-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Science and Technology
p-ISSN: 2163-2669 e-ISSN: 2163-2677
2012; 2(5): 135-141
doi: 10.5923/j.scit.20120205.05
Comparative Study of Anion Exchange Resins Indion H-IP and Indion-NSSR by Application of 131I and 82 Br as a Tracer Isotope
Pravin U. Singare
Department of Chemistry, Bhavan’s College, Munshi Nagar, Andheri (West), Mumbai, 400 058, India
Correspondence to: Pravin U. Singare , Department of Chemistry, Bhavan’s College, Munshi Nagar, Andheri (West), Mumbai, 400 058, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The present investigation deals with characterization of weakly basic and strongly basic industrial grade anion exchange resins Indion H-IP and Indion-NSSR. The characterization was performed on the basis of iodide and bromide ion-isotopic exchange reaction kinetics by application of 131I and 82 Br tracer isotopes. It was observed that due to solvation effect the iodide ions are exchanged at faster rate as compared to bromide ions when the experimental conditions are kept identical. For both the ion-isotopic exchange reactions it was observed that the reaction rate is having negative correlationship with temperature and positive correlationship with concentration of exchangeable ions in solution. Also under identical experimental conditions, Indion-NSSR shows higher percentage of ion exchange than Indion H-IP resins.
Keywords: Indion H-IP, Indion-NSSR, Solvation Effect, Ion-isotopic Exchange Reactions, Tracer Applications, Reaction Kinetics, Radioactive Isotopes, 131I, 82Br
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The use of ion exchange procedures in chemical processing, water and wastewater treatments was well developed by the time the technique was first applied in the nuclear industry. Since then much progress has been made in improving the technology, and ion exchange methods have been widely used to remove soluble radionuclides from liquid waste. Recent developments in ion exchange technology and applications are described in other publications[1, 2]. The process involves the exchange of ionic species between a liquid solution and a solid matrix containing ionizable polar groups. Efforts to develop new organic ion exchangers for specific applications are continuing[3-7] and various aspects of ion exchange technologies have been continuously studied to improve the efficiency and economy of their application in various technological applications[8-11]. However, since the selection of the appropriate ion-exchange material depends on the needs of the system, it is expected that the data obtained from the actual experimental trials will prove to be more helpful. Hence there is a need to evaluate systematically the performance of such organic ion exchange resins under various operational conditions. Hence in the present investigation, it is proposed to test the performance of industrial grade ion exchange resin under different experimental conditions like temperature and concentration of ionic species present in the external exchanging medium.
2. Experimental
2.1. Conditioning of Ion Exchange Resins
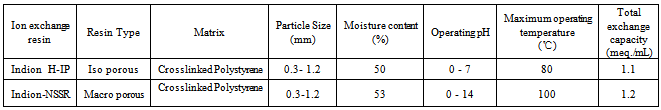
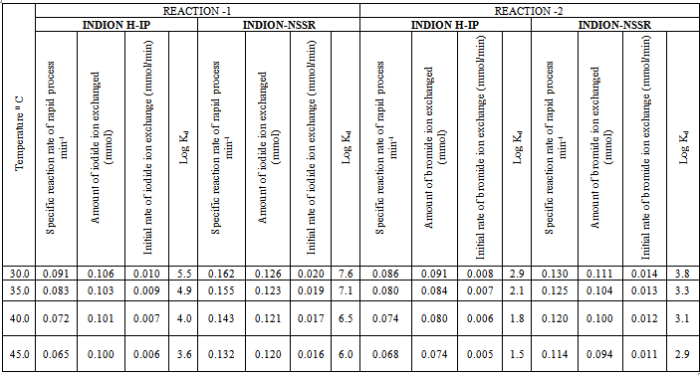
- Ion exchange resin Indion H-IP is a weekly (intermediate) basic anion exchange resin while Indion-NSSR is a strongly basic anion exchange resin supplied by Ion Exchange India Ltd., Mumbai. Both the resins as supplied by the manufacturer were in chloride form having quaternary ammonium -N+R3 functional group. Details regarding the properties of the resins used are given in Table 1. These resins were converted separately in to iodide / bromide form by treatment with 10 % KI / KBr solution in a conditioning column which is adjusted at the flow rate as 1 mL / min. The resins were then washed with double distilled water, until the washings were free from iodide/bromide ions as tested by AgNO3 solution. These resins in bromide and iodide form were then dried separately over P2O5 in desiccators at room temperature.
2.2. Radioactive Tracer Isotopes
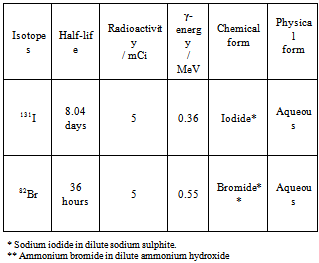
- The radioisotope 131I and 82Br used in the present experimental work was obtained from Board of Radiation and Isotope Technology (BRIT), Mumbai. Details regarding the isotopes used in the present experimental work are given in Table 2.
|
|
2.3. Study on Kinetics of Iodide Ion-isotopic Exchange Reaction
- In a stoppered bottle 250 mL (V) of 0.001 M iodide ion solution was labeled with diluted 131I radioactive solution using a micro syringe, such that 1.0 mL of labeled solution has a radioactivity of around 15,000 cpm (counts per minute) when measured with γ -ray spectrometer having NaI (Tl) scintillation detector. Since only about 50–100 μL of the radioactive iodide ion solution was required for labeling the solution, its concentration will remain unchanged, which was further confirmed by potentiometer titration against AgNO3 solution. The above labeled solution of known initial activity (Ai) was kept in a thermostat adjusted to 30.0℃. The swelled and conditioned dry ion exchange resins in iodide form weighing exactly 1.000 g (m) were transferred quickly into this labeled solution which was vigorously stirred by using mechanical stirrer and the activity in cpm of 1.0 mL of solution was measured. The solution was transferred back to the same bottle containing labeled solution after measuring activity. The iodide ion-isotopic exchange reaction can be represented as:
 | (1) |
2.4. Study on Kinetics of Bromide Ion-isotopic Exchange Reaction
- The experiment was also performed to study the kinetics of bromide ion- isotopic exchange reaction by equilibrating 1.000 g of ion exchange resin in bromide form with labeled bromide ion solution in the same concentration and temperature range as above. The labeling of bromide ion solution was done by using 82Br as a radioactive tracer isotope for which the same procedure as explained above was followed. The bromide ion-isotopic exchange reaction can be represented as:
 | (2) |
|
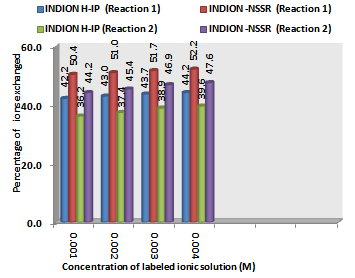 | Figure 2. Variation in Percentage Ions Exchanged with Concentration of labeled Ionic Solution Amount of ion exchange resin = 1.000 g, Volume of labeled ionic solution = 250 mL, Temperature = 30.0℃ |
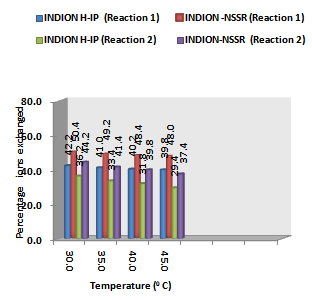 | Figure 3. Variation in Percentage Ions Exchanged with Temperature of labeled Ionic Solution Amount of ion exchange resin = 1.000 g, Concentration of labeled exchangeable ionic solution = 0.001M, Volume of labeled ionic solution = 250 mL, Amount of exchangeable ions in 250 mL labeled solution = 0.250 mmol |
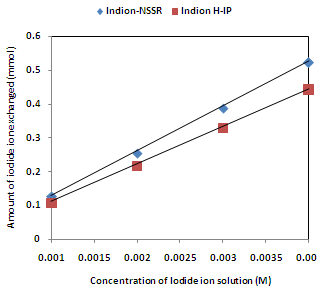 | Figure 4. Correlation between concentrations of iodide ion solution and amount of iodide ion exchanged Amount of ion exchange resin = 1.000 g, Volume of labeled ionic solution = 250 mL, Temperature = 30.0 ℃ Correlation coefficient (r) for Indion H-IP =1.0000 Correlation coefficient (r) for Indion-NSSR =1.0000 |
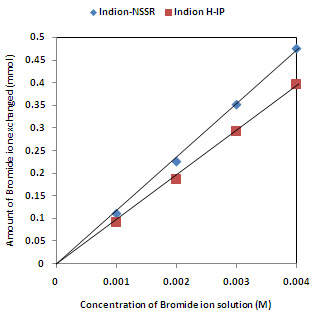 | Figure 5. Correlation between concentrations of bromide ion solution and amount of bromide ion exchanged Amount of ion exchange resin = 1.000 g, Volume of labeled ionic solution = 250 mL, Temperature = 30.0 ℃ Correlation coefficient (r) for Indion H-IP = 0.9998 Correlation coefficient (r) for Indion-NSSR = 0.9999 |
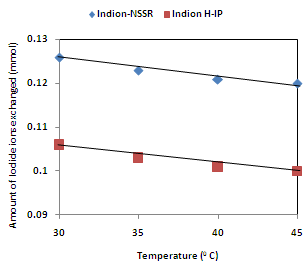 | Figure 6. Correlation between Temperatures of exchanging medium and amount of iodide ion exchanged Amount of ion exchange resin = 1.000 g, Concentration of labeled exchangeable ionic solution = 0.001M, Volume of labeled ionic solution = 250 mL, Amount of exchangeable ions in 250 mL labeled solution = 0.250 mmol Correlation coefficient (r) for Indion H-IP = -0.9759 Correlation coefficient (r) for Indion-NSSR = -0.9759 |
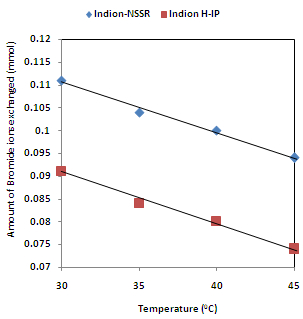 | Figure 7. Correlation between Temperatures of exchanging medium and amount of bromide ion exchanged Amount of ion exchange resin = 1.000 g, Concentration of labeled exchangeable ionic solution = 0.001M, Volume of labeled ionic solution = 250 mL, Amount of exchangeable ions in 250 mL labeled solution = 0.250 mmol Correlation coefficient (r) for Indion H-IP = -0.9951 Correlation coefficient (r) for Indion-NSSR = -0.9951 |
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Comparative Study of Ion-isotopic Exchange Reactions
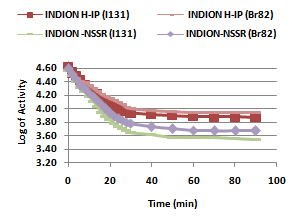
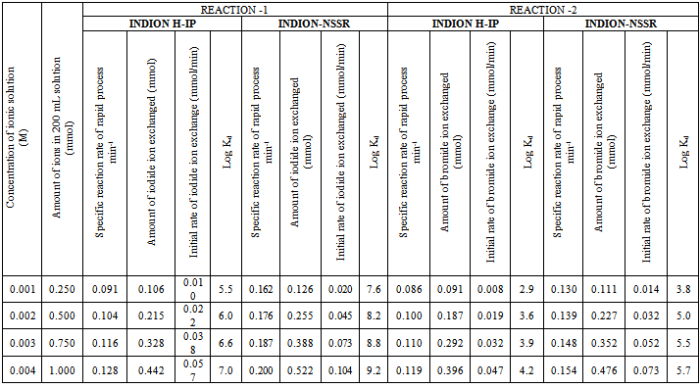
- In the present investigation it was observed that due to the rapid ion-isotopic exchange reaction taking place, the activity of solution decreases rapidly initially, then due to the slow exchange the activity of the solution decreases slowly and finally remains nearly constant. Preliminary studies show that the above exchange reactions are of first order[19, 20]. Therefore logarithm of activity when plotted against time gives a composite curve in which the activity initially decreases sharply and thereafter very slowly giving nearly straight line (Figure 1), evidently rapid and slow ion-isotopic exchange reactions were occurring simultaneously[13-18]. Now the straight line was extrapolated back to zero time. The extrapolated portion represents the contribution of slow process to the total activity which now includes rapid process also. The activity due to slow process was subtracted from the total activity at various time intervals. The difference gives the activity due to rapid process only. From the activity exchanged due to rapid process at various time intervals, the specific reaction rates (k) of rapid ion-isotopic exchange reaction were calculated. The amount of iodide / bromide ions exchanged (mmol) on the resin were obtained from the initial and final activity of solution and the amount of exchangeable ions in 250 mL of solution. From the amount of ions exchanged on the resin (mmol) and the specific reaction rates (min-1), the initial rate of ion exchanged (mmol/min) was calculated.Because of larger solvated size of bromide ions as compared to that of iodide ions, it was observed that the exchange of bromide ions occurs at the slower rate than that of iodide ions[21]. Hence under identical experimental conditions, the values of specific reaction rate (min-1), amount of ion exchanged (mmol) and initial rate of ion exchange (mmol/min) are calculated to be lower for bromide ion-isotopic exchange reaction than that for iodide ion-isotopic exchange reaction as summarized in Tables 3 and 4. For both bromide and iodide ion-isotopic exchange reactions, under identical experimental conditions, the values of specific reaction rate increases with increase in concentration of ionic solution from 0.001M to 0.004M (Table 3). However, with rise in temperature from 30.0℃ to 45.0℃, the specific reaction rate was observed to decrease (Table 4). From the results, it appears that iodide ions exchange at the faster rate as compared to that of bromide ions which was related to the extent of solvation (Tables 3 and 4).From the knowledge of Ai, Af, volume of the exchangeable ionic solution (V) and mass of ion exchange resin (m), the Kd value was calculated by the equation
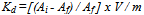 | (3) |
3.2. Comparative Study of Anion Exchange Resins
- From the Table 3, it is observed that for iodide ion-isotopic exchange reaction by using Indion-NSSR resin, the values of specific reaction rate (min-1), amount of iodide ion exchanged (mmol), initial rate of iodide ion exchange (mmol/min) and log Kd were 0.162, 0.126, 0.020 and 7.6 respectively, which was higher than 0.091, 0.106, 0.010 and 5.5 respectively as that obtained by using Indion H-IP resins under identical experimental conditions of 30.00C, 1.000 g of ion exchange resins and 0.001 M labeled iodide ion solution. The identical trend was observed for the two resins during bromide ion-isotopic exchange reaction.From Table 3, it is observed that using Indion-NSSR resins, at a constant temperature of 30.0 0C, as the concentration of labeled iodide ion solution increases 0.001 M to 0.004 M, the percentage of iodide ions exchanged increases from 50.4 % to 52.2 %. While using Indion H-IP resins under identical experimental conditions the percentage of iodide ions exchanged increases from 42.2 % to 44.2 %. Similarly in case of bromide ion-isotopic exchange reaction, the percentage of bromide ions exchanged increases from 44.2 % to 47.6 % using Indion-NSSR resin, while for Indion H-IP resin it increases from 36.2 % to 39.6 %. The effect of ionic concentration on percentage of ions exchanged is graphically represented in Figure 2.From Table 4, it is observed that using Indion-NSSR resins, for 0.001 M labeled iodide ion solution, as the temperature increases 30.0 0C to 45.0 0C, the percentage of iodide ions exchanged decreases from 50.4 % to 48.0 %. While using Indion H-IP resins under identical experimental conditions the percentage of iodide ions exchanged decreases from 42.2 % to 39.8 %. Similarly in case of bromide ion-isotopic exchange reaction, the percentage of bromide ions exchanged decreases from 44.2 % to 37.4 % using Indion-NSSR resin, while for Indion H-IP resin it decreases from 36.2 % to 29.4 %. The effect of temperature on percentage of ions exchanged is graphically represented in Figure 3.The overall results indicate that under identical experimental conditions, as compared to Indion H-IP resins, Indion-NSSR resins shows higher percentage of ions exchanged. Thus Indion-NSSR resins show superior performance than Indion H-IP resins.
3.3. Statistical Correlations
- The results of present investigation show a strong positive linear co-relationship between amount of ions exchanged and concentration of ionic solution (Figures 4, 5). In case of iodide ion-isotopic exchange using Indion-NSSR and Indion H-IP resins, the values of correlation coefficient (r) were found to be 1.0000 for both the resins, while for bromide ion-isotopic exchange the values of r were calculated as 0.9999 and 0.9998 respectively. There also exist a strong negative co-relationship between amount of ions exchanged and temperature of exchanging medium (Figures 6, 7). For Indion-NSSR and Indion H-IP resins, during iodide ion-isotopic exchange the values of r were found to be -0.9759; while for bromide ion-isotopic exchange the values were calculated as -0.9951 for the two resins.
4. Conclusions
- The experimental work carried out in the present investigation will help to standardize the operational process parameters so as to improve the performance of selected ion exchange resins. The radioactive tracer technique used here can also be applied for characterization of different nuclear as well as non-nuclear grade ion exchange resins.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The author is thankful to Professor Dr. R.S. Lokhande for his valuable help and support in carrying out the experimental work in Radiochemistry Laboratory of Department of Chemistry, University of Mumbai, Vidyanagari, Mumbai -58.The authors are extremely thankful to SAP Productions for developing and maintaining the manuscript template.
References
| [1] | International Atomic Energy Agency, 1984, Treatment of Low and Intermediate Level Liquid Radioactive Wastes, Technical Reports Series No. 236, IAEA, Vienna. |
| [2] | International Atomic Energy Agency,1994, Advances in Technologies for the Treatment of Low and Intermediate Level Radioactive Liquid Wastes, Technical Reports Series No.370, IAEA, Vienna. |
| [3] | Zhu, L., Liu, Y., and Chen, J., 2009, Synthesis of N-Methylimidazolium Functionalized Strongly Basic Anion Exchange Resins for Adsorption of Cr(VI)., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 48(7), 3261–3267. |
| [4] | Korshak, V.V., Rogozhin, S.V., Davankov, V.A., and Vyrbanov, S.G., 1966, Synthesis of optically active ion exchange resins., Russian Chemical Bulletin, 15(3), 510-512. |
| [5] | Yergozhin, Ye. Ye., Abdrakhmanova, I.K., and Menligaziyev, Ye.Zh., 1981, Synthesis and investigation of the properties of organosilicon anion-exchange resins., Polymer Science U.S.S.R., 23(11), 2671-2678. |
| [6] | Sugii, A., Ogawa, N., Nozaki, Y., and Haratake, M., 1988, Preparation of macroreticular anion-exchange resins having spacers and an evaluation of these resins in the synthesis of sulfones., Reactive Polymers, Ion Exchangers, Sorbents, 8(1), 3-6. |
| [7] | Zaidi, S.A.R., and Shah, G.B., 2000, Synthesis of strongly basic anion exchange resins based on glycidyl methacrylate-ethylene glycol dimethacrylate copolymer. Effect of amount and nature of diluent, and the degree of crosslinkage on the resins properties., Macromolecular chemistry and physics, 201(18), 2760-2764. |
| [8] | Iwai, Y., Yamanishi, T., Hiroki, A., and Tamada, M., 2009, Radiation-Induced Degradation in Ion Exchange Resins for a water Detritiation System., Fusion Science and Technology, 56(1), 163-167. |
| [9] | Gonder, Z.B., Kaya, Y., Vergili, I., and Barlas, H., 2006, Capacity Loss in Organically Fouled Anion Exchanger., Desalination, 189(1-3), 303-307. |
| [10] | Chambree, D., Cornelia, I., Segal, E., and Cesro, A., 2005, The study of non-isothermal degradation of acrylic ion-exchange resins., J. Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry,82(3), 803-811. |
| [11] | Simister, C., Caron, F., and Gedye, R., 2004, Determination of the thermal degradation rate of polystyrene-divinyl benzene ion exchange resins in ultra-pure water at ambient and service temperature., J. Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 261(3), 523-531. |
| [12] | Sood, D.D., 1998, Proc. Int. Conf. on Applications of Radioisotopes and Radiation in Industrial Development, ed. Sood, D.D., Reddy, A.V.R., Iyer, S.R.K., Gangadharan, S., and Singh, G., (B.A.R.C., India) 35–53. |
| [13] | Lokhande, R.S., Singare, P.U., and Kolte, A.R., 2010, Application of Radioactive Tracer Technique for Characterization of Strongly Basic Anion Exchange Resins Duolite A 101D and Duolite A 102D., Radiochemistry, 52(1), 81–86. |
| [14] | Singare, P.U., and Lokhande, R.S., 2009, Behaviour of Radioactive Iodide and Bromide ions from Aqueous Solution on Ion Exchange Resins Amberlite IRA-400., Natural Science, 1(1),191-194. |
| [15] | Lokhande, R.S., Singare, P.U., and Parab, S.A., 2008,Application of Radioactive Tracer Technique to Study the Kinetics of Iodide Ion- Isotopic Exchange Reaction using Strongly Basic Anion Exchange Resin Duolite A-116., Radiochemistry, 50(6), 642-644. |
| [16] | Lokhande, R.S., Singare, P.U., and Patil, V.V., 2008, Application of Radioactive Tracer Technique To Study the Kinetics and Mechanism of Reversible Ion- Isotopic Exchange Reaction using Strongly Basic Anion Exchange Resin Indion -850., Radiochemistry, 50(6), 638-641. |
| [17] | Lokhande, R.S., Singare, P.U., and Dole, M.H., 2007,Application of Radiotracer Technique to Study the Ion Isotope Exchange Reactions Using a Strongly Basic Anion-Exchange Resin Duolite A-113., Radiochemistry, 49(5), 519-522. |
| [18] | Lokhande, R.S., Singare, P.U., and Karthikeyan, P., 2007, The Kinetics and Mechanism of Bromide Ion Isotope Exchange Reaction in Strongly Basic Anion-Exchange Resin Duolite A-162 Determined by the Radioactive Tracer Technique., Russ. J. Physical Chemistry A, 81(11), 1768–1773. |
| [19] | Lokhande, R.S., and Singare, P.U., 2003, Study of reversible ion-isotopic self diffusion reaction using 82 Br as a radioactive tracer isotope., Asian J. Chem., 15(1), 33-37. |
| [20] | Lokhande, R.S., and Singare, P.U., 2005, Study on kinetics of self diffusion reaction by application of 82 Br as a radioactive tracer isotope., Asian J. Chem., 17(1), 125-128. |
| [21] | Shannon, R.D., 1976, Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides., Acta Crystallographica, A32, 751-767. |
| [22] | Heumann, K.G., and Baier, K., 1982, Chloride distribution coefficient on strongly basic anion-exchange resin: Dependence on co-ion in alkali fluoride solutions., Chromatographia, 15(11), 701-703. |
| [23] | Adachi, S., Mizuno, T., and Matsuno, R., 1995, Concentration dependence of the distribution coefficient of maltooligosaccharides on a cation-exchange resin., J. Chromatography A, 708(2), 177-183. |
| [24] | Shuji, A., Takcshi, M., and Ryuichi, M., 1996, Temperature dependence of the distribution coefficient of maltooligosaccharides on cation-exchange resin in Na+ form., Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 60(2), 338-340. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML