-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Science and Technology
p-ISSN: 2163-2669 e-ISSN: 2163-2677
2022; 12(1): 1-13
doi:10.5923/j.scit.20221201.01
Received: Jul. 22, 2022; Accepted: Aug. 10, 2022; Published: Aug. 15, 2022

The Role of ICT in the Effect of Statistical Capacity on Governance in Africa
Moïse Lawin, Arouna Ogouchôni Lekoyo
Ingenieur in Statistics and Economy, General Direction of Economy, Ministry of Economy and Finances, Cotonou, Benin
Correspondence to: Moïse Lawin, Ingenieur in Statistics and Economy, General Direction of Economy, Ministry of Economy and Finances, Cotonou, Benin.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Despite the established roles of governance and ICT in development, the literature on good governance has not yet given the link between quality official statistics (quality information) needed for good decision making and good governance a research interest worth examining. The objective of this study is to examine how ICT development complements the development of official statistics in influencing governance outcomes in 33 African countries for the period 2010-2019. Governance outcomes are measured by the Mo Ibrahim Foundation's Governance Index. The ICT Development Index is constructed using the principal component analysis method while the Statistical Capacity Index is derived from the World Bank database. The regression model used is the generalized method of moments (GMM). The results show that there is a causality between the capacity of African statistical offices to produce and make available the data and information needed for good decision-making and governance on the one hand, and a causality from ICT development to statistical capacity and from ICT development to governance on the other. The estimation results show that the net effect on governance is positive, significant and large when the development of official statistics is accompanied by the development of ICT. Overall, the results suggest that investments should be made in both ICT development and official statistics production for good decision making, better governance and socio-economic development in Africa.
Keywords: Governance, ICT development, Institutions, Official statistics, Africa
Cite this paper: Moïse Lawin, Arouna Ogouchôni Lekoyo, The Role of ICT in the Effect of Statistical Capacity on Governance in Africa, Science and Technology, Vol. 12 No. 1, 2022, pp. 1-13. doi: 10.5923/j.scit.20221201.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The issue of governance in developing countries, and in Africa in particular, has been the subject of growing interest since the years following independence. For a long time, governance referred to the action of piloting a tank or a ship, but today it appears to be a multidimensional concept whose definition is still not the subject of a consensus (Asongu, 2016). Since the early 1990s, the concept of governance has received renewed interest in the reports of international financial institutions such as the World Bank, the International Monetary Fund, and the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). In 1997, the UNDP defined governance as "the exercise of political, economic and administrative authority in the management of a country's affairs at all levels. It thus includes the complex mechanisms, processes, relationships and institutions through which citizens and groups articulate their interests, exercise their rights and meet their obligations, and to which they turn to resolve their differences. In 2007, the World Bank proposed a new definition of governance as the exercise of economic, political and administrative authority to manage a country's affairs. These different definitions evolve over time and undergo reformulations and improvements according to the orientations and new approaches that are taken to governance. A new definition by the World Bank (2017) gives governance "the process by which state and non-state actors interact to design and implement policies within a given set of formal and informal rules that shape and are shaped by power". Several researchers have subsequently revealed that the state of governance varies from region to region.The analyses of several researchers reveal that the state of governance varies from one region to another. Overall, the work highlights a critical state of governance in developing countries, particularly in Africa. The analyses of Gallego-álvarez et al. (2021) show that over the period 2002-2019, countries in Europe, Central Asia and North America achieved high values on all WGI (World Government Indicators) indicators, while countries in the Middle East, North and Sub-Saharan Africa, and South Asia score low on all indicators. Similarly, the Mo Ibrahim Foundation's 2020 report on the Ibrahim Index of African Governance, in which a country's governance performance is captured by four main components (i) Security and Rule of Law; (ii) Participation and Human Rights; (iii) Sustainable Economic Development; and (iv) Human Development, shows that on a scale of 0 to 100, Africa has remained globally below from 50 since 2010. These results raise questions about the policies or measures to be implemented to improve the state of governance in developing countries, particularly in Africa where the situation is the most deteriorated. They also demonstrate the major challenges to governance in Africa and the interest of researchers in looking at factors that promote good governance in developing countries.Thus, from the literary reflections, several questions emerge regarding the challenges and explanatory or enabling factors for development and good governance. The works of several authors, including (Thomas, 2010; Javaid, 2010; Wan, 2014; Dessie, 2019; Absadykov, 2020), have addressed the determinants of good governance. The Mo Ibrahim Foundation approaches governance along four dimensions: (i) Security and rule of law; (ii) Participation and human rights; (iii) Sustainable economic development; and (iv) Human development. According to the researchers, the factors or dimensions identified constitute levers on which countries can rely to achieve the sustainable development objectives. Beyond the above-mentioned factors whose improvement could contribute to the improvement of good governance, a lot of attention has been given over the last two decades to the link between modern information and communication technologies and good governance and development. The work of Pradhan, et al. (2022), Singh et al.) Chohan et al. (2022), Canares (2016), Alshammari et al. (2022). Raja et al. (2013). Zhang et al. (2022), Xiong et al. (2022), Maaten (2004), Inescu (2015), Scott et al. (2016), Rakauskienė et al. (2017), Asongu et al. (2019) link modern information and communication technologies to good governance and development.In addition to the above factors, thinking has very recently turned to the role that good quality official statistics play in decision-making and good governance policies. With this in mind, the Mo Ibrahim Foundation stated in its Africa 2020 Governance Report that improving the availability of official statistics on African countries is essential for achieving the Sustainable Development Goals. The foundation also stresses that African countries and their partners must redouble their efforts to fill the "data gap" that hinders monitoring of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and Agenda 2063. Other researchers also point out that the future of Africa's development depends on the ability of state institutions to mobilize the quality official statistics needed for sustainable development policymaking. International institutions, Lomell (2010), Devarajan (2013), Chen et al. (2013), Bedecarrats et al. (2016), Hudecek et al. (2019), Radermacher (2019) and many others find that the availability of good quality official statistics is a foundation or compass for the development, planning and implementation of sustainable development goals and good governance in Africa. Our research has shown that most of the fields of investigation that have assessed the role of ICT on governance have focused on correlation analyses that limit the scope of their results. For example, Snow (2009) finds a negative relationship between corruption and ICT, while Chohan et al. (2022) find a positive correlation between digital use and social exclusion in society. Porter al. (2016) highlight the significance of cell phone use by youth in improving practical and political harmony in a sample of selected African countries. Asongu (2019), although he establishes a positive link between ICT development and governance using a GMM model, his model does not take into account the important role, so emphasized by international institutions and researchers, of official statistics in the development and implementation of good governance policies. In other words, no study has so far made (i) an empirical link between the development of good quality official statistics (information quality) and good governance (ii) or given importance to the interaction between ICT and good quality official statistics (information quality) on good governance. Yet, the work of Alshammari et al. (2022) and Peter Keen (1978) cited by Qureshi, S. (2022) clearly show that the degree to which the information provided (accuracy, timeliness, and completeness of information) adequately meets the users' requirements is necessary for better organizational decision making. In addition to the above limitations, it is important to note that much of the literature is oriented toward specific surveys of target individuals in the countries considered in the analyses, which sometimes poses a problem in generalizing the conclusion of the studies.It is to overcome the above limitations of the literature that this study proposes to examine the effect of the interaction between ICT and the capacity of African countries to produce official statistics on governance. Specifically, this study asks two fundamental questions: do ICT and the capacity of African countries to produce quality statistical data cause good governance in Africa? and what is the effect of the interaction between ICT and the capacity of African countries to produce quality statistical data on good governance?In order to provide answers to the two questions posed, the paper is organized into five sections. The first section deals with the introduction which describes the context of the study. This is followed by a review of the literature and the methodologies used, namely the Granger causality testing procedure and the GMM model. The fourth section presents the results. The fifth section presents the conclusion and policy recommendations.
2. Literature Review
- Kraay et al (1999) define governance as the traditions and institutions by which authority is exercised in a country for the common.The determinants of governance have been the subject of research over the past three decades. Bekele's (2013) work on Kenya has highlighted factors such as transparency, accountability, rule of law and human rights as determinants of good governance. His analysis makes it clear that good governance in Kenya is rarely practiced since the decision-making process is not transparent. Dessie (2018) concluded the existence of a causal relationship between governance and its predictors, including education level, corruption, bureaucracy, conflict and poor service delivery. His results revealed that predictors such as education, corruption, bureaucracy and conflict have a significant impact on good governance. However, education has a positive impact, while corruption, bureaucracy and conflict also have a negative and significant impact on good governance. Security and rule of law, participation and human rights, sustainable economic development and human development are also found in the literature to be explanatory factors of governance. Other research has linked ICT development to good governance and development. Their benefits for governance and development are highlighted in many theoretical and empirical reviews. Increasingly, ICTs are being integrated into the development strategies of developed and developing countries. They have great potential to bring about desired social transformations by improving access to people, services, information and other technologies (Dutton et al., 2004; Malhotra et al., 2007). This role that ICTs play in development today was first highlighted at the 1988 conference in New Delhi on the social implications of computers in developing countries (Singh et al., 2018). Since then, research establishing that ICT use could potentially provide economic, social, civic, and environmental benefits has been prolific. A challenge of understanding how ICT can improve people's lives is embedded in the research. The literature classifies their applications in governance processes as improving government processes and creating interaction within civil society (Malhotra et al., 2007). As far as civil society is concerned, the intervention of ICTs improves its participation in the e-governance process (Andersen et al., 2006). Their interactions in the public domain also facilitate the provision of accurate information about social problems and possible solutions. Analyses by Canares (2016) show that ICT offers two opportunities for government. The first concerns the increased efficiency they offer by reducing costs and increasing productivity of government services. And the second concerns the provision of higher quality services to citizens. These opportunities increasingly extend to transparency and accountability, promoting economic development and facilitating an electronic society. Today, online citizen service, integrated tax systems, online social insurance systems, resident registration and passport applications, real estate information management, vehicle administration, e-procurement, integrated accounting, and education management are evidence of innovations that enable an easy relationship between government, citizens, and the private sector (Canares, 2016). In the same vein, the work of Rosenberg (2019), Hu et al. (2019), and Chohan et al. (2022) have not failed to convey that the development of artificial intelligence has enormous potential for the development of smart societies and can bring innovative advances in agriculture, education, and transportation and decision making. For these authors, m-government can improve the efficiency and quality of public services, especially in several areas including security. The benefits of ICT have also been highlighted in other dimensions of governance and development. Indeed, technological tools are nowadays indispensable for promoting transparency and reducing corruption (Trimi & Sheng, 2008; Wang et al., 2020, Alshammari et al. (2022). ICTs have also shown their utility in monitoring government actions and reaching a wider population in the implementation of development policies (Mahmood et al., 2019; Alshammari et al. 2022). In the field of health, information and communication technologies (ICTs) play a prominent role due to their significant impact on the health system of countries. The results of the work of Kouton et al. (2020) and Zhang et al. (2022) are evidence of their influences on health status. Indeed, Kouton et al. (2020) showed the role of ICT development in reducing under-five mortality in Africa. Zhang et al. (2022) gave a similar conclusion to Kouton et al. (2020) on the health status of the elderly. Other research has also shown the effectiveness of ICT in implementing youth employment policies (Raja et al. (2013) and in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (Xiong et al., 2022).The article by Strielkowski et al. (2017) focuses on the use of modern technologies in public sector management. These authors show through their analyses that if the new information and communication technologies (ICT) are properly implemented and managed, they could represent a disruption in the traditional management of the state and municipalities. But measures to protect personal data should be put in place to accompany the use of ICT in public governance. Fath-Allah et al. (2014) point out that ICT can facilitate the way public services are delivered to citizens, from job search portals to websites and applications that collect citizens' opinions on how municipalities manage their districts and administrative units. Pollifroni (2014), on the other hand, points out that the most interesting and impressive application of ICT could be the identification of citizens and allowing them to participate in public life online through the Internet. Other works such as Arora (2008), Pang et al. (2014) have also addressed the issue of the value of ICT in public administration governance. The analysis by Imhonopi et al (2011) in the case of Nigeria, points out that ICTs contribute to e-governance and create more open spaces for citizens, organizations and agencies to interact with the government and its representatives. For the authors, ICTs have a facilitating role in public order management and their interventions promote better service delivery to citizens, empowerment of people through dematerialized access to information, improved productivity and cost reduction in doing business with government suppliers and customers, and participation in public policy making. It is in the same logic that Hellström, (2007) revealed that ICT is an essential tool for improving governance because it can improve transparency, accountability and the free flow of information between several institutions and departments within a government. The author shows that ICT not only facilitates the participation of citizens in the adoption of decisions that affect their standard of living, but also the dissemination of information between institutions and departments. Several other authors, such as Pierskalla et al. (2013), Shapiro et al. (2015), and Manacorda et al. (2020), support the thesis that ICT could promote good governance. Pierskalla et al. (2013) and Shapiro et al. (2015) highlight the importance of cell phones in managing violence in Africa.Beyond the established links between governance and educational attainment, corruption, bureaucracy, and poor service delivery, security and rule of law, participation and human rights, sustainable economic development, human development, and ICT development, more thought is now being given to the relationship between official statistical data (quality information) and good governance. This relationship is rooted in the theory of governance and information asymmetry. In the private sector, several research works among which Cormier et al. (2010), Salehi et al. (2014), Dolla et al. (2020). Mahdavi et al. (2018) mentioned the fact that the manager of a company needs the right information and real time for a better decision making and governance. In the public sector, information literacy, statistical data, and intelligence data are also very crucial for better policy making and governance. The work of Keen (1978) and Alshammari et al. (2022) provides a clear understanding of how organizational decision making requires good information. Chohan et al. (2022) grants big data power in predicting various future government policies. Cairo (2017) points out in his analyses that statistics enable more effective actions, and facilitate the evaluation of policies that improve how we respond. For the author, data demands now cover a wide range of aspects of society, including relatively new areas such as well-being, climate change, and new economic models. Cairo (2017) also draws attention to the fact that the statistical community needs to work closely with politicians to provide the evidence that government needs for future policy development and planning. Other research studies have also discussed the importance of the availability of statistical data in the process of implementing public policies. Giovannini et al (2009) examined the role of statistical information in economic and political systems based on the European Barometer survey. For these authors, the importance of statistics in governance mechanisms and the rapidly changing environment create specific challenges for official statistical institutions. They point to the need to create a forward-looking and outward-looking culture in statistical institutions in order to provide the most relevant information possible for society as a whole and its different components. Their results provide evidence of a positive link between trust in statistics and trust in institutions.In the same vein, Lomell, (2010) highlights the importance of the availability of crime-related statistics in managing national security and addressing justice issues. Bedecarrats et al. (2016) give governance through statistics a dual mission: to help monitor and evaluate the SDGs and to help measure democratic progress. Hudecek et al. (2019) highlight the importance of statistics in public housing management in Prague cities. They point out that regular collection of quality data would be an asset for good planning of more effective government policies. For Radermacher (2019), the availability of quality data is fundamental to the implementation of successful economic policies. For him, statistics mobilize socially important information and indicators that can be useful in the policymaking process for guiding priorities and identifying future policy issues. His analyses reveal that official statistics are needed to reconcile three fundamental rights: the right to confidentiality of personal data, the right to access information and the right to live in a civilized and well-informed society. It draws attention to the fact that excellent communication of the facts and figures produced must also be declared and explained in such a way that potential users of the information can orient themselves to them. Despite the amount of work done on good governance, no empirical link has been established between the capacity of countries to produce and make available the official statistics necessary for good decision-making and good governance. It is this limitation of the literature that this study seeks to address by testing for causality in the Granger sense between variables and using the GMM method.
3. Data and Methods
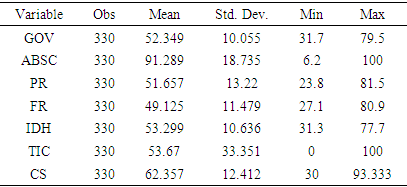
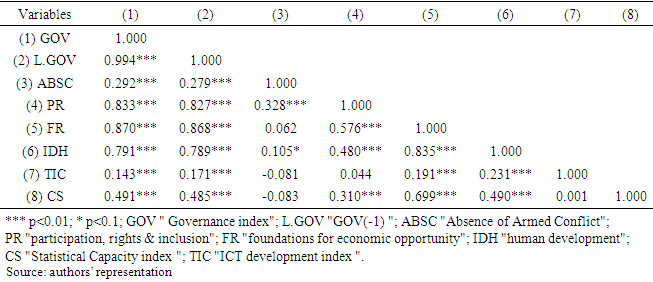
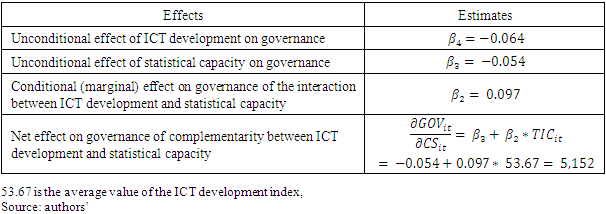
- Data Source This study uses a balanced panel of 33 African countries. The data is drawn from the World Bank and Mo Ibrahim Foundation's World Development Indicators (WDI) database, and spans the period from 2010 to 2019. Variables such as Gov (Governance index), ABSC (Absence of Armed Conflict), PR (participation, rights & inclusion), FR (foundations for economic opportunity) and IDH (human development) are taken from the Mo Ibrahim Foundation database, while the CS (Statistical Capacity index) variables and those used for the construction of the ICT development index are from the World Bank data. The choice of the period considered depends on the availability of data. The countries considered for the study are South Africa, Algeria, Angola, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Benin, Cameroon, Comoros, Republic of Congo, Côte d'Ivoire, Gabon, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Kenya, Lesotho, Liberia, Mali, Morocco, Mauritius, Mozambique, Namibia, Nigeria, Rwanda, Sierra Leone, Senegal, Tanzania, Togo, Tunisia, Zimbabwe, Egypt.Governance is one of the important factors for sustainable development. To explain certain dimensions or aspects of governance, several authors have alluded to several factors. Javaid (2010) alludes to corruption, transparency and level of education. Malhotra et al (2007) explain governance through rural development, community participation, quality of institutions and ICT development. Avom et al. (2020) refer to ICT development, level of democracy, participation of the military in politics, democratic participation of citizens, security and rule of law, sustainable economic development and human development. In the work of Thomas (2010), Wani (2014), Dessie (2019), Asongu et al. (2019), Gallego-álvarez et al. (2021), Anser et al. (2021) we find explanatory variables such as level of education, corruption, bureaucracy, conflict, lack of civil society and vibrant governments, transparency, voice and accountability, rule of law, quality of regulation, government effectiveness, political stability. Other works have taken a literal and summary approach to statistics as an explanatory factor for good decision making and governance (Giovannini, n.d.; Bedecarrats et al., 2016; Hudecek et al., 2019).In this study, we use the variable Governance Index of Mo Ibrahim Foundation. The Mo Ibrahim Foundation constructs this index from 79 governance measurement indicators. For the Mo Ibrahim Foundation, the Governance index variable is explained by four major dimensions or categories of indicators, which are (i) security and rule of law, (ii) participation, rights and inclusion, (iii) foundations of economic opportunity and (iv) human development. Thus, we have considered each of the dimensions as an explanatory variable of governance. Table 1 shows some descriptive statistics on the variables studied. Table 2 shows the correlation matrix between the variables studied. The analysis of this table shows that all variables are positively and significantly correlated with governance. The scatterplots in Figure 1 and Figure 2 show that ICT development and statistical capacity are correlated with governance. This gives a first indication of the relationship between these variables. However, a multivariate analysis in an econometric framework will help to better situate the relationships. The analysis of Table 2 shows a strong positive and significant correlation (0.994) between the current value of governance and its one-period lagged value, which suggests a persistence of this variable, which should be taken into account in the model.
|
|
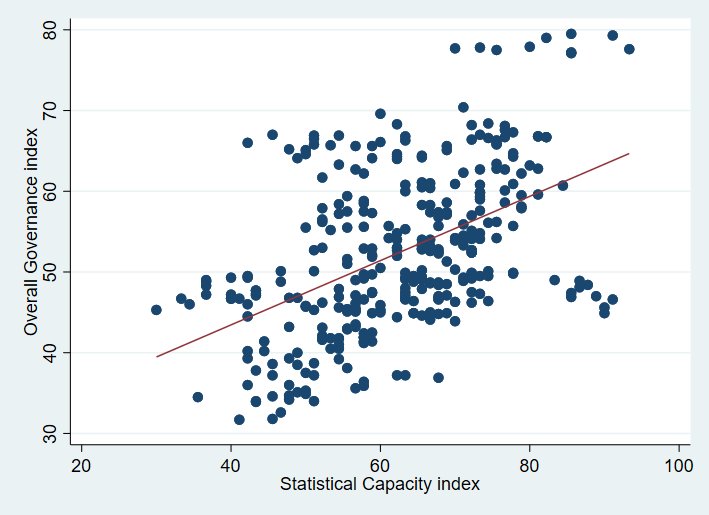 | Figure 1. Statistical Capacity and Governance. Source: authors’ representation |
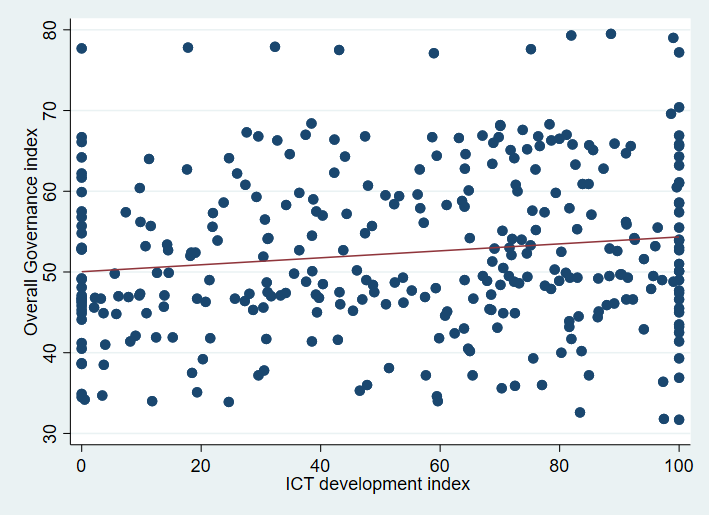 | Figure 2. ICT development and governance. Source: authors’ representation |
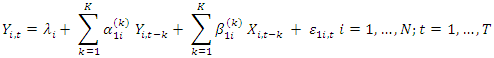 Under the null hypothesis of Homogeneous Non-Causality, there is no causality from X to Y for all the cross-over units in the panel.
Under the null hypothesis of Homogeneous Non-Causality, there is no causality from X to Y for all the cross-over units in the panel. 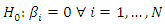 The alternative hypothesis assumes the existence of causality from X to Y for at least one country
The alternative hypothesis assumes the existence of causality from X to Y for at least one country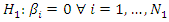
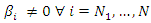 The null and alternative hypothesis of causality from y to x is specified in the same way.To test these hypotheses, Dumitrescu and Hurlin (2012) propose a procedure that consists of running the N individual regressions of the model and performing F-tests of the K linear hypotheses
The null and alternative hypothesis of causality from y to x is specified in the same way.To test these hypotheses, Dumitrescu and Hurlin (2012) propose a procedure that consists of running the N individual regressions of the model and performing F-tests of the K linear hypotheses 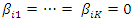 to recover the individual Wald statistic
to recover the individual Wald statistic 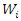 and finally to compute the average Wald statistic
and finally to compute the average Wald statistic 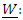
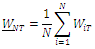 where
where 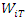 are the individual Wald statistics for the Granger causality test. Assuming that the statistics
are the individual Wald statistics for the Granger causality test. Assuming that the statistics 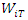 are independent and identically distributed, we compute a standardized statistic, Z-bar:
are independent and identically distributed, we compute a standardized statistic, Z-bar: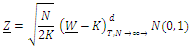 GMM modelThe objective of the study is to introduce statistical capacity indicators into a regression whose explained variable is a performance indicator, initially focusing on governance. Thus, the specification of the empirical model used in this study has the following expression:
GMM modelThe objective of the study is to introduce statistical capacity indicators into a regression whose explained variable is a performance indicator, initially focusing on governance. Thus, the specification of the empirical model used in this study has the following expression: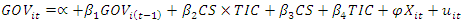 Where
Where 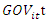 is the Governance Index, CS is the Statistical Capacity Index, TIC is the ICT Development Index, and
is the Governance Index, CS is the Statistical Capacity Index, TIC is the ICT Development Index, and 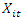 a vector of control variables including: absence of armed conflict; participation, rights and inclusion; foundations of economic opportunity; Human Development Index and
a vector of control variables including: absence of armed conflict; participation, rights and inclusion; foundations of economic opportunity; Human Development Index and 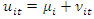 where
where 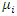 is the country-specific constant term that captures unmeasured heterogeneity, and
is the country-specific constant term that captures unmeasured heterogeneity, and 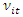 is the error term, i = 1,2,..., N is the country, t = 1,2,... T, is the time period. Because of the inclusion of a lagged dependent variable in the right-hand side of the equation, some econometric issues need to be considered for a good estimation of the model.
is the error term, i = 1,2,..., N is the country, t = 1,2,... T, is the time period. Because of the inclusion of a lagged dependent variable in the right-hand side of the equation, some econometric issues need to be considered for a good estimation of the model. 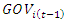 in the right-hand side of the equation, some econometric issues arise and need to be taken into account for a good estimation of the model. Indeed, the unobserved time-invariant features (fixed effects) of the countries are in the error term and are most likely correlated with the regressors. Note that
in the right-hand side of the equation, some econometric issues arise and need to be taken into account for a good estimation of the model. Indeed, the unobserved time-invariant features (fixed effects) of the countries are in the error term and are most likely correlated with the regressors. Note that 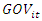 and
and 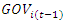 depend on μi, and thus
depend on μi, and thus 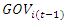 is necessarily correlated with
is necessarily correlated with 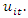 It follows that, the traditional estimators of the static panel data model are inconsistent. These rules out the random effects (RE) model assumption as well as the fixed effect model (Baltagi, 2013) in a dynamic panel setting. The standard static panel regression with dynamic panel data thus poses a problem, dynamic panel bias". This actually raises an endogeneity problem, and static estimation will generate biased and inconsistent results. The GMM method proposed in this work also avoids problems of simultaneity or reverse causality: the ICT associated with statistical governance may be endogenous, and thus there is more likely to be a feedback effect of governance on statistical governance. The GMM allows for variable omission bias: there are indeed important (mostly time-invariant) variables that may be omitted from our regression model, but are considered important determinants of governance and are correlated with certain explanatory variables. Finally, measurement error: governance variables are more likely to have measurement error, especially in the case of developing countries. All these reasons make the GMM the best estimator. The GMM technique comes in two versions: the GMM difference where lagged levels of the explanatory variables are used as instruments and systems. GMM where the combination of difference regression and level regression is used. However, Bond et al. (2001) recommended that the system GMM estimator developed by Arellano and Bover (1995) and Blundell and Bond (1998) can significantly improve the efficiency and avoid the problem of weak instruments in the GMM estimator in the first place. However, Windmeijer (2005) showed from Monte Carlo simulations that the estimated asymptotic standard deviations of the two-stage GMM estimator can be biased downward in a finite sample. To eliminate the possibility of such a bias, we use the correction procedure proposed by Windmeijer (2005).The consistency of the GMM estimator depends on two things: the validity of the assumption that the error term is not serially correlated (AR (2)) and the validity of the instruments (Hansen test). In the following, we will use the GMM system estimator developed by Arellano and Bover (1995) and Blundell and Bond (1998) to estimate the parameters of our regression.
It follows that, the traditional estimators of the static panel data model are inconsistent. These rules out the random effects (RE) model assumption as well as the fixed effect model (Baltagi, 2013) in a dynamic panel setting. The standard static panel regression with dynamic panel data thus poses a problem, dynamic panel bias". This actually raises an endogeneity problem, and static estimation will generate biased and inconsistent results. The GMM method proposed in this work also avoids problems of simultaneity or reverse causality: the ICT associated with statistical governance may be endogenous, and thus there is more likely to be a feedback effect of governance on statistical governance. The GMM allows for variable omission bias: there are indeed important (mostly time-invariant) variables that may be omitted from our regression model, but are considered important determinants of governance and are correlated with certain explanatory variables. Finally, measurement error: governance variables are more likely to have measurement error, especially in the case of developing countries. All these reasons make the GMM the best estimator. The GMM technique comes in two versions: the GMM difference where lagged levels of the explanatory variables are used as instruments and systems. GMM where the combination of difference regression and level regression is used. However, Bond et al. (2001) recommended that the system GMM estimator developed by Arellano and Bover (1995) and Blundell and Bond (1998) can significantly improve the efficiency and avoid the problem of weak instruments in the GMM estimator in the first place. However, Windmeijer (2005) showed from Monte Carlo simulations that the estimated asymptotic standard deviations of the two-stage GMM estimator can be biased downward in a finite sample. To eliminate the possibility of such a bias, we use the correction procedure proposed by Windmeijer (2005).The consistency of the GMM estimator depends on two things: the validity of the assumption that the error term is not serially correlated (AR (2)) and the validity of the instruments (Hansen test). In the following, we will use the GMM system estimator developed by Arellano and Bover (1995) and Blundell and Bond (1998) to estimate the parameters of our regression.4. Results
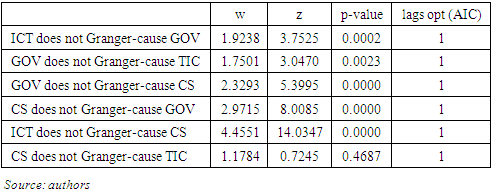
- The relationship between governance and statistical capacity is examined using the panel causality test of Dumitrescu and Hurlin, 2012). The results of this test are presented in Table 3. The optimal number of lags is selected using the AIC criterion. The optimal number of delays is 1. The results show causality from statistical ability to governance. Indeed, the probability associated with the test corresponding to the optimal delay is 0.0000, a value well below 5%, the threshold considered. This result means that the null hypothesis of non-causality of governance by statistical capacity is rejected, suggesting that statistical capacity has a predictive capacity for governance. In other words, an improvement in the official statistical system of African countries is likely to improve good governance. Similarly, with a probability of 0.0000, the null hypothesis that statistical capacity is not causal for governance is rejected. This means that the causality between statistical capacity and governance goes both ways. These results are intuitively justified. Indeed, an improvement in a country's statistical capacity should improve outcomes in terms of development policymaking and good governance. Improving a country's statistical capacity translates into improved objectivity in collecting, compiling, and disseminating the statistics needed for municipal and national development policymaking and for economic and social policy decisions. It is also reflected in the reliability of public statistics, transparency in data production, compliance with international data production techniques and standards, and appropriate periodicity in data production. All this is accompanied by an improvement in the availability of data and ease of access to data for users. In addition, an improvement in the capacity of official statistical offices to produce quality data that meet international standards is likely to increase the confidence of data users and technical and financial partners to support the government in development programs. Conversely, an improvement in governance implies an improvement in its measurement components, namely transparency, democracy, security, human capital development, etc., all of which public statistical offices need to freely and transparently carry out their missions. These results are in line with the analyses of Giovannini (2009), and Radermacher (2019) who emphasize that the availability of statistical data is fundamental in the process of better decision making.
|
|
|
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
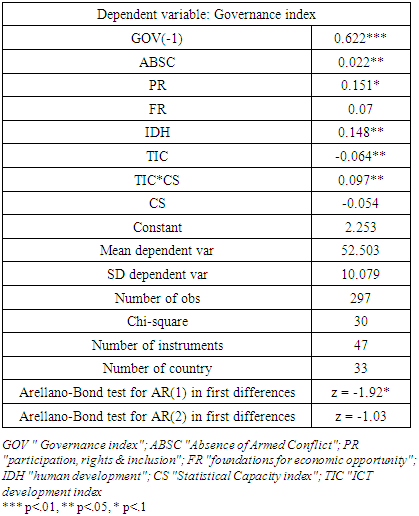
- In the face of failed structural adjustment policies in developing countries, a consensus has emerged internationally on the importance of official statistics and their quality in implementing economic and social policies. This study examines how ICT development complements the development of official statistics to influence governance outcomes in 33 African countries for the period 2010-2019. Two basic research questions were posed: Do ICTs and the capacity of African countries to produce quality statistical data influence good governance in Africa? And what is the effect of the interaction between ICTs and the capacity of African countries to produce quality statistical data (quality information needed for public policy making) on good governance? The first question was explored by analyzing the Granger panel causality test procedure between ICT development and governance on the one hand and between statistical capacity and governance on the other, while the exploration of the second question focused on the results of the GMM model estimations. The data used were collected from the World Bank database and the Mo Ibrahim Foundation database. The ICT development index was constructed using a principal component analysis (PCA) approach in which two variables were used Internet users (as a % of the population) (i.e., the share of the population with Internet access) and the number of cell phone subscriptions (per 100 inhabitants) (D'el Mehdi, 2011; Kouton et al., 2020). The results show a positive and significant correlation between governance and the explanatory variables. The initial conclusion that can be drawn from the results is that there is a bidirectional causality between the capacity of African statistical offices to produce and make accessible the data and information necessary for good decision-making and governance. This is, to our knowledge, a new empirical result in the literature. Similarly, we find a causal link between ICT development and good governance in Africa, a result that is not entirely new in the literature, but which is informative insofar as the data used are macroeconomic data for each country and not surveys specific to particular regions of the countries considered. The answer to the second question essentially reveals that the development of good quality official statistics needs to be accompanied by investments in ICT development to produce a significant and important positive effect on governance. These findings show that if African governments are to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals, they need to invest more in ICT development and in improving the production of quality statistical data that authorities at various levels need for good socio-economic and environmental policy making.From these findings, a few recommendations emerge. First, African governments should strengthen their financial and human capital support to statistical offices in order to build the capacity to produce the quality statistical data needed to implement good governance policies. Secondly, African states should invest more in improving the development of and access to information and communication technologies, including access to high-speed internet connection. Finally, African statistical offices need to improve access to statistics for data users, using new information technology tools to collect, store, process and disseminate information. In the future, studies can examine the effect of mobilizing statistical data on local development in African countries.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML