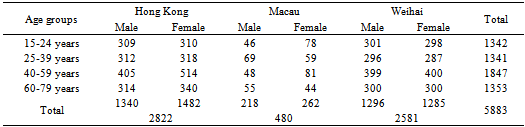
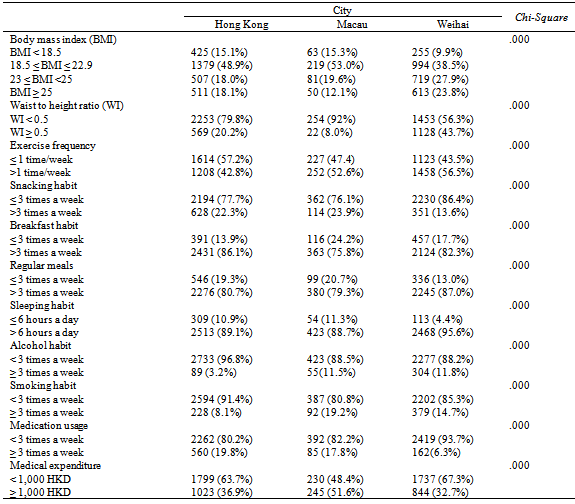
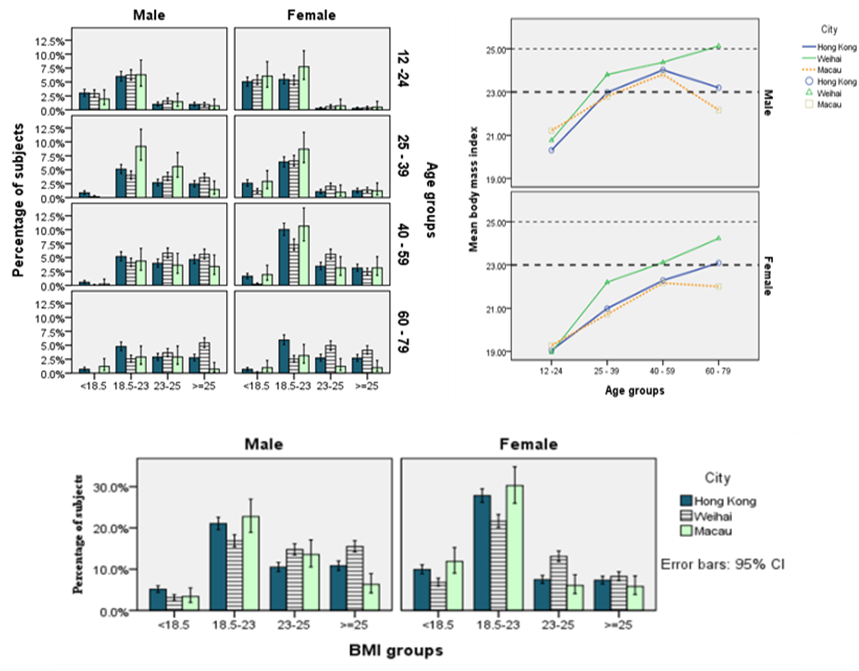
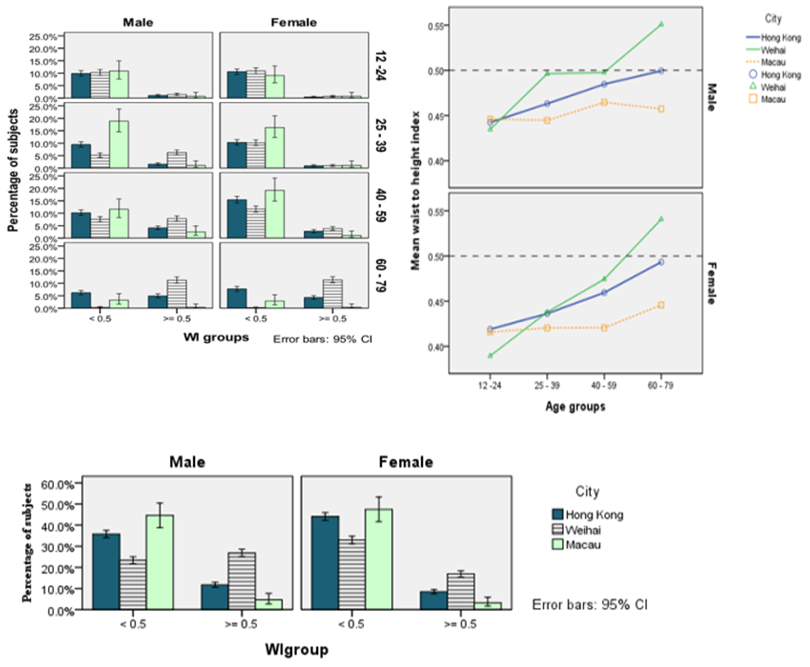
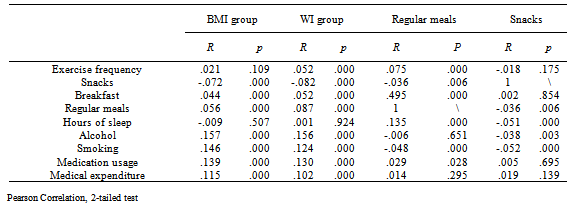
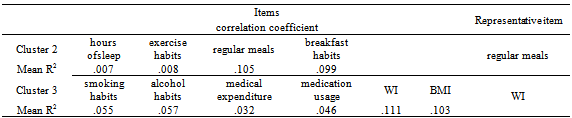
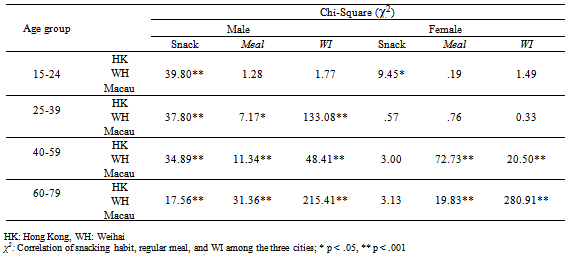
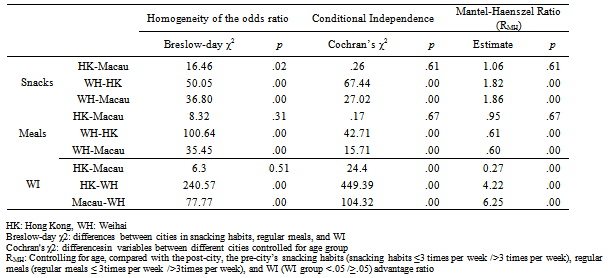
| [1] | Khaw, K. T., Wareham, N., Bingham, S., Welch, A., Luben, R., & Day, N. (2008). Combined impact of health behaviors and mortality in men and women: the EPIC-Norfolk prospective population study. PLoS Medicine, 5(1), e12. |
| [2] | Sanderson, S. C., Waller, J., Jarvis, M. J., Humphries, S. E., & Wardle, J. (2009). Awareness of lifestyle risk factors for cancer and heart disease among adults in the UK (abstract). Patient Education and Counseling, 74(2), 221-227. |
| [3] | Kvaavik, E., Batty, G. D., Ursin, G., Huxley, R., & Gale, C. R. (2010). Influence of individual and combined health behaviors on total and cause-specific mortality in men and women: the United Kingdom health and lifestyle survey. Archives of Internal Medicine, 170(8), 711-718. |
| [4] | Kumar, S. (2011). Occupational, environmental and lifestyle factors associated with spontaneous abortion. Reproductive Sciences, 18(10), 915-930. |
| [5] | Gami, A. S., Witt, B.J., Howard, D. E., Erwin, P. J., Gami, L. A., Somers, V. K., &Montori, V. M. (2007). Metabolic syndrome and risk incident cardiovascular events and death: a systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 49(4), 403-414. |
| [6] | Dalle Grave, R., Calugi, S, Centis, E., Marzocchi, R., Ghoch, M. E., &Marchesini, G. (2010). Lifestyle modification in the management of the metabolic syndrome: achievements and challenges. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndromes and Obesity, 3, 375-385. |
| [7] | Elmer, P. J., Obarzanek, E., Vollmer, W. M., Simons-Morton, D., Stevens V. J., Young, D. R., Lin, P. H., Champagne, C., Harsha, D. W., Svetkey, L. P., Ard, J., Brantley, P. J., Proschan, M. A., Erlinger, T. P., Appel, L. J., & PREMIER Collaborative Research Group (2006). Effects of comprehensive lifestyle modification on diet, weight, physical fitness, and blood pressure control: 18-month results of a randomized trial. Annals of Internal Medicine, 144(7), 485-495. |
| [8] | Jafar, T. H., Islam, M., Hatcher, J., Hashmi, S., Bux, R., Khan, A., Poulter, N., Badruddin, S., Chaturvedi, N., &Hypertension Research Group (2010). Community based lifestyle intervention for blood pressure reduction in children and young adults in development country: cluster randomized controlled trial. British Medical Journal, 340, c2641. |
| [9] | Zhang, W. & Li, N. (2011). Prevalence, risk factors, and management of prehypertension. International Journal of Hypertension, 2011, 605359. |
| [10] | Maruthur, N. M., Wang, N. Y., &Appel, L. J. (2009). Lifestyle interventions reduce coronary heart disease risk: results from the PREMIER Trial. Circulation, 119(15), 2026-2031. |
| [11] | Khan, N., Afaq, F., &Mukhtar, H. (2010). Lifestyle as risk factors for cancer: evidence from human studies. Cancer Letters, 293(2), 133-143. |
| [12] | Esposito, K., Ciltola, M., Maiorino, M. I., &Giugliano, D. (2008). Lifestyle approach for type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Current Atherosclerosis Reports, 10(6), 523-528. |
| [13] | Hu, G., Lakka, T. A., Lakka, H. M., &Tuomilehto, J. (2006). Lifestyle management in the metabolic syndrome. Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders, 4(4), 270-286. |
| [14] | Dyson, P. A. (2010). The therapeutics of lifestyle management on obesity. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism, 12(11), 941-946. |
| [15] | Burke, L. E., & Wang, J. (2011). Treatment strategies for overweight and obesity. Journal of Nursing Scholarship, 43(4), 368-375. |
| [16] | Wadden, T. A., Butryn, M. L., & Wilson, C. (2007). Lifestyle modification for the management of obesity. Gastroenterology, 132(6), 2226-2238. |
| [17] | Myint, P. K., Smith, R. D., Luben, R. N., Surtees, P. G., Wainwright, N. W., Wareham, N. J., &Khaw, K. T. (2011). Lifestyle behaviors and quality-adjusted life years in middle and older age. Age Ageing, 40(5), 589-595. |
| [18] | World Health Organization (WHO) Expert Consultation (2004). Appropriate body-mass index for Asian populations and its implication for policy and intervention strategies. Lancet, 363, 157-163. |
| [19] | Schneider, H. J., Friedrich, N., Klotsche, J., Pieper, L., Nauck, M., John, U., Dörr, M., Felix, S., Lehnert, H., Pittrow, D., Silber, S., Völzke, H., Stalla, G. K., Wallaschofski, H., &Wittchen, H. U. (2010). The predictive value of different measures of obesity for incident cardiovascular events and mortality. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 95(4), 1777-1785. |
| [20] | Ashwell, M., Gunn, P., & Gibson, S. (2012). Waist-to-height ratio is a better screening tool than waist circumference and BMI for adult cardiometrabolic risk factors: systematical review and meta-analysis. Obesity Review, 13(3), 275-286. |
| [21] | Browning, L. M., Hsieh, S. D., &Ashwell, M. (2010). A systematic review of waist-to-height ratio as a screening tool for the prediction of cardiovascular disease and diabetes: 0.5 could be a suitable global boundary value. Nutrition Research Reviews, 23(2), 247-269. |
| [22] | Dong, X., Liu, Y., Yang, J., Sun, Y., & Chen, L. (2011). Efficiency of anthropometric indicators of obesity for identifying cardiovascular risk factors in a Chinese population. Postgraduate Medical Journal, 87(1026), 251-256. |
| [23] | Wisse, B. E., Kim, F., & Schwartz, M. W. (2007). An integrative view of obesity. Science, 318(5852), 928-929. |
| [24] | Heber, D. (2010). An integrative view of obesity. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 91(1), 280S-283S. |
| [25] | Karlsson, E. A. & Beck, M. A. (2010). The burden of obesity on infectious disease. Experimental Biology and Medicine, 235(12), 1412-1424. |
| [26] | Balluz, L. S., Okoro, C. A., &Mokdad, A. (2008). Association between selected unhealthy lifestyle factors, body mass index, and chronic health conditions among individuals 50 years of age or older, by race/ethnicity. Ethnicity & Disease, 18(4), 450-457. |
| [27] | Kushner, R. F. & Choi. S.W. (2010). Prevalence of unhealthy lifestyle patterns among overweight and obese adults. Obesity (Sliver Spring), 18(6):1160-7. |
| [28] | Temelkova-Kurktschiev, T. &Stefanov, T. (2012). Lifestyle and genetics in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes, 120(1), 1-6. |
| [29] | Robroek, S. J., van den Berg, T. I., Plat, J. F., &Burdorf, A. (2011). The role of obesity and lifestyle behaviors in a productive workforce. Occupational and Environmental Medicine, 68(2), 134-139. |
| [30] | Mak, K. K., & Tan, S. H. (2012). Underweight problems in Asian children and adolescents. European Journal of Pediatrics, 171(5), 779-785. |
| [31] | Nishida, T., &Sakakibara, H. (2010). Association between underweight and low lymphocyte count as an indicator of malnutrition in Japanese women. Journal of Women’s Health (Larchmt), 9(7), 1377-1383. |
| [32] | Kang, K. T., Lee, P. L., Weng, W. C., & Hsu, W. C. (2012). Body weight status and obstructive sleep apnea in children. International Journal of Obesity advance online publication 24 January 2012. |
| [33] | Deutsch, A. B., Lynch, O., Alio, A. P., Salihu, H. M., &Spellacy, W. N. (2010). Increased risk of placental abruption in underweight women. American Journal of Perinatology, 27(3), 235-240. |
| [34] | Han, Z., Mulla, S. Beyene, J., Liao, G., McDonald, S. D., & Knowledge Synthesis Group (2011). Maternal underweight and the risk of preterm birth and low borth weight: a systematic review and meta-analyses. International Journal of Epidemiology, 40(1), 65-101. |
| [35] | Thorogood, M., Appleby, P., Key, T., & Mann, J. (2003). Relation between body mass index and mortality in an unusually slim cohort. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 57(2), 130–133. |
| [36] | Romero-Corral, A., Montori, V. M., Somers, V. K., Korinek, J., Thomas, R. J., Allison, T. G., Mookadam, F., & Lopez-Jimenez, F. (2006). Association of bodyweight with total mortality and with cardiovascular events in coronary artery disease: a systematic review of cohort studies. Lancet, 368(9536), 666-678. |
| [37] | Mond, J., Rodgers, B., Hay, P., & Owen, C. (2011). Mental health impairment in underweight women: do body dissatisfaction and eating-disordered behavior play a role? BMC Public Health,11, 547. |
| [38] | Weili, Y., He, B., Yao, H., Dai, J., Cui, J., Ge, D., Zheng, Y., Li, L., Guo, Y., Xiao, K., Fu, X., & Ma, D. (2007). Waist-to-height ratio is an accurate and easier index for evaluating obesity in children and adolescents. Obesity (Silver Spring), 15(3), 748-752. |
| [39] | Schneider, H. J., Klotsche, J., Silber, S., Stalla, G. K., &Wittchen, H. U. (2011). Measuring abdominal obesity: effects of height on distribution of cardiometabolic risk factors risk using waist circumference and waist-to-height ratio. Diabetes Care 34(1), e7. |
| [40] | Farshchi, H. R., Taylor, M. A., & Macdonald, I. A. (2005). Beneficial metabolic effects of regular meal frequency on dietary thermogenesis, insulin sensitivity, and fasting lipid profiles in healthy obese women. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 81(1), 16-24. |
| [41] | Toschke, A. M., Thorsteinsdottir, K. H., von Kries, R., & GME Study Group (2009). Meal frequency, breakfast consumption and childhood obesity. International Journal of Pediatric Obesity, 4(4), 242-248. |
| [42] | Pereira, M. A., Erickson, E., McKee, P., Schrankler, K., Raatz, S. K., Lytle, L. A., &Pellegrini, A. D. (2011). Breakfast frequency and quality may affect glycemia and appetite in adults and children. Journal of Nutrition, 141(1), 163-168. |
| [43] | Antonogeorgos, G., Panagiotakos, D. B., Papadimitrious, A., Priftis, K. N., Anthracopoulos, M., &Nicolaidou, P. (2012). Breakfast consumption and meal frequency interaction with childhood obesity. Pediatric Obesity, 7(1), 65-72. |
| [44] | Howarth, N. C., Huang, T. T., Roberts, S. B., Lin, B. H., &McCrory, M. A. (2007). Eating pattern and dietary composition in relation to BMI in younger and older adults. International Journal of Obesity, 31, 675-684. |
| [45] | Chapelot, D. (2011). The role of snacking in energy balance: a biobehavioral approach. Journal of Nutrition, 141(1), 158-162. |
| [46] | De Graaf, C. (2006). Effects of snacks on energy intake: An evolutionary perspective. Appetite, 47(1), 18-23. |
| [47] | BertéusForslund H., Klingström S., Hagberg H., Löndahl M., Torgerson J. S., &Lindroos A. K. (2008). Should snacks be recommended in obesity treatment? A 1-year randomized clinical trial. Eur J ClinNutr. 62(11):1308-17. |
| [48] | Viskaal-van Dongen, M., Kok, F. J., & de Graaf, C. (2010). Effects of snack consumption for 8 weeks on energy intake and body weight. International Journal of Obesity, 34(2), 319-326. |
| [49] | Kong, A., Beresford, S. A., Alfano, C. M., Foster-Schubert, K. E., Neuhourser, M. L., Johnson, D. B., Duggan, C., Wang, C. Y., Xiao, L., Bain, C. E., &McTiernan, A. (2011). Associations between snacking and weight loss and nutrient intake among postmenopausal overweight to obese women in a dietary weight-loss intervention. Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 111(12), 1898-1903. |
| [50] | Bulló, M., Garcia-Aloy, M., Martínez-González, M. A., Corella, D., Fernández-Ballart, J. D., Fiol, M., Gómez-Gracia, E., Estruch, R., Ortega-Calvo, M., Francisco, S., Flores-Mateo, G., Serra-Majem, L., Pintó, X., Covas, M. I., Ros, E., Lamuela-Raventós, R., & Salas-Salvadó, J. (2011). Association between a healthy lifestyle and general obesity and abdominal obesity in an elderly population at high cardiovascular risk. Preventive Medicine, 53(3), 155-161. |
| [51] | Neve, M. J., Morgan, P. J., & Collins, C. E. (2011). Behavioural factors related with successful weight loss 15 months post-enrolment in a commercial web-based weight loss programme. Public Health Nutrition, Nov 29, 1-11.[Epub ahead of print]. |
| [52] | Wendel-Vos G. C., Dutman A. E., Verschuren W. M., Ronckers E. T., Ament A., van Assema P. et al (2009). Lifestyle factors of a five-year community-intervention program: the Hartslag Limburg intervention. Am J Prev Med. 37(1):50-6. |
| [53] | Haby, M. M., Doherty, R., Welch, N., & Mason, V. (2012). Community-based interventions for obesity prevention: lessons learned by Australian policy-maker. BMC Research Notes, 5, 20. |
| [54] | Stensvold D., Nauman J., Nilsen T. I., Wisløff U., Slørdahl S. A., &Vatten L. (2011). Even low level of physical activity is associated with reduced mortality among people with metabolic syndrome, a population based study (the HUNT 2 study, Norway). BMC Med. 9:109. |
| [55] | Wen, C. P., Wai, J. P., Tsai, M. K., Yang, Y. C., Cheng, T. Y., Lee, M. C., Chan H. T., Tsao, C. K., Tsai, S. P., &Wu, X. (2011). Minimum amount of physical activity for reduced mortality and extended life expectancy: a prospective cohort study. Lancet, 378(9798), 1244-1253. |
| [56] | Nédó, E., &Paulik, E. (2012). Association of smoking, physical activity, and dietary habits with socioeconomic variables: a cross-sectional study in adults on both sides of the Hungarian-Romanian border. BMC Public Health, 12, 60. |
| [57] | Vathesatogkit, P., Woodward, M., Tanomsup, S., Hengprasith, B., Aekplakorn, W., Yamwong, S., &Sritara, P. (2012). Long-term effects of socioeconomic status on incident hypertension and progression of blood pressure. Journal of Hypertension, 2012 May 8.[Epub ahead of print]. |
| [58] | World Health Organization (2012) World Health Statistics 2012. Switzerland: WHO. |

 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML