-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Sports Science
p-ISSN: 2169-8759 e-ISSN: 2169-8791
2015; 5(1): 19-26
doi:10.5923/j.sports.20150501.04
Reference Values for Six Minute Walk Distance in Apparently Healthy Young Nigerian Adults (Age 18-35 Years)
Chidozie E. Mbada1, Oluwafemi A. Jaiyeola1, Olubusola E. Johnson1, Olumide O. Dada2, Abiola O. Ogundele1, Taofeek O. Awotidebe3, Olabisi A. Akinwande4
1Department of Medical Rehabilitation, College of Health Sciences, Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile – Ife, Nigeria
2Department of Physiotherapy, University Health Services, University of Ibadan, Ibadan, Nigeria
3Department of Physiotherapy, Obafemi Awolowo University Teaching Hospitals Complex, Ile – Ife, Nigeria, Nigeria
4Department of Physiotherapy, University College Hospital, Ibadan, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Chidozie E. Mbada, Department of Medical Rehabilitation, College of Health Sciences, Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile – Ife, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Background and objectives: Six-Minute Walk Test is a physical performance assessment tool. However, limited data on normative values for Six-Minute Walk Distance (6MWD) is a significant shortcoming. This study established reference values for 6MWD in apparently healthy Nigerian young adults. In addition, the study investigated the influence of demographic and anthropometric variables on 6MWD and the cardiovascular response and Perceived Rate of Exertion (PRE) to 6MWT. Materials and Methods: 618 apparently healthy individuals volunteered for this study. 6MWT was conducted according to the American Thoracic Society protocol. Pre and post 6MWT cardiovascular parameters were measured using automated Omron device. PRE was assessed using the Modified Borg Scale. Data were analyzed using descriptive and inferential statistics. Alpha level was set at 0.05. Results: The mean age and 6MWD of the participants was 23.2 ±3.58 years and 619.41±125.76m respectively. 6MWD differed significantly across age groups (F = 5.050; p = 0.001) with males having higher mean 6MWD than the females (608.2±207.79m vs. 565.9±69.49m; t = 2.201, p=0.028). Using percentile cut-points, less than 25th, between 25th and 75th, and greater than 75th percentile were regarded as low, average and high 6MWD respectively. Overall, low, average and high 6MWD were  562.7, 562.7-660.1,
562.7, 562.7-660.1, 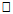 660.1 respectively. SBP, DBP, and HR significantly (p<0.05) reduced following 6MWT. However, PRE significantly increased (p= 0.001) following 6MWT. There was no significant sex difference in cardiovascular response (p>0.05) to 6MWT. There were significant relationship between 6MWD and each of demographic and anthropometric variables (p<0.05) except for the weight and LBM. Conclusions: This study provided reference values for the 6MWD in apparently healthy adults in Ile-Ife, Nigeria. The mean 6MWD obtained in this study was within the range for normal adults as reported in literature. Socio-demographical and anthropometrical variables have significant influence on the performance of 6MWT. 6MWT evoked significant cardiovascular response and exertion in apparently healthy adults.
660.1 respectively. SBP, DBP, and HR significantly (p<0.05) reduced following 6MWT. However, PRE significantly increased (p= 0.001) following 6MWT. There was no significant sex difference in cardiovascular response (p>0.05) to 6MWT. There were significant relationship between 6MWD and each of demographic and anthropometric variables (p<0.05) except for the weight and LBM. Conclusions: This study provided reference values for the 6MWD in apparently healthy adults in Ile-Ife, Nigeria. The mean 6MWD obtained in this study was within the range for normal adults as reported in literature. Socio-demographical and anthropometrical variables have significant influence on the performance of 6MWT. 6MWT evoked significant cardiovascular response and exertion in apparently healthy adults.
Keywords: Six-minute walk test, Functional exercise capacity, Reference value, Nigeria
Cite this paper: Chidozie E. Mbada, Oluwafemi A. Jaiyeola, Olubusola E. Johnson, Olumide O. Dada, Abiola O. Ogundele, Taofeek O. Awotidebe, Olabisi A. Akinwande, Reference Values for Six Minute Walk Distance in Apparently Healthy Young Nigerian Adults (Age 18-35 Years), International Journal of Sports Science, Vol. 5 No. 1, 2015, pp. 19-26. doi: 10.5923/j.sports.20150501.04.
1. Background
- The Six Minute Walk Test (6MWT) is an important tool in the assessment of functional exercise capacity in patients with chronic illnesses [1-4]. The 6MWT as a sub-maximal exercise test, evaluates the global and integrated responses of the pulmonary, cardiovascular and muscular components and reflects the functional exercise level for daily physical activities [5, 6]. In addition, 6MWT is reported to accurately estimate maximal oxygen uptake [7-9]. The 6MWT has substantial data on its psychometric properties and clinical usability, and it appears to be better tolerated and more reflective of the activities of daily living than other walk tests [5-7, 10, 11]. As a rehabilitative physical performance assessment tool, the 6MWT evaluates functional status, monitors effectiveness of treatment, assesses progression of functional exercise capacity and helps in predicting prognosis [5, 6, 12]. Numerous studies on 6MWT have been published for various age groups [13-19], disease conditions [1-4], occupations and from diverse populations [20, 21]. However, limited data on normative values for Six-Minute Walk Distance (6MWD) is a significant shortcoming. Normative database on 6MWD is important in identifying alterations of functional exercise capacity from normal and in setting rehabilitation goals. Comparing 6MWD of patients with chronic illnesses with reference values of healthy subjects may help identify the extent of impairment in functional exercise capacity and in turn inform plan for appropriate treatment. The American Thoracic Society (ATS) recommends the establishment of specific reference values for 6MWD for each continental population globally [5]. As a result, there are increasing studies on 6MWD reference values for various populations [13-19, 22-24] and the values vary considerably from population to population [25, 26]. Unfortunately, there is an apparent dearth of reference values for 6MWD in sub-Sahara Africa based on standardized guidelines such as those recommended by the American Thoracic Society [5]. Considering that reference values derived from western population may have limited applicability among Africans due to significant influence of demographic, anthropometric, psychosocial characteristics [5] and cultural and racial differences [27, 28], therefore, the aim of this study was to establish reference values for the 6MWD in apparently healthy young Nigerian adults. Furthermore, this study aimed to investigate the influence of demographic and anthropometric variables on 6MWD, in addition to evaluating the cardiovascular response and the Perceived Rate of Exertion (PRE) to 6MWD.
2. Methods
- A total of 618 (306(49.5%) male and 312(50.5%) female) consecutive apparently healthy individuals whose ages ranged between 18 and 35years participated in this study. Exclusion criteria for the study included a positive report of asthma, unstable angina or myocardial infarction. Volunteers with sickle cell disorder, elevated blood pressure (BP = >140/90mmHg) or a positive history of hypertension or were on antihypertensive drugs were also excluded. Ethical approval for the study was obtained from the Ethical Review Committee of the Institute of Public Health, Obafemi Awolowo University Ile-Ife, Nigeria. Informed consent was also obtained from each participant before the commencement of the test. For the purpose of analysis, the participants were classified into age groups of approximately five year interval, below 20, 20-25, 26-30 and 31-35. Following standard procedures, total body weight (kg) and height (m) of the participants were measured using a standard bathroom scale (Mechanical Personnal Scale) and stadiometer (Seca Alpha brand model 19066) respectively. Body mass index was obtained by calculating the ratio of the weight in (kg) and the height square in (m)². Digital sphygmomanometer (Omron-IM-HEM-7102-E(V)-01-08/08 was used to measure blood pressure (mmHg) and pulse rate (bpm) of the participants respectively. Percentage Body Fat (PBF) was measured using a Bioelectric Impedance Analysis (BIA) machine (Omron BF 306 (HBF-306-E), Kyoto, Japan) following the manufacturer’s instructions. The participants were instructed to stand erect with the two feet together while holding the BIA machine with both hands with the arms straight at 90° of shoulder flexion such that the palmar surface of the hands covered the metal sensor of the BIA. During the assessment, the participants were instructed to remove all metal objects (such as earrings, chains, wrist watches etc.). Dryness of the palms were ensured by using a dry towel for cleaning if the palms were wet (none of the participants had any symptom of hyperhidrosis which could have led to exclusion from the BIA test). Lean body mass (kg) was calculated from the PBF by subtracting fat weight (kg) from total body weight (kg). Lean Body mass = Total body weight – Fat weight. Fat weight was calculated from PBF using the following formula: Percentage body fat = (fat weight/total body weight) * 100. Therefore, Fat weight = (percentage body fat X total body weight)/100.ProcedureThe purpose and procedure of the study was explained to the participants. The participants’ bio-data were obtained before the commencement of the test. 6MWT was conducted following the guidelines of ATS guidelines standards [5]. A 30-metre marked hallway was provided for participants to walk at self-determined pace from one end to the other while attempting to cover as much ground as possible within six minutes. Two small traffic cones were used to mark the corridor at every 3 metres according to ATS guideline. Participants were reminded of the time remaining for test completion every minute by the second author of this paper in an even tone of voice. Standardized Instructions and verbal encouragement such as “You're doing well” or “Keep up the good work,” were strictly given to the participants at every minute until the end of test. Participants were also asked at the end of the test if they experienced any symptoms of dyspnea, chest pain, lightheadedness or leg pain [5]. The 6MWD (m) was obtained by calculating the number of turns made by the participant and multiplying it by 30m the distance of the walkway and adding the additional extra distance covered after the turns. The perceived rate of exertion was assessed using the modified Borg’s scale at the end of the walk. Data were obtained on pre and post 6MWT cardiovascular parameters (blood pressure and pulse pressure). In order to allow for learning effect, the test was repeated two times with a rest interval of 10 minutes between test and the mean value was used for analysis. This study was carried out at the departments of Medical Rehabilitation, OAU and Physiotherapy of Obafemi Awolowo Teaching Hospitals Complex, Ile-Ife, respectively.Data AnalysisDescriptive statistic of mean and standard deviation was used to summarize the variables. Inferential statistic of independent t-test, ANOVA, and Pearson’s product moment correlation were used to analyze data. Alpha level was set at 5% level of significance. Data analysis was carried out using SPSS 16.0 version software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, Illinois, USA).
3. Results
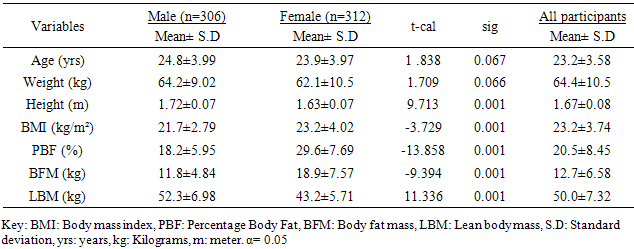
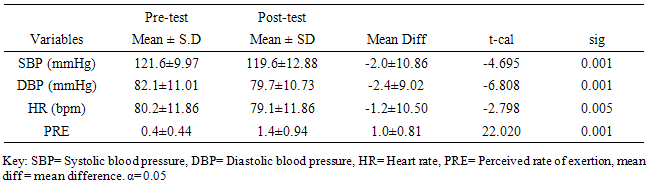
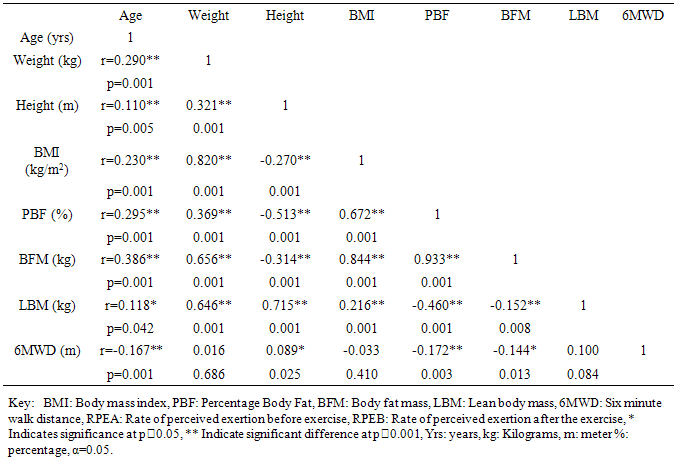
- The participants’ ages ranged between 18 and 65years. Table 1 shows the general characteristics of the participants. The mean age, weight, height, body mass index, percentage body fat, body fat mass and lean body mass of the participants were 23.2±3.58years, 64.4±10.5kg, 1.67±0.08m, 23.2±3.74kg/m², 20.5±8.45%, 12.7±6.58kg, and 50.0±7.32 kg respectively (table 1). Table 1 also shows the independent t-test comparison of the general characteristics between the male and female participants. The female participants had significant higher mean scores in the measures of body adiposity (BMI, PBF and BFM) (p<0.05).
|
|
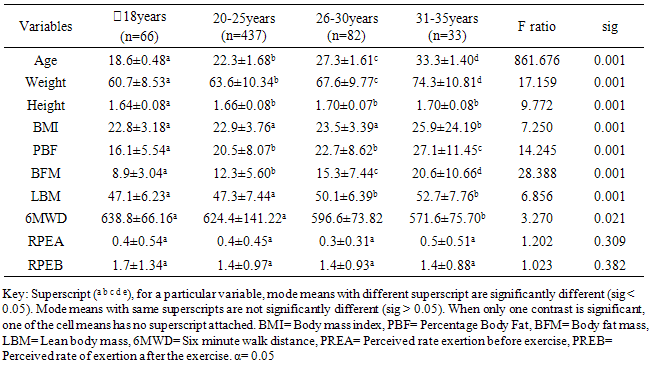
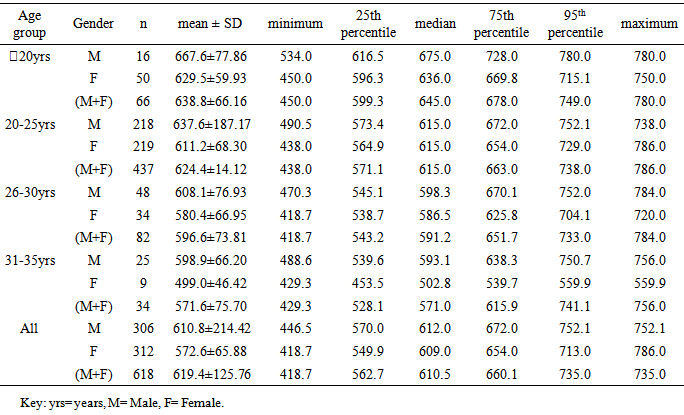
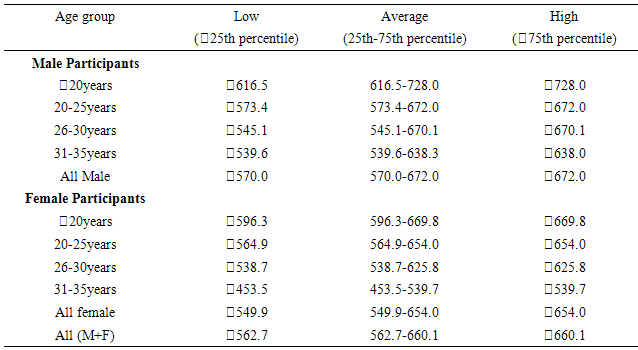
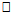 20years. Similar pattern was found for both males (667.6±66.16m) and females (629.5±59.93m) in the <20 years age group. The mean and median values indicated that 6MWD decreased with increasing age. However, males and females in the age group 20-25years had same median values for 6MWD. Using the percentile cut-points, less than 25th percentile were regarded as ‘low 6MWD’, between 25th and 75th percentile were regarded to as ‘average 6MWD’, while above 75th percentile were regarded as ‘high 6MWD’ for male and female participants respectively (table 4). Overall, low, average and high 6MWD was
20years. Similar pattern was found for both males (667.6±66.16m) and females (629.5±59.93m) in the <20 years age group. The mean and median values indicated that 6MWD decreased with increasing age. However, males and females in the age group 20-25years had same median values for 6MWD. Using the percentile cut-points, less than 25th percentile were regarded as ‘low 6MWD’, between 25th and 75th percentile were regarded to as ‘average 6MWD’, while above 75th percentile were regarded as ‘high 6MWD’ for male and female participants respectively (table 4). Overall, low, average and high 6MWD was 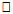 562.7m, 562.7m-660.1m,
562.7m, 562.7m-660.1m, 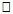 660.1m respectively.
660.1m respectively.
|
|
|
|
|
4. Discussion
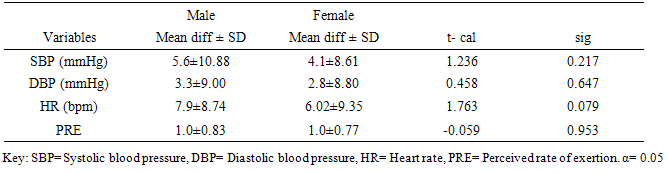
- This study established reference values for 6MWD in apparently healthy young Nigerian adults. The age-and-sex reference values obtained in this study by following the 6MWT protocol proposed by the ATS guidelines [5] may be useful in interpreting 6MWT performance in patients with significant respiratory or cardiac dysfunction, such as those with cystic fibrosis, obesity, interstitial lung disease, or dilatative cardiomyopathy. Based on the ATS guidelines, some recommendations and suggestions concerning technical aspects and quality assurance of the 6MWT were implemented in this study. Specifically, the recommended length of the corridor was 30m so as to avoid too many turns during the test. One practice walk was considered to allow for the learning effect and also encouragement was given regularly to ensure maximal motivation and performance. Conversely, most previous studies did not take into account some of these methodological aspects of the 6MWT. For example, in the study by Gibbons and colleagues [22], a 20-m corridor was used, while in the study by Enright and Sherrill [29] practice test was not performed. Although, according to Cunha et al [30], there was no significant difference in the 6MWD reached at two time points, separated by a mean of 18 days, and the within-subject correlation coefficient was excellent. This present study also reveals that there was no significant difference between the first and second six minute distance walked separated by a fifteen -minute time interval but some other studies reported that 6MWD was influenced by learning effect [13, 22, 31, 32].This present study showed considerable variability in the 6MWD of the participants with the range of 418.7–735.0m with an average score of 619.41±125.76m. Literature on reference values for 6MWD in healthy individuals provides wide range of values [13, 20, 22-24, 29]. These values are reported to be influenced by factors such as the participants’ age, sex, height, BMI and the degree of test familiarization provided [33]. Comparison of reference values across population is believed to be difficult because of variations in the method used in previous studies and race and demographical difference. However, the 6MWD in healthy adults has been reported to range from 400m to 700m [34]. Therefore, the mean 6MWD value obtained in this study is within the range reported for health adults. A significant difference in the 6MWD between the male and female participants was observed in this study. The males had a significantly higher mean 6MWD (610.77±214.42m vs. 572.63±65.88m) than the females counterparts. The gender pattern for 6MWD observed in this study is consistent with the other reports among healthy participants. Tsang et al [21] reported 645m and 606m for male and female participants respectively while Gibbons et al [22] found 800m and 699m for male and female participants respectively. Other studies have attributed the female to lower 6MWD [34, 35]. The anatomical variations between the male and female have been implicated for the difference. Generally, females have shorter leg and longer torsos than men [36] and consequently shorter stride [34]. In this study significant differences were observed in the anthropometric variables of the participants compared according to age categories. Similarly, the 6MWD also differed across the age groups. The shorter distance walked as age increased can be explained by decreases in muscle mass and strength and the maximum oxygen consumption, inherent. Some studies involving healthy individuals reported that age significantly influenced performance on the 6MWT [18, 19, 21, 37] while some other studies did not [24, 28, 38]. In this study there was significant cardiovascular response to 6MWT assessed in terms of SBP, DBP, and HR. Similarly, significant difference was observed in the rate of perceived exertion following 6MWT. However, no significant difference in sex was observed in the cardiovascular response and response to exertion following 6MWT. Previous studies showed gender related differences in heart rate and reported an increase in resting heart rate in women [39,40]. Additionally, Jones [41] reported higher heart rates in women following submaximal exercise when compared to those of men. Baroreflex heart rate regulation may be different between women and men [42, 43] and the effects of estrogen on baroreflex regulation can also occur in humans [44]. From this study, using the percentile cut-points, less than 25th percentile were regarded as ‘low 6MWD’, between 25th and 75th percentile were regarded to as ‘average 6MWD’, while above 75th percentile were regarded as ‘high 6MWD’ for male and female participants respectively. Overall, low, average and high 6MWD were
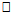 562.7m, 562.7m-660.1m,
562.7m, 562.7m-660.1m, 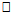 660.1m respectively. In this study 6MWD was found to correlate significantly with age, sex, height, BMI, PBF, BFM, and PRE except the LBM and weight. A similar result was reported in a study by Soaresi et al [33] among apparently healthy adult Brazilian population. They reported age (r = -0.66; p < 0.01), stature (r = 0.42; p < 0.01), and BMI (r = -0.37; p < 0.01) as anthropometric variables that significantly correlated with the 6MWD. It is adduced that age, anthropometric and body composition variations will significantly influence 6MWT performance.
660.1m respectively. In this study 6MWD was found to correlate significantly with age, sex, height, BMI, PBF, BFM, and PRE except the LBM and weight. A similar result was reported in a study by Soaresi et al [33] among apparently healthy adult Brazilian population. They reported age (r = -0.66; p < 0.01), stature (r = 0.42; p < 0.01), and BMI (r = -0.37; p < 0.01) as anthropometric variables that significantly correlated with the 6MWD. It is adduced that age, anthropometric and body composition variations will significantly influence 6MWT performance. 5. Conclusions
- This study provides reference values for the 6MWD in apparently healthy young Nigerian adults. The mean 6MWD obtained in this study was within the range for normal adults as reported in literature. Socio-demographical and anthropometrical variables have significant influence on the performance of 6MWT. 6MWT evoked significant cardiovascular response and exertion in apparently healthy adults.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- The authors gratefully acknowledge the clinical and clerical staffs of the departments of Medical Rehabilitation, OAU and Physiotherapy, OAUTHC for their support during the course of the study. Also, we thank all the participants for their time and co-operation.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML