-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Sports Science
p-ISSN: 2169-8759 e-ISSN: 2169-8791
2016; 6(1): 1-5
doi:10.5923/j.sports.20160601.01

Does Mini-Trampoline Training More Effective than Running on Body Weight, Body Fat, VO2 max and Vertical Jump in Young Men?
Gülşah Şahin1, Erdal Demir1, Halide Aydın2
1Coaching Education Department, Canakkale Onsekiz Mart University, Canakkale, Turkey
2Faculty of Medicine, Canakkale Onsekiz Mart University, Canakkale, Turkey
Correspondence to: Gülşah Şahin, Coaching Education Department, Canakkale Onsekiz Mart University, Canakkale, Turkey.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The aim of this study was to examine the effect of mini-trampoline training on VO2max, body weight, fat % and vertical jumping height. The participants were randomly separated into 2 groups as the trampoline group (n:6, age 21.8±2.04 years, height 174±5.78 cm, weight 71.73±4.58 kg) and the running group (n:6, age 20.7±1.51 years, height 179±7.18 cm, weight 72.68±9.5 kg). All the participants completed 8 weeks of trampoline and running training. The trampoline training was prepared with standard choreography comprised of high skipping, landing jump on each legs. The trampoline and running training were started as 30-minute sessions and in the last two weeks were extended to 35 minutes. The yo-yo intermittent recovery test level 1, vertical jumping test and body composition analysis were applied to participants. All the tests were applied at pre and post-training periods. After the eight week training intervention, there was a significant (p<0.05) difference in VO2 max and vertical jump height between running and trampoline groups. There was no significant (p>0.05) difference in fat % and body weight between trampoline and running groups. These results support the hypothesis that the use mini-trampoline may improve VO2 max, vertical jumping distance and reduce body fat %.
Keywords: VO2 max, Body weight, Running, Healthy, Men
Cite this paper: Gülşah Şahin, Erdal Demir, Halide Aydın, Does Mini-Trampoline Training More Effective than Running on Body Weight, Body Fat, VO2 max and Vertical Jump in Young Men?, International Journal of Sports Science, Vol. 6 No. 1, 2016, pp. 1-5. doi: 10.5923/j.sports.20160601.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Currently the most popular method of involves activities jumping on a flexible surface such as mini-trampoline [1, 2, 3]. Although trampoline training is not a new method, recently the use of equipment has increased. The flexible surface of the equipment is highly integrative and demanding on the neuromuscular system. The increase in oxygen capacity and jumping distance and the reduction in body weight and body fat percentage are important in both general fitness and athletic performance. Aerobic activities such as jogging, long-distance running, walking and dancing are known to be effective for increasing oxygen capacity and reducing in body weight [4, 5, 6]. In addition, there are many studies which have examined the effect of trampoline training on body weight and oxygen capacity [7, 8]. The research has reported that mini-trampoline training has positive effect on body weight and oxygen capacity. The other one study has stated that the trampoline training improved oxygen capacity, but no change in body weight [9].Trampoline training is used as an alternative to running and aerobic training to reduce body weight and to increase cardio-respiratory resistance in fitness. However, no such studies have ever been performed to examine the effects of undertaking trampoline training. It is not clear that trampoline training is more effective than running training on maximal oxygen consumption capacity (VO2 max), vertical jumping distance, body weight and fat %.The aim of this study is to examine the effects of mini-trampoline training on VO2 max, body weight, fat % and vertical jumping distance.
2. Matherial & Methods
2.1. Participants
- The study comprised 12 young healthy men who had been involved in training recreationally for at least 2 years. Inclusion criteria were to be participated in a regular training program recreationally and no injuries or health problems. Exclusion criteria were any injuries or health problems, or the following of another fitness program of sports training.
2.2. Study Design and Tests
- The study was conducted between January 2015 and March 2015. All methods and tests were approved by the Ethics Committee of University. Informed consent was obtained from all participants. Each stage of the research was carried out in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Yo-Yo Intermittent Recovery Test Level 1: The distance achieved was recorded for those who finished the test and the maximal oxygen consumption capacity was calculated [10]. Exercise heart rate measurement: A Polar R800CX heart rate device was used to measure the heart rate. Body weight and fat % were measured with a TANITA-TBF-300 Body Composition Analyser. Vertical Jump: The Newtest Powertimer 300-Series testing system was used. All repetitions were performed on a mat, with hands placed on hips. The participants performed squat jumps. At the start, the knee angle was approximately 90° and after the jump, the knee angle was kept extended at 180° [11].
2.3. Training Procedure
- Participants trained 3 times per week for 8 weeks. They performed on different equipment and intensity. Each training session started with standardized warm-up exercises at the lower muscles (gluteal, quadriceps, hamstring). It finished with five-minute cool-down. The trampoline training was prepared with standard choreography comprised of high skipping, landing each jump on alternating legs. The trampoline and running training were started as 30-minute sessions and in the last two weeks were extended to 35 minutes. The mini-trampolines used in the study (127cm in diameter and 27.5cm in height). The running training was performed in the sports hall. A maximum heart rate of 60% was taken into consideration for running intensity. The trampoline group’ target heart rate was 75%. Karvonen method was used for the calculation of the target heart rate (target heart rate range = ([HRmax – Hrrest] * percentage intensity) + Hrrest)” [12]. The heart rate was monitored by polar heart rate device. Groups did not see each other during the training, tests or measurements. All subjects were asked to maintain their usual diet and lifestyle habits during the study period.
2.4. Data Analysis
- Mean and SDs were calculated for the all parameters. Data were tested for normality using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov normality test. Levene test was used to homogeneity. The Wilcoxon test and the independent t-test were used to compare between groups. Paired t-test and the Mann Whitney U-test were used to evaluate for differences between before and post-training data. For all comparisons, a significance level of p ≤ 0.05 was used.
3. Results
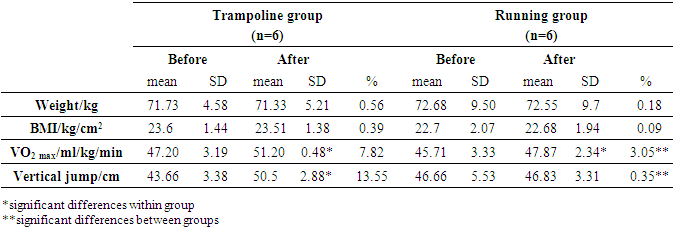
- There was no significant difference between trampoline group and running group in yo-yo test distance (t=.71; p=.49), VO2 max (t=.78; p=.44); fat % (t=.22; p=.82), BMI (t=.57; p=.58), vertical jump distance (t=-1.13; p=.28), height (t=-.65; p=.53), body weight (t=-.11; p=.91) and age (t=1.12; p =.28) at the baseline (p>.05) (Table 1).
|
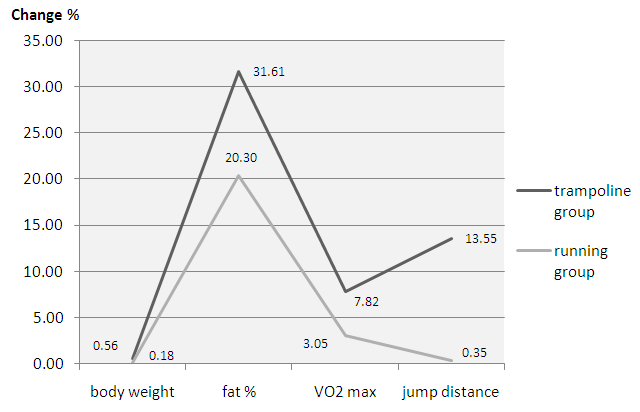 | Figure 1. The percentage values of two groups in after training |
4. Discussion
- In this study, the effects of two different training methods on VO2max, fat %, vertical jump distance and body weight were investigated. At the end of the study, according to yo-yo intermittent recovery test results, a significant increase was determined in VO2 max in the running group and the trampoline group. When the two groups were compared, a more significant improvement was observed in the trampoline group. The knee bending, running and jumping, in contrast to running alone, are performed on an elastic base with exposure to reactive ground force in mini-trampoline training. It is thought that in contrast to the cyclical movements of running, there is increased energy expenditure with the use of these varied movements in trampoline and thereby an increase in oxygen consumption.Research has demonstrated that there is no difference between high-intensity training and low-intensity traditional training [13]. Nevertheless, Talanian et al. (2007) determined a 7–12% increase in VO2max after 2 weeks of high-intensity training [5]. Reeves and Darby (1991) compared the VO2max values of 10 fit females following aerobic dance with long periods of traditional running and no difference was found between the two forms of exercise [4]. Tabata et al. (1996) recommended high intensity training to achieve a significant increase in VO2 max [14]. Roxburgh et al. (2014) found that the high and moderate intensity exercises improved VO2max. [15]. Lee et al. (2012) stated that high-intensity exercise (70% of VO2max) was more beneficial on cardiorespiratory resistance than low-intensity exercise (50 % of VO2max) [16]. When previous studies are examined, it can be seen that although long periods of aerobic exercise used to increase in VO2max more, high-intensity or jumping exercises make a significant contribution to oxygen consumption. In a study of children with cystic fibrosis by Stanghelle et al. (1988) the mini-trampoline were used, an improvement in VO2max from 45 to 49 ml/kg/min was determined and these programs were recommended for these children [17]. Tomassoni et al. (1995) determined a significant increase in VO2max after eight weeks of mini-trampoline training in females [18]. Similar to the findings of the current study, the increase in VO2max was found to be more significant in the trampoline group than the running group. In both groups there was an improvement compared to pre-training values, but the increase in the trampoline group compared to the baseline was 7.82% (4 ml/kg/min) and in the running group, 3.05% (1.16 ml/kg/min)(Figure 1). Owing to the increase in energy expenditure and oxygen consumption, VO2max increased and fat % decreased; these results confirmed hypothesis of this study. In a study by Edin et al. (1990) a 4.4% improvement was determined in VO2max with 11 weeks of trampoline training, but no significant difference was found in body composition [9]. Katch et al. (1981) investigated energy expenditure on a mini-trampoline and, compared to the pre-training values, VO2max was improved when additional weights were used at different intensities [7]. Stanghelle et al. (1988) in a study among children with cystic fibrosis, found a 9.2% improvement in VO2max and in respiratory parameters after eight weeks of mini-trampoline exercises [17]. Plyometric training is often used to improve vertical jumping in various sports [19, 20]. The another aim of the current study was to examine the effect of trampoline training on vertical jumping height. It is known that jumping on a trampoline differs from plyometric training as it is not just a cycle of extension and contraction movements, but is performed on an elastic base. In this study, there was a 13.55% improvement in vertical jump distance, and this improvement was statistically significant. The baseline mean vertical jump distance increased by 6.84cm after the mini-trampoline training. This result shows that mini-trampoline training is effective on vertical jump distance. There was no similar improvement in the running group. Running training can not be used for the development of vertical jumping ability. However, in this study, to confirm the hypothesis that trampoline training could achieve an improvement in cardiorespiratory, body composition and vertical jumping, a comparison was made with running training. Nevertheless, despite significant improvement in the trampoline group after the training program, there was no significant difference between in two groups. This could be considered to be due to a higher mean vertical jump distance in the running group at the start of the study. The hypothesis of the study was confirmed. With a program of trampoline training, it is possible to achieve improvements in oxygen consumption, body composition and also vertical jumping ability. Aragão et al. (2011) implemented a 14-week period of mini-trampoline training with elderly individuals and concluded that it made a contribution to dynamic balance [21]. Miklitsch et al. (2013) used a mini-trampoline with a rehabilitation program for stroke patients and determined an improvement in postural control [22]. Karakollukçu et al. (2015) also implemented 12 weeks of trampoline training and a significant improvement was found in acceleration, vertical jump and anaerobic performance [23]. Several researchers have examined the relationship between trampoline training and body composition. Edin et al. (1990) determined a change in body composition and blood lipids after 11 weeks of trampoline training [9]. Lee et al. (2012) reported that high-intensity exercise (70 % of VO2max) was more beneficial than low-intensity exercise for the reduction of overall body fat and abdominal area fat (50 % of VO2max) [16]. Other studies have also shown that high-intensity exercise is proportionally more effective than low-intensity exercise for the reduction of body fat perception [13, 24, 24]. In the trampoline group, fat % decreased and mean total body weight reduced, but this difference was not statistically significant. In the running training group, there was a reduction in fat % and total body weight but, the change was not significant. Thus, trampoline group did not make any difference in total body weight and BMI, the reduction in fat% was statistically significant. Previous studies have determined that, generally speaking, high-intensity training creates significant difference in regional and total fat loss [25, 26].
5. Conclusions
- The results of this study have shown that trampoline training is a more effective training method than traditional running training to increase maximal oxygen consumption and reducing fat %. In addition, trampoline training had a significant effect on vertical jumping distance in young healthy men.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- Authors thank Canakkale Mart University and the Head of Coaching Education Department for their support on this research, and the voluntary university students for their participation on this study.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML