-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Sports Science
p-ISSN: 2169-8759 e-ISSN: 2169-8791
2015; 5(3): 113-116
doi:10.5923/j.sports.20150503.04
The Model Transformational Leadership Behaviors of Head Coaches and Job Satisfaction
Duangkrai Taweesuk
Department of Health and Sport Science, Mahasarakham University, Thailand
Correspondence to: Duangkrai Taweesuk, Department of Health and Sport Science, Mahasarakham University, Thailand.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The objective of this study is to model transformational leadership behaviors of head coaches and job satisfaction of assistant coaches. The model was subjected to statistical analysis using Amos 16. Satisfaction of assistant coaches the result shows the model poor fit. This study found the modified model transformational leadership behaviours of head coaches was model fit in four dimensions: vision, providing, supports and stimulation. The modified model job satisfaction of assistant coaches was model fit dimension, contingent rewards, operating procedures, nature of work and communication.
Keywords: Confirmatory Factor Analysis, Job Satisfaction, Transformational Leadership Behaviours
Cite this paper: Duangkrai Taweesuk, The Model Transformational Leadership Behaviors of Head Coaches and Job Satisfaction, International Journal of Sports Science, Vol. 5 No. 3, 2015, pp. 113-116. doi: 10.5923/j.sports.20150503.04.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The theory of transformational leadership was developed by bass (1985) and has attracted considerable attention since then (Bass, 1998). Transformational leadership display certain characteristics, such as espousing ideals, acting as role models, and showing care and concern for each subordinate. Satisfaction with the job as a significant contributor to organizational very few have focused on the job satisfaction on sport setting. Hence, the objective of the study is to measurement models transformational leadership behaviors of head coaches and job satisfaction of assistant coaches.
2. Methodology
- The measurement models with confirmatory factor analysis (CFA). Survey instrument will be used in this study where the subjects (assistant coaches) will be asked to evaluate the leadership behaviors of their supervisor (head coaches). The independent variable in this study is the transformational leadership behaviors of head coaches while the dependent variables assistant coaches’ job satisfaction. The population in this study assistant coaches from 30 sport type focus on the main sport type have competition at Sea Games (N= 2,513) coaches of 250 assistant coaches will be selected using simple random sample technique. This study the assistant coaches 250 will be selection use simple random sample technique. The name of assistant coaches will be obtained from registration (2006-2008) each sport in Thailand. Name will be giving a number from 0001 to 2513.
3. Results
3.1. Confirmatory Factor Analysis Model Transformational Leadership Behaviours of Head Coaches
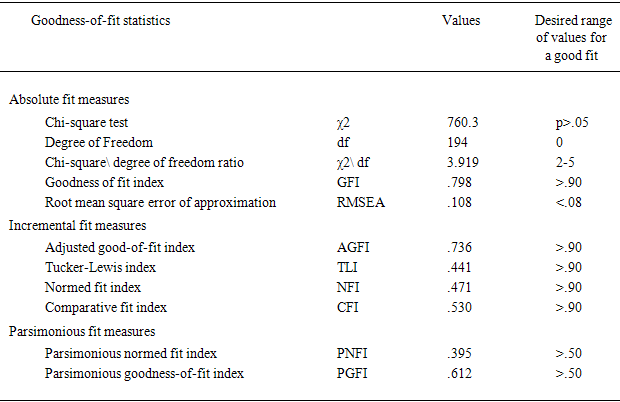
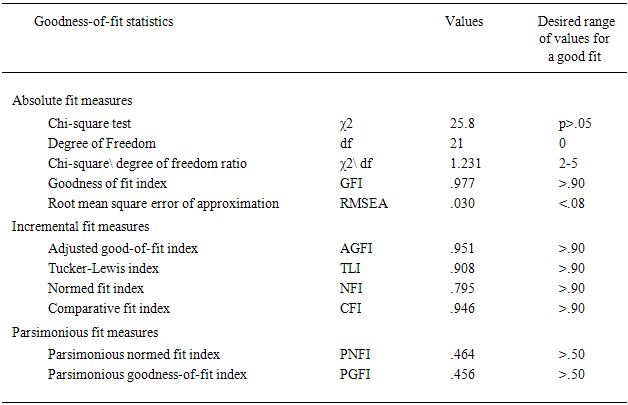
- An overall confirmatory factor analysis was conducted on all items and constructs to examine the adequacy of the construct measures. Table 1 shows the model poor fit GFI and AGFI not passed by the recommended level of .090; PNFI and PGFI were greater than the recommended level of 0.05. The chi-square statistic was 760.3, (df = 194, p>.05). The TLI, NFI, and CFI value did not the threshold of .09, there values were remarkably improved. And for the RMSEA = .108 not passed by were lager than the recommended level of level .08. Table 2 Modification confirmatory factor analysis shows the model fit GFI and AGFI passed by the recommended level of .090, PNFI and PGFI were grater less than the recommended level of 0.05. The chi-square statistic was 25.8, (df = 21, p) The TLI and CFI value did the threshold of .09, Only NFI not did the threshold of .09. And for the RMSEA = .030 passed by were the recommended level of level .08.
|
|
3.2. Confirmatory Factor Analysis Model Job Satisfaction of Assistant Coaches
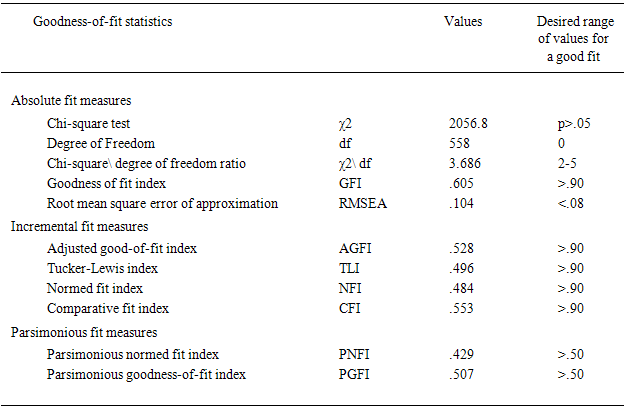
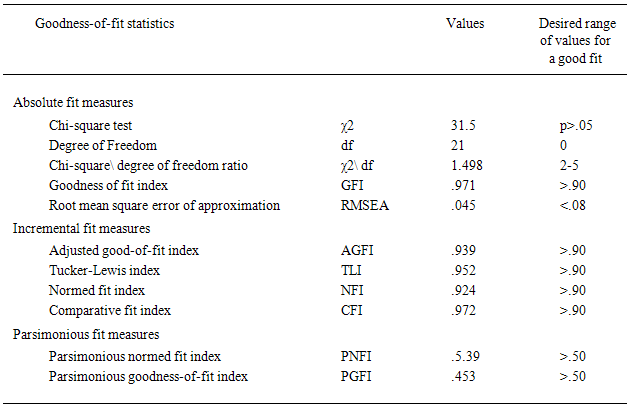
- Table 3 shows the model poor fit GFI and AGFI not passed by the recommended level of .090; PNFI and PGFI were greater than the recommended level of 0.05. The chi-square statistic was 2056.8 (df = 194, p>.05). The TLI, NFI, and CFI value did not the threshold of .09, there values were remarkably improved. And for the RMSEA = .104 not passed by were lager than the recommended level of level .08. Table 4 Modification confirmatory factor analysis shows the model fit GFI and AGFI passed by the recommended level of .090, PNFI and PGFI were grater less than the recommended level of 0.05. The chi-square statistic was 31.5 (df = 21, p>.05) The TLI, NFI, and CFI value did the threshold of .09. And for the RMSEA = .045 passed by were the recommended level of level .08.
|
|
4. Conclusions
- This research is an important in measuring the modeling of transformational leadership behaviours of head coaches and job satisfaction of assistant coaches. This study found the modified model transformational leadership behaviours of head coaches was model fit 4 dimension, vision, providing, supports and stimulation from all 9 items. The modified model job satisfaction of assistant coaches was model fit dimension, contingent rewards, operating procedures, nature of work and communication all 9 items. Factor scores could be calculated by weighting each variable with the values from the rotated factor pattern matrix. A factor is calculated by using the mean or sum of variables that load, are highly correlated with the factor. Factor scores could be calculated with a mean as illustrated below.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML