-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Sports Science
p-ISSN: 2169-8759 e-ISSN: 2169-8791
2014; 4(2): 60-66
doi:10.5923/j.sports.20140402.04
Effects of a 14-strain Probiotics Supplement on Salivary Antimicrobial Proteins at Rest and in Response to an Acute Bout of Prolonged Exercise
Ayu Muhamad1, Michael Gleeson2
1Sports Science Unit, University Science Malaysia, Kubang Kerian, 16150, Malaysia
2School of Sports, Exercise, and Health Sciences, Loughborough University, Loughborough, LE11 3TU, United Kingdom
Correspondence to: Ayu Muhamad, Sports Science Unit, University Science Malaysia, Kubang Kerian, 16150, Malaysia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This study was designed to determine the effects of a period of supplementation with a 14-strain probiotics supplement on salivary antimicrobial proteins (AMPs) at rest and in response to an acute bout of prolonged exercise in active, healthy adults. In this study, 11 participants (age: 22 ± 1 years, weight: 69.5 ± 12.2 kg, body mass index: 23.0 ± 1.8 kg/m2) cycled for 2 h at 60% VO2max (maximum oxygen uptake) on 2 occasions (2 trials separated by 30 days). During each trial, participants came to the lab in the morning, 2 h after having their breakfast. They were asked to have a similar breakfast before each trial. The second trial was performed after 30 days of supplementation with a 14-strain probiotics. The probiotics were in capsule form and taken as 1 capsule 3 times daily (morning, midday, and evening). Timed, unstimulated saliva samples were collected pre-, post-, 1 h post-, and 2 h post-exercise. Saliva samples were analysed for secretory immunoglobulin A (S-IgA), alpha (α)-amylase, lactoferrin, and lysozyme concentrations. Results showed that 30 days of supplementation with the 14-strain probiotics did not alter salivary AMPs at rest and in response to an acute bout of prolonged exercise. However, prolonged exercise significantly increased lactoferrin concentration and α-amylase activity post-exercise. It was concluded that the supplementation period and/or the dose/concentration of the 14-strain probiotics used in this study were insufficient to induce any beneficial effects on athletes’ salivary AMPs at rest and in response to an acute bout of prolonged exercise.
Keywords: Prolonged exercise, Salivary antimicrobial proteins, Probiotic, S-IgA
Cite this paper: Ayu Muhamad, Michael Gleeson, Effects of a 14-strain Probiotics Supplement on Salivary Antimicrobial Proteins at Rest and in Response to an Acute Bout of Prolonged Exercise, International Journal of Sports Science, Vol. 4 No. 2, 2014, pp. 60-66. doi: 10.5923/j.sports.20140402.04.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- As defined by World Health Organisation, probiotics are live micro-organisms which when administered in adequate amounts confer a health benefit on the host (Sanders, M. E., 2008). There is now a reasonable body of evidence that regular consumption of probiotics can modify the population of the gut microbiota and influence immune function (Gill and Prasad, 2008; Borchers, A. T., Selmi, C., Meyers, F. J., Keen, C. L. and Gershwin, M. E., 2009) though it should be noted that such effects are strain specific. Suggested possible mechanism of actions of probiotics include modulation of the intestinal immune system, and displacement of potential pathogens through competitive exclusion or production of antimicrobial agents (Rowland et al., 2010). Documented health effects of probiotics include treatment of travellers’ diarrhoea, relief of milk allergy in infants, reduction in the risk of atopic diseases, treatment of some inflammatory conditions, increased resistance to enteric pathogens, promotion of anti-tumour activity, and alleviation of some allergic and respiratory disorders in children (Hatakka et al., 2001; Rowland et al., 2010). Furthermore, it has been reported that probiotic supplementation enhances host resistance to upper respiratory tract infection (URTI) in the general population (Winkler, P., de Vrese, M., Laue, Ch. and Schrezenmeir, J., 2005; de Vrese et al., 2006; Berggren, A., Lazou Ahrén, I., Larsson, N. and Önning, G., 2011). Several recent studies have indicated that some Lactobacillus probiotics can reduce URTI incidence in athletes (Cox, A. J., Pyne, D. B., Saunders, P. U. and Fricker, P. A., 2010; Gleeson, M., Bishop, N. C., Oliveira, M. and Tauler, P., 2011; West et al., 2011) who are generally considered to be a marginally immunocompromised population due to the depressive effects of hard physical exercise, psychological stress, sleep disturbance and negative energy balance on their immune system (Walsh et al., 2011).The efficacy of single strains of probiotics on immune function in both healthy individuals and clinical patients has been widely investigated. For example, 2 studies reported that regular ingestion of single strain probiotic (Lactobacillus casei) may modify the salivary secretory immunoglobulin A (S-IgA) level (O’Connell, E., Allgrove, J., Pollard, L., Xiang, M. and Harbige, L. S., 2010; Gleeson et al., 2011). Nevertheless, studies on the effects of mixtures of probiotic strains are far fewer compared to those that have examined single strain probiotic supplements. Some have reported that probiotic mixtures are more effective in modifying immune function and preventing respiratory tract infection (Chapman, C. M., Gibson, G. R. and Rowland, I., 2011). However, it is unknown if this is a result of synergistic interactions between strains or a consequence of the higher probiotic dose used in some studies. Most multi-strain probiotic studies do not directly compare between a mixture and its component strains. This makes us unable to make a definite conclusion about the efficacy of the probiotic mixtures or their component strains. Several multi-strain probiotic studies have reported reduced number of days with fever, duration of cold episode, total symptom score, reduced incidence of respiratory tract infections and reduction in gastrointestinal infections (Winkler et al., 2005; de Vrese et al., 2006; Lin et al., 2009). However, their effect on salivary antimicrobial proteins has not been investigated. The mucosal membranes covering the oral cavity, respiratory, gastrointestinal, and genitourinary tracts are continuously exposed to pathogenic microorganisms, thus effective protection of mucosal surfaces is important in conferring resistance to infection and depends on several components of the innate and acquired immune system. Antimicrobial proteins (AMPs) including S-IgA, lactoferrin and lysozyme are well established humoral factors of the innate immune system with antibacterial, antiviral and fungicidal properties (West, N. P., Pyne, D. B., Renshaw, G. and Cripps, A. W., 2006). Reduced levels of salivary AMPs in athletes may contribute to their increased risk of URTI (Gleeson et al., 1999, West et al., 2006; Gleeson, M., Bishop, N. C, Oliveira, M. and Tauler, P., 2013; Walsh et al., 2011). Salivary IgA levels have been observed to fall during intensive periods of athletic or military training (Gleeson et al., 1999; Tiollier et al., 2007) but some studies suggest that probiotic supplements may increase S-IgA (O’Connell, et al., 2010) or help to maintain S-IgA during periods of intensive physical activity (Tiollier et al., 2007; Gleeson et al., 2011). However, the effects of probiotic supplementation on other AMPs have not been extensively studied even though exercise induced reduction in their concentrations has previously been reported (Cox et al., 1999; Innoue et al., 2004).Thus, the purpose of the present study was to investigate the efficacy of a multi-strain probiotic supplement on recreational athletes’ salivary antimicrobial proteins at rest and in response to an acute bout of prolonged exercise.
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
- This study obtained ethics approval from the Loughborough University ethics Committee. Before this study was conducted, participants were informed about the study background and procedures before they signed the written informed consent form. Eleven healthy, active Loughborough University students were involved in this study. Inclusion criteria include healthy, age between 18 and 25 years, not smoking, performed endurance exercise at least 3 times per week with at least 30 min per session, and not on any medication at least 3 months before. To confirm their overall health status, they were asked to complete a health screening questionnaire before participating in this study. At least 3 months before and during the study period, participants abstained from probiotic products and also other supplements believed to affect immune function.
2.2. Study Intervention
- The multi-strain probiotics supplement used in this study contained 14 strains of beneficial micro-organisms at a concentration of 10 billion per gram (with a minimum of 2 billion probiotic micro-organisms per capsule). The microorganisms it contained were Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus, Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis, Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus helveticus, Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Lactobacillus salivarius ssp. salivarius, Bifidobacterium breve, Bifidobacterium bifidum, Bifidobacterium infantis, Bifidobacterium longum, Bacillus subtilis, and Streptococcus thermophilus.The probiotics were in capsule form and taken as 1 capsule 3 times daily (morning, midday, and evening). Participants start taking the 14-strain probiotics supplementation for 30 days after the first experimental trial. The supplementation period of 30 days was chosen because previous studies had shown positive effects of probiotic supplementation after 4 weeks of supplementation (Pohjavuori et al., 2004; Meyer, A. L., Micksche, M., Herbacek, I. and Elmadfa, I., 2006; Sierra et al., 2010; Martarelli et al., 2011). After 30 days supplementation, they came to the laboratory for the second experimental trial which followed exactly the same protocol as the first experimental trial.
2.3. Study Protocol
- The design of this study is a pre and post intervention design. Cross over design is the best design to avoid any bias, however, since this study measure only the objective parameters, the pre and post intervention design will not be an issue. If subjective parameters (e.g. feelings, pain, etc.) are to be measured, cross over design will be the best design.During the first visit, participants completed the health screen questionnaire form and consent form. Then, their body mass and height were measured. After that, participants performed a VO2max (maximum oxygen uptake) test. After a few days, participants came back to the laboratory for the first experimental trial; cycling at 60% VO2max for 2 h. Then, for the next 30 days, participants start taking the supplement, 1 capsule 3 times daily (morning, midday, and evening). After 30 days supplementation, participants performed the second experimental trial. Two hours cycling at 60% of VO2max was chosen because according to Gleeson (2006), exercise-induced depression in immune function is most pronounced when the exercise is continuous, prolonged, of moderate to high intensity (55 – 75% VO2max), and performed without food intake.
2.4. Experimental Trial
- This study is a pre- and post-supplementation design. During the first visit, participants completed the health screen questionnaire form and consent form. Then, their body mass and height were measured. After that, participants performed a VO2max (maximum oxygen uptake) test. After a few days, participants came back to the laboratory after an overnight fast (from 10pm; plain water is permitted) for the first experimental trial; cycling at 60% VO2max for 2 h. During the cycling, heart rate (HR) and rating of perceived exertion (RPE) were recorded at every 20 min. Then, for the next 30 days, participants start taking the supplement, 1 capsule 3 times daily (morning, midday, and evening). After 30 days supplementation, participants performed the second experimental trial after an overnight fast (from 10pm; plain water is permitted).
2.5. Saliva Samples Collection and Analysis
- In order to make sure the saliva samples collected is under parasympathetic stimulation rather than sympathetic, participants were seated for at least 10 min before saliva samples collection. This 10 min allows them to calm down because some of them were walking and others were cycling to get to the lab. Saliva under parasympathetic stimulation is more favourable because it has secretory elements of the major salivary glands. Furthermore, parasympathetic stimulation evokes a copious flow of saliva compared to sympathetic stimulation.Saliva samples were obtained by 2 min unstimulated passive dribbling into a pre-weighed sterile bijou tube (Sterilin, Staffordshire, UK). They were asked to sit on a chair, lean the head forward and let the saliva passively dribble into the tube; without using their tongue or any mouth movement. Whenever the saliva volume collected in 2 min was insufficient (< 3ml) for analysis, the collection was continued further for another 1 or 2 min. The bijou tube (with saliva sample) was then weighed.The saliva volume was estimated from the difference in bijou tube’s weight pre- and post- saliva collection. Saliva samples were analysed for S-IgA using an Enzymed-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit (Salimetrics, Philadelphia, USA) and α-amylase activity was carried out in a micro-titration plate by using a kit (Amylase-20, No. 577, Sigma-Aldrich, Poole, UK). Salivary lactoferrin and lysozyme were analysed using commercially available ELISA kits (Calbiochem, USA and Biomedical Technologies, USA, respectively). Secretion rates for each of the salivary AMPs were calculated as the multiple of the saliva flow rate and the AMP concentration. All saliva assays were carried out in duplicate. Coefficients of variation for the assays were < 5% for all salivary AMPs.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
- Data were analysed using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) version 17 (SPSS Inc., USA). Descriptive analysis was used to measure mean and standard deviation (SD). Statistical significance of differences between means was analysed using paired samples t-test. Two-Way ANOVA with repeated measure was used. However, whenever the data was not normally distributed, the Friedman test was used to examine the main effect of time in each trial and the Wilcoxon signed rank test was used to find the differences between trials in each time point value. All the data were expressed as mean ± SD. The accepted level of significance was P < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Physiological Parameter
- Rating of perceived exertion and HR were significantly increased over time (P < 0.05), although, they were not significantly different between trials. Average body mass index (BMI) of the participants is 23.0 ± 1.8 kg/m2.
3.2. Saliva Flow Rate, S-IgA Concentration, and Secretion Rate
- There were no significant main effects of groups for saliva flow rate, S-IgA concentration, and S-IgA secretion rate (P = 0.281, P = 0.314, and P = 0.768 respectively). There were also no significant main effects of time for saliva flow rate, S-IgA concentration, and S-IgA secretion rate (P > 0.05).
3.3. Alpha (α)-amylase
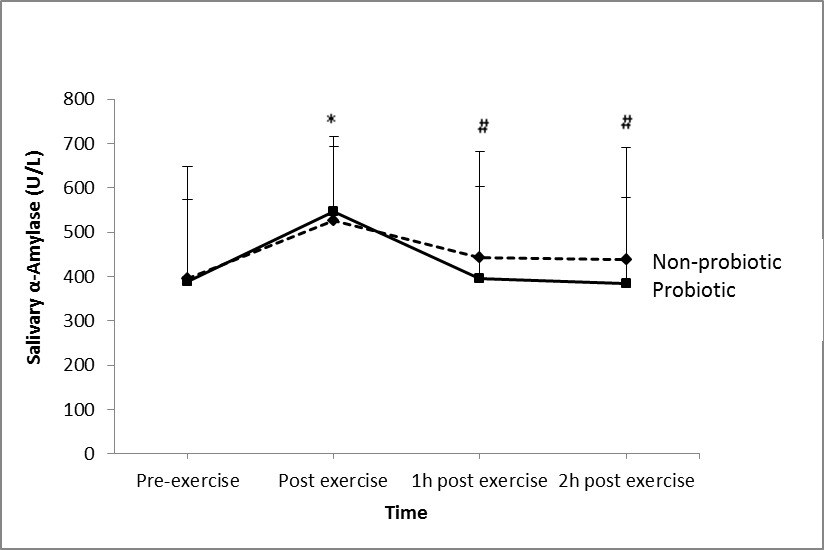
- There was significant main effects of groups for α-amylase concentration (P = 0.025; Figure 1). There was also a significant main effect of time on α-amylase activity (P = 0.032). However, there was no significant effect (P = 0.53) of the probiotic on salivary α-amylase concentration.
3.4. Lysozyme
- There was no significant main effect of groups for lysozyme (P = 0.673) and no significant main effect of time (P = 0.41) on lysozyme concentration in both groups. There was also no significant effect (P = 0.75) of the probiotic on lysozyme concentration.
3.5. Lactoferrin
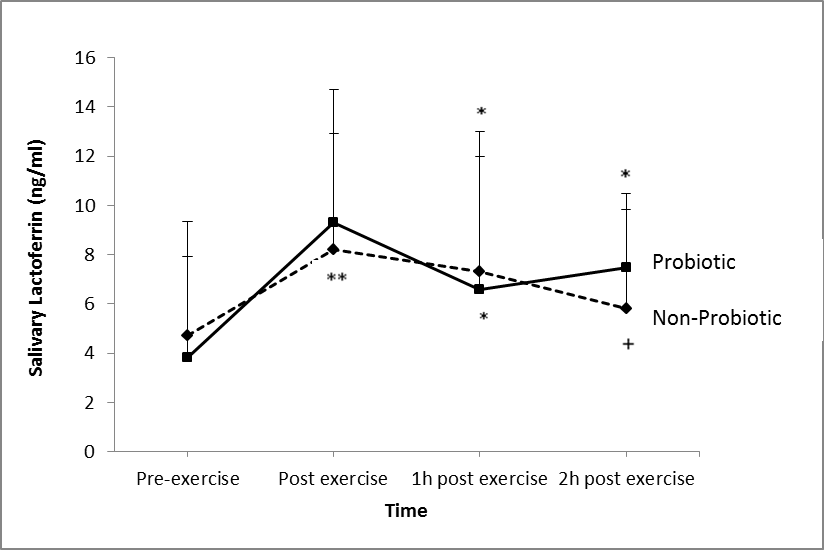
- There was a significant main effect of groups for lactoferrin (P = 0.01; Figure 2). There was also a significant main effect of time on lactoferrin production in both groups (P = 0.025). However, there was no significant effect of the probiotic supplementation on lactoferrin production (P = 0.312).
4. Discussion
- This study found that 30 days supplementation of the 14-strain probiotics did not affect the saliva AMPs measured. Previous studies with 4 weeks (Cox et al., 2010) and 3 weeks (Tiollier et al., 2007) of probiotics supplementation were also found no effect on the S-IgA concentration. However, S-IgA concentration was reported to be increased after 8 weeks and 16 weeks of a single strain probiotic supplementation (Gleeson et al., 2011). Furthermore, Kotani and colleagues (2010) also reported an accelerated S-IgA secretion after 12 weeks of daily ingestion of a single strain probiotic. Thus it is speculated that the supplementation period (30 days) of the probiotic used in the present study was not enough to induce any beneficial effects of the probiotic.To date, there were no published studies (PubMed search on February 2014) regarding the effects of mixtures of probiotics on salivary AMPs. Nevertheless, there have been a few published studies reporting beneficial effects of multi-strain probiotics on incidence and duration of respiratory tract infection. Winkler and colleagues (2005) found that a mixture of probiotics decreased the incidence of infection by 13.6%. They also reported lower symptom severity and fewer numbers of days with fever in the multi-strain probiotic group compared to the placebo group. Similarly, de Vrese et al., (2006) reported reduced number of days with fever, duration of cold episode, and total symptom score in a mixtures probiotic group compared to a placebo group. A meta-analysis in a recent review article found that there was a marginal beneficial effect of probiotics on the prevention of the common cold (Kang, E. J., Kim, S. Y., Hwang, I. H. and Ji, Y. J., 2013).The possible mechanism of action of this effect might be due to its modulation of immune function through their effects on epithelial cell function, including epithelial cell barrier function, epithelial cytokine secretion, and their antibacterial effects relating to colonization of the epithelial layer (Boirivant and Strober, 2007). Probiotics also interact with the receptors on M cells and gastro intestinal tract and so may influence aspects of systemic immune function (Kudsk, 2002). From the present study results, it may be worth investigating the effects of this multi-strain probiotic on salivary responses, but at a higher dose and for a longer supplementation period.Several studies have reported that S-IgA concentration is reduced after intense exercise (Steerenberg et al., 1997; Fahlman et al., 2001), increased after moderate or lower intensity exercise (Dorrington, L., Gleeson, M. and Callister, R., 2003; Li and Gleeson, 2004) or not affected by exercise intensity (Blannin et al., 1998; McDowell, S. L., Chaloa, K., Housh, T. J., Tharp, G. D. and Johnson, G. O., 1991). The later studies were in agreement with the present study. Findings about the effects of exercise on S-IgA were inconsistent due to several reasons. This discrepancy may be attributed to the different method of expressing S-IgA, nutritional status of the individual, and the exercise protocol employed. Having said that, it is speculated that having a standardised breakfast at least 2 h before each experimental trial might explain the insignificant effects of exercise on S-IgA response. It seems that the breakfast might prevent exercise-induced immunodepression from occurring; hence S-IgA response was not affected. Thus, this becomes one of the limitations of this study.It has been suggested that α-amylase can be a tool for evaluating the relationship between sympathetic nervous system and mucosal immunity following psychological and/or physical stress (Walsh et al., 1999). This is because α-amylase is regulated by neuronal pathways and has been suggested to reflect changes in plasma noradrenaline and increased sympathetic activity under stressful conditions including exercise (Chatterton, R. T. Jr., Vogelsong, K. M., Lu, Y. C., Ellman, A, B. and Hudgens, G. A., 1996). On the other hand, previous studies reported an increase in α-amylase activity in saliva and that this effect is related to the exercise intensity (Walsh et al., 1999; Bishop, N. C., Blannin, A. K., Armstrong, E., Rickman, M. and Gleeson, M., 2000). In the present study, 2 h cycling at 60% VO2max increased α-amylase (Figure 1) activity suggesting an increased in sympathetic activity due to stressful exercise. In agreement with the present study, one study reported that α-amylase secretion was increased after cycling at 75% VO2max and after incremental exercise to exhaustion (Allgrove, J. E., Gomes, E., Hough, J. and Gleeson, M., 2008). Li and Gleeson (2004) also reported an increase in α-amylase activity after strenuous exercise. Alpha-amylase accounts for about half of the total protein in saliva. It is an enzyme that breaks down starch into maltose, and also functions to interrupt the adherence and growth of certain bacteria (Scannapieco, F. A., Torres, G. and Levine, M. J., 1993). Lactoferrin and lysozyme both possess antimicrobial activity (bacteriocide and fungicide) and are part of the innate defense, mainly at mucosa (Sánchez, L., Calvo, M. and Brock, J. H, 1992). Following an intense training session, saliva lactoferrin (Cox et al., 1999) and lysozyme (Innoue et al., 2004) concentrations were reported to be decreased. However, in contrast, others have reported that lactoferrin (West et al., 2006) and lysozyme (Allgrove et al., 2008; West et al., 2006) concentrations were increased after an exhaustive bout of exercise. The present study found that 2 h cycling at 60% VO2max significantly increased saliva lactoferrin (Figure 2) concentration but had no effect on lysozyme concentration. Exercise-induced increases in the concentration of AMPs are most likely related to sympathetic nervous system activity (Allgrove et al., 2008). Damage to epithelial cells through hyperventilation and subsequent exposure to environmental irritants, and the activation of neutrophils that follows may have led to increased secretion of these AMPs. Following physical damage (Dorschner et al., 2001) and contact with microbes (Duits et al., 2003), epithelial cells increase their expression of AMPs. Following these findings, further investigation is warranted with longer supplementation period and higher dose. The results will be very valuable since to date there was no other study investigating multi-strain probiotics on athletes’ immune function.
5. Conclusions
- The present study found that 30 days supplementation of the 14-strain probiotic did not alter salivary antimicrobial proteins at rest and in response to an acute bout of prolonged exercise. However, prolonged exercise significantly increased lactoferrin and α-amylase concentration post-exercise. It appears that the 30 days supplementation period and the dose/concentration of the 14-strain probiotic used in this study were not enough to induce any beneficial effects on athletes’ salivary antimicrobial proteins at rest and in response to an acute bout of prolonged exercise.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- We would like to thank all the participants involved in this study for their participation and commitment.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML