-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Sociological Research
p-ISSN: 2166-5443 e-ISSN: 2166-5451
2016; 6(4): 99-110
doi:10.5923/j.sociology.20160604.02

Qatar University Campus: Built Form, Culture and Livability
Shiney Rachel Rajan , Abdulla Al Nuaimi , Raffaello Furlan
College of Engineering, Department of Architecture and Urban Planning, Qatar University, Doha, State of Qatar
Correspondence to: Raffaello Furlan , College of Engineering, Department of Architecture and Urban Planning, Qatar University, Doha, State of Qatar.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Since the 1940s discovery of oil, the State of Qatar has experienced a rapid growth, which radically influenced the country’s physical, economic, cultural and demographical status. Qatar became an independent state in 1977, after the end of the British rule. This paved the way for education: within the same year, the national academic institution, Qatar University, was established to allow Qatari students to study in their home country. In turn, in the past two decades, the State of Qatar has become highly competitive in the fields of construction, technology and education. The aim of this paper is exploring how and the extent to which the built form of Qatar University’s campus (1) encourages the formation of enhanced levels of social and community interactions (i.e., social life) and (2) can be implemented in order to further enhance social interactions and/or livability. The study investigates the extent to which the public realm of the campus can be revitalized in order to enhance students’ levels of social interactions. In order to reply to the main question, the system and setting of activities performed by students at Qatar University is explored and analyzed, through data obtained from (A) a survey, (B) students’ interviews, and (C) visual material. The analysis indicates that the selected public open space around the campus should be implemented in order to encourage social activities and enhance livability in accordance with the preservation of the users’ cultural identity.
Keywords: Qatar University, Sustainable Urbanism, Human Behavior, Social Activities
Cite this paper: Shiney Rachel Rajan , Abdulla Al Nuaimi , Raffaello Furlan , Qatar University Campus: Built Form, Culture and Livability, American Journal of Sociological Research, Vol. 6 No. 4, 2016, pp. 99-110. doi: 10.5923/j.sociology.20160604.02.
Article Outline
1. Background
- The urban planning process of Doha, the capital city of Qatar, began in the 1970s, when several multi-national consultancies started developing a master-plan guiding the urban development of the State. The first master-plan was designed and developed in 1974 by the British consultant Llewelyn Davis, who worked within the Ministry of Municipal Affairs and Agriculture. The following year, the Ministry commissioned the American planning consultancy William L. Pereira Associates to develop a new master-plan for the Northern District of Doha, also known as the West Bay district. It was in the Northern District of Doha that the development of Qatar University was formulated (Rizzo, 2014). Planning a new academic institution for the State of Qatar included the participation of UNESCO, who conducted a preliminary study to foresee the conception of a higher education system with supporting physical facilities for the State. This resulted in the design of the campus of Qatar University under the guidance of the late Kamal El-Kafrawi, a Paris based Egyptian architect who was asked to propose a master plan of the campus with a distinctive style. Theuniversity grounds featured octagonal shaped classrooms topped by wind towers or wind catchers also known in Arabic as “Badgir” (Fromherz, 2012; Jodidio & Halbe, 2015; Salama, 2007). The inauguration of the campus occurred in 1985, when less than 1000 students were enrolled: the university-campus received much appreciation for its design and architectural features. The campus, located 7km North of Doha and 2km from the Gulf shore, is situated on an elevated site. Currently the campus accommodates a central library, research complex and stadium along with the different college buildings, student centers, and recreational facilities, which include food courts, health care facilities and several central service units (Jodidio & Halbe, 2015).The primary concept was to position academic buildings along the edge of the ring-roads that served the campus with sports and ancillary facilities on the exterior. The early buildings of the campus site were planned in a low-rise modular style constructed out of high quality concrete. The use of repetitive pre-cast structural elements could be seen as a fundamental concept of the campus. The academic buildings were based on octagonal grid layout of 8x4m in width and squares with sides of 3×5m. The modular pattern was repetitive and made using the octagons which were adjacent to each other and connected to the squares as seen in the plan (Figure 1). While examining the plan of the octagonal classroom module it is seen that each of the units is connected to two lobby spaces. The functions of these lobby spaces could vary where one can be used as an entrance lobby and the other as a transition space between classrooms or as an additional classroom space, while the other lobby acts as a source of natural light, which could also function as a meeting place (Fromherz, 2012; Jodidio & Halbe, 2015).
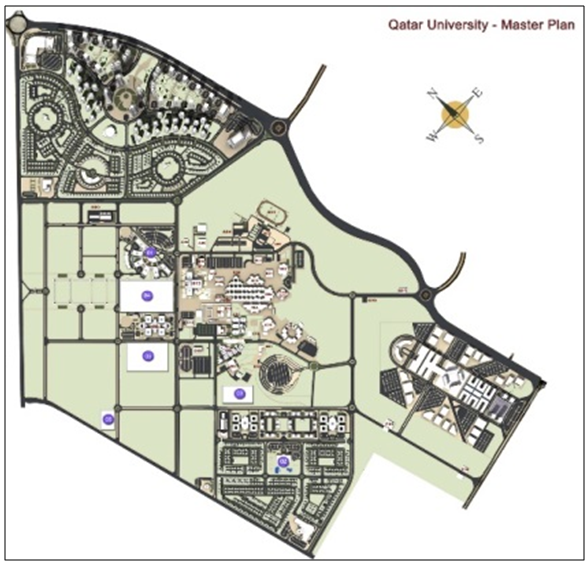 | Figure 1. The master plan of Qatar University campus |
 | Figure 2. A view of one of the educational clusters in Qatar University Campus |
 | Figure 3. Educational/Academic Life of a Student |
 | Figure 4. Expressions of the Built Environment |
2. Methodology and Data Collection
- In order to investigate the extent to which livability and sustainable urbanism can be implemented within the physical setting of Qatar University’s Female Student’s facilities, oral data was collected from students of the College of Engineering through a survey. The oral survey was structured into three parts. The first part aimed at identifying whether students preferred outdoor to indoor spaces and the location of such spaces. Among 40 students who participated in the initial part of the survey, 26 students preferred 6 outside locations. These locations, listed in order of most desired, are the Engineering Building and Female Building space, the Engineering Building and Food Court space, the Engineering Building and Activity Building space, the Science Building and Female Building space, the Science Building and Activity Building space, and the Engineering Building and Sharia Building space. Namely, the Engineering Building and Female Building space were selected by 13 students; the Engineering Building and Food Court Space was selected by 11 students; the Engineering Building and Activity Building space was selected by 8 students; the Science Building and Female Building space was selected by 8 students; the Science Building and Activity Building space was selected by 5 students; and the Engineering Building and Sharia Building space was selected by 3 students (Figure 5 and Figure 6).
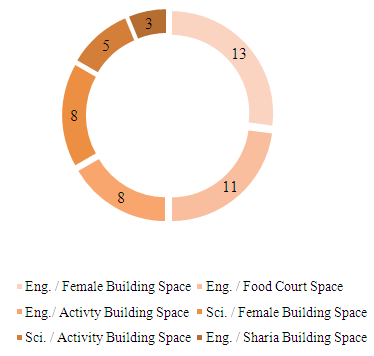 | Figure 5. Selection of Spaces by students |
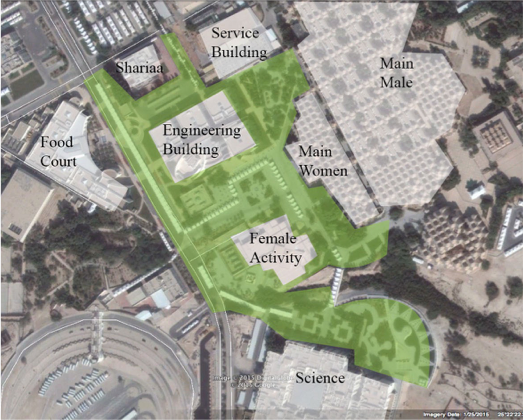 | Figure 6. Female Campus Map |
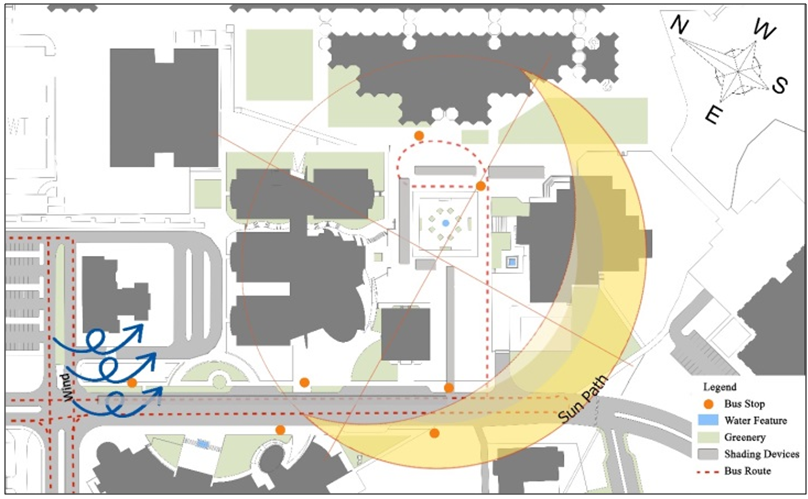 | Figure 7. Female Campus Site Analysis |
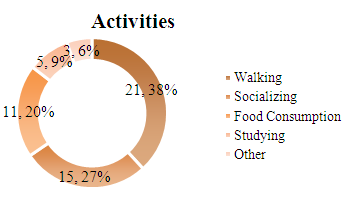 | Figure 8. Survey Results for different activities |
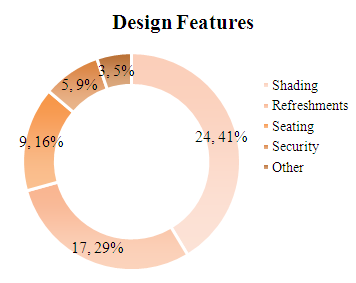 | Figure 9. Survey Results for different design features |
3. Findings
- The findings, revealed thought the analysis of the collected oral data, are structured into 3 locations, as selected by the selected students-participants. Location 1The first listed area is represented by the Engineering Building, the Food Court, the Engineering Building and the Sharia Building area (Figure 10). Regarding size, this is the largest outdoor space on the Female campus. This area, the main social hub for the students, is of high importance because there are busses passing by the buildings and dropping students. This area also serves as a main connection to the food court building.
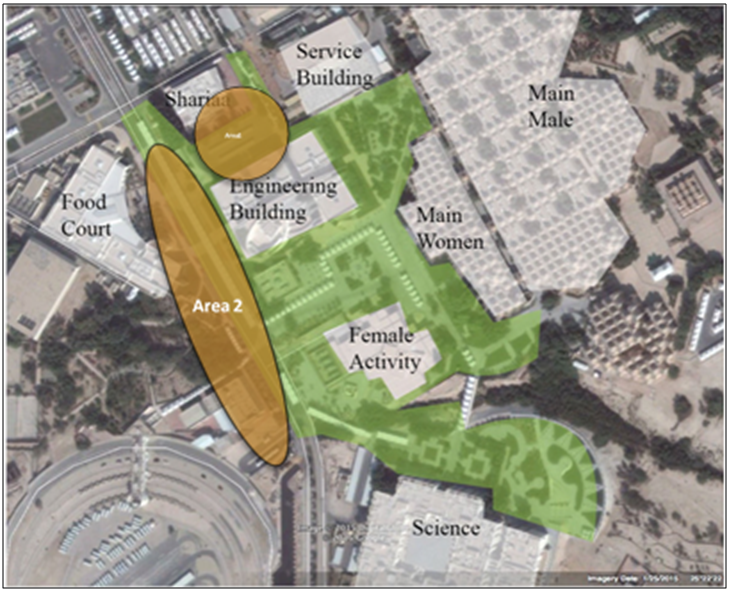 | Figure 10. Location 1 Map |
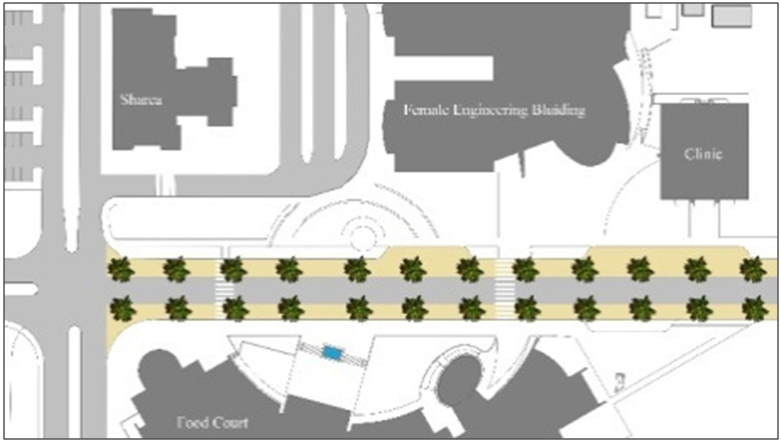 | Figure 11. Proposed Architectural Design Solutions in plan |
 | Figure 12. Proposed Architectural Design Solutions |
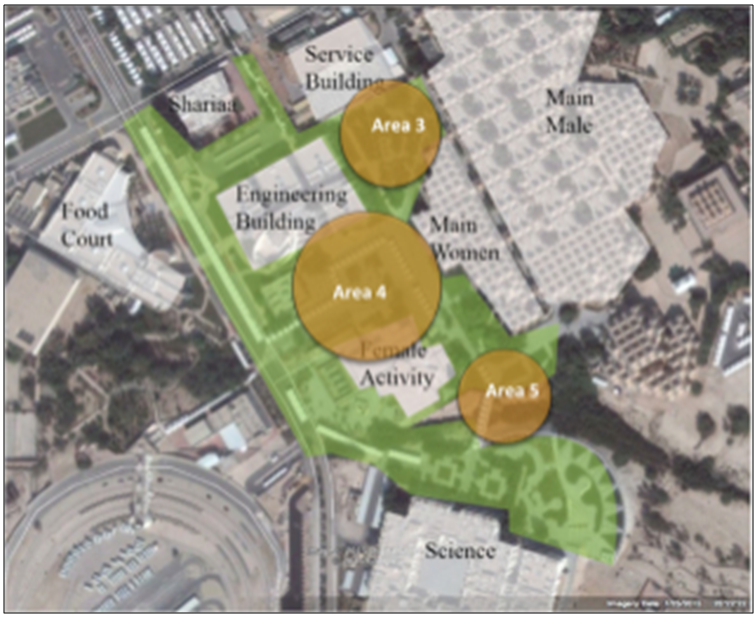 | Figure 13. Location 2 Map |
 | Figure 14. Proposed Plaza before Architectural Design intervention |
 | Figure 15. Proposed design features in the plaza after Architectural Design intervention |
 | Figure 16. Students utilizing the shaded area between buildings for eating/relaxation activities |
 | Figure 17. Students seeking for outdoor shaded areas of the plaza for reading/studying activities |
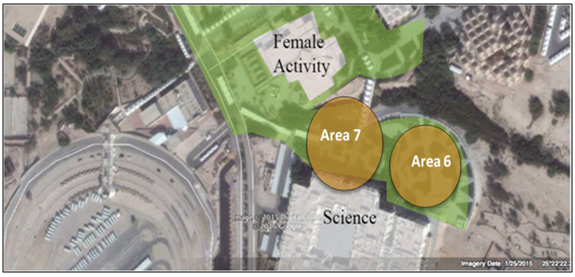 | Figure 18. Location 3 Map |
 | Figure 19. Exposed Walkway of the Women’s Engineering Building |
 | Figure 20. Exposed Walkway of the Women’s Engineering Building |
 | Figure 21. Exposed Plaza in front of Female Engineering Building |
 | Figure 22. Shading devices for walkway to the Sharia Parking |
 | Figure 23. Proposed Plaza before Architectural Design intervention |
 | Figure 24. Proposed design features in the plaza after Architectural Design intervention |
4. Conclusions
- Qatar University campus has evolved in the past decades. The campus, designed with a peculiar overriding building style, has acquired its own identity and character: the campus is the National ‘academic crossroads’ where students from different multi-disciplinary schools meet and share views. Its character is set by the density, proportion, materials, the traditional appearance of its buildings and interconnecting open spaces.This paper discusses how to implement the campus’s physical setting of Qatar University in order to enhance livability. It explores the perception of students of the spatial form of the campus, highlighting the extent to which open areas between various buildings should be revitalized and/or implemented. The findings revealed in this study highlight the importance of actively involving students into the design of the campus: their think about should therefore be integrated into the campus design process and contribute to set guiding principles and recommendations for future development. Namely, within the analyzed areas, students highlighted the criteria with which to define a strategy for the implementation of the selected areas and/or for creating livable public-open environments. Namely, students participating in the survey stressed that an addition of sun-shading devices, seating benches, trees and green areas, water features and kiosks/cafes would severely contribute to enhancing livability, to encourage students’ social activities and to create vibrant recreational spaces, which are currently under-utilized or mainly utilized as transiting pathways, due to their low level of livability.Also, buildings and surrounding revitalized open areas can contribute to creating an environment enhancing intellectual and social exchange among diverse people, belonging to different backgrounds and culture. It is the physical character and quality of the campus, defined by both its facilities and its open spaces, which have the potential for enhancing livability within the shared space of the campus. The sense of community can be promoted through the actively shared open spaces, the shaded walkways, green areas, courtyards and plazas, which can facilitate the enriching experience of both planned and accidental gathering. These public outdoor spaces should be designed with the purpose to enhance social and intellectual exchange, through casual encountering and conversation. In addition and significantly, the strategy for implementation of the outdoor areas and/or for enhancing livability within the campus should respect the traditional culture, which has to be maintained. In Qatar the culture understands privacy and segregation between males and females within public spaces. Privacy and/or segregation are principles which have been highly considered along with the design of Qatar University campus. Segregation between male and female has been around since the pre-Islamic era and is deeply rooted in Arabic and Islamic traditions. This ideal is held by both the students attending Qatar University and also by their families visiting the campus. The Qatari community tends to adhere to their traditional and cultural values, embedded in the way of life and/or culture. Therefore, the segregation between males and females represents a crucial aspect of public Qatari life and is visible within the community. The requirement of segregation within the campus contributes to the formation of a safe environment, where families feel comfortable and safe with the environment where their siblings spend years of their life to pursue an education. Also, as stated, students themselves belonging to an Islamic culture feel more comfortable when a cultural principle such as privacy and segregation is maintained within the physical environment. A physical environment where such cultural principle is maintained is preferred to environments where this principle is neglected. Therefore, the physical embedment of segregation is appraised by the student-community.This principle is deeply embedded within the past and current Qatari way of life and culture. The 2030 Qatari National Vision stresses this aspect under the term ‘Modernization and Preservation of Traditions’, highlighting the need for modernization while maintaining a cultural identity, which belongs to a community. Namely, QNV-2030 states that ‘Preservation of cultural traditions is a major challenge that confronts many societies in a rapidly globalizing and increasingly interconnected world. Qatar’s very rapid economic and population growth have created intense strains between the old and new in almost every aspect of life. Modern work patterns and pressures of competitiveness sometimes clash with traditional relationships based on trust and personal ties and create strains for family life. Moreover, the greater freedoms and wider choices that accompany economic and social progress pose a challenge to deep-rooted social values highly cherished by society’ (Planning, 2008). This represents a challenge not just to the State of Qatar, but around the GCC and Arab countries. In the past two decades, university campuses in the Middle East were designed to create a contemporary work of architecture, which would resonate with the global scientific community while being firmly rooted in the local Arabian culture. For example, Qatar Foundation campus is one of the prime and leading institutions of the State, which is primarily focusing on the founding vision of Her Excellency Mozah bint Nasser Al Missned, who specified education and human development as a pillar of their country’s vision with a goal of building a bridge between the present and the future. Traditional elements have merged with modern design to create a unique architectural concept. The campus provides a welcoming and comfortable environment that is conducive to study, learning, and communication and delivers an exterior and interior design that is memorable and worthy of the institution. Respecting the cultural and traditional values, male and female students have separate cafeterias, student lounges and recreational areas with swimming pools. The building design aims to inspire and encourage both the students and the local community to appreciate the innovative and pioneering design solutions that reinforce their enthusiasm for a sustainable development of Doha. The design approach in the institutions often enables the building to act as a learning resource in its own right, embracing the College students’ enthusiasm for protecting their environment. The complex design incorporates local culture, which is mixed with modern technology to create a unique, world-class facility for the students of Education City. Aiming at preserving the cultural and traditional principles embedded into the Islamic city, buildings are joined by streets to the main plaza. Another institution promoting values based on traditions within its campus is the internationally acclaimed ‘King Abdullah University of Science and Technology’ (KAUST) located in Ryad, the capital city of Saudi Arabia. The goal of the design of the campus was to respond to extremely hot arid climate, seeking inspiration from the traditional architecture of Middle Eastern regional context. Features that aid in the campus planning include the compactness of the buildings: this feature embedded into the traditional Arab city, where buildings are closely spaced, helps minimize the areas of the building façade that is exposed to the direct sunlight, thereby bringing in the cool breeze and naturally ventilating the spaces in-between. This feature also helps to temper the extreme micro-climate, which along with the outdoor walking is critical to foster outdoor activities and interactions. Another feature, often visible in Middle Eastern university campuses is the use of the traditional wind towers, which is one of the older passive ventilation strategies encouraging air flow into the pedestrian walkway. Courtyards connecting buildings often act as interactive and collaborative spaces. Mashrabiya helps to filter the light and create beautiful light and shade patterns. In conclusion, public open spaces among buildings at the Qatar University campus should be providing a livable and productive learning setting, which also contributes to establishing a strong bond between the user and the physical environment. The respect of cultural values, which influence the way of life and/or culture, contribute to significantly implement livability of the physical setting and namely to the enhancement of the users’ feeling of comfortability. This key-aspect should not be neglected.
5. Future Research Opportunities
- This current study was limited to an exploration of the link between the spatial configuration of specific and/or bounded public open spaces within Qatar University’s campus and students’ social interactions, in order to understand to which extent the physical setting of specific open spaces can be implemented and, therefore, contribute to enhancing social interactions among students. In addition to the limitation represented by a specified physical setting, the selected case study was also bounded by a limited number of students to be consulted. This suggests that the findings obtained through this exploration are related to a case study selected by restricted and manageable limits.Therefore, based on the findings revealed through this research study and on the limitations listed above, further studies investigating various public areas within the campus of Qatar University, and/or the physical setting of various campuses located in the Middle East, could be engaged to provide a deeper understanding of the sociological interconnections between space and social interactions, possible specific traits of socio-cultural factors and perspectives on gender in Islamic countries. In turn, this would contribute to shaping a comprehensive framework for the future development or implementation of the urban setting of Universities’ campuses in GCC.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors would like to acknowledge the support of Qatar University for creating an environment that encourages scientific research. This research study was developed as an assignment for the course ‘Engineering Skills and Ethics’ (GENG 107-Spring 2015) taught at the College of Engineering, Qatar University, by Dr Raffaello Furlan. The authors would like to acknowledge the effort of the contributors in this research study: the students from the College of Engineering of Qatar University, namely Ms Maryam Al Darwish, Ms Aisha Al Kuwari, Ms Fatma Almohammadi, who collected relevant visual data and cardinal documents for the purpose of this research study. Finally, the authors thank the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments on the earlier draft. Their observations contributed to an improvement of this paper. The authors are solely responsible for the statements made herein.
References
| [1] | Aasen, B. (2002). Urban Squares. Basel, Switzerland: Birkhauser. |
| [2] | Benninson, A. K., & Gascoigne, A. L. (2007). Cities in the Pre-Modent Islamic World - The Urban Impact of Religion, State and Society. US: Routledge. |
| [3] | Brown, L. J., Dixon, D., & Gillham, O. (2014). Urban Design for an Urban Century-Shaping More Liveable, Equitable, and Resilient Cities. New Jersey, USA: John Wiley & Sons. |
| [4] | Carmona, M., Tiesdell, S., Heath, T., & Oc, T. (2010). Public Places Urban Spaces-The Dimension of Urban Design. New York, USA: Routledge. |
| [5] | Coulson, N. J. (1964). A History of Islamic Law. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press. |
| [6] | Day, K. (2003). New urbanism and the challenges of designing for diversity. Journal of Planning Education and Research, 23(1), 83-95. |
| [7] | Elsheshtawy, Y. (2004). Planning Middle Eastern Cities. An urban kaleidoscope in a globalizing world. London: Routledge. |
| [8] | Farr, D. (2008). Sustainable Urbanism - Urban Design with Nature. United States: Wiley. |
| [9] | Fromherz, A. (2012). Qatar: A Modern History. Washington, DC: Georgetown University Press. |
| [10] | Furlan, R. (2015). Liveability and Social Capital in West Bay, the New Business Precinct of Doha. Arts and Social Sciences Journal’, 6(3), 1-11. |
| [11] | Furlan, R. (2016a). Modern and Vernacular Settlements in Doha: An Urban Planning Strategy to Pursue Modernity and Consolidate Cultural identity. Arts and Social Sciences Journal, 5(2). |
| [12] | Furlan, R. (2016b). Urban Design and Livability: The Regeneration of the Corniche in Doha. American Journal of Environmental Engineering’, 10(2). |
| [13] | Furlan, R., Eissa, B., Awwad, R., & Awwaad, R. (2015). Neighborhoods and Social Interactions: The Case of Al-Najada Area in Doha. American Journal of Sociological Research, 5(4). |
| [14] | Furlan, R., & Faggion, L. (2015). The Souq Waqif Heritage Site in Doha: Spatial Form and Livability. American Journal of Environmental Engineering, 5(5), 146-160. |
| [15] | Furlan, R., Muneerudeen, A., & Khani, F. A. (2016). Urban Revitalization of Public Spaces in the Pearl in Qatar. American Journal of Sociological Research, 6(1), 1-9. |
| [16] | Furlan, R., N.Eiraibe, & AL-Malki, A. (2015). Exploration of Sustainable Urban Qualities of Al Saad Area in Doha. American Journal of Sociological Research, 5(4). |
| [17] | Furlan, R., Nafi, S., & Alattar, D. (2015). Urban Built Form of the Souq Waqif in Doha and User’s Social Engagement. American Journal of Sociological Research, 5(3), 73-88. |
| [18] | Givoni, B. (1989). Urban Design in Different Climates: World Metereological Organization Publication. |
| [19] | Jodidio, P., & Halbe, R. (2015). The New Architecture of Qatar. New York: Skira Rizzoli. |
| [20] | Kaspirin, R. (2011). Urban Design-The Composition of Complexity. New York, USA: Routledge. |
| [21] | Kent, S. (1984). Analyzing Activity Areas: An Ethnoarchaelogical Study of the Use of Space. Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press. |
| [22] | Kent, S. (1990). Domestic Architecture of the Use of Space: An Interdisciplinary Cross-Cultural Study. New York, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. |
| [23] | Kent, S. (1997). A Cross-cultural Study of Segmentation, Architecture, and the Use of Space. In S. Kent (Ed.), Domestic Architecture and the Use of Space: an Interdisciplinary Cross-cultural Study (pp. 127-152). New York, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. |
| [24] | Lang, J. (2005). Urban Design - A Typology of Procedures and Products. United States: Routledge. |
| [25] | Petruccioli, A. (2007). After Amnesia-Learning from the the Islamic Mediterranean Urban Fabric. Altamura Bari Italy: Grafica & Stampa. |
| [26] | Petruccioli, A., & Pirani, K. K. (2003). Understanding Islamic Architecture Routledge. |
| [27] | Planning, G. S. F. D. (2008). Qatar National Vision 2030. In QNV2030_English_v2.pdf (Ed.). |
| [28] | Rapoport, A. (1969). House, Form and Culture. New Jersey: Prentice-Hall. |
| [29] | Rapoport, A. (1982a). Housing and Identity. Cross-Cultural Perspectives. New York: Holmes & Meier Publishers. |
| [30] | Rapoport, A. (1982b). The Meaning of the Built Environment: A Nonverbal Communication Approach. Beverly Hills, California: Sage Publications. |
| [31] | Rapoport, A. (1984). Vernacular Architecture and the Cultural Determinants of Form. In A. D. King (Ed.), Buildings and Society: Essays on the Social Development of the Built Environment. London, Boston and Henley: Routledge & Kegan Paul. |
| [32] | Rapoport, A. (1997). Systems of Activities and Systems of Settings. In S. Kent (Ed.), Domestic Architecture and the Use of Space: an Interdisciplinary Cross-cultural Study (pp. 9-20). Cambridge: Cambridge Univeristy Press. |
| [33] | Rapoport, A. (2000). Culture and Built Form: a Reconsideration. In K. D. Moore (Ed.), Culture - Meaning - Architecture: Critical Reflections on the Work of Amos Rapoport. Brookfield: Ashgate Publishing Company. |
| [34] | Rizzo, A. (2014). Rapid Urban Development and National Master Planning in Arab Gulf Countries. Qatar as a Case Study. Cities, 39, 50-57. |
| [35] | Salama, A. M. (2007). Contemporary Qatari Architecture as an Open Textbook. Archnet-IJAR, International Journal of Architectural Research, 1(3), 112. |
| [36] | Saliba, R. (2015). Urban Design in the Arab World: Reconceptualizing Boundaries (Design and the Built Environment). US: Routledge. |
| [37] | Zyscovich, B., & Porter, D. R. (2008). Getting Real about Urbanism : Contextual Design for Cities. Washington: Urban Land Institute. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML