-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Science and Technology
p-ISSN: 2163-2669 e-ISSN: 2163-2677
2023; 13(2): 29-35
doi:10.5923/j.scit.20231302.04
Received: May 12, 2023; Accepted: May 31, 2023; Published: Jun. 2, 2023

Impact of Controls on Data Integrity and Information Systems
Sasidhar Duggineni
Compliance Manager at PPD part of Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA
Correspondence to: Sasidhar Duggineni , Compliance Manager at PPD part of Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Data has changed and revolutionized the world around us. With the amount of data use and its need increasing every day, there comes an essential responsibility and a requirement of maintaining the integrity and security of the data. Data integrity and data security are critical issues in today's digital and electronic world, as organizations rely increasingly on electronic data intake, storage, and transmission. Data integrity refers to the accuracy, reliability, and consistency of data over its lifecycle, while data security usually refers to the protection of data from unauthorized access or modification or deletion or theft. This research paper aims to explore the various measures and new improvisation techniques that organizations can take to enhance and retrospect the existing controls for ensuring the integrity and security of their data in accordance with their business, applicable legal and regulatory requirements. These measures may include but not limited to data encryption, access control, data backup and recovery, audit trails, data privacy, cybersecurity, legal and regulatory compliance. This research paper will discuss the benefits and challenges for implementing these measures, as well as best practices for achieving highest level of data integrity and security. Ultimately, the goal of this research is to provide organizations with a comprehensive control option for data integrity and delve into new improvisation controls and techniques in product development to pro-actively address data element risks in a more effective manner. We will also further look at the different ways data can be managed and secured by having adequate controls for data integrity, security, and confidentiality.
Keywords: Data Governance, Data Integrity, Regulatory Compliance, Data Management, Clinical Data Integrity
Cite this paper: Sasidhar Duggineni , Impact of Controls on Data Integrity and Information Systems, Science and Technology, Vol. 13 No. 2, 2023, pp. 29-35. doi: 10.5923/j.scit.20231302.04.
Article Outline
1. Background
- In the digital age, data has become an important asset for organizations of all sizes and industries. From financial records, customer information, intellectual property and proprietary research, data is essential for the operation and success of modern businesses. However, as organizations rely more heavily on electronic data storage and transmission, the risk of data loss or compromise increases exponentially. Hence, data integrity and data security evolved to become an integral aspect of data life cycle or system development life cycle (SDLC).Data integrity is elucidated as the accuracy, reliability, and consistency of data over its lifecycle. In simpler terms, data integrity ensures that data is not corrupted or modified in an unauthorized manner, either intentionally or unintentionally. These concepts are important in the context of data storage, data flow and data management because they ensure that data is protected from unauthorized access and modifications, and that it is accurate, untampered, and reliable. On the other hand, data security, refers to the protection of data from security exploits. It involves measures to prevent unauthorized parties from accessing, stealing, or altering data, as well as ensuring the confidentiality and privacy of sensitive information. Ensuring data integrity and security is crucial for the success and reputation of any organization. Data breaches can have serious consequences, including financial losses, damage to reputation, and legal liabilities. Therefore, it is essential for organizations to have robust measures in place to safeguard their data. In the context of data storage, data flow and data management, data security measures could include encryption, access controls, backup, and recovery procedures, while data integrity measures could include but not limited to checksums, version control, audit trails and log monitoring. Both data security and data integrity are essential for reliable and effective operation of systems and business critical processes that rely on data. Figure 1 and Figure 2 presents the data for Global number of data breaches with confirmed data loss from November 2020 to October 2021, by organization size and target industry respectively [4].
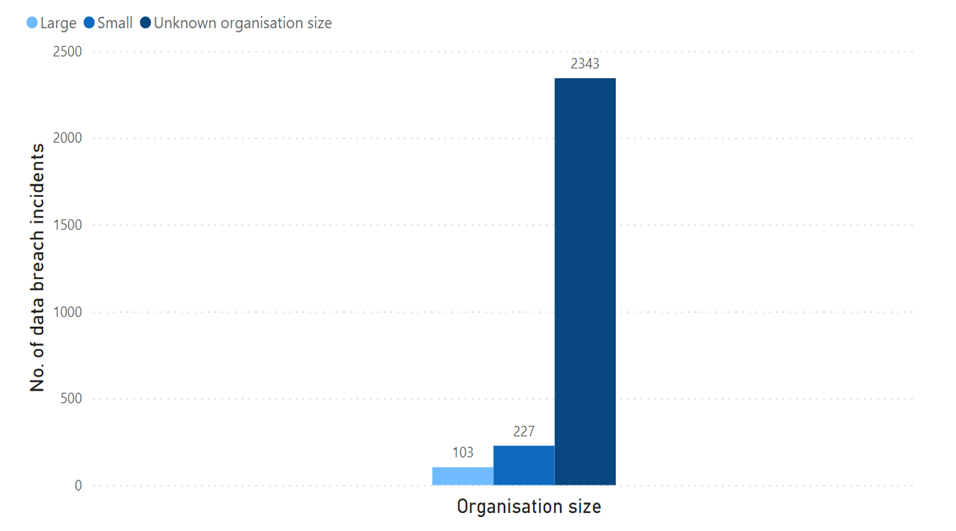 | Figure 1. No. of data breach incidents by organization size (November 2020 to October 2021) |
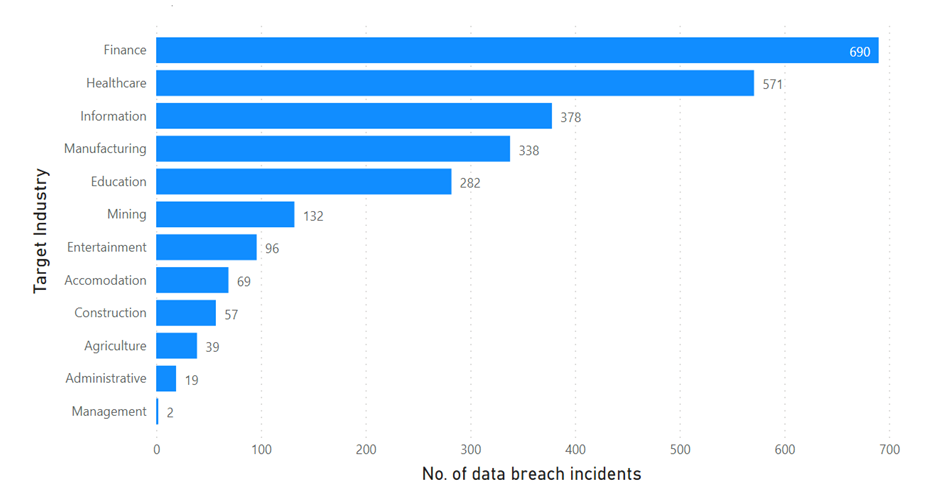 | Figure 2. No. of data breach incidents by industry (November 2020 to October 2021) |
2. Regulatory Implications for Data Integrity and Data Security
- Meeting Regulatory Expectations for Data Integrity is crucial for many local, national, and global organizations. These expectations are enforced in the form of regulations, rules, and laws. In United States, regulations meant to ensure data integrity in pharmaceutical industry are found in several parts of 21 Code of Federal Regulations and have been enforced by the US Food and Drug Administration Agency for decades. 21 CFR Part 11 went into effect in 1997 to extend data integrity regulations into the modern era with electronic records and electronic signatures. World Health Organization, European Medical Agency, and United Kingdom's Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency has introduced their own guidance’s for data integrity compliance. Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) is a US federal law which sets strict standards for safeguarding integrity of financial data. United States Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) provides federal protection for patient’s health data against misuse or exposure and requires technical and administrative controls to ensure compliance with HIPAA.
3. Methods (An Experimental Case Study)
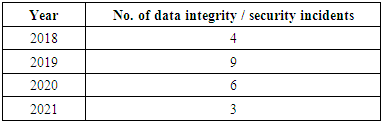
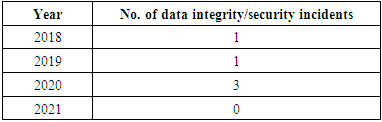
- There are several things to consider when evaluating the dangers to data security and data integrity in reference to any given system. This is explained with the help of an example, an ecommerce application called Order Management System (OMS) which entered development in the year 2018 to intake, store and manage sensitive customer data for a large retail company. The main business use case for the application is to track customer purchases, preferences and to provide personalized recommendations and offers.During the requirements gathering and analysis phase, the data security requirements were not adequately defined, analysed, and documented. Further, to trace the consequential data breach incidents the integrity measures such as providing administered access controls and maintaining audit trails were missing. The development team did not receive adequate clearly defined data integrity requirements from the business stakeholders and security standards during the code building phase did not adequately assess the potential risks to the customer data. This lack of proper requirements gathering, and analysis led to a design that did not consider the best practices of data security thoroughly. As a result, the data security and data integrity requirements were incomplete and did not adequately address the security controls needed for handling of the customer data. In addition, the application did not include adequate authentication and version controls to protect the customer data. During the coding phase, the developers left off important secure coding practices like encrypting data with modern cryptographic algorithms, password management, default deny, input validation and output encoding. Furthermore, the application was not tested comprehensively for data security vulnerabilities before being deployed to production as the testers and other stakeholders were not adequately trained on data security best practices. As a result, several vulnerabilities went undetected, proper security protocols were not followed while working with the customer data and potential vulnerabilities were not reported in a timely manner.When the application was deployed, it was discovered that the systems and infrastructure were not properly configured to secure the data. The customer account and financial data was not encrypted, and the insecure coding methods implemented by the developers made the platform powerless against the Packet Sniffing attacks during the data flow from the frontend to backend. The network was not properly segmented, and the database backups did not have limited access, making it easy for attackers to access the customer data. Consequently, there were multiple data breaches by the hackers over a period for which the stats can be viewed below in the Table 1. As the system was vulnerable to attacks by the hackers, it became an easy target once they could peak into the system and multiple attacks took place which led to breach of millions of user records which is described in the fig. 4 below.
4. Results
|
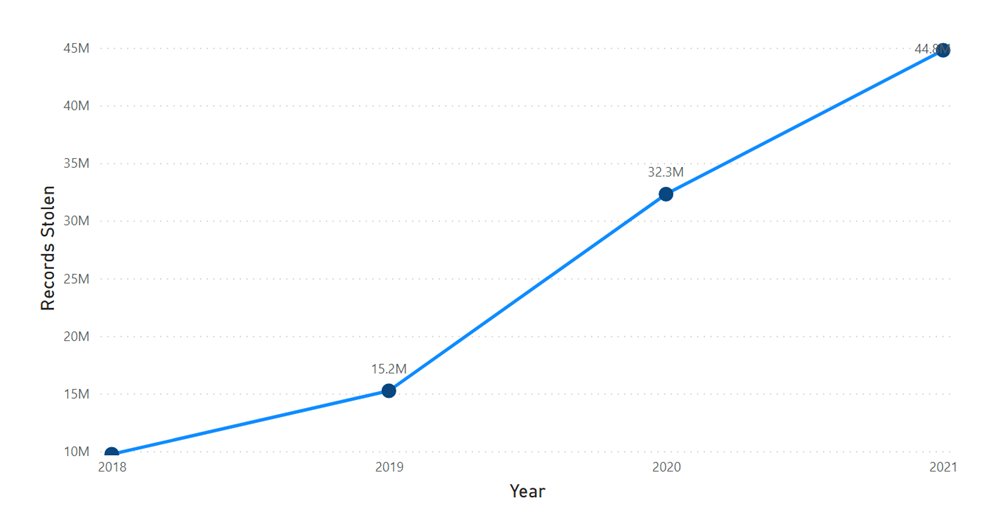 | Figure 3. No. of records stolen and corrupted yearly |
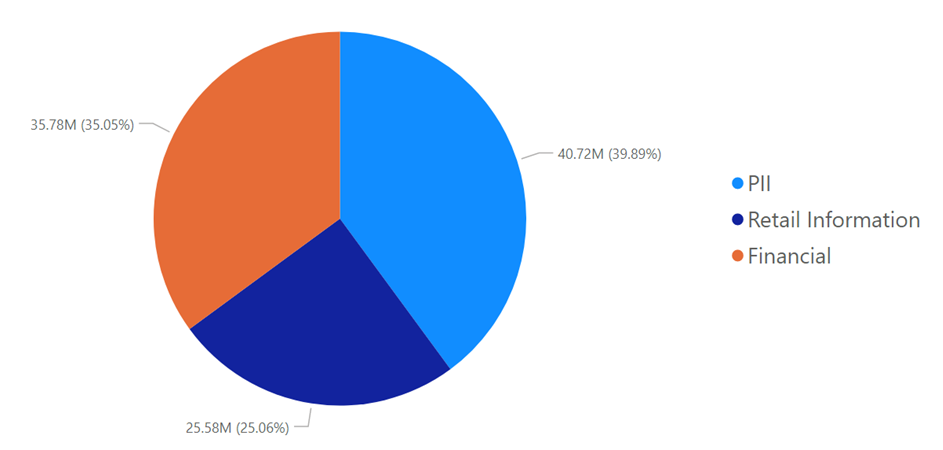 | Figure 4. No. of data records stolen for various data categories |
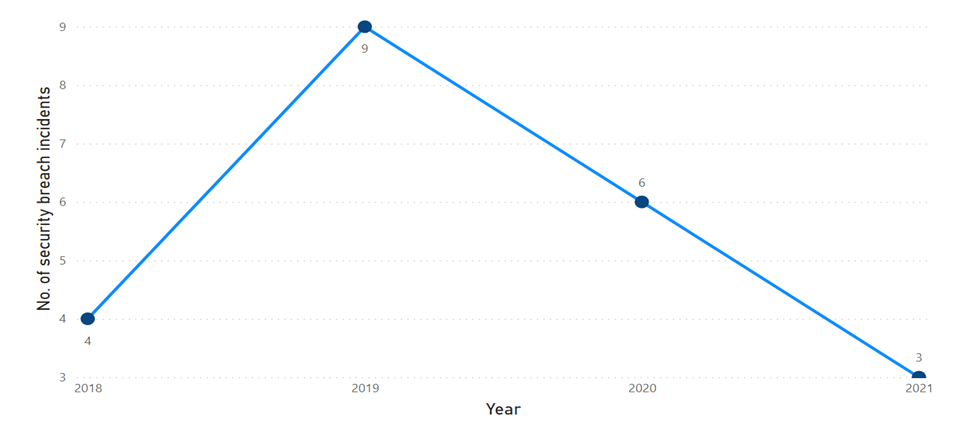 | Figure 5. No. of data breach incidents year wise |
|
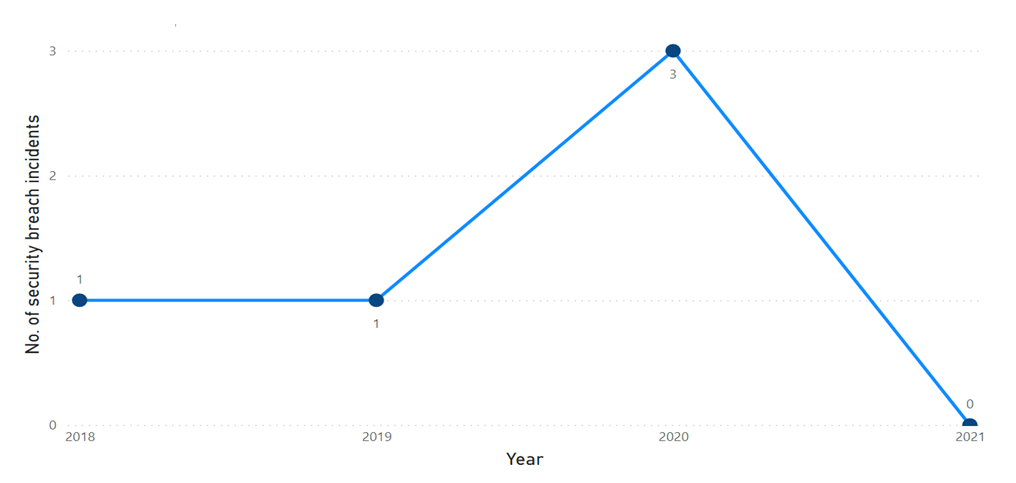 | Figure 6. No. of data breach incidents year wise |
|
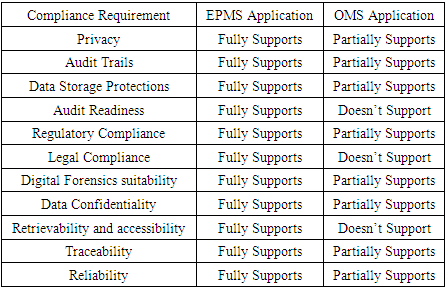
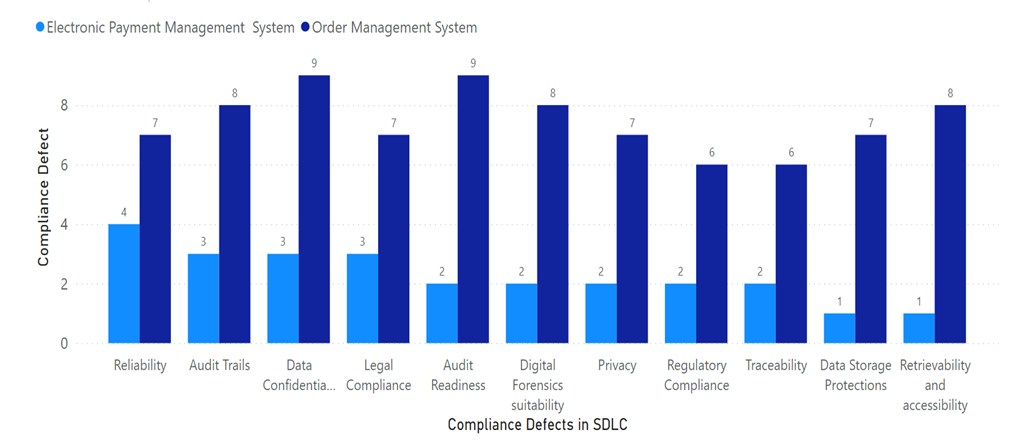 | Figure 7. Quantitative Analysis of Compliance State for both systems (EPMS in Light Blue and OMS in Dark Blue) |
5. Data Security and Data Integrity Measures
- By the above elaborated case studies, we have understood the significance of having systems which are robust in terms of securing the data and maintaining its integrity. And to build such systems there is a need to keep an eye on certain procedures which include conducting thorough assessment of data security risks at the beginning of the project, using secure coding practices, and testing techniques, properly configuring systems and infrastructure, and training developers and other stakeholders on best practices for assuring data integrity and data security. Below listed are some of the highly impactful measures for ensuring the integrity and security of data throughout its life cycle to keep it complete, accurate and safe. • Validating input dataBefore entering the servers or data storage system or database, input data should always be verified. It is the process of ensuring that data is accurate and trustable. Regardless of the source of the data, whether it is being ingested from internal systems, external sources, or end-users of an application, the data should be validated for accuracy and trustability.• Implementing access controlsData access permissions should be strictly controlled to guarantee that only individuals with the necessary authorizations have access to the data. Access should only be allowed to those who require it and adhere to a least privileged model of security. Data should be segregated to reduce the likelihood of unwanted access within different groups of users.• Keeping audit trailsMaintaining an automatic audit monitoring system that can identify the origin of data changes is essential. In the event of a data breach, the audit trail should also be able to identify the breach's origin and keep track of data events like creation, deletion, and updating as well as the moment they took place and the person who performed them.• Backing up dataA backup procedure makes sure that no data is lost in the event of a data loss. Hence, it is crucial to have regular, trustworthy, and timely backups of data systems which have controlled access to limited users. • Guiding the staffThe employees in an organization should be educated to always maintain the integrity of data in all work processes. It is important to build a culture of effective data management where team members are always encouraged to handle data in a way that assures the consistency and dependability of data and where individuals abide by the principles of data integrity.• Code development improvisationsSystem development can be reinforced by incorporating a variety of controls during various phases of system development. There is no one size fits all approach to accomplish this goal. Starting from the coding standards developers can be proactive and incorporate data integrity and data quality as a code flowing through the build and deploy processes. Examples of these controls include but not limited to ensuring code doesn’t carry integrity violations such as modules/libraries from untrusted sources, performing code reviews with targeted data integrity benchmarks, development of critical system functionalities with required attributes such as audit trails, traceability, authentication, enforcing integrity of values in database columns and rows, implementing logs and input data validations. During the stages of requirement gathering for the product, emphasis should be given on effective translation of data integrity requirements into formal product requirement documents for easy conveyance of data integrity expectations to product designers/developers from business user community.
6. Conclusions
- Throughout the course of this article, we have deeply investigated the possible causes of data integrity, data security breaches and the technical and procedural measures that can be followed and improvised to keep the user data confidential, accurate and reliable for businesses. By putting data security and integrity measures into place, a business can protect itself from data breaches, unnecessary financial expenditures, loss of public trust, potential threats to brand reputation, and loss of future revenue. A coordinated data security architecture also protects the organisation from the negative legal and regulatory repercussions associated with data breaches and guards against unwanted access to computers, laptops, smart devices, websites, networks, and devices.Hence, it is important for individuals and organizations to be fully cognizant of these ever-evolving types of threats and to take new improvised steps to better protect themselves and their data against them. All things considered; data security and integrity are a multidisciplinary team effort that should be tackled on a comprehensive scale.
Competing Interests
- Author reports no Competing Interests.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML