-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Sports Science
p-ISSN: 2169-8759 e-ISSN: 2169-8791
2015; 5(3): 108-112
doi:10.5923/j.sports.20150503.03
Prevalence of Various Diving Related Health Problems in SCUBA Divers
Sheeba Ahmed
Assistant Professor and certified Diver (SSI & PADI), Department of Zoology, DS (PG) College, Aligarh, UP, India
Correspondence to: Sheeba Ahmed, Assistant Professor and certified Diver (SSI & PADI), Department of Zoology, DS (PG) College, Aligarh, UP, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
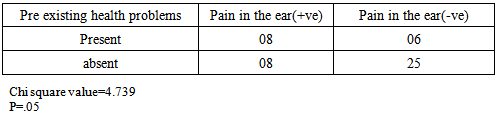
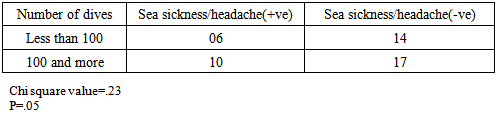
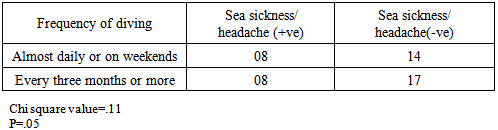
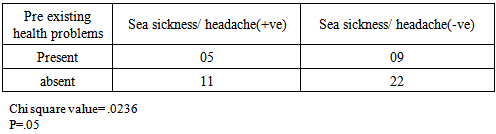
There is a dearth of scientific studies on some common health related problems as sea sickness and headache that do not pose any immediate danger to a diver’s life. However, these problems are ruining the diving holidays of numerous people and may also lead to other life threatening situations like drowning.Present study is aimed to outline prevalent health problems in SCUBA divers and if these problems are associated with frequency of diving, certification level, age, experience, and some other pre-existing medical conditions of a diver?An electronic questionnaire was prepared using the Google form application feature of the Google. The questionnaire contained multiple questions on pre-existing illness and most common diving related health problems experienced by divers. Through a social networking site, responses of divers were collected. A total of forty seven divers responded. Calculations were performed using the Chi square test.Pain in the ear was the most prevalent problem, experienced by 35% divers, followed by headache (21% divers) and sea sickness (17% divers). Most common problem for divers was pain in the ear (25% divers), sea sickness (15%), and headache (8%). These problems were not found associated with frequency of diving, certification level, number of dives, age of the diver, and some pre existing medical conditions, except pain in the ear that was found associated with pre existing medical conditions (motion sickness, any form of respiratory discomfort, panic attack & phobias, recurrent ear problems, and migraine headaches).Present study reveals that sea sickness is very common among the divers, thus it requires greater scientific attention. As expected, pain in the ear, turned out to be the most common problem experienced by the divers. However, experience and certification level of a diver did not improve a diver’s ability to handle this problem. This indicates that present equalization techniques require amelioration.
Keywords: Scuba diving, Sea sickness, Barotraumas of the ear, Diving health, Auditory complaints
Cite this paper: Sheeba Ahmed, Prevalence of Various Diving Related Health Problems in SCUBA Divers, International Journal of Sports Science, Vol. 5 No. 3, 2015, pp. 108-112. doi: 10.5923/j.sports.20150503.03.
1. Introduction
- Recreational SCUBA diving is gaining popularity around the world in recent years, with an estimated 4 million divers in US alone [1]. With the growth of the sport, number of divers facing different health problems associated with diving is also increasing. These conditions range from life threatening rare events like Arterial Gas Embolism (AGE), Decompression Illness (DCI), and Pulmonary Barotraumas to apparently less dangerous but common conditions like barotraumas of the ear and sea sickness [2]. Arterial Gas Embolism, Decompression Illness, and Pulmonary Barotraumas receive much scientific attention because of their serious nature, despite their low incidence rate [3]. On the other hand, very common conditions like Barotraumas of the ear and sea sickness do not pose any immediate threat to life but can be very debilitating for a diver and may lead to other life threatening situations like drowning. Out of these two problems, sea sickness has been completely overlooked by the scientific community and little documentation exists regarding it’s prevention and management [4]. Divers often take anti histamines such as dimenhydrinate and diphenhydramine as well as anticholinergic agents such as hyoscine to alleviate sea sickness. However, these antiemetics have potential to alter mental alertness and increase the risk of nitrogen narcosis and drowning. Furthermore, only a few studies have evaluated the effects of anti-emetics in the hyperbaric environment [5, 6, 7, 8].Barotraumas of the ear has been reported in scientific literature to be the most common health related problem associated with diving [9]. This condition usually arises due to failure equalizing ears during descent. Divers are taught to perform valsalva maneuver, frenzel maneuver or the combination there of to equalize ears [10].The purpose of the present study is to find out the prevalence of common diving related health problems and how they are related to age, certification level, frequency of diving, and some pre-existing medical conditions of a diver.
2. Materials and Methods
- Through a social networking site, divers were asked to retrospectively complete a questionnaire consisting of 11 questions, primarily with tick box answers. Questionnaire contained questions on age, gender, level of certification, health problems not associated with diving, as well as associated with diving. Following is the link for the questionnaire-https://docs.google.com/…/1Z-7g6s1m1PKX1xVusc5S9E…/viewform…The results obtained were tabulated on an excel spread sheet. Chi square test was used to investigate associations between different variables.
3. Results
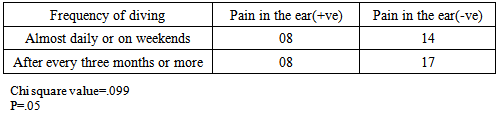
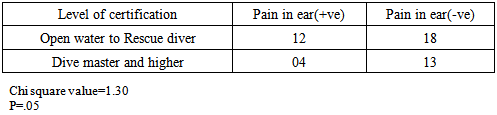
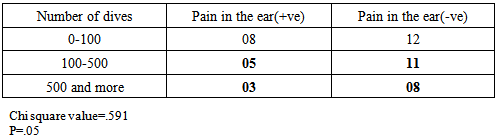
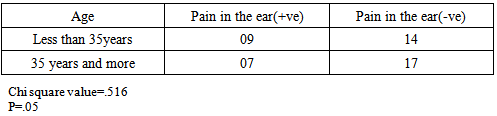
- A total of 47 responses were received during 19th October 2014 to 19th November 2014. Pain in the ear was most prevalent problem associated with diving (25% divers), followed by headache (21%), and sea sickness (17%). Figure 1. According to 25% divers, pain in the ear was their most frequently experienced problem associated with diving, next was sea sickness (15% divers), and headache (8%). figure 2.Regarding health problems not associated with diving, about 69% divers were not having any pre existing illness, 10% were suffering from any form of respiratory discomfort, 10% suffered from panic attacks or phobias, 4% were susceptible to motion sickness, 13% had recurrent ear problems, 6% had migraine headaches, and none of the divers had any heart related problem.
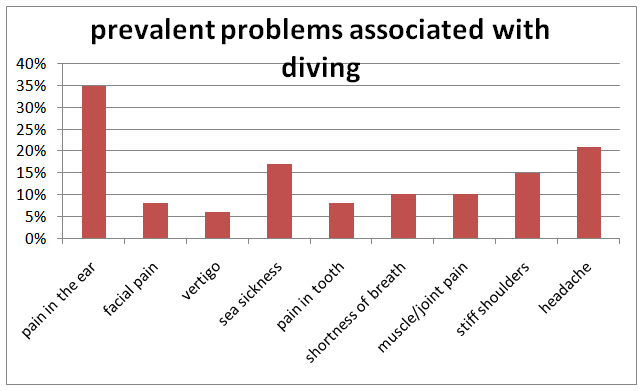 | Figure 1. |
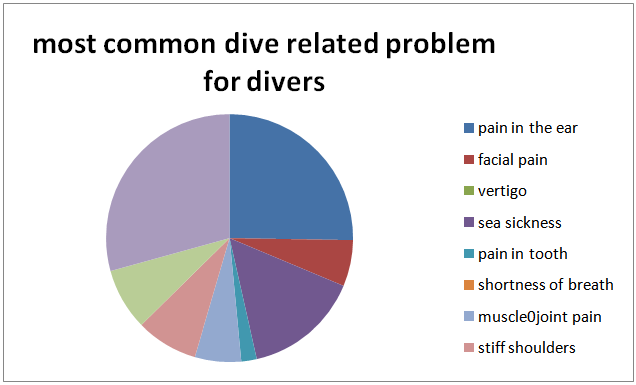 | Figure 2. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. Discussion
- Barotrauma of the ear has been reported in scientific literature to be the most common complaint in SCUBA divers [11]. It manifests itself as an acute ear pain and is sometimes associated with vertigo and conductive hearing loss. Clinical findings range from infection of tympanic membrane to hymatympanum with or without ruptured tympanic membrane [2]. This mostly arises due to inability to clear ears by divers. Various techniques are taught during diving courses to mitigate this problem. According to one study, auditory complaints have been positively correlated with methods of equalizing, number of dives and female gender, while not associated with training level, age and education of a diver [12]. According to another study middle ear squeeze is the most common diving injury, occurring in 30% of first time divers and 10% of experienced divers [13].However in our study we did not find any association with frequency of diving, certification level, diving experience and age of the diver. It was only found associated with pre existing health conditions.Advanced experience level and certifications did not improve the ability of a diver to reduce this problem, this may be an indication that present training techniques fail to handle these problems for medically fit divers. Furthermore divers with pre existing health problems require extra attention to mitigate this problem.According to DAN 2008 report, most frequent non DCI injury reported by divers was related to ear equalization followed by sea sickness. Acute health problems before diving reported by Project Dive Exploration (PDE) divers, sea sickness was most common (13%).Sea sickness is still not clearly understood in scientific literature. Symptoms of sea sickness include visual and postural instability, pallor, diaphoresis, excess salivation, headaches and anxiety, nausea and vomiting [14, 15, 16, 17, 18]. Visual vestibular conflicts have been implicated as the provocative stimulus in sea sickness [19]. There are many theories of it that need to be fully tested. One theory to manage sea sickness is ocular-vestibular habituation that states, after repeated exposure to ocular and vestibular conflicts, sea sickness could be prevented. In a study, a case report of 34 year old woman, who suffered from severe sea sickness, following 10 weeks of a primarily home based program of visual vestibular habituation and balance training, her symptoms were alleviated and she could resume all work related activities [4]. However, we did not find any correlation of sea sickness with frequency of diving and experience level. More scientific studies are needed to test this hypothesis with greater sample size.Further research is indicated to understand the pharmacodynamics of anti emetics under hyperbaric environment and its dangers to manage sea sickness safely.
5. Conclusions
- Pain in the ear, sea sickness and headache are the most prevalent diving related health problems in scuba divers. Sea sickness was very common among divers, yet little documentation exists to tackle this problem. Theories like ocular-vestibular habituation appear a promising solution to safely manage this problem because it does not involve use of any drug, thus altered pharmacodynamics of a drug is not a concern. However present study did not find any association of sea sickness with experience level and frequency of diving. More scientific studies with greater sample size are required to understand and handle sea sickness safely, that includes understanding the pharmacodynamics of antiemetic drugs in hyperbaric environment.In accordance with the scientific literature available, pain in ear was the most common problem experienced by the divers. It was found associated with some pre existing medical conditions of the divers, while not associated with experience level, certification level, and frequency of diving. This might be an indication that different techniques taught to equalize ears during dive courses are not sufficient to mitigate the barotraumas of the ear in medically fit divers. Furthermore, divers with pre existing health conditions require extra attention. More emphasis should be given to improve present equalization techniques with special attention to divers with pre existing illness.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML