-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Sociological Research
p-ISSN: 2166-5443 e-ISSN: 2166-5451
2014; 4(2): 60-66
doi:10.5923/j.sociology.20140402.06
Analysis of Sendang Agropolitan Area Development, Tulungagung
Adi Prasetiya1, 2, Suyadi1, 3, Mohammad Bisri1, 4, Soemarno1, 5
1Environmental Science and Technology Graduate Program, University of Brawijaya, Indonesia
2Department of Revenue, Tulungagung Regency, East Java Province, Indonesia
3Department of Animal Husbandry, Faculty of Animal Husbandry, University of Brawijaya, Indonesia
4Department of Water Resource Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University of Brawijaya, Indonesia
5Department of Soil, Faculty of Agriculture, University of Brawijaya, Indonesia
Correspondence to: Adi Prasetiya, Environmental Science and Technology Graduate Program, University of Brawijaya, Indonesia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The purpose of this study is to analyze the development of Sendang Agropolitan Regency, Tulungagung, East Java. We also explain the strengths and weaknesses in the development of Sendang Agropolitan, to be a concern for Tulungagung Regency to follow up the issue. This study used analysis tools of Structural Equation Modeling (SEM). Data collected from respondent in Sendang Regency, Tulungagung. The results show the strong affecting factors are work ethic, the availability of natural resources, availability of facilities, social organizations (the network), and adequate number and variety of infrastructure and facilities to support system development and agribusiness. Otherwise, weak affecting factors are income/ productivity, the impact caused by the available natural resources, accessibility to facilities, regulations/norms and potential resources and the environment. The results of this study have empirically proved the basic framework on the theory of Agropolitan development which attempts to integrate human resource capability and utilization of natural resources by increasing its additional value and artificial resource (man-made capital) and social capital that will enhance the ability of the region in the implementation of development.
Keywords: Agropolitan, Human resources, Artificial resources, Social resources, Natural resources
Cite this paper: Adi Prasetiya, Suyadi, Mohammad Bisri, Soemarno, Analysis of Sendang Agropolitan Area Development, Tulungagung, American Journal of Sociological Research, Vol. 4 No. 2, 2014, pp. 60-66. doi: 10.5923/j.sociology.20140402.06.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Agropolitan development becomes crucial in the context of regional development, considering: (1) region and the sector were developed appropriate to the local uniqueness; (2) agropolitan area development improved the equity considering selected sectors are the base activities of community; (3) sustainability of regional and sectoral development becomes more certain due to the chosen sector has competitive advantage compared to others; (4) the determination of Agropolitan center related to the system of national provincial, and district centers, to create a harmonious and balanced regional development [1]. Agropolitan is a farming county that grew and developed as the system passes agribusiness and able to serve and support agricultural development activities (agribusiness) in surrounding area. Agropolitan is an integrated government program that is implemented across sectors between the Ministry of Agriculture, Ministry of Settlement and Regional Infrastructure, and the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Regional Autonomy. This program is intended to establish Agropolitan area that based on agribusiness of livestock, crops, food crops and horticulture [2].The successful of regional autonomy implementation is highly dependent on the ability of local finance, local human resources, and the regional ability to develop all potential within the autonomy region. Centralized and qualified human resources in large cities can be distributed to smaller regions in line with the implementation of regional autonomy, because the construction activities will be shifted from central to regional. Exploration of potential resource area is highly prioritized, with the aim to increase local revenue that is based on the principles of justice and independence that will ultimately improve the welfare of the community. Such efforts could be realized by combine the capabilities of human resources (human capital) and the use of natural resources (natural capital) to increase the additional value, artificial resource (man-made capital) and social capital that will enhance regional ability in the implementation of development. These four aspects of these resources will be optimized by concerning the empowerment efforts of local community to support rural financial market towards rural institutions strengthening [3].The gap between urban, rural areas and rural poverty has pushed development efforts in rural areas. Nevertheless, the development approach of rural areas often separated from the urban area. This has resulted in the development process, i.e. the urban bias of rural areas which was originally intended to improve the welfare of the rural population areas turned oppositely, rural potential in terms of human resources, nature, and even capital that flow into the urban area [4, 5, 6].The fact has been proved and aware us on the crucial strategic role of agricultural sector as a pillar or the main base of the national economy in the response against more severe crisis impacts. Smallholder agriculture sector as well as small and medium enterprises relatively resilient in the face of economic crisis and save our country from a more severe situation. Agriculture sector, small and medium enterprises relatively resilient against economic crisis and recover our country from a more severe situation. In addition to the partnership approach and network strengthening, it would also synergized with the approach of value improving on the production of small businesses which market or export-oriented appropriate to economic competence of local region [7].Agropolitan area is defined as an area of regional agribusiness or selected agricultural production centers, where there is a farm county (Agropolis) as the agribusiness service centers that serve, encourage and support agricultural area and surrounding areas development [8-12]. Region requirements to be developed into an Agropolitan area are: land resources with appropriate agro-climate to develop marketable agricultural commodities (prime commodity), has adequate agribusiness infrastructure (markets, financial institutions, institutional farmers, Integrated Counseling Center, technology application assessment, accessibility and agricultural inputs), have adequate social facilities (health centers, school, etc.), public facilities and have sufficient infrastructure (transport, electricity, telephone, water) and assured environmental sustainability [13].Terms and goal of Agropolitan is decentralization and autonomy authority in managing the resources of the region. It can be achieved if Agropolitan development coordinated vertically. On that basis, the district becomes the administrative thresholds for Agropolitan regional development. This is related to the tendency of public administration that realizes the greatest autonomy at Local Government District/City. Restrictions relations with outside Agropolitan territories can hamper Agropolitan economic sustainability. Horizontal coordination is needed between regions that have similar commodity/products with the same market area. For example, cooperation on the inter-regional production planning aligned the producers with consumers to create price stability. Selection of less prime commodity in an area also needed to minimize land reform. Commodity that has the potential and received more by public requires minimal rearrangement of agricultural lands. Equitable development and welfare improvement of the rural population is expected to be achieved by the Agropolitan development [14].Tulungagung is an East Java district that has predominately (42,44%) livelihood of farmers [15]. Supporting natural conditions and resource made agriculture as one of the primary commodity for regional economy and as the locomotive of development in Tulungagung. However, agricultural activities is limited to the cultivation and support of natural resource potential, and has not been followed up by processing and marketing. Potential agricultural sector in Tulungagung can be used as capital for regional development if managed optimally. Based on these considerations, Tulungagung government made agricultural sector as a focus in development. Agriculture developed further by predetermined Sendang District as Agropolitan area according to Regents Decree No. 524 of 2004. Agropolitan development concept is done through the efforts and consideration to create integration, not only in the cultivation (on farm) but also includes the development of agribusiness and supporting services. The activities that developed in this agropolitan area is in horticulture and dairy farm activities [16].Encountered problems in the development area of Tulungagung Agropolitan are the utilization of prime product that has distinguished competitiveness especially unoptimized agribusiness products. Strong commitment from the local government to build supporting facilities is to accelerate sustainable Agropolitan development. Agropolitan is the concept of rural development that integrates regional development and community empowerment. Less developed community empowerment is a development concept that promotes participation and partnerships that lead to the people development. Agropolitan based on the concept of regional development with emphasis on infrastructure, institutional, entrepreneurship, and capital development.In developing the Agropolitan concept in Tulungagung needed specific policies and strategies to strengthen the results of conducted research. Internal problems of Tulungagung Agropolitan include unoptimal supporting infrastructure, the government's role constrained to limited funding, and people in the region is not ready in developing Agropolitan region.This study aimed to analyse the Sendang Agropolitan development, Tulungagung reviewed from human resources, natural resources, artificial resources, facilities and infrastructure, and social resources as basic problems solving that exist in the site of Sendang Agropolitan development area.
2. Materials and Methods
- The study analyzes the development of Sendang, Tulungagung Agropolitan area by mixed method approach (quantitative and qualitative methods) [17]. Quantitative approach was done to obtain an overview of human resources, natural resources, artificial resources, facilities and infrastructure, and social resources in Sendang Agropolitan area. Otherwise, qualitative approach was done to gain description clarity of the resource on Sendang Agropolitan. Period of this study is four months (April-August 2013) by involving four field personnel to engage interview to respondents.
2.1. Study Area
- The site was selected by criterion-based selection method, i.e. selection based on specified criteria to ensure certain events actually attempted to achieve information completeness [18]. This study conducted in Sendang District, Tulungagung, East Java Province. We use Regent Decree No. 524 of 2004 as a basic consideration. The sample villages are Geger Village, Krosok Village and Tugu Village. Agropolitan activities in Sendang District are concentrated in these three villages (Fig. 1).
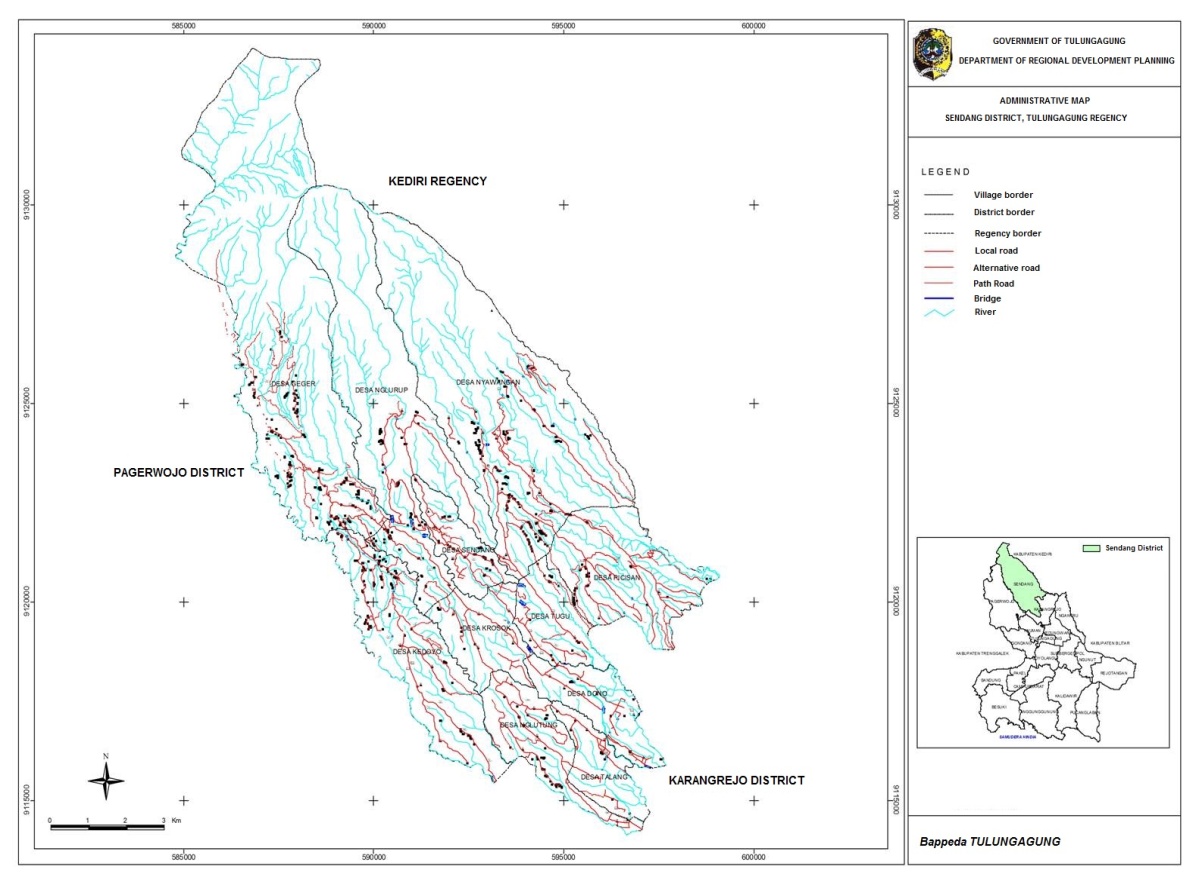 | Figure 1. Sendang Agropolitan Study Area [19] |
2.2. Data Collection
- Quantitative data obtained from households respondents in the study site by questionnaire. Otherwise, qualitative data were from three community leaders as the key person to the problems by interviews. Sampling technique (respondent) is a method to determine the sample size according to Solimun [20]. This study used 18 indicators with 90 respondents (village communities) as subjects. Total respondents from three villages are 270 respondents (villagers).
2.3. Data Analysis
- This study uses analysis of Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) to assess the models structurally and the effect of exogenous variables, i.e. human resources (X1), natural resources (X2), artificial/infrastructure resource (X3), and social resources (X4), to exogenous variables of Agropolitan Area Development (Y). We also tested the correlation between the four exogenous variables. All variables in this study are unobservable (latent variable), which mean the variable cannot be measured directly via the indicator, but it must be analyzed by Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA).Stages in the SEM analysis are [21, 22]: (1) the development of theory-based models. Development on a series theoretical model of scientific exploration was conducted by literature review to obtain a theoretical justification for the developed model; (2) development of flow charts. Theoretical models that have been built previously described in a path diagram, to make it show a clear causal relationships. In the diagram, the relationship between the constructs will be expressed with arrows. Straight arrows indicate a direct causal relationship between the constructions, while curved lines with arrows on each end showed inter-construction correlation. Measurement of the relationship between variables in SEM named structural models; (3) Goodness of Fit criteria evaluation; (4) assessment on the SEM model assumptions; and (5) assessment on the structural model.
3. Results and Discussion
- The results of the goodness of fit overall model of this study were described in Table 1. Goodness of Fit overall on almost all criteria showed poor models. However, the value of the Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA) and CMIN/DF for 0,067 and 1,888 have met the cut off value that is smaller than 0,08. Therefore, the model is suitable and feasible to use. The depiction of the model is showed in Fig. 2.
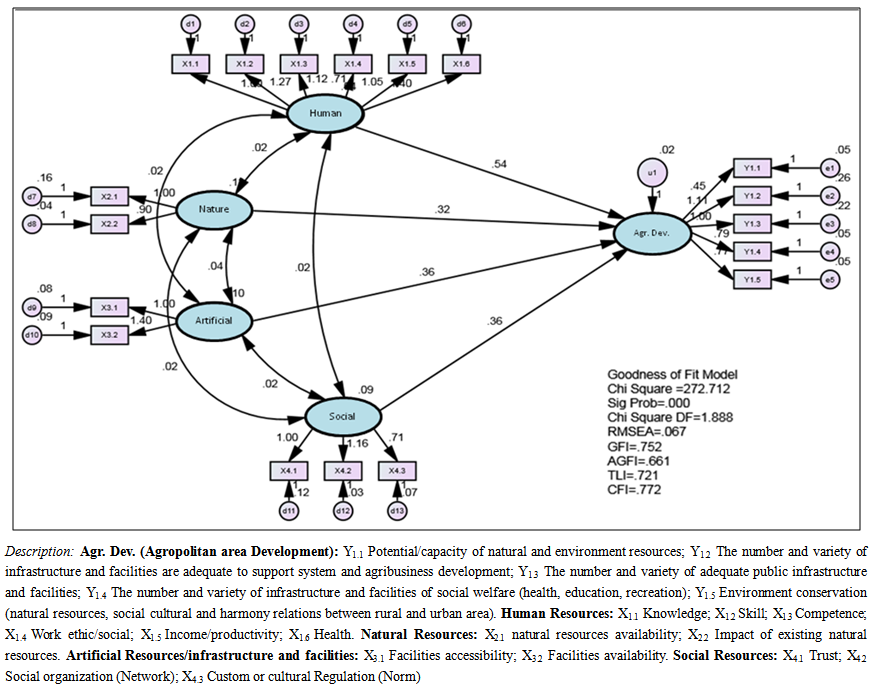 | Figure 2. Analysis of Sendang Agropolitan Development, Tulungagung |
4. Conclusions
- Human resource is the most powerful aspect in the development of Sendang Agropolitan, followed by artificial resources, social resources, and natural resource respectively. The strong indicators in development of Sendang Agropolitan are work ethic, availability of natural resources and facilities, social organizations (network) and the number and variety of adequate infrastructure and facilities to support the system and agribusiness development. Otherwise, the weak indicators are income/productivity, impacts caused by the available natural resources, accessibility to facilities, regulations/norms and potential resources and environment. Unoptimal utilization of natural and environment resources in the Sendang Agropolitan area is one causal factor that led to the less successful of Agropolitan development programs. Another causal factor is the lack effort of government in socialized the Sendang Agropolitan area to the local community.
References
| [1] | Djakapermana, R. D., 2003, Regional development principles, Ministry of Settlement and Regional Infrastructure, Jakarta. Jurnal Perencanaan Wilayah dan Kota, 16 (3). |
| [2] | Dardak, E., 2004, The role of Agropolitan in addressing the underlying cause of land degradation, Experts Meeting on Infrastructure Development in the Asia Pacific Region, Langkawi, 29-30 November. |
| [3] | Dardak, E., 2005, The development of agricultural-based small urban areas, National Spatial Planning Conference, Jakarta, 15 July. |
| [4] | Douglas, M., 1998, A regional network strategy for reciprocal rural-urban linkages, J. Agenda for Pol. Res., Special Issues with reference to Indonesia. |
| [5] | Douglas, W., 2000, The new importance of the periphery in emerging East Asian Cities: suburbia and peri-urbanization: The case of the extended Bangkok Region, East Asia and City Management Course. |
| [6] | Douglas, W., 2001, Regionalization and decentralization: implications for peri-urban East Asia, WB-ADB Asian Development Forum, Bangkok, Thailand. |
| [7] | Syahrani, and Husainie, H. A., 2001, The application of the Agropolitan and Agrobusiness in regional economy development, Fontir No. 33. |
| [8] | Friedmann, J., and Douglass, M., 1975, Agropolitan development: towards a new strategy of regional planning in Asia, Seminar on Industrialization Strategies and the Growth Pole Approach to Regional Planning and Development, The Asian Experience. |
| [9] | Bell, C., and Hazell, P., 1978, Measuring the indirect effects of an agricultural investment project on its surrounding region, World Bank- Mimco, Washington D.C. |
| [10] | Bromley, R., 1984, The urban road to rural development: reflections on USAID’s Urban Functions Approach, Kammeier, H. D., and Swan, P. J., (Eds), Equity with Growth? Planning Perspectives for Small Towns in Developing Countries, Asian Institute of Technology Press. |
| [11] | Broadway, M. J., 2000, Planning for change in small towns or trying to avoid the slaughterhouse blues, J. of Rural Stud., 16 (1). |
| [12] | Ministry of Agriculture, 2002, Agropolitan, Ministry of Agriculture, Jakarta. |
| [13] | Soenarno, 2002, Agropolitan area development in the context of regional development. |
| [14] | Suweda, I. W., 2011, Sustainable urban spatial, competitive and autonomy: a review, Jurnal Ilmiah Teknik Sipil, 15 (2). |
| [15] | Local Government of Tulungagung Regency, 2007, Tulungagung in Numbers, Government of Tulungagung. |
| [16] | Local Government of Tulungagung Regency, 2004, Medium Term Development Plan (RPJM) - Sendang Agropolitan Areas, Tulungagung Regency, 2007-2011. Government of Tulungagung Regency. |
| [17] | Creswell, J. W., 2011, Designing and conducting Mixed Methods research, University of Nebraska, Lincoln, Sage Publications, California. |
| [18] | Kanto, S., 2003, Sampling, validity and reliability in qualitative research, Bungin, B., (Ed.), Data Analysis of Qualitative Research, Understanding the Philosophical and Methodological towards Control Model Application, 1st Edition, PT Raja Grafindo Persada, Jakarta. |
| [19] | Department of Regional Development of Tulungagung, 2007, Sendang District, Government of Tulungagung. |
| [20] | Solimun, 2002, Multivariate analysis Structural Equation Modelling: Lisrel and Amos, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, University of Brawijaya. |
| [21] | Bollen, K. A., 1989, Structural Equation with latent’s variable, Wiley, New York. |
| [22] | Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., and Anderson, R. E., 2006, Multivariate Data Analysis, 6th Ed., New Jersey, Prentice Hall. |
| [23] | Smith, A. C., 1976, Regional analysis: Volume I Economic System, Department of Anthropology, Duke University, Durham. |
| [24] | Rondinelli, A. D., 1985, Applied methods of regional analysis – the spatial dimensions of development policy, Westview Press/Boulder. London. |
| [25] | Jong, W., 1988, The role of towns in rural development: a case study of Banjarnegara, Central Java, UGM Press, Yogyakarta. |
| [26] | Pradhan, K. P., 2003, Manual for urban rural linkage and rural development analysis, New Hira Books Enterprises, Kathmandu. |
| [27] | Rustiadi, E., 2004, A study on the development of model and typology for Agropolitan region, Ministry of Public Works, Jakarta. |
| [28] | Habibah, B. A., Hamzah, J., and Ratnawati, Y. S., 2011, The Agropolitan way of re-empowering the rural poor, World App. Sci. J., 13, Special Issue of Human Dimensions of Development. |
| [29] | Parmawati, R., Soemarno, Santoso B., and Nugroho I., 2012, Level of sustainable livelihood approach at central agriculture city of Batu, J. of Basic and App. Sci. Res., 2 (6). |
| [30] | Rodrigue, J. P., 2004, Transport geography: course notes, Hofstra University, Long Island. |
| [31] | Francois, P., 2003, Social capital and economic development, London: Routledge. |
| [32] | Salleh, I., 2004, Rural development and improving inequality, Embong, A. R., (Ed.), Globalization, Culture and Inequalities: In Honor of the Late Ishak Shari, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Bangi. |
| [33] | Saravanamuttu, J., and Loh, F. K. W., 2004, Development and democracy in Southeast Asia, Embong, A. R., (Ed.), Globalization, Culture and Inequalities: In Honor of the Late Ishak Shari, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Bangi. |
| [34] | Suprihanti, A., 2011, Impact of Agropolitan development on socio-economic of farmer in Sleman Agro Tourism District, Yogyakarta, Proceeding of International Seminar of Agro Tourism Development. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML