-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Sociological Research
p-ISSN: 2166-5443 e-ISSN: 2166-5451
2021; 11(1): 7-17
doi:10.5923/j.sociology.20211101.02
Received: Sep. 26, 2021; Accepted: Oct. 20, 2021; Published: Oct. 30, 2021

Exploring the Delinquent Behaviour among Alleged Detainees at Police Stations and Associated Causes: A Case Study of Quetta City, Balochistan
Abdul Razique Bazai 1, Sanaullah Panezai 2, Said Qasim 2
1Degree College Pishin District, Balochistan
2Department of Geography and Regional Planning, University of Balochistan, Quetta
Correspondence to: Sanaullah Panezai , Department of Geography and Regional Planning, University of Balochistan, Quetta.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Background: Delinquent behavior has been a serious social problem and literature has explored it at global, regional and national levels. Objectives: The purpose of this research study is to explore the delinquent behavior among detainees and associated causes in Quetta city of Balochistan province. Methods: This study adopted survey research design for exploring delinquent behavior among detainees. Primary data were gathered from 105 detainees at twenty-two police stations at Quetta city through interviewee-administrated questionnaire. Police stations were selected through universal sampling for this research study. The data were analyzed through descriptive statistics. Results: The socio-demographic profile of the criminals showed that 43.8% were illiterate, age group 42.9% were aged 20-29 years, 61.0% married, 72.4% were living in nuclear family and 55.2%. had fair economic status. Of the total, 91% of the detainees were the dwellers of Balochistan province. Majority (63.8%) of them were arrested for the 1st time. The significant delinquencies included drug use (22.2%), stolen others’ money (13.8%), bought stolen goods (10.0%), involved in gang fighting (10.0%), and injured people (8.6%). The detainees reported the causes of delinquent behavior as criminal emotions (29.5%), peer influence (35.2%), lack of parental attention (11.4%) and crime dominated area (6.7%). Conclusions: This study concluded that poor educational background had strong association with the criminal behavior. The criminal behavior is triggered by criminal emotions, peer influence and lack of parental attention. The findings imply that education together with parental supervision can plan an important role in reducing the criminal offenses by youth. Thuse, parents must monitor the activities of their family members. Moreover, policymakers should ensure that each child have access to free and mandatory education in order to nourish the youth as law abiding citizens.
Keywords: Delinquency, Delinquent behavior, Criminal behavior, Police station, Quetta, Balochistan, Pakistan
Cite this paper: Abdul Razique Bazai , Sanaullah Panezai , Said Qasim , Exploring the Delinquent Behaviour among Alleged Detainees at Police Stations and Associated Causes: A Case Study of Quetta City, Balochistan, American Journal of Sociological Research, Vol. 11 No. 1, 2021, pp. 7-17. doi: 10.5923/j.sociology.20211101.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Since 1940s, the delinquent behavior has been a subject of prominent importance in criminological studies (Ellis et al., 2019). Literature has explored the delinquent behaviour at global, regional and national levels. It has got a global importance and is expanding in developed and developing countries in ordered and semi-ordered manners. It is defined as “a criminal action committed by a human confronting the laws of the civil society” (Kenchadze, 2015). Similarly, delinquency is defined by acts, the detection of which is thought to result in punishment of the person committing them by agents of the larger society (Moore, 2001). Aggressive behaviour is one of the components of the conduct disorder that consists of physical or verbal behaviour that harm or threaten with harming others; and it can be self-protective or self-destructive. According to Sikand and Reddy (2017), ″Criminal behaviour is any behaviour or act that is in violation of the criminal law, whereas crime is the particular action representing such behaviour″. Similarly, according to Latessa and Lowenkamp (2005), “A criminal behaviour happens when there is an intention, a method, and an opportunity”. Criminal behaviour may refer to wide range of exercises that the greater part in the public arena may see as unpredictable, unsafe, irritating, odd, amazing and so forth (Hagan, 2010). Kausar et al. (2012) explained in their study that the term is used for juvenile's action which would be measured illegal for an adult. Breckenridge define the delinquency as a condition emerging in the framework of socio individual confusion and in the arrangement of experience and impacts that shape behavioural issues (Bano et al., 2009). Redl and Winelian defined the delinquency as that the legitimate idea of delinquency basically states which sort of behaviour is illegal by law. Several factors cause delinquent behaviour. The environmental and biological factors act both autonomously and in relationship to develop aggressive and delinquent behaviour (Mendes et al., 2009). The risky environment might worsen existing delinquency and the people possessing delinquent behaviour were living in unhealthy, broken family environment (Müller-Fabiana, 2016). Criminal behaviour is also caused by the genetic factors, recently it is reported about the molecular genetics studies that a serotonin system's related gene may be linked with enhanced risk for the development of alcoholism and violence (Tehrani & Mednick, 2000). Several other factors affect the development of all types of behaviour and criminal actions (Kenchadze, 2015). Several research studies related to the delinquency and delinquent behaviour were conducted in Pakistan. Literature review showed that there are numerous psychological as well as socio-economic factors influencing adolescent delinquency in Punjab, Pakistan. Majority of respondents reported about family environment for example improper supervision, negligence, delinquent behaviour and restrictive behaviour of their parents leads to delinquent behaviour (Ahmed & Murtaza, 2016). The research work showed inferiority complex, land dispute, large family size, honour killing, friend’s motivation and income disparity as the main determinants of the juvenile delinquent behaviour (Mahmood & Cheema, 2008). A medical research study explored the causes of delinquent behaviour in adolescents in Pakistan, that schizophrenia, depression and psychopathic deviate is the result of personality traits related with hypochondriac (Kausar et al., 2012). According to Bano et al. (2009), in Pakistan, the low socio-economic backgrounds and low literacy rate of the adolescents leads to delinquent behaviour and also explored their urban background have less tendency toward delinquent behaviour than rural. The research study revealed that broken homes, worse economic conditions, delinquent friends, dropout from education and family members play an important role in leading to violent behaviour among juveniles in Pakistan (Haider & Mahsud, 2010). The alarming situation of delinquent behaviour in adolescent in Punjab Pakistan was explored through a research work that the most of the respondents were responsible for murder (70.6%), while the remaining respondents were involved in theft, dacoity, kidnapping and drugs (Mahmood & Cheema, 2004). A gender-wise study showed that the significant gender differences in school and social setting on peer influence, as female adolescents reflect low peer influence as compared to male students. The study also found that children have more peer influence in early age stage as compare to children in late stage (Khan, 2018). Another study showed the delinquent behaviour that included smoking cigarettes, using drugs, damaging property and stealing money from family in the juveniles and defection from school, self-control, drug use, lack of scheduling daily activities and peer influence were significant factors of delinquency (Panezai et al., 2019).Social and educational factors are the stronger and higher than any other factors which influence the delinquency. Research reports that peer group and lack of supervision causes an increase in the criminal behaviour (Weerman et al., 2015). The adolescents’ delinquent behaviour is influenced by peer relations and family environment (Hyun, 2018). A rising tendency of delinquent behaviour was associated with the slowing down of growth rate over the high school years. Female adolescents reported lower levels of violent behaviour and showed gradual increase of violent behaviour relative to male juveniles (Shek & Lin, 2016). A research study citing the work of (South & Messner, 2000, p. 83), found that demographic factors affect delinquent behaviour to a great extent. (Li et al., 2015). The age group (16-18) are often found involved in criminal activities and their first crime was theft influenced by bad company (Nourollah et al., 2015). Psychological factors such as a high degree of impulsivity (Donohew et al., 2000), and low self-control (Hampson et al., 2001) leads to criminal behaviour among adolescents. Crime occurs in any social system or a society and is well-known to human being since they started living on earth (Adel et al., 2016). Controlling crime and criminal behaviour is a major concern for law enforcement agencies, policy makers and society. Crimes are responsible for the instability and fear and these affected the political, social, psychological and economical status of any society. It is inevitable to control the crimes, otherwise it will result in the deterioration of society and moral degradation. Therefore, controlling the criminal activities and understanding the criminal behaviour of criminals are necessary at any cost for law enforcement agencies, society and government.Quetta city, the provincial capital of Balochistan province, has a great importance due to its geostrategic location. This location provides it the central hosting place and suitable facilities to the migrants from Afghanistan. The city is confronted with sectarian violence, ethno-political violence, and terrorism. Quetta city consists of multi-ethnic population. According to the 1998 census, the ethnic population consists of Pashtoon (30%), Baloch and Brahvi (27.6%), Settler (25%) others (17.4%) respectively (Pakistan Bureau of Statistics, 1998). Pashtoon and Baloch are mostly Sunni, a little portion of Quetta′s population is Hazara community, Shia by sect. The Hazara community has been harmed by terrorists since 2001. This has damaged the social fabric of the Quetta city (Minority Support Pakistan, 2012). Another criminal base is ethno-political. During the Baloch widespread insurgencies and localised uprisings back in 1948, 1958, 1963, 1973-1977 and the last from 2003 onward have caused severe human causalities (Gazdar et al., 2010). Proximity of Pakistan with Afghanistan has boosted crime ratios in Pakistan owing to its role in Afghan war since 1979. The violence was triggered, in border areas including Quetta, after the invasion of Afghanistan by US and Allied Forces in 2001 (Gazdar et al., 2010; Rashid, 2000). The involvement of Pakistan in Afghan wars has brough the Gun and Heroin cultures and the terrorism.The literature has covered several aspects of criminal behaviour and pattern of crime. A research study found that the urbanization and crime in Pakistan shown the unique and positive relationship (Jalil & Iqbal, 2010). Crime and poverty have a positive relationship (Khan et al., 2015). The crime rate in Pakistan is lowering the economic growth (Ahmad et al., 2014). The lack of employment has pursued the youth to join the criminal gangs (Hinds, 2014). The results about sexual assault in Quetta city showed that about 41% cases of sodomy, accused and victimized rape of 28% and Zina cases were 31% (Burnham et al., 2004). Limited research studies have been conducted on the crime situation in Quetta city (Minority Support Pakistan, 2012). Similarly, there is an acute shortage of literature that has assessed the criminal behavior among detainees in Quetta city. Therefore, it is direly needed to assess crime situation in Quetta city. The purpose of this study is to explore the criminal behaviour and associated factors.
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
- This study used survey design and quantitative research techniques for collecting and analysis of data related to delinquent behaviour among detainees at police stations in Quetta city, Balochistan, Pakistan.
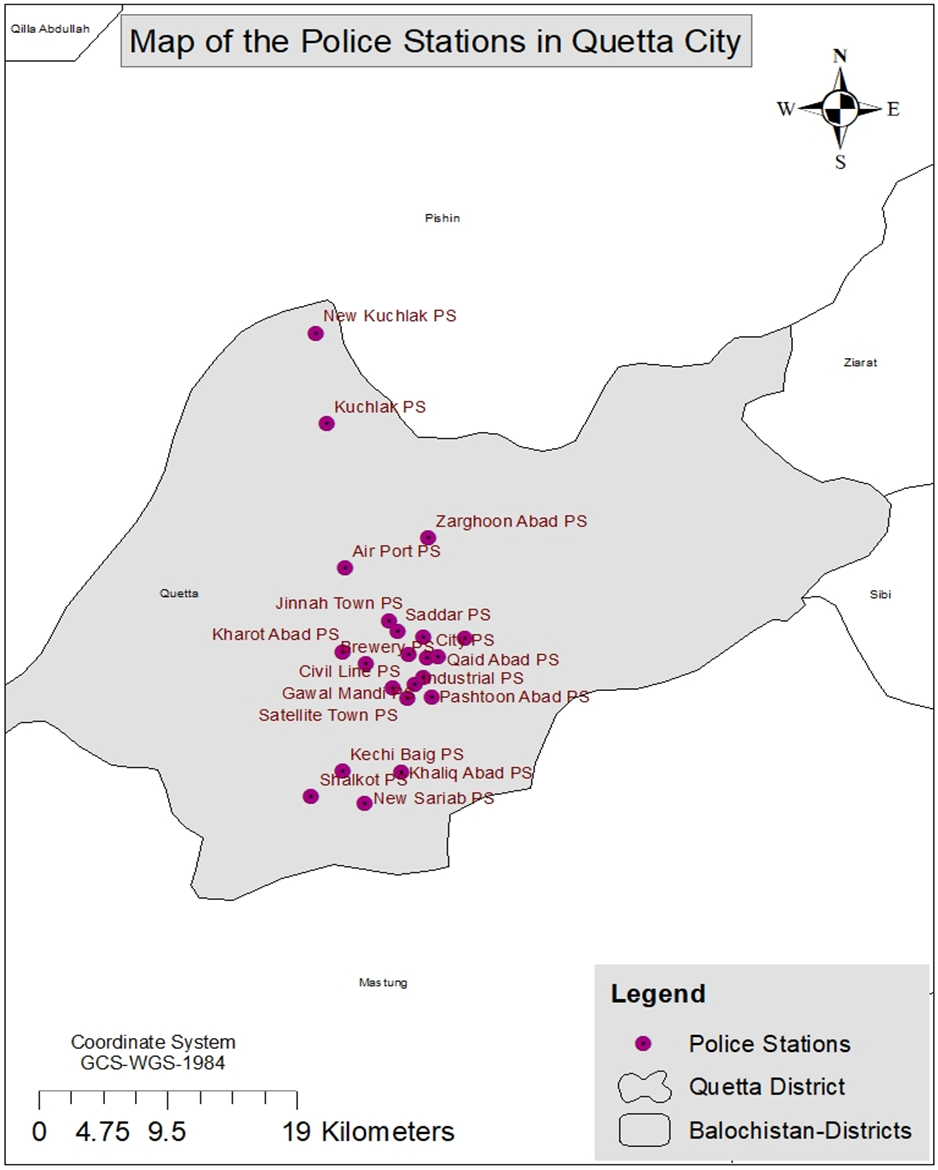 | Figure 1. Map showing locations of Police Stations in Quetta City |
2.2. Setting
- For the current study, Quetta city, the capital of Balochistan province, Pakistan was chosen as a study area. The motive behind the selection of Quetta city was that the Quetta is most populous city, district headquarter and provincial capital. The geographical location of Quetta city is lie on the Latitude 30° 10' 58.7" and Longitude 66° 59' 55.4"N (Bazai & Panezai, 2020). The elevation from sea level is 1780 meters. The area of Quetta city is encompassed by various slope ranges. On the north of Quetta city, lays the Takatu range. The eastern border of Quetta city is covered by Murdar and Zarghoon mountains (Khan et al., 2020). The southern side of the Quetta is limited by Chilton Mountain. The Quetta city has the Mashlak range in the west. According to the census of 2017, the population of Quetta District is 22,75, 699 (Pakistan Bureau of Statistics, 2017). The Quetta city is inhabited by a mixed-population comprising of Pashtoon, Baloch, Brahvi, Urdu Speaking, Panjabi, Sindhi and Hazara tribes. There are also a number of settlers including Punjabi, Urdu speaking, Sindhi and Saraiki speaking people. The climate of the city is dry and chilly. Quetta city has a moderate summer season. The hottest month is July. The mean maximum and minimum temperature of July is about 36°C and 20°C respectively. Winter season is severe and dry. January is the coldest month with mean maximum and minimum temperature of about 11°C and -3°C respectively. Annual precipitation is 260 mm (UNICEF, 2011).
2.3. Participants
- Alleged detainees who were detained in the selected police stations of Quetta city were selected as respondents for this study. The total respondents were one hundred and five (105).
2.4. Variables
- The delinquent behaviour of the alleged detainees is the dependent variable of the study. The dependent variable consists of 14 items of delinquency as suggested by (Elliott et al., 1983). The questions were asked from the respondents as; how many times (0-5) in your previous life have you committed the following: 1) property damaged, 2) stolen money from others, 3) stolen money from family members, 4) bought stolen goods, 5) gang fighting, 6) injured people, 7) domestic violence, 8) had sexual relation, 9) sold drugs, 10) drug used, 11) cheated in business, 12) got money by force using weapons, 13) snatched money/things, and14) involved in gambling. The times 0-5 is interpreted into the scale of measurement as, never = 0 and 1, rare = 2 and 3, sometimes = 4 and often = for 5 and more.
2.5. Data Sources
- The primary data were used for this study. The data were collected from 22 police stations in Quetta city through questionnaire survey from 105 detainees. The data were collected from February to June 2019. The prior permission was taken from the Senior Superintendent of Police (SSP) Legal, Quetta City.
2.6. Universal Sampling Method
- For this study, universal sampling method was used in which all delinquents at the police stations were interviewed from February to June 2021 for the data collection. The reason behind the universal sampling method was the fact that detainees at police stations do not last for long and they were less in numbers.
2.7. Data Analysis Methods
- The descriptive statistics were used for data analysis and presentations. The Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) Version 23.0 was used for data entry and analysis.
3. Results
3.1. Socio-Demographic Profile of Delinquents
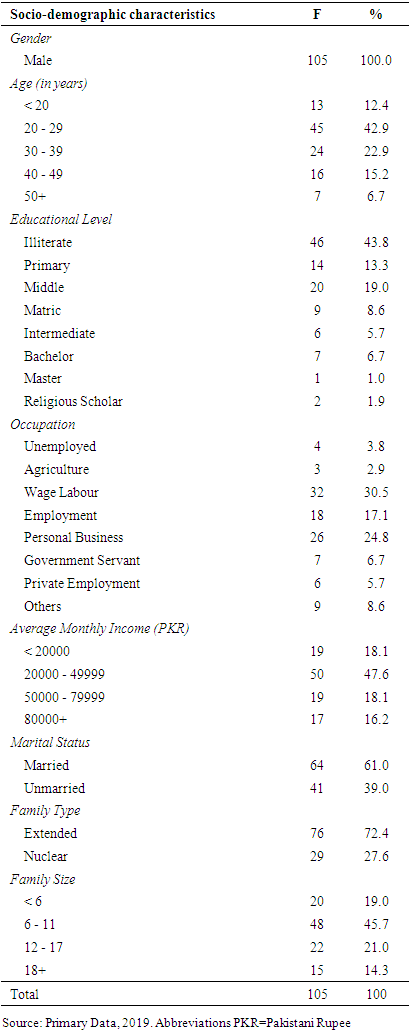
- Results in Table 1 explain the socio-demographic characteristics of the detainees in police stations in Quetta City. Majority of the detainees were involved in the delinquency in the age group of 20-29 years (42.9%). It was followed by the age group of 30-39 years (22.9%). The age group of 40-49 years detained in the police stations were 15.2%. The age groups of < 20 years and > 50 years detained in the police stations were 12.4% and 6.7% respectively. Most of the detainees were illiterate (43.8%). The second highest number of detainees were 19.0%, who's education level was only middle. While 13.3% of the detained persons had primary level. The % age of matriculates was 8.6% and about 5.7% were intermediate. Graduates and post graduates were 6.7% and 1.0% respectively, while 1.9% of the detainees were religious scholars. Occupationally, the share of wage labours was 30.5% and followed by personal business with 24.8% respondents. The employed detainees were 17.1%. The remaining detainees were in different categories like, others (8.6%), Government servants (6.7%), private servants (5.7%), unemployed (3.8%) and agriculture (2.9%). The average monthly income groups of detainees were < 20000 PKR (18.1%), 20000-49999 PKR (47.6%), 50000-79999 PKR (18.1%) and >80000 PKR (16.2%). Of the detainees, 72.4% belonged to the extended and 27.6% to the nuclear family. Marital status of the delinquents showed that 61.0% of detainees were married and 39% unmarried%. The delinquents by family size showed, in the < 6 (19.0%), 6-11 (45.7%), 12-17 (21.0%) and >18 was (14.3%).
|
3.2. Distribution of the Delinquents at Police Station Level
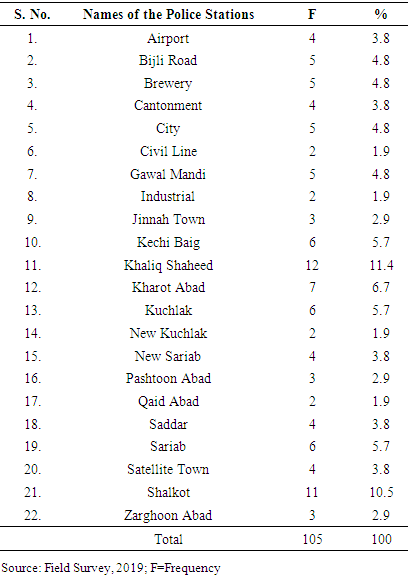
- The table shows the distribution of detainees in the different police stations of Quetta city. The maximum number of detainees is twelve and eleven in the Khaliq Shaheed and Shalkot police stations respectively. It is followed by seven detainees in the Kharot Abad police station and the next lower number of detainees is six in the Sariab, Kechi Baig and Kuchlak police stations. Khaliq Shaheed and Shalkot police stations are located in the outer most suburb of Quetta city. The settlements consist on mostly slums with high population growth and the dwellers are mostly uneducated and unemployed. While the number of detainees were 5 and <5 in the police stations located near to center and sub center of Quetta city except Pashtoonabad, Zarghoonabad and New Kuchlak police stations. The lowest number of detainees 2 was found in the Qaid Abad, New Kuchlak, Industrial and Civil Line police stations.
|
3.3. Province-Wise Distribution of Delinquents
- The result in the graph is about the province-wise affiliation of delinquents. Of the total, 91% of the detainees were dwellers of Balochistan province. It is followed by 3.8% of the detainees were the resident of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. The detainees related to Punjab province comprised 2.9% and only 1.9% of detainees were related to Sindh province.
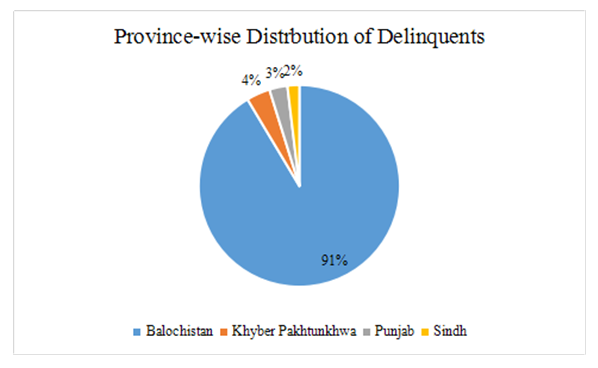 | Figure 2. Province-wise Distribution of Delinquents (Source: Field Survey, 2019.) |
3.4. Occurrence of Delinquent Behavior
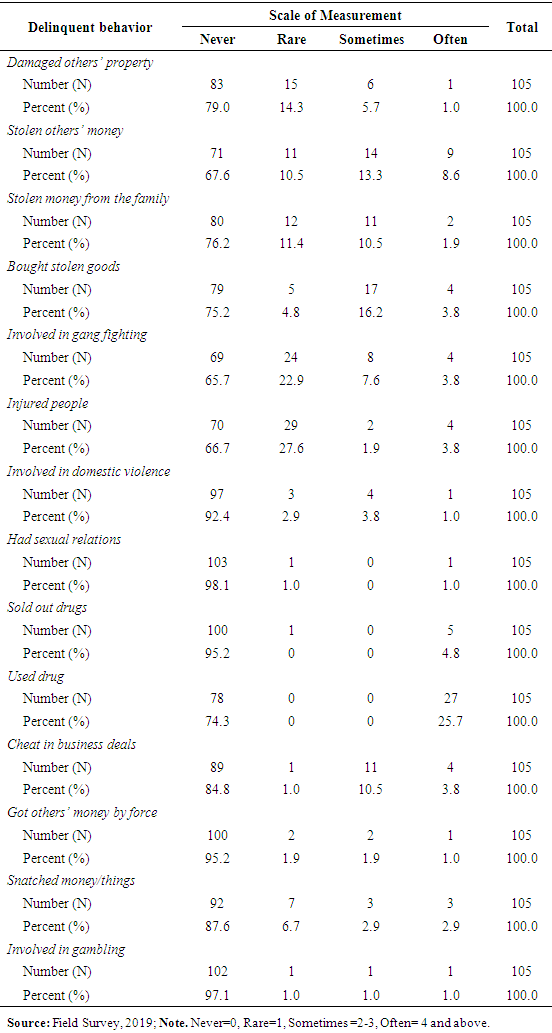
- The results in Table 3 show the occurrence of delinquent behaviour. Regarding the “damage to others property” 79% of the respondents were never involved into this crime. In the rare category the occurrence of this delinquent behaviour was 14.3%. The 5.7% delinquents showed their tendency in sometimes category. Only 1.0% of the respondents responded about the category “often”. About the delinquent behaviour “stolen others money” 67.6% respondents mentioned the “never occurred” category. The 10.5% of the delinquents shown their tendency toward the stolen others money in the category of “only once”. 13.3% of the delinquents were committed this crime sometimes. The 8.6% of the detainees had often committed the act of stolen others money. The delinquent behaviour regard to “stolen money from the family” showed that 76.2% never did it and 11.4% had committed this “only once.” About 102% and 2% reported for “sometimes” and “often” respectively. For the delinquent behaviour “bought stolen goods” about 75.2% reported that they never committed this crime. The 4.8% of the detainees had committed this crime only once. About 16.2% of the detainees committed this act sometimes and 3.8% of the detainees committed this crime “very often”. About the delinquent behaviour regarding “involved in gang fighting”, 65.5% never committed this crime and 22.9% had committed only once. About 7.6% and 3.8% respondents reported that they committed it sometimes and often respectively. Regarding the “injured people” about 66.7% of the respondents were never involved in this crime. In the rare category the occurrence of this delinquent behaviour About 22.9% respondents reported that they rarely committed this crime. The 7.6% delinquents were showed their tendency in “sometimes” category. Only 3.8% respondents reported that they committed this crime very often. About the delinquent behaviour “involved in domestic violence” 92.4% reported that they never committed this crime. The 2.9% of the detainees had committed this act only once. 3.8% of the detainees had committed this act sometimes. Only 1.0% of the detainees had committed this crime very often. About the delinquent behaviour “sexual relations” almost 98% respondents reported that they never committed this crime and 1.0% respondents reported that they committed it only once. About 1.0% respondents committed it very often. With regard to the “sold-out drugs” about 95.2% respondents reported that they were never involved in this crime. While 4.8% of the detainees reported that they committed this crime very often. Regarding “used drugs” about 74.3% of the respondents reported that they were never involved into this crime. While 25.7% of the detainees reported that they committed this crime very often.
|
3.5. Types and Ranking of Delinquent Behaviour
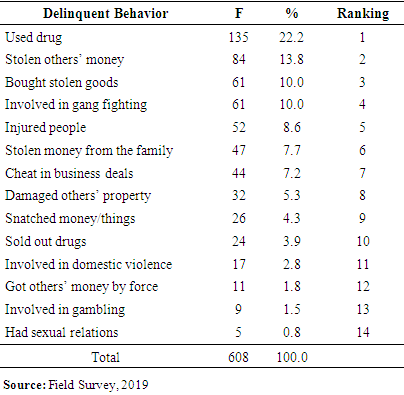
- Table 4 shows the types and ranking of delinquent behaviour. The highest crime committed by delinquents was “drug use” 22.2% ranked first. It is followed by the “stolen others money” with 13.8% on the second rank. Bought stolen goods and involving in gang fighting were placed in the third 10.0% and 4rth (10%) rank, respectively. It was followed by injured people 8.6%. The next high delinquent behaviour was stolen money from family members 7.7%, while cheat in business deals was 7.2%. Share of the damaged others property was 5.3% and snatched money and things was comprised 4.3%. Sold out drugs was the next delinquent behaviour occurred 3.9% and 2.8% was involved in domestic violence. It is followed by delinquent behaviour of got others money or things by force 1.8%. Involved in gambling was the second lowest occurred delinquent behaviour comprised 1.5%, while the lowest occurrence was of had sexual relations only 0.8%.
|
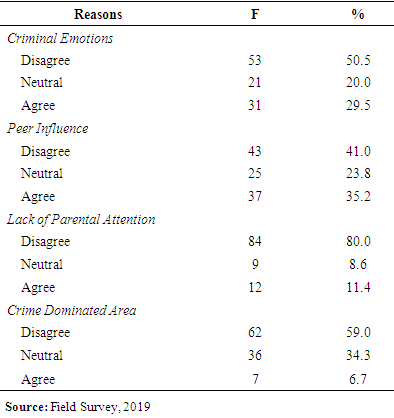
3.6. Reasons for Delinquent Behavior
- The effect of any factor was asked through the self-interview from the delinquents.The first question was asked “Do you agree that you committed crimes because you could not control your emotions?” The result of the response was 50.5% “disagree” with the statement. It means in crime committing time the respondents were in full sense and they committed crimes intentionally. The respondent who told that they had no control on their emotions and unintentionally crime had been committed by them was 29.5%, and the 20% response of detainees was neutral.The second question was asked “Do you agree that you committed a crime because of your peer group influence?” In this regard 41% of the delinquent denied the statement that no influence of the peer group was linked to their delinquent behavior. About 35.2% respondents admitted the friends influence in crime committing. 23.8% of the respondents neither disagreed nor agreed about friends’ motivation for crime. The third question was asked “Do you agree that you committed crimes because of lack of parental or family attention?” Only 11.4% showed their positive response about it and told that they committed crime because of the lack of parental attention, while 80.0% of the delinquent denied the statement. The remaining 8.6% of the respondents were neutral to the statement.The fourth question was asked “Do you agree that you committed crime because of living in a crime dominated area?” Majority (59.0%) respondents view was against the question and they denied involvement in crime due to it. The neutral response of the delinquent in this regard was 34.3% and only 6.7% respondents admitted and linked their criminal behavior to the crime dominated area.
|
4. Discussion
- The findings of this study revealed that several factors were responsible for criminal behavior among detainees at the police stations in Quetta city. The variables were chosen to explore the delinquent behaviour among alleged detainees at police stations and associated factors many of those are interrelated. It is very difficult to claim that the single variable caused the delinquent behaviour, but the variables collectively influenced the behaviour of delinquents. The findings show that majority of the detainees were 20-29 years old, illiterate, employed, and belong to middle income profile of the society. Moreover, they were married and living in extended family system with a family size of 6-11 persons. It is obvious that majority of youth committed crimes. The higher rate of involvement in crimes is connected with the illiteracy of the delinquents. Marriage is an important factor in the understanding of a person's most near and interaction with life. Any sense of failure, frustration, or victimization on this front may provoke unusual behavior. This shows that role of education has significant effect on the behaviour of people. Education originates sense of responsibility, keep individuals away from delinquency and polish them useful for society. Another significant finding of this study is that the delinquents belong to extended families where they need to be the bread winner for the family. Therefore, their interaction with the outside people is more than the dependent members of the family. This could be the reason behind his involvement in criminal activities. The findings of current study are similar with those of (Panezai et al., 2019) who was found the majority of criminals were the part of medium to large family size (5-10) in Pakistan and same result was found by the Iranian researcher (Nourollah et al., 2015). The similar result was found by (Gupta et al.) that Majority of delinquents were in young age group 20 to 40 year and married. Most of the criminals were married, belonged to 21–30 age group and were presently unemployed, educated to some extent, and possessing lower socioeconomic status (Aggarwal et al., 2015). Another research study supports the findings of author that the large family size and low income were responsible for delinquency (Mahmood & Cheema, 2008). The research work of (Haider & Mahsud, 2010) and (Mohseni et al., 2019) also found that lack of education was an effective factor of delinquent behaviour. Therefore, it is mandatory that preventive measures should be taken by the government, policy makers, social institutes and others to play their respective role in reducing illiteracy, poverty, and inequality and especially consider the problems of youth. The findings show that the number of detainees were detained in the suburbs police stations are more than the central police stations. It is seen that the dwellers of suburbs are living in poor conditions as compared to the main city area residents. They are living in slums with the shortage of schools, proper sanitation, and electricity and gas facilities. Earning means are less in such slums. These conditions push the people toward delinquency. The findings of the research study are in contrast to (Burnham et al., 2004) who found the violent crimes were less in suburbs than the central city. The reason of low crimes in the suburbs of developed countries is the proper construction, structure of suburbs and applied safety measure. They have been working on suburbs since almost three decades to bring the crime rate down. The mixing of commercial zones with residential area brought down the rate of crimes. (Anderson et al., 2013). The research study suggests that the government and relevant urban institutes should take the preventive measure with the mode like developed countries. The findings show that the majority of delinquents committed crimes intentionally and deliberately and peer group was the strong factor behind the criminal activities, while the parental attention, absence of self-control and living in crime dominated area was also show the positive links with criminal activities. They do not feel the fear of justice. It shows the weakness and flaws in the justice system of the country and also a question mark on law enforcing agencies. The role of parental attention and peer group cannot be ignored in the regard of delinquency. Those individuals who are not properly monitored by their parents in the adolescence period, they will prone to delinquency in young age. The findings of this research study are the same that the findings of (de Vries et al., 2016) who claimed the company of the deviant peers and low parental monitoring lead the individuals toward delinquent behaviour. The findings of (Khan, 2018) also support the work of author that individuals influenced by peers and adopted the criminal behaviours. The same result in the regard of self-control, delinquent behaviour and criminal activities were been contributed by the absence of self-control (Ellis et al., 2019). The findings suggests that the government, law enforcing agencies and other relevant departments keenly treat the delinquents who have no self-control and deliberately committed crimes with the psychological treatment. The parents should be attentive with their young and monitor their peer groups. The education department should be taken measures for the preventing of crime through lectures related the law and norms at school, college and university levels. The findings indicate the majority of the delinquents showed their tendency toward the nature of delinquency like, used drug and the stolen others money. Bought stolen goods, cheating in business deal, involved in gang fighting and injured people were also the delinquent behaviour of the respondents. The used drugs and theft are the highest-ranking delinquent behaviour find by the present study. Used drug is a multifaceted delinquent behaviour which is itself a crime and also a big factor to cause delinquency. From the findings of this study, it is evident that the drug users committed crimes like theft, fighting and injured people. The result of the present study similar to (Nourollah et al., 2015) who found the highest rank of delinquent behaviour was theft, while the 2nd ranked was used drugs. Almost the same result regarded to Pakistani delinquent behaviour that smoking cigarette, used drug, damage property and stolen money is given (Panezai et al., 2019). Drug users usually are jobless or engage in low-income jobs. Thus, to fill their drug addiction they commit crimes. Fighting and injured individuals are common in our society due to low tolerance for others. The delinquents with the nature of offence cheating in business deal are common in the centre of city, because most of the business dealing occurred in the city central commercial area. Illiteracy, poverty, absence of jobs leads the individuals toward delinquency. The findings suggest that the education should be provided to the poor. The electronic media should be on air the reformative programs for youth. The government should be taken steps for poverty alleviation.
5. Conclusions
- This study aimed to to explore the delinquent behavior among detainees and associated causes in Quetta city of Balochistan province. The findings of this study revealed that majority of the criminals were illiterate, young, and married. Drug use was the most committed crime. Moreover, this was also noted that they had committed crime for the first time. The major causes reported by the delinquents included having criminal emotions, peer influence, lack of parental attention and living in crime dominated area. This study concluded that poor educational background had strong association with the criminal behavior. The criminal behavior is triggered by criminal emotions, peer influence and lack of parental attention. The findings imply that education together with parental supervision can plan an important role in reducing the criminal offenses by youth. Thuse, parents must monitor the activities of their family members. Moreover, policymakers should ensure that each child have access to free and mandatory education in order to nourish the youth as law abiding citizens. The law enforcement agencies and anti-narcotics department should focus on ceasing to exist the drugs in the city in order to save the general public, particularly the vulnerable adolescents.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors acknowledge the Superintendent of Police Quetta for granting permission to conducted survey for this study. We are also thankful to Mr. Abdul Basit, GIS Specialist, who created the map of police stations in Quetta city.
Declarations
- Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. Ethical considerations: The confidentially of the detainees were ensured.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML