-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Sports Science
p-ISSN: 2169-8759 e-ISSN: 2169-8791
2015; 5(5): 180-186
doi:10.5923/j.sports.20150505.02
Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors among Nigerian Pre-Adolescent, Adolescent and Adult Males and Females
Mamman Iro Dikko (PhD)
Department of Physical and Health Education, Federal College of Education Zaria, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Mamman Iro Dikko (PhD) , Department of Physical and Health Education, Federal College of Education Zaria, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
An increased in cardiovascular disease risk has been reported to be associated with body fat composition, blood pressure and lower aerobic fitness. This study was conducted to find out the difference between pre-adolescent, adolescent and adult males and females in selected disease risk factors. Topography of body fat composition, blood pressure and lower physical fitness were found to be risk factors of cardio vascular disease. A total of one hundred and eighty (180) subjects comprising preadolescents aged 7-11 years (60; M-30, F=30), adolescents aged 12-18 years (70; M=35, F=35) and adults aged 19-30 years (50; M=29, F=21) were selected at random from primary and post-primary schools in Zaria – 12 Minute Run Test was conducted in the evening after all measurements have been carried out. The results of this study revealed significant sex differences between preadolescents, adolescents and adults in blood pressure, body fat percent, BMI, GT, TC, VLDL-C, TC: HDL-C ratio and Vo2 max as the values increased with advancing age from preadolescent through adolescent to adulthood. While height and weight significantly different, sex differences were mainly due to higher values in female subjects than in male subjects in all the listed variables except in VO2 max where females recorded lower values than males. Results however, did not show any significant difference between the three groups in HDL-C, and TG suggesting that they had similar HDL-C, and TG levels, whereas insignificant sex differences are found in systolic blood pressure (SBP, TC, LDL-C, HDL-C, TC: HDL-C, ratio TG in the three different age groups indicating that they were very much similar in both male and female subjects. Based on the findings of this study, it was suggested that tracking of changes in blood pressure, fat content and lipoprotein profiles be started early in life, and physical education should form the basis of intervention against sedentary lifestyle.
Keywords: Cardiovascular, Risk, Factors, Disease, Pressure
Cite this paper: Mamman Iro Dikko (PhD) , Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors among Nigerian Pre-Adolescent, Adolescent and Adult Males and Females, International Journal of Sports Science, Vol. 5 No. 5, 2015, pp. 180-186. doi: 10.5923/j.sports.20150505.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Physical activity is essential for the health and well-being of all individuals irrespective of age and sex. However, modern scientific and technological developments have led to the production of energy saving machines such as automobiles, grinding amines, electronics (i.e. video and television and radio), milling machines, which have lessened the physical demand of everyday routine activities like going to work, milling stable foods, grinding grains and trekking short and long distances. Though what would have once required an hour or more can now be accomplished in a few minutes by pressing a button. This new trend has led to more leisure activities. This increased leisure is utilized in the pursuit of sedentary activities (Venkateswarlu, 1996; Heyward, 1998; Surgeon General’s Report on Physical Activity and Health, 2003).As a consequence of the high rates of physical inactivity, the number of individuals irrespective of age and sex suffer a host of health problems such as coronary heart disease, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, obesity, diabetes, overweight, cancer and musculoskeletal disorders (Nieman, 2003; Heyward, 1998).According to U.S Department of Health and Human Services (2000), reported that people who are physically inactive are at a greater risk of developing and increasing in the accidence of degenerative diseases commonly known as hypokinetic diseases. Current trends in the field of epidemiology, and exercise physiology have shown that disease risk factors tend to influence human health and performance. This led to much discussion among scientific circles regarding the magnitude and direction of the incidence of these disease risks among preadolescents, adolescents, and adults. Although cardiovascular disease risk factors form the broad theme of this paper. However, it was not clear how the different risk factors were modified during growth and development. Another interesting finding was that advancing in age have been found to be a factor for predisposing individuals to high blood pressure, elevated cholesterol and triglycerides, elevated glucose level, body fat percent, body mass index, and low aerobic fitness.
2. Materials and Methods
- An ex-post factor design was used in this research as all the variables measured in this study were already developed. A total of one hundred and eighty (180) subjects preadolescents aged 7-11 years (60) M=30, F=30), adolescents aged 12-18 years (70), M=35, F=35) and adults aged 19-30 years (50) M=29, F=21) whom were selected at random from primary and post-primary schools in Zaria. Series of testing protocols based on age and sex groups were conducted on the subjects. One short case study design was used because it involved a single measurement of performance status without treatment procedure. The three by two by seven (3 x 2 x 7) factorial) design was used for factor analysis and 12 minute run test was conducted in the evening after all measurements have been carried out on the subjects.
3. Measurement Tools
- Subject age, sex, height and weight were measured in light clothing (without shoes) with a studio meter and calibrated physicals scale. Anthropometric measurements were taken and these include height, weight, body mass index (BMI) determined by dividing weight and height indices (Wt) as suggested by Trowbridge 1983, Valerie et al. (1996). Body fat percent (BFP) by using skinfold measures of trunk and limbs (the trunk skinfolds include abdominal, surprailiac, and subscapular; while the limb skin folds include triceps, biceps, and medial calf) as suggested by Australian Health and Fitness survey (1985) and Heyward (1998).1. Height and heights were measured by using a standardized anthropometric techniques and were recorded in centimeters using a stadiometer (Williams et al, 1986).2. Weight: Subjects weights were measured by using a calibrated physician’s scale (Shemond) while subjects dressed in light cloth without-shoes. All subjects were weighted three times and the average was used to determine the exact weight (Australian Health and Fitness Survey, 1985).
4. Body Fat Percent
- A standardized calibrated skinfold calipers was used for the measurement of trunk (abdominal suprailiac, and subscapular), while limb skinfold (triceps, biceps, and medial calf). The calipers was used to measured folds of skin only, and no muscle tissue was included. The fold of the skin and subcutaneous fat was held firmly between thumb and index finger, pulling it away from the underlying muscular tissue and following the natural contour of the fat fold. The caliper was then placed on the skinfold as closely as possible (usually about ½ inch (0.5cm) and a constant with the skin (Heyward 1998, Venkateswarlu, 1992). Skinfold measurements were taken on the right side of the body as suggested by Heyward, 1998; Wilmore, et al, 1994). Three measurements for each side were made and the average was used to determine the fat fold score. Percent body fat was calculated based on age and sex using skinfold prediction equation formular (Slaughter et al, (1988), Jackson and Pallock, 1980).
5. Blood Pressure
- Blood pressure was taken in sitting positon (Guyton, 1996) each subject was well-composed while seated on a chair and the calf of the sphygmomanometer was wrapped around his or her left upper arm and gently inflated to a pressure of between 140 to 160mmHg (Guyton, 1996). Heyward, 1998). Subjects were not allowed to see the inflated pressure as this is in order to avoid any anxiety, fear and psychological tremor/effect. Gradually culf was delated at the rate of 2 to 3mmHg per second by unscrewing the control valve of the inflator slowly but steadily while carefully watching the pressure gauge. Systolic blood pressure was recorded by hearing the first highly tapped sound regarded as the first arterial sound, while the arterial sound disappeared a Korotochoff was heard and recorded as diastolic blood pressure (Ganong, 1995). Three measurements were taken and the average found and recorded. Two minutes waited with the culf fully deflated before repeating in order to avoid artifacts caused by venous filling while culf is about venous pressure (Guyton, 1996).
6. Glucose Tolerance Test (GTT)
- Sensitive and calorimetric methods for determining blood glucose intolerance was used (function of insulin resistance) among subjects (Juhan-Vague et al., 1993, Morja-Ritta, 1997). Non-fasting blood sample (3mml) were taken and was put into a heparinized tools for blood sugar analysis.
7. Testing Techniques
- Blood sugar test was measured by glucose oxidase method using 4 – aminophenazone as oxygen acceptor (Garfield, 1971) and HBA, C was determined by colorimetric method (Parker et al., 1981) with results expressed as fructose equivalents (Heyward, 1998; Marga-Rita, 1997; Zavaroni, et al, 1993).
8. Blood Lipid Profiles (TC & TG) Techniques
- Blood lipids obtained from subjects articulated vein without venstasis and collected into a hepanized tubers for blood lipids analysis. (Cooper, Myers, Smith & Sampson, 1988).
9. Statistical Analysis
- 1. Student’s t-Test was used to detect any significance difference between male and female preadolescents, adolescents and adults of the same age group among independent variables.2. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA-1) was used to compare demographic and descriptive variables among different age and sex groups in blood pressure, percent body fat, body mass index, glucose tolerance, HDL-C, LDL-C, CLDL-C, and Triglycerides at significant level of 0.05.3. Scheffes Post-Hoc Multiple Comparison test was used to locate significant difference among independent available (i.e. high blood pressure, percent body fat, body mass index, glucose tolerance, low density LDL-C, HDL-C, age, highest, sex, weight and VO2 max.
10. Results
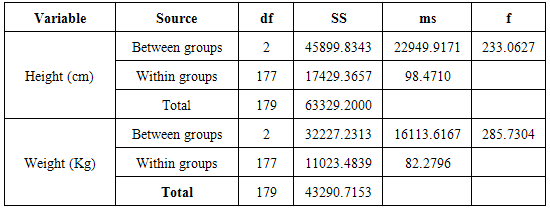
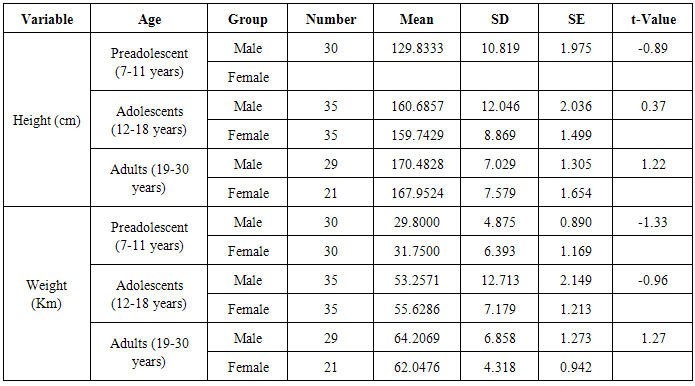
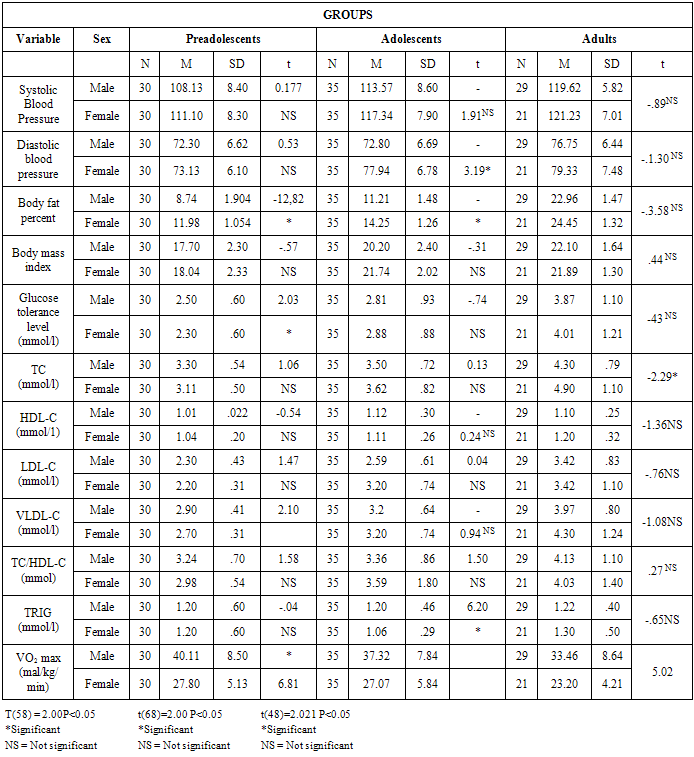
- Analysis were conducted to identify the differences in cardiovascular diseases risk factors between preadolescents, adolescent and adult males and females in height, weight, blood pressure, bone fat percent, body mass index, glucose tolerance, total cholesterol, triglyceride, LDL-C, HDL-C, VLDL TC/HDL-C, and VO2 Max and as inferred from the coopers 12 minute Run Test.One way analysis of variance (ANOVA-1) was performed for differences between preadolescent, and adolescent and adult group in their Height (CM) and weight (Kg) as shown in table two (1) below:
|
|
|
|
11. Discussion
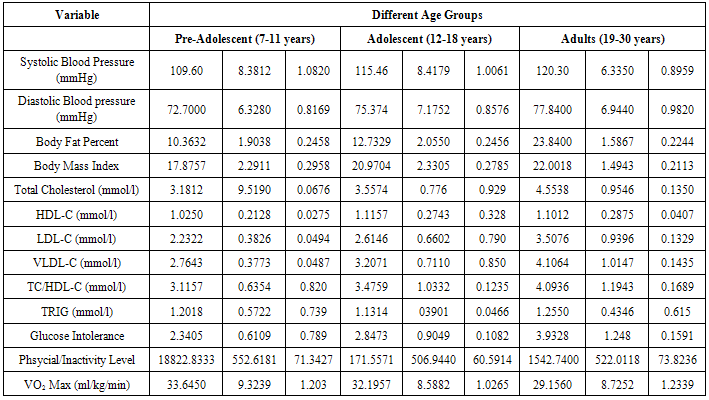
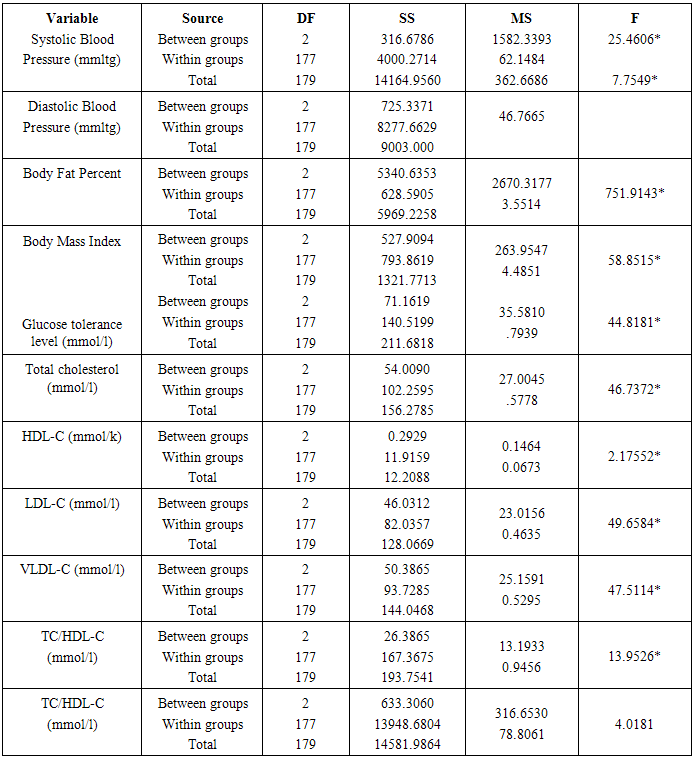
- On the basis of the findings of this study, the differences between preadolescents, adolescents and adults in disease risk factors which included blood pressure, body fat percent, body mass index, glucose tolerance, total cholesterol, HDL-C, LDL-C, triglycerides and aerobic fitness which was determined by VO2 max, that was inferred from 12 minutes run test were identified. Research evidence revealed that pre-disposing disease risk factors tend to accelerate the rate of degenerative disorders, like coronary heart disease, atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, hypercholesterolemia, musculoskeletal disorders and different types of cancer (Wilmore et al, 1994; Venkateswarly 1998; Heyward, 1998; and Maline, 2001).Results of this study showed significant differences in systolic blood pressure between preadolescents, adolescents and adolescent and adults. One explanation for this difference was mainly because of a gradual increase form the systolic blood pressure level of 109.60 + 8.18mmHg in preadolescents through 115.46 + 8.12 mmHg in adults. This gradual increase in systolic blood pressure is attributed to the increase in height and weight from preadolescents to adolescent and growth associated hormonal modification in both males and females (Williamson, 1993; Fahey, et al 2003). Further explanation revealed that physical activity level during preadolescence and adolescence is much greater than during adulthood and that increased physical activity level decreases blood pressure (Warcham, Man-Yu, Susie, Joanne, Kirsten, Kennedy & Nicholas, 2000; Fahey, et al, 2003). In addition, it has been shown for example, one standard deviation increase in the physical activity level can be associated with a 5mmHg decease in systolic blood pressure in women and a 3mmHg decrease in men (Ebrahim and Smith, 1998). Similarly, growth in stature and the underlying mechanisms that control growth during puberty have independent effect on blood pressure of preadolescents and adolescent males and females (Kazue, et al, 1997). Thus, the underlying mechanisms for the control of lineer growth seen to involved a number of factors, especially genes) nutrition and thyroid hormones 9Kerrigen and Rogel, 1992; Glustin and Veldhuis, 1998). In this regard growth hormone (GH) and thyroid hormone (TH) are considered responsible for preadolescent growth, while gonadal steroids, especially, their interaction with growth harmone (GH) and (IGH) – 1 are of primary importance for the acceleration of growth rate at puberty (Prader, 1984).Although systolic and diastolic blood pressures for preadolescents, adolescents and adults significantly differs, they were all within, the normal acceptable range for their respective age group-suggesting that they were all normal in their cardiovascular health. This implies that of the age of adolescent and adult groups of this age may not be pre-disposed to cardiovascular diseases due to raise in blood pressure. At the same time this appeared to be an indication of relatively strong hearts, indicating low risk levels for the onset of cardiovascular disease such as heart attack and strokes among these subjects (Hoeger & Hoeger, 2002).The observations made in this study could be explained on the basis of the fact that the subjects used in this study had no history of insulin dependent diabetes mellitus, therefore glucose level may not change from the normal range (Betteridge, 1997). An alternative explanation is that the subject were non-obese and not overweight.
12. Conclusions
- In view of the limitation of this study the following conclusions are drawn from this results. i. Blood pressure, both systolic and diastolic increased during growth and development with the increased in height and weight.ii. Body composition changes during growth and development with age, height and weight, as body fat percent, body mass index and TC increased. However, changes in TG during growth and development are insignificant.iii. Lipoprotein like LDL-C, VLDL-C, and development with age. However, changes in HDL-C during growth and development are insignificant.iv. Physical working capacity (PWC) as determined by VO2 max increases from preadolescents through adolescents to adulthood.v. Although, female have greater body fat percent and lesser physical working capacity (PWC) in different age groups, their TC and HDL-C levels are not significantly different from their male counterparts.
13. Recommendations
- On the basis of the findings of the study, the following recommendations are made to improve the health of preadolescents, adolescents and adults. This study shows increase in blood pressure and fat composition of the body with increasing age. It is therefore suggested that tracking of changes in blood pressure, fat content and lipoproteins should be started right from preadolescence period so as to take appropriate measures to control body composition and lipoprotein levels of preadolescents as they grow.This study has shown increased physical working capacity (PWC) with increase in age. However, previous studies have shown that inactivity leads to the incidence of a variety of degenerative diseases. As pre-adolescents are fit enough to undergo exercise, suggesting that they should be encouraged to participate in moderate to vigorous physical activities through school physical education programme and community fitness programmes. Introduction of such programmes at an early age will help individuals maintain active lifestyle throughout their lives that would enhance their health and productivity.This study has shown that fat composition and lipoproteins of the body dramatically increases right from preadolescent period, especially in females. It is therefore suggested that through medical examination should be conducted during adolescence in order to determine the direction of lipid and lipoprotein modifications so as to use appropriate interventions that can promote the health of the individuals. It is also therefore suggested that public, private and non-profit organizations should utilize different means to educate the general populace about the importance of leading an active lifestyle. This can easily be achieve through mass media and voluntary organizations.
References
| [1] | Australian Council for Health Physical Education and Recreation (1987): Australian Health and Fitness Survey. 1985 Park Side, South Australia. |
| [2] | Betteridge, D. J. (1997): Diabetic Dyslipidemia, What Does it Mean? Diabetes, International Developments IN Diagnosis and Therapy, Published by Except Mediator Bochinger Mannheim, Vol. 17 (2) 1-8. |
| [3] | Boucbard, C., Despres, J.P., & Mauriege, P. (1995): genetic and Non-Genetic Determinants of Regional Fat Distribution, Endror. Rev., 14:72-93. |
| [4] | Cooper, O.R., Myers, C.L., Smith, S.J. & Sampson, E.J. (1988): Standardization of Lipid, Lipoprotein and Apolipoproetin Measurements, Clinical Chemistry, 34: Pp. 1395-B 105. |
| [5] | Fahey, T.D., Insel, P.M. & Roth, W.T. (2003): Fit and Well: Core Concepts and Labs in Physical Fitness and Wellness. Dubuque, IA: McGraw-Hill. |
| [6] | Guyton, A. (1971): Testbook of Medical Physiology, W.B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia. |
| [7] | Heyward, V.H. (1998). Advanced Fitness Assessment and Exercise Prescription, 3rd Edition, Human Kinetics, Published in Canada. |
| [8] | Heyward, V.H. & Lisa, M.S. (1996): Applied Body Composition Assessment Printed in Canada. |
| [9] | Ho, K.Y., Evans, W.S., Blizzard, R.M., Velhuis, J.D., Merriam, G.R., Samojlik, E. Furlanetto, R., Rogol, A.D., Kaisar, D. L (1987): Effects of Sex and Age of the 24 Hour Profile of Growth Homone Secretion in Man: Importance of Endogenous Estradiol Concentrations, Journal of Clinical Endocrinologica metabolism, 64:51-58. |
| [10] | Juhan-Vague, I., Thompson, S.G. & Jesperson, J. (1993): Involvement of the Hemiostatic System, in the Insulin Resistance Syndrome, Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, Vol. 13, 1865-1873. |
| [11] | National Institute of Health (NIH); (1998) Clinical Guidelines for the Identification, Evaluation and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults. Bethesda, M.D: National Institutes of Health. |
| [12] | Nieman, D.C. (2003): Exercise Testing and prescription: A Health Related Approach. New York: McGraw-Hill Higher Education. |
| [13] | Prader, A. (1984): Bio-Medical and Endocrinological Aspects of Normal Growth and Development, In: Borms, I, Hauspie, R., Sand, A., Susanne, C., Hebbelinck, M., Editors: Human Growth and Development, New York, Plenum Press, P. 1-4-A. |
| [14] | Surgeon General’s Repot on Physical Actviity and Health (1996). Retrieved October 21, 2003, fromhttp://www.cdc.gov/nccdphp/sgr/sgr.htm. |
| [15] | U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 91996); Physical Activity and Health. A Report of the Surgeon General at a Glance Atlanta, G.A: U.S. Department. |
| [16] | Venkateswarlu, K. (1996): Health, Fitness and Physical Actviity Patter of Children: A Public Health Perspective (Key Note Paper, Presented at the 1990, Annual Conference of Nigerian Association of Sport Sciences and Medicine (NASSM), Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria, Nigeria, 18/10/1990. |
| [17] | Venkateswarlu, K. (1990): Physical and Health Issues in Science and Technology Education for National development. A Lead Paper Presented at the National Conference on Science and Technology for National development Organized by Federal College of Education, Pankshin, Plateau State, Nigeria, from 26th to 30th November. |
| [18] | Warcham, J.N., Man-Yu, W., Susie, H., Joanne, M., Kirsten, R., Kennedy, C. & Nicholas, E.D. (2000), Quantifying the Association between Habitual Energy Expenditure and Blood Pressure, International Journal of Epidemiology, 29:655-660. |
| [19] | Williams, P. Stefanick, NI., Vranizan, K. (1994); The Effects of Weight Loss by Exercise or by Dieting on Plasma High Density Lipoprotein (HDL) levels in men with low, Intermediate, and Normal-to-high 1-IDL at Baseline. Metabolism 43:917-924. |
| [20] | Williamson, D.F. (1993): Descriptive Epidemiology of Body Weight and Weight Change in U.S. Adults. Annual of International Medicine, 119, 646-649. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML