-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Sports Science
p-ISSN: 2169-8759 e-ISSN: 2169-8791
2013; 3(4): 107-114
doi:10.5923/j.sports.20130304.03
Review the Repeated Bout Effect in Resistance
Adilson J. Meneghel1, Alex H. Crisp1, Rozangela Verlengia1, Charles R. Lopes2
1Human Performance Research Group - College of Health Science (FACIS), Methodist University of Piracicaba (UNIMEP), Piracicaba, SP, 13.400-911, Brazil
2Faculty Adventist of Hortolândia (UNASP), Hortolândia, SP. 13184-010, Brazil
Correspondence to: Adilson J. Meneghel, Human Performance Research Group - College of Health Science (FACIS), Methodist University of Piracicaba (UNIMEP), Piracicaba, SP, 13.400-911, Brazil.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
When we conducted a new series of exercises particularly eccentric, have different responses at both the performance and as well as in indirect markers of muscle damage, especially in untrained or not used to this type of exercise. But it is also evident that even when the exercise is performed for a period of time, their results are attenuated primarily with regard to the muscular damage, compared to the first session. This adaptation has been reported in the literature as Repeated Bouts Effects (RBE). The RBE has been approached in various ways is kind of contractions, actions, intensity, repetitions, speed of execution, muscle groups. The duration of the protective effect is also one of the aspects discussed which is being processed from days to months, but the rest of the effect appears to be influenced by the magnitude of muscle damage in the initial session. Theories of the mechanism of neural adaptations, cellular and mechanical, are presented and responsible for RBE, although these theories require further investigation. The purpose of doing this review is to demonstrate the importance that the magnitude of muscle damage RBE is the most efficient intervention prescient.
Keywords: Eccentric Exercise, Muscle Damage, Repeated Bout Effects (RBE)
Cite this paper: Adilson J. Meneghel, Alex H. Crisp, Rozangela Verlengia, Charles R. Lopes, Review the Repeated Bout Effect in Resistance, International Journal of Sports Science, Vol. 3 No. 4, 2013, pp. 107-114. doi: 10.5923/j.sports.20130304.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
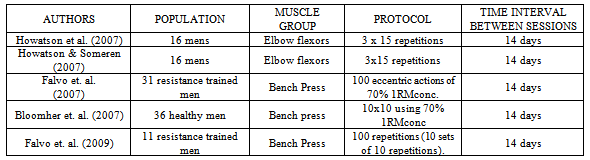
- There is a consensus in the literature that performance of strenuous resistance exercise bout, results in damage to muscle tissue due to mechanical and metabolic factors[1],[2]. The extension of muscle damage is dependent on the manipulation of acute training variables, such as: intensity, volume, rest interval, muscle action, contraction velocity, and range of motion, choice and order of exercises[3]. With greater magnitude show in exercises that emphasize high-intensity or volume eccentric muscle actions[4]The muscle damage is characterized by disruption to the extracellular matrix, basal lamina, and sarcolemma of muscle cells, resultion in the release of intracellular proteins into bloodstream[5],[6].From the functional point of view and perception, the muscle damage can promote changes in neuromuscular performance, resulting in delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS); symptoms that can be present several days after resistance exercise bout[7],[8],[9].Thus, studies uses eccentric exercises (especially controlled by isokinetic equipment) to induce muscle damage, and the analyzes are obtained by indirect measurements over time post resistance exercise bout[6],[10]. Among these, the increase in subjective perception of DOMS, creatine kinase (CK) activity in blood and decreased of muscle strength are commonly used to determine the magnitude of muscle damage[11],[12]. However, the performance of a single eccentric exercise bout can protect the skeletal muscle, decreasing the magnitude of indirect markers of muscle damage in subsequent repeated eccentric bouts. This phenomenon is referred in the literature as repeated bout effect (RBE)[13],[14]. The exact mechanism of the RBE is not fully understood, however, the neural, mechanical and cellular adaptations, or a combination thereof, has been hypothesized as a possible adaptative mechanism of muscle protection [14],[15],[16]. The possible adaptative mechanism after isokinetic eccentric bout, has been reported last more than 6 months, but diminished between 9 and 12 months, when assessed untrained men[17]. In addition, previously only two maximal voluntary isometric contractions can confer a protective effect on muscle damage markers after eccentric exercise bout in untrained men.In this way, methodologically the majority of RBE studies assess untrained and/or detrained individuals for a minimum period of 6 months, in order to avoid the protective effect muscular[18]. On the other hand, symptoms arising from muscle damage persist even in athletes and/or well-trained individuals, although in a lesser degree than untrained individuals[9].Considering this possibility, the present study aim to review and discuss the papers that investigated the RBE in resistance-trained population. Were searched and selected articles indexed in PubMed and High wire, with relevance to the theme proposed using the words: muscle damage, repeated bout effect, resistance trained, and eccentric exercise.The RBE and adaptive mechanismsThe RBE refers to the protective effect of a single training session with eccentric component observed in other subsequent sessions[19],[14],[20],[21],[22],[23],[24],[25]. The RBE is characterized by a rapid recovery mechanisms spoiled by all MTAs. That is, the muscle strength and power, the restriction on range of motion, sensation of DOMS and plasma concentrations of cytosolic proteins such as CK, LDH, troponin I, myoglobin and fragments of myosin heavy chain (MHC) found in high concentrations the bloodstream post-workout, are often used as indirect markers of muscle damage arising thereof[26],[27].The RBE and the theory of mechanisms of adaptationThe adjustments related to RBE are characterized as neural, molecular and mechanics order. A lot of studies have clearly demonstrated that RBE is sustained by all of his theories, however, there is no consensus between the theories and proposals.The first theory proposed is neural adaptation, according to[14], which is supported by two possible mechanisms, the increased recruitment of motor units of slow contraction and activation of more motor units.[15]. Changes in motor unit activation between repeated bouts were examined by electromyography (EMG) in humans[28],[29]. Theoretically an increase in the amplitude of the EMG relative to torque production in the repeated session indicates contractile stress redistribution among a large number of fibers. This effect is evident with the eccentric strength training[30],[31]. Conversely, a decrease in the frequency of the EMG signal in the session repeated theoretically indicate a change for the recruitment of motor units slow contraction and / or increase the synchronization of the motor unit. There was no evidence of a change in EMG amplitude between repeated sessions in eccentric hamstring muscles[29] of the tibialis anterior[28]. However, the median frequency was decreased in the session repeated for the tibialis anterior muscle and this effect was attributed to increased recruitment of slow-twitch motor units[28]. Alternatively, this effect could be attributed to the increased synchronization of the motor unit. That effect would be indicative of a neural adaptation to a single bout of eccentric exercise.However, although the results of[28] are the first direct evidence of a neural adaptation for a single eccentric exercise session, it is evident that the effect of repeated session can occur independent of a neural adaptation[32],[33]. The RBE has been demonstrated in electrically stimulated eccentric contractions, in rats performed, in tibialis anterior muscles[32] and more recently in human elbow flexors[33]. In humans, the initial series of electrically stimulated eccentric contractions results in severe loss of strength increase the angle of the elbow relaxed reduced the angle of the elbow flexed, increasing the circumference of the arm, increase muscle thickness in ultrasound images, elevated serum CK activity and myoglobin concentration and muscle pain. Following a repeated series of the same stimulation protocol 2 weeks later, the responses had significantly in all eight markers lesions. The authors concluded that "the involvement of the central nervous system in RBE is minimal, and peripheral adaptations play a more important role." However, not alluded to any specific peripheral adaptations.A second theory is mobile, according[14], which is supported by three possible mechanisms to adding longitudinal sarcomere: for adaptation to maintain the coupling Excitation - Contraction (EC) and inflammatory responses by adjusting the eccentric contractions[15]. Morgan (1990)[34], shows that the muscular damage is irreversible due to the tension during the sarcomere eccentric contractions and, in particular, muscle contractions at lengths on the descending limb of the length’s voltage curve. Countless animal studies[35],[36],[37] and voluntary contractions in humans[38],[39], has shown that muscle length during the eccentric contraction is the critical factor in determining the extent of muscle damage. And consequently large contractions of muscles result in large elongated symptoms of damage. Based on the theory of voltage sarcomere muscle injury[34] predicted that the results of the repair process of increasing the number of sarcomeres connected in series and this serves to reduce the voltage during an attack sarcomere repeated thereby limiting myofibrillar disruption. Theoretically, the lost of strength after a session of eccentric exercise could be due to an inability to voluntarily activate motor units secondary to pain or injury, physical disruption of structures that generate power or a failure to activate intact structures in the generation of force within the fiber muscle (EC coupling). Mchugh et al,[40] and Saxton & Donnelly,[41] support the voluntary activation of the motor unit is not considered damage after eccentric exercise. Warren et al,[42] mentions that the lost of strength appears to be the combination of physical damage and decrease in EC coupling. The injury in eccentric contractions is due to a mechanical disruption of myofibrils. This initial damage triggers a local inflammatory response that leads to an exacerbation of damage before signs of recovery. These events can be referred to as primary and secondary damage. Mitigate a series of repeated inflammatory response may reflect an adaptation to avoid the proliferation of myofibrils’ mechanical disruption. The reduction of the inflammatory response for a session of repeated eccentric exercise may simply reflect the fact that there was a small break in the series repeated mechanical and therefore a lesser degree of stimulation in the inflammatory response. The third theory is the mechanics, according to[14], which is supported by factors of possible mechanisms, increased muscle stiffness and dynamic passive[15].Muscle damage has been described as the material fatigue typical ductile material subjected to a cyclic tensile load[43]. It is believed that the lesion induced by eccentric contraction starts with a mechanical rupture of myofibrils. It follows that an adjustment serves to protect against injury which might change the mechanical properties of the musculoskeletal system[15]. Material fatigue refers to a structural failure caused by the accumulated tension and is distinct from the fault caused by applying a voltage only material that exceeds the tensile strength. A ductile material by traction experiences plastic deformation before failure, in contrast to a brittle material without deformation prior to failure. Skeletal muscle is a ductile material and its behavior during repeated eccentric contractions is consistent with the fatigue of materials[43]. Another important factor is the intermediate filament, where the length-tension curve is determined by myofilaments overlap that is a function of sarcomere length[44],[45]. During the stretch of the sarcomere, eccentric contractions are highly non-uniform, with some maintaining sarcomere length, while others are stretched beyond the point of overlap of filaments[46],[34]. This stretch of the sarcomere has been referred to as "snap"[34]. When a sarcomere is stretched beyond overlapping filaments ("popped"), greater reliance is placed on the passive structures to maintain tension in series, as the number of series sarcomere shortened. Morgan[34] reported that the muscle injury is not a result of the real "snap" (as thinking as occurs with most eccentric contractions), but may be caused by the cyclic stress when placed structures Passive following support of eccentric contractions keeps a generate "popping". These elements are referred to an intermediate filament protein desmin and consist of vimentin and sinemina[47],[48]. Intermediate filaments are responsible for maintaining the structural integrity of the sarcomeres in series and parallels,[47],[49]. Through the power flow within skeletal muscle can be increased by the intermediate filament system[49],[50], demonstrated that the intermediate filament system provides a link between areas to bypass damaged and maintain output power Serial. While this may be beneficial to maintain power production during eccentric exercise, the final effect may be to raise subsequent damage. When sarcomeres are stretched beyond myofilament overlapping the intermediate filament system, this must bear the burden of repeated charge and subsequent contraction will result in mechanical failure of the intermediate filament system.Thus the aim of this study is to discuss the mechanisms responsible for RBE in trained men.Table I shows the RBE studies in individuals trained men.When we started a new training program, the effect of first practice makes feel muscle aches for several days after the first session. This effect also applies to when increasing your training volume or intensity, or doing a different training or not used. DOMS, loss of muscle function, changes in surrogate markers of CK, Mb, PGE are typical symptoms of muscle damage, specifically induced by eccentric contractions[51]. A minor pain or no pain is experienced when we repeat the same or similar exercises within a few days or weeks or even months, reducing DOMS these results, which we call RBE[51],[52].Already[53], mentioning that when comparing the second session with the first session is less DOMS and muscle function recovery is faster.The RBE is characterized by a lower swelling muscle, increases or smaller discrete markers of muscle damage to blood, CK, PGE and Mb,[19],[54].Studies have shown that the interval between the first and second session can vary from 48 hours to 2 days[55],[56] until 9 months[17].The damage and muscular exercise eccentricMuscle damage after a session of high intensity and / or volume eccentric exercise different or unusual is characterized by disruptions ultrastructural specifically, protein degradation, inflammation and increased cytoskeletal proteins in the bloodstream[7],[57]. Countless markers indicate the presence of muscle damage. The most common are: muscular strength, muscular pain late onset, range of motion, circumference, blood creatine kinase activity, indirect markers of collagen degradation, the median frequency of the EMG signal[5],[12]. The most common research method for the analysis of muscle damage induced by exercise is realized through indirect measures[12]. There are few data on muscle injury induced by acute concentric and eccentric exercise[7],[58],[59] considering the same absolute loads and there is no consensus among the results. Hollander et al.[60] have shown that eccentric contractions when performed with the same load to which absolute concentric contraction, has a less pronounced damage of the markers.
|
2. Indirect Markers, Damages of Muscle Paind and the Rbe
- The studies of surrogate markers show results that contribute to determining the RBE. The indirect markers of muscle damage in trained individuals[73], demonstrated a significant attenuation of CK after session 2 compared to session 1 (F 1.14 = 28.5, P <0.001). There were no significant differences between groups in session 1, but CK showed lower significance in the LI group compared to the CL attack at 96 h 2 (P = 0.002). Muscle pain was significantly higher in session 1 than in session 2 (F1, 14 = 34.5, P <0.001). Pain was also attenuated in the second session compared to session 1 in the CL group at 48 h (P = 0.007). Moreover, there was less pain after session 2 in 48 h in IL than the CL group (P = 0.009). Bloomer et. al[77] showed that an effect of time was observed for CK activity (P <0.0001) together with values peaking at 24 hours post-exercise (317 ± 29U • L-1) compared to pre-exercise (139 ± 29U • L -1). Creatine kinase activity was significantly higher than the pre exercise at 24 and 48 hours post-exercise (P <0.05), corroborating these studies The study by Falvo et. al[78], support the hypothesis that the RBE is absent in resistance trained men. And yet supported due to the lack of significant differences observed between sets for all other markers of muscle damage, with the exception of the effect observed for the perception of muscle pain. In the absence of an RBE for any measure variable, it is possible that adaptations associated with the RBE are already present in the exercises of resistance force trained men[77].Contrasting these studies[55], demonstrated that both the DOMS as CK, had no significant differences in RBE, with an interval of 2 days between the first and second session corroborated with this study. Nosaka and Newton[7] showed that performing the same eccentric exercise 2 days after the initial series does not affect the recovery of muscle function responses of plasma CK activity and development of DOMS. Similarly[56],[72], reported that the second session of maximal eccentric exercise of the elbow flexors performed 3 days after the first attack did not affect changes in indicators of muscle injury. It should be noted that the exercise intensity in these studies was between 50 and 80% of the maximum power, and the present study used eccentric exercise of higher intensity for the first (100%) (80-100%) the second session. ECC1 resulted in significant reductions in MIF and ROM, increasing the CIR, muscle thickness, and intensity, blood markers of muscle damage (CK, LDH, Mb), and development of DOMS for all groups. These changes were similar to findings from previous studies in an exercise protocol similar to this study. It should be noted that the study subjects were athletes and used a high load. Nosaka & Newton[7] investigated the concentric or eccentric contractions of the elbow flexors, applying a load of 50% of 1 RM (3x10 reps) for both modes of contraction, saw a more significant increase in delayed onset muscle soreness during eccentric contractions. And also Nosaka & Newton[7] study showed that submaximal concentric contraction (50% of maximal isometric force), produces changes indirect markers of muscle damage and CK DOM), which, although less pronounced than those found in maximal eccentric contractions, still show changes five days after the workout in such intensity.Paschalis et. al[79] reported no significant difference between DOMS high intensity (12 sets of 10 repetitions of maximal eccentric contractions) and low intensity (continuous eccentric contractions at 50% of maximum torque cam) with eccentric exercise of the quadriceps, where the total work was the same in the two exercise protocols. This was supported by this study Uchida et. al[80], which confirmed that the intensity of muscle contractions was not a major factor determining the magnitude of DOMS. Therefore, we can assume that the total volume, rather than the intensity, determines the magnitude of DOMS.
3. Conclusions
- Definitely understand the mechanisms of adaptation, their applicability and results of RBE will require much research and studies to elucidate these aspects. There are so many variables that guide the RBE study, such as different types of people, different exercises since its intensity, volume, induction for being eccentric, concentric, or submaximal maximum interval between sessions, finally. Allied to all these prerequisites, are the complexities of neural mechanisms, cellular and mechanical, its association, direct or indirect markers of muscle damage. The relationship between muscle damage and RBE is not new, but needs further research in order to clarify and understand the mechanisms of exercise-induced muscle damage, which does not have answer.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML