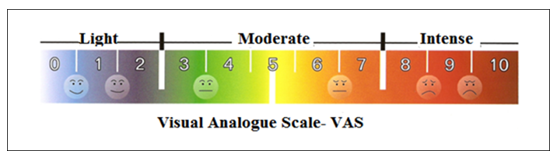 | Figure 1. Visual Analog Pain Scale (VAS) |
2.3. Statistical Analysis
- Given the characteristics of the data, it applied the Friedman ANOVA for intergroup comparison and the Wilcoxon test for intergroup comparison. Thus, the significance value was α ≤ 0.05. All procedures were realized with support of the software Statistical Package for the Social Sciences 22.0 for Windows (SPSS® IBM®).
3. Results
- Significant intragroup differences were found for children, far higher than the 6. The median time 1 (p = 0.016) and 5 time relative to the time 4 (p = 0.004) according to EVA. For adults, intergroup differences were also found, so that the median VAS scale had the time difference 6 for the first time (p = 0.014). There were no statistical differences between groups. All data are shown in Table 1.
|
4. Discussion
- Regular physical activity is important for any age group, so that the ST should be considered as an important tool for their promotion. However, the achievement of results in any activity is related to motivation with which it is performed [21] in order to understand the kinetics of perception of DOMS in different populations will contribute to the prescription of appropriate training, and consequently adherence to the practice of the sport.Thus, the aim of this study was to investigate the influence of an eccentric training on the perception of DOMS in children and adults. In order that the results show that the times of evaluation of the perception of DOMS (24h and 48h after the 5th Grade) the response was shown to be significantly different in both groups. However, although no statistically significant differences between children and adults, have been submitted, it is noted that adults had DOMS perception trend higher for children 48 hours after the intervention, a fact that corroborates the findings of Marginson et al (2005) that when assessing a protocol of EST with 8 sets of 10 jumps on the DOMS, in children and adults, found lower values for children [24].In a study by Brazilian researchers [14], children and adults were subjected to a strength training protocol that involved different rest intervals: 30, 60 and 120 seconds after exercises performed in bench press with 3 sets 10 MR to the concentric failure, so that the children showed a more rapid recovery compared to adults.The literature also reports that the effect of muscle damage associated with eccentric exercise, have less effect on muscle recovery of children, and these are recovered in a shorter time interval than 24 hours, while adults have decreased force for up to 72 hours [23, 24].Therefore, different responses found between populations have important reasons, so that they have reported that the angle of the corner joint in children, is shifted to a higher elongation compared to adults, in order to have less susceptibility to damage muscle by EST [25, 26]. However, children also have improved immune response and appear to exhibit a greater resistance related to the acute inflammatory response than adults, while activities are performed with the same duration and intensity [22, 27]. Therefore, it is noted that the capacity or metabolic demand between groups is different, while children have a lower proportion of anaerobic glycolytic fibers which are predominantly susceptible to injury when compared to adults [28, 29].Furthermore, this study rise important questions about the differences between the persistence of DOMS in the population studied, emphasizing that individuals evaluated in this study were already accustomed to the practice of ST and perhaps the requirement of the protocol used was not enough to cause statistically similar responses to other studies cited above. It is emphasized that this study has some limitations, so that the sample pre-adolescence was defined by literary concept and not by analysis of stage Tanner sexual maturation as well as the acute nature of the study limits arguments on chronic adaptations to training.The results of this study aplly specifically to the population, exercise and musculature involved. Even though professionals involved in the prescription of resistance exercises have many aspects to consider, the instruments utilized such as VAS and the application of the EST open many possibilities to prescription and research. In this sense, a better understanding of the responses coming from the EST practice could help in a more correct and safe prescribing, also contributing to an active lifestyle, since an inadequate recovery time can lead to muscle discomfort and cause a lack of interest in practice.Moreover, according to Peake (2005), eccentric exercise typically results in muscle damage due to lack of adaptation to exercise [30]. So that, in addition to membership, the practice of this type of exercise can contribute to the injury preventing and a more functional life.Remember too, that this is the first study to focus on the effects of EST on DOMS in children and adults, using a protocol for upper limb, and finally, it is suggested that more studies be carried out to investigate the effects of more intense sessions, as well as other methodologies on DOMS in different populations (children, adolescents, adults and seniors).
5. Conclusions
- After all the analyses it is concluded that adolescents and adults trained, have similar answers about the perception of DOMS, both of which are likely to peak DOMS up to 24 hours after an eccentric strength training. Thus, we consider that these results are important for the inclusion of a timeline and systematic variation of adequate training, as well as to their choice regarding the type of work to be executed.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML