-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Science and Technology
p-ISSN: 2163-2669 e-ISSN: 2163-2677
2012; 2(2): 8-15
doi: 10.5923/j.scit.20120202.02
Comparative Study between Conventional and Thermoreversible Mucoadhesive Nasal Gels of Midazolam Hydrochloride
Shyamoshree Basu 1, Amal K. Bandyopadhyay 2
1NSHM Knowledge Campus, Kolkata – Group of Institutions, Kolkata, 700053, India
2Department of Pharmaceutical Technology, Jadavpur University, Kolkata , 700032, India
Correspondence to: Amal K. Bandyopadhyay , Department of Pharmaceutical Technology, Jadavpur University, Kolkata , 700032, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The aim of the present study was to prepare conventional and thermoreversible or in situ mucoadhesive nasal formulations of midazolam hydrochloride (HCl) prepared from a natural mucilage isolated from Linum usitatissimum L. seeds and to compare the various parameters like texture profile analysis, viscosity, mucoadhesive strength, ex vivo permeation study and in vivo drug absorption study. The formulations were prepared using three different concentrations of the isolated mucilage and sodium taurocholate was used as a penetration enhancer to obtain rapid delivery of the drug into systemic circulation.
Keywords: Mucoadhesive, Nasal, Mucilage
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Seizures are a common medical emergency, accounting for 1%–2% of all emergency department (ED) visits, and status epilepticus (SE) exists in approximately 6% of these encounters[1]. SE is associated with high morbidity and mortality. Common complications of SE include aspiration, anoxic brain injury, cardiac instability, metabolic and autonomic dysfunction, and direct neuronal damage[2-9]. Midazolam is administered via intranasal (IN) and buccal routes but has not been developed for rectal administration[10-28]. Intranasal midazolam is an effective medication that can be given safely. Midazolam is also effective after buccal administration but has not been studied in the prehospital setting[24-28]. Midazolam is water soluble but becomes fat-soluble at physiological pH, allowing it to cross the nasal mucosa into adjacent tissues including the cerebrospinal fluid, resulting in rapid onset of action[29]. Moreover, the convenience of IN administration and the social acceptability may make IN midazolam the preferred treatment of seizures in the prehospital setting.A few studies have compared diazepam and midazolam in the prehospital or emergency department setting and have shown midazolam to be equally or more effective in treating seizures, sometimes with fewer adverse effects[10,11,15-20, 29-31]. Fisgin et al compared intranasal midazolam with rectal diazepam (RD) in the ED setting[19]. Intranasal midazolam was more successful in controlling seizure acdazo-lam was more successful in controlling seizure activity. Bhattacharyya et al[20] compared intranasal midazolam or RD in children and found seizure control to be faster with intranasal midazolam, with fewer adverse effects. In both studies, study medication was given by a physician in an ED setting. Holsti et al conducted a randomized trial comparing intranasal midazolam with RD and reported that Intranasal Midazolam Mucosal Atomization Device (IN-MMAD) controlled seizures better than RD in the prehospital setting, due to ease of administration and more cost effectiveness[10].However, the above studies were conducted with either solution or spray dosage forms of midazolam[32]. Mucoadhesive nasal gels provide a firm platform from which drug diffuses into systemic circulation through nasal mucosa[33]. But conventional gels suffer from the disadvantage of high viscosity and hence cannot be administered properly to the nasal cavity and accurate dose of drug cannot be delivered[34]. This will affect the underlying bioavailability of the drug adversely. To overcome this problem, idea of thermoreversible or in situ gels was conceived.In situ gels are basically liquid at room temperature and convert to a firm gel when instilled into the nasal cavity[34-37]. Hence, accurate dose is delivered via this route. In our previous works we have shown that mucoadhesive gels of midazolam hydrochloride prepared from Linum usitatissimum L. mucilage showed better rheological and mechanical properties as well as better drug release profiles and in vivo drug absorption pattern than those prepared with synthetic polymers. The aim of the present study is focused on comparision between mucoadhesive conventional and in situ nasal gels containing midazolam hydrochloride prepared from Linum usitatissimum L. mucilage.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Materials
- Midazolam hydrochloride was obtained as a gift from Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Gujarat, India. Flaxseeds were purchased from local market. Pluronic F127 was purchased from Sigma Aldrich Pvt. Ltd., India. Sodium taurocholate was purchased from Loba Chemie Pvt. Ltd., Mumbai, India. All other reagents and chemicals used were of analytical grade.
2.2. Preparation of Mucoadhesive Nasal Gel
- Conventional mucoadhesive nasal gels were prepared by dissolving midazolam hydrochloride in nasal solution (0.65% NaCl, 0.04% KH2PO4, 0.09% K2HPO4 and 0.02% benzalkonium chloride) (pH 6)[38] in a constant stirring condition. Required amounts of LUM was added to the solution and stirred on a magnetic stirrer until a uniform solution was obtained which was kept at 4°C overnight to allow complete swelling so that a homogenous gel was formed. Penetration enhancers (sodium taurocholate) were also added to the formulations at a concentration of 0.50 % (w/v).
|
|
2.3. Determination of Viscosity
- Viscosities of different formulations were measured with TV-10 viscometer (Toki Sangyo Co. Ltd., Japan) at five different speeds of 10, 20, 30, 60 and 100 rpm, respectively, using spindle M4 and cord no. 23 at 37±1℃[8]. The corresponding viscosities were plotted against spindle rpm as depicted in Figure 1.
 | Figure 1. Comparative study of viscosities of formulations at 37±1℃ |
2.4. Determination of Mechanical Properties
- Texture profile analysis of the formulations determines mechanical properties of a gel like hardness, adhesiveness and cohesiveness. These parameters were determined using QTS-25 Texture Analyser (Brookfield Engineering Labs, USA). The method involves depression of an analytical probe of diameter 1.2 cm twice into each sample to a defined depth (15 mm), at a defined rate (30 mm/min), with a defined recovery period (15 s), between the end of the first compression and the beginning of the second. A trigger force of 4 g was applied. At least six analyses of each sample were performed at 37±1℃. Data collection and calculation were done by Texture pro software, version 2.1[38]. The analysis was done using a 5-kg load cell instrument.
2.5. Determination of Mucoadhesive Strength
- Mucoadhesive strength of each formulation was determined by measuring force required to detach nasal mucous membrane from the formulation using the same texture analyser. The goat nose was collected from local slaughterhouse within 15 min after the goat was sacrificed. After removing the skin, the nose was stored on ice cold phosphate buffer (pH 7.4, 0.05 M). The septum was fully exposed, and nasal mucosa was carefully removed using forceps and surgical scissors. The mucosal tissues were immediately immersed in Ringer’s solution[33,37,38]. Freshly excised goat nasal membrane was attached to the upper probe of the instrument, and fixed amount of formulation was kept below that. The upper probe was then lowered at a speed of 10 mm/min to touch the surface of the gel. A force of 0.1 N was applied for 5 min to ensure intimate contact between the membrane and the gel. The surface area of exposed mucous membrane was 1.13 cm2.
2.6. Ex vivo Drug Permeation Study
- Based on texture profile analysis and drug release pattern of the formulations, LUM1 and LUM1 (P) containing 0.5% sodium taurocholate were selected for ex vivo study.Ex vivo permeation study was conducted using a Franz diffusion cell containing 100 ml of phosphate buffer (pH 6, 0.1 M) using an excised goat nasal mucosa. The freshly excised nasal mucosa was mounted on the diffusion cell. 100 μl of gel containing 5 mg midazolam was placed on the membrane dispersed in 100 ml phosphate buffer and stirred at a constant rate by a PTFE-coated magnetic bar at 600 rpm. Cells were kept under constant oxycarbon flow (95% O2, 5% CO2).Throughout the study, the buffer solution in the chamber was maintained at 37±1℃ by connecting the Franz diffusion cell with water bath. At predetermined time intervals, 1 ml of the sample was withdrawn at a time and replenished with an equal amount of phosphate buffer. The samples were diluted appropriately and filtered. Absorbances of the samples were measured spectrophotometrically at 218 nm using Jasco V-550 UV/Vis Spectrophotometer (Tokyo, Japan), taking phosphate buffer (pH 6) as the blank.The amount of drug permeated was calculated from the calibration curve (linearity range =2.4 to 120 μg/ml; r2= 0.9996). The mean cumulative percentage of drug permeated was plotted against time (Figure 2). Permeation area was 2.54 sq cm[38].
2.7. In vivo Drug Absorption Study
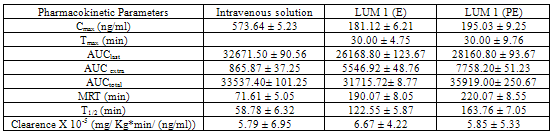
- In vivo studies were conducted on 12 New Zealand albino male rabbits weighing between 1.5 and 2 kg. Based on texture profile analysis and drug release pattern of the formulations, LUM1 and LUM1 (P) containing 0.5% sodium taurocholate were selected for in vivo study. Animals were kept in individual metal cages and acclamatised at 25℃ for 10 days prior to the experiment. They were provided with standard diet and water ad libitum. The approval of the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee was obtained before starting the study, and it was conducted according to the institutional guidelines. The rabbits were kept in fasting condition for 24 h before the experiment commenced. The rabbits were grouped into three (group I, II and III), each group containing three rabbits. Group I was administered intravenous bolus injection of midazolam. Groups II and III were administered nasal gels of LUM1 and LUM1 (P) containing 0.5% sodium taurocholate. Single dose of midazolam (2mg/kg body weight of rabbit) was administrated intravenously to compare the pharmacokinetic parameters. No anaesthesia was used for the intravenous study. Midazolam was injected through cannulated marginal ear vein. Two millilitres of blood samples each time were collected before intravenous injection and then at 5-, 10-, 15-, 20-, 30-, 45-, 60-, 90-, 120-, 180-, 240- and 300 min intervals in eppendorfs containing heparin sodium (100 U/ml). In case of nasal gels, the dose of midazolam that was administered was also 2 mg/kg body weight of rabbit. Before application of gel, each rabbit was lightly anaesthetized by intramuscular injection of a mixture of xylazine (3 mg/kg) and ketamine (35 mg/kg). Following induction of anaesthesia, a catheter was fixed into the central artery for blood sample collection. About 2 ml blood sample was collected prior to the application of gel and then at 5, 10, 15, 20, 30, 45, 60, 90, 120, 180, 240 and 300 min intervals in eppendorfs as above.After every 20 min, each rabbit was administered one-third of the initial dose of xylazine and ketamine intramuscularly to maintain a light plane of anaesthesia. The blood samples were kept on ice and centrifuged at 3,000 rpm for 10 min immediately after collection to separate the plasma and stored at −20℃ until the time of analysis. Immediately after each blood sample collection, the catheter was flushed with 0.2 ml of a 10% (v/v) heparin/normal saline solution to prevent blood clotting inside the catheter[40].All animal experiments are performed as per the standard norms and guidelines of the Animal Ethics Committee of Dr. B. C. Roy College of Pharmacy and Allied Health Sciences, West Bengal University of Technology, as recognized by the Committee for the Purpose of Control and Supervision on Experiments on Animals, India.
2.8. HPLC Analysis of Midazolam in Plasma
- Reverse phase HPLC was used to quantitate Midazolam in plasma samples. Midazolam was extracted with 3 ml of cyclohexane/diethyl ether (3:7) after the addition of 10 μl of 2% sodium hydroxide41. The organic phase was removed and evaporated to dryness under nitrogen, and the residue was reconstituted in 200 μl of the mobile phase (10 mM phosphate buffer, pH 6.0)/acetonitrile, 80:20). Of the mixture, 100 μl was injected for chromatographic analysis. The mobile phase was delivered into the HPLC apparatus at a flow rate of 1 ml/min (isocratic pump, Model LC-10AS, Jasco, Japan). The detection wavelength was 218 nm (ultraviolet variable wavelength detector, Model SPD-10A), and a C18 column was used.All assays were performed at ambient temperature. Calibration curve of midazolam hydrochloride prepared in rabbit plasma was found to be linear over the concentration range of 10–1,000 ng/ml (r2=0.9999). Pharmacokinetic parameters like peak plasma concentration (Cmax), time to reach peak plasma concentration (Tmax) and area under the concentration–time curve (AUC), Mean residence time (MRT), T1/2 and Clearence (Cl) were calculated following non- compartment model by Kinetica 4.4, PK/PD Analysis, Thermoelectron Corporation. All the parameters were calculated for i.v. bolus injection of midazolam and nasal formulations.Fraction of dose absorbed (F) was calculated by the following equation:
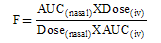 | (1) |
2.9. Statistics
- Data were analysed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD test using Vassar stat software (USA). p<0.001 has been considered to be significant statistically.
3. Results
3.1. Determination of Viscosity
- Viscosities of different formulations at different spindle rpm at 37±1℃ are shown in Figure 1. With increase in spindle rpm, viscosity of formulations decreased. It was observed that all the LUM gels showed higher viscosity than the gels prepared from synthetic polymers.
3.2. Determination of Mechanical Properties
- Texture profile analyses of the gels were studied at 37±1℃ using QTS-25 texture Analyser. The results of texture profile analysis were displayed in Figure 2. Minimum hardness was shown by LUM1 gel, and maximum was shown by LUM3(P) gel (Figure 2a). Adhesiveness of the formulations displayed in Figure 2b, showed that with increase in concentration of LUM from 3% to 5%, adhesiveness increased by 1.26 times (from -89.00 ± 7.12 to -112.08 ± 5.89 gs). And, for in situ gels, with increase in concentration of LUM from 0.5% to 1.5%, adhesiveness increased by 2.1 times (from - 1300.75 ± 15.26 to -2940.87 ± 20.77 gs) (Figure 2b). Values of cohesiveness, shown in Figure2c, report that for conventional gels, cohesiveness decreased from 1.01 ± 0.05 to 0.97 ± 0.03. And for in situ formulations, it decreased from 1.16 ± 0.03 to 0.98 ± 0.05. However, the formulations containing sodium taurocholate did not show any change in the values of hardness, adhesiveness and cohesiveness.
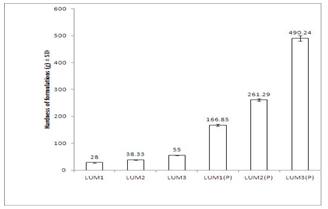 | Figure 2a. Comparitive study of hardness of different formulations at 37±1℃. Mean values ± SD (n=6) |
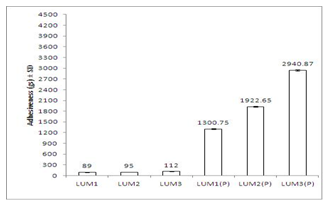 | Figure 2b. Comparative study of adhesiveness of different formulations at 37±1℃. Mean values ± SD (n=6) |
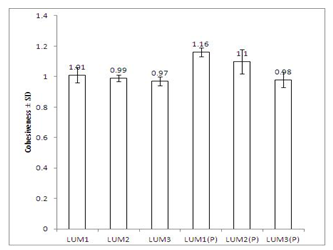 | Figure 2c. Comparative study of cohesiveness of different formulations at 37±1℃. Mean values ± SD (n=6) |
3.3. Determination of Mucoadhesive Strength
- Mucoadhesive strengths of the gels were also measured in texture analyzer. Results are shown in Figure 3. In case of conventional gels, with increase in concentration of LUM from 3 to 5% mucoadhesive strength increased from 16.26 ± 0.98g to 22.45 ± 1.02g. For in situ gels, the mucoadhesive strength increased from 72.26 ± 2.25g to 92.33 ± 4.11g, with increase in concentration of LUM from 0.5 to 1.5%.
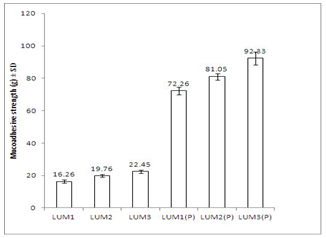 | Figure 3. Comparative study of mucoadhesive strength values of formulations at 37±1℃. Data represent mean values ± SD (n=6) |
3.4. Ex vivo Drug Permeation Study
- Ex vivo release profiles of midazolam from various gels were studied in phosphate buffer (pH 6.0). Considering the values of hardness, adhesiveness and cohesiveness, LUM1 and LUM1(P) were selected for ex vivo drug permeation and in vivo drug absorption studies. The formulations containing 0.5% sodium taurocholate as permeation enhancer, were named as LUM1(E) and LUM1(PE). Figure 4 depicts the drug permeation profiles of the formulations with and without enhancer. Results show that cumulative percentage of drug permeated from LUM1 and LUM1(P) were 300 and 200 min, respectively and from LUM1(E) and LUM1(PE) were 120 and 80 min, respectively.
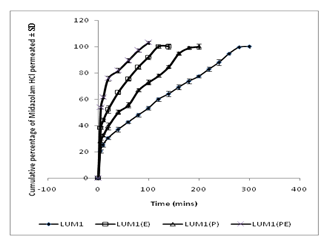 | Figure 4. Comparative result of ex vivo release profiles of midazolam hydrochloride from the both in situ and conventional nasal gels prepared with 0.5 % Linum usitatissimum L. mucilage with and without 0.5% w/v of sodium taurocholate (E) in phosphate buffer (pH 6) at 37±1℃. Data represent mean values ± SD (n=6). |
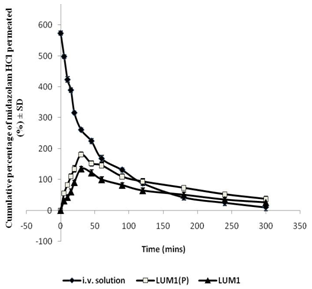 | Figure 5. In vivo drug plasma absorption profiles3.5. In vivo drug absorption study |
4. Discussion
- Viscosity of the formulations was determined at 37±1℃. At this temperature, LUM formulations containing Pluronic F 127 got converted to gels. Figure 1 shows viscosity profile of all formulations and they exhibit pseudoplastic flow. Moreover, with increase in concentration of mucoadhesive agent (LUM), viscosity is found to increase. However, viscosity of in situ gels was higher than those of conventional ones. This may be due to the presence of Pluronic F 127 in thermoreversible gels which led to the formation of a firm gel when formulation was administered into nasal cavity. Mechanical properties of the formulations like hardness, adhesiveness and cohesiveness were evaluated by texture profile analyser. Results are shown in Figure 2. Hardness was defined as the force required to attain a given deformation or as the maximum peak force during the first compression cycle. Adhesiveness is the negative force area for the first compression cycle and represented the work required to overcome the attractive forces between the surface of the gel and the surface of the probe. Cohesiveness is the ratio of the area under the force–time curve produced on the second compression cycle to that produced on the first compression cycle, where successive compressions were separated by a defined recovery period. It was reported that the hardness of gel formulations were significantly affected by the molecular weight and concentration of the polymer[42]. Low gel hardness ensures that the minimum work is required for removal of gels from the container and the applicability onto the desired site. However, less value decreases the retention time of gel formulation on the site of application and hence a gel should have optimum hardness value for obtaining proper therapeutic effect[43,44]. From Figure 2a, it is observed that hardness values of conventional gels are lesser than in situ gels. And, with increase in concentration of mucoadhesive agent, value of hardness increases for both types of gels.For better release it is important for the gel to spread uniformly on the nasal mucosa. So values of adhesiveness of formulations should be better. Values of adhesiveness as in Figure 2b, show that as the amount of mucoadhesive agent increases, adhesiveness of gels increases.The cohesiveness is important to determine the reconstruction ability of the gel after application[45,46]. The high cohesiveness value increases the performance of the product at the application site by providing full structural recovery following gel application[42,44]. But Figure 2c shows that with increase in amount of mucoadhesive agent, cohesiveness values of gels decreases and this is observed both in case of conventional and in situ gels.Mucoadhesive strength determines force required to detach gel applied on nasal mucosa. It is also measured with the help of Texture Profile Analyser. Mucoadhesive strength mainly depends on two factors - concentration of mucoadhesive strength and contact time of formulation with nasal mucosa[47]. It was observed that on increasing contact time beyond 5 min, there was hardly any significant change in mucoadhesive strength. Hence, evaluation of this parameter was done keeping the contact time at 5 min only. From the results shown in Figure 3, it can be deciphered that in situ formulations are more mucoadhesive than the conventional ones. And with increase in amount of mucoadhesive agent used, there was a corresponding increase in amount of mucoadhesive strength of the gels.Ex vivo drug permeation study was conducted in phosphate buffer (pH 6.0) and results are shown in Figure 4. It is observed that formulations containing enhancer exhibited faster release than the ones without enhancer. This may be attributed to the fact that the enhancer which is used here is sodium taurocholate, which being a bile salt can enhance paracellular transport of drugs by opening the tight junctions of the nasal mucosa[46]. Moreover, drug release from in situ gels was faster than conventional ones. This happens because in situ gels contain Pluronic F127, a block copolymer, which enhances transport of drugs by opening tight junctions of nasal mucosa[49].In vivo drug absorption profiles depicted in Figure 5, show that drug absorption from in situ gels was far better than from conventional gels. For in situ gels, Cmax was higher, AUC was higher, t1/2 was more, MRT of drug was better and clearence was lesser than conventional gels. However, Tmax was same for both types of gels. From the figure, it is evident that a better plasma absorption profile of midazolam was shown by in situ formulations than conventional gels.
5. Conclusions
- Midazolam is an important drug used widely for treatment of status epilepticus. Hence, nasal gel of midazolam will provide a firm platform from which drug will be released directly into systemic circulation and therapeutic effect can be obtained for a prolonged period. In comparision to conventional formulations, thermoreversible or in situ formulations provided reproducible results in all aspects as is evident from the above study. Moreover, it is easier to administer such formulations into nasal cavity as they remain liquid at room temperature and convert to gels at nasal temperature. Thus, thermoreversible nasal gel of midazolam prepared from a natural mucoadhesive agent will provide a cost effective dosage form for the treatment of status epilepticus.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- This work has been supported by grants from All India Council for Technical Education (National Doctoral Fellowship).
References
| [1] | Huff JS, Morris DL, Kothari RU, Gibbs MA. Emergency department management of patients with seizures: a multicenter study. Acad Emerg Med. 2001; 8:622–8. |
| [2] | Meldrum, B.S., and Horton, R.W., 1973, Physiology of status epilepticus in primates. Arch Neurol. 28:1–9. |
| [3] | Lothman E. The biochemical basis and pathophysiology of status epilepticus. Neurology 1990; 40:13–23. |
| [4] | Aminoff, M.J. and Simon, R.P., 1980, Status epilepticus, Causes, clinical features and consequences in 98 patients, Am J Med., 69, 657–66. |
| [5] | Bayne, L.L., Simon, R.P., 1981, Systemic and pulmonary vascular pressures during generalized seizures in sheep, Ann Neurol., 10, 566–9. |
| [6] | White, P.T., Grant, P., Mosier, J., Craig, A., 1961, Changes in cerebral dynamics associated with seizures, Neurology, 11, 354–61. |
| [7] | Boggs, J.G., Painter, J.A., DeLorenzo, R.J., 1993, Analysis of electrocardiographic changes in status epilepticus, Epilepsy Res., 14, 87–94. |
| [8] | Boggs, J.,G., Marmarou, A., Agnew, J.P., et al, 1998, Hemodynamic monitoring prior to and at the time of death in status epilepticus, Epilepsy Res., 31,199–209. |
| [9] | Haut, S.R., Veliskova, J., Moshe, S.L., 2004, Susceptibility of immature and adult brains to seizure effects, Lancet Neurol., 3, 608–17. |
| [10] | Holsti, M., Sill, B.L., Firth, S.D., Filloux, F.M., Joyce, S.M., Furnival, R.A., Prehospital intranasal midazolam for the treatment of pediatric seizures, Pediatr Emerg Care, 2007, 23,148-153. |
| [11] | Lahat, E., Goldman, M., Barr, J., Bistritzer, T., Berkovitch, M., 2000, Comparison of intranasal midazolam with intravenous diazepam for treating febrile seizures in children: prospective randomised study, BMJ, 321, 83-86. |
| [12] | Kutlu, N.,O., Yakinci, C., Dogrul, M., Durmaz, Y., 2000, Intranasal midazolam for prolonged convulsive seizures. Brain Dev., 22, 359-361. |
| [13] | Scheepers, M., Scheepers, B., Clarke, M., Comish, S., Ibitoye, M., 2000, Is intranasal midazolam an effective rescue medication in adolescents and adults with severe epilepsy?, Seizure, 9, 417-422. |
| [14] | McGlone, R., Smith, M., 2001, Intranasal midazolam: an alternative in childhood seizures, Emerg Med J.,18, 234. |
| [15] | Rainbow, J., Browne, G.,J., Lam, L.,T., 2002, Controlling seizures in the prehospital setting: diazepam or midazolam. J Paediatr Child Health, 38, 582-586. |
| [16] | Lahat, E., Goldman, M., Barr, J., Eshel, G., Berkovitch, M., 1998, Intranasal midazolam for childhood seizures. Lancet, 352, 620. |
| [17] | Mahmoudian, T., Zadeh, M.,M., 2004, Comparison of intranasal midazolam with intravenous diazepam for treating acute seizure in children, Epilepsy Behav., 5, 253-255. |
| [18] | Warden, C.,R., and Frederick, C., 2006, Midazolam and diazepam for pediatric seizures in the prehospital setting., Prehosp Emerg Care. 2006,10, 463-467. |
| [19] | Fisgin, T., Gurer, Y., Tezic¸ T., et al, 2002, Effects of intranasal midazolam and rectal diazepam on acute convulsions in children: prospective randomized study. J Child Neurol., 17, 123-126. |
| [20] | Bhattacharyya, M., Kalra, V., Gulati, S., 2006, Intranasal midazolam vs rectal diazepam in acute childhood seizures., Pediatr Neurol., 34, 355-359. |
| [21] | Jeannet, P.,Y., Roulet, E., Maeder-Ingvar, M., Gehri, M., Jutzi, A., Deonna, T., 1999, Home and hospital treatment of acute seizures in children with nasal midazolam., Eur J Paediatr Neurol.,3, 73-77. |
| [22] | Wilson, M.,T., Macleod, S., and O'Regan, M.,E., 2004, Nasal/buccal midazolam use in the community., Arch Dis Child, 89, 50-51. |
| [23] | Harbord, M.,G., Kyrkou, N.,E., et al., 2004, Use of intranasal midazolam to treat acute seizures in paediatric community settings., J Paediatr Child Health,40, 556-558. |
| [24] | McIntyre, J., Robertson, S., Norris, E., et al., 2005, Safety and efficiacy of buccal midazolam versus rectal diazepam for emergency treatment of seizures in children: a randomized controlled trial., Lancet, 366, 205-210. |
| [25] | Scott, R.,C., Besag, F.,M., Neville, B.,G., 2001, Intranasal midazolam for treating febrile seizures in children: buccal midazolam should be preferred to nasal midazolam., BMJ, 322, 107. |
| [26] | Scott, R.,C., Besag, F.,M., Neville, B.,G., 1999, Buccal midazolam and rectal diazepam for treatment of prolonged seizures in childhood and adolescence: a randomised trial., Lancet, 353, 623-626. |
| [27] | Mpimbaza, A., Ndeezi, G., Staedke, S., Rosenthal, P.,J., Byarugaba, J., 2008, Comparison of buccal midazolam with rectal diazepam in the treatment of prolonged seizures in Ugandan children: a randomized clinical trial., Pediatrics, 121,e58-e64. |
| [28] | Scott, R.,C., 2005, Buccal midazolam as rescue therapy for acute seizures, Lancet Neurol., 4, 592-593. |
| [29] | Scheepers, M., Scheepers, B., Clough, P., 1998, Midazolam via the intranasal route: an effective rescue medication for severe epilepsy in adults with a learning disability. Seizure, 7, 509-512. |
| [30] | Lahat, E., 1997, A prospective, randomized study comparing intramuscular midazolam with intravenous diazepam for the treatment of seizures in children, Pediatr Emerg Care, 13, 449. |
| [31] | Chamberlain, J.,M., Altieri, M.,A., Futterman, C., Young, G.,M., Ochsenschlager, D.,W., Waisman, Y., 1997, A prospective, randomized study comparing intramuscular midazolam with intravenous diazepam for the treatment of seizures in children. Pediatr Emerg Care. 13,92- 94. |
| [32] | Knoester, P.,D., Jonker, D.,M., van der Hoeven, R.,T.,M., et al. 2002, Pharmacokinectics and pharmacodynamics of midazolam administered as a concentrated intranasal spray: a study in health volunteers, Br J Clin Pharmacol., 53, 501-507. |
| [33] | Datta, R., and Bandyopadhyay, A., K., 2006, A new nasal drug delivery system for diazepam using natural mucoadhesive polysaccharide obtained from tamarind seeds, Saudi Pharm J., 14, 115–119. |
| [34] | Miyazaki, S., Nakamura, T., Yokouchi, C., Takada, M., 1987, Effect of Pluronic gels on the rectal absorption of indomethacin in rabbits, Chem Pharm Bull, 1987, 35, 1243–1248. |
| [35] | Majithiya, R., J., Ghosh, P.,K., Umrethia, M.,L., Murthy, R., S., 2006, Thermoreversible mucoadhesive gel for nasal delivery of sumatriptan, AAPS PharmSciTech., 7(3):Article 67. |
| [36] | Zhang, L., Parsons, D.,L., Navarre, C., and Kompella, U.,B., 2002, Development and in vitro evaluation of sustained release Poloxamer 407 (P407) gel formulations of ceftiofur, J Contr. Rel.,85,73–81. |
| [37] | Basu, S., Chakrabatorty, S., and Bandyopadhyay, A., K., 2009, Development and evaluation of a mucoadhesive nasal gel of midazolam prepared with Linum usitatissimum L. seed mucilage, Sci Pharm., 77, 899–910. |
| [38] | Loyd, V., Allen, J.,R., Compounding Nasal Preparations. Current and Practical Compounding Information for the Pharmacist in Secundum Artem, (www.paddocklabs.com) vol 7, no.1 |
| [39] | Schmolka, I., R., 1972, Artificial skin. I. Preparation and properties of Pluronic F-127 gels for the treatment of burns. J Biomed Mater Res., 6, 571–582 |
| [40] | Basu, S., and Bandyopadhyay, A., K., 2010, Development and characterization of mucoadhesive in situ nasal gel of midazolam prepared with Ficus carica mucilage, AAPS PharmSciTech, 11, 1223-1231. |
| [41] | Shih, P.,E., and Huang, J.,D., 2002, Pharmacokinetics of midazolam and 1-hydroxymidazolam in Chinese with different cyp3a5 genotypes, Drug Metab Dispos., 30, 1491–1496. |
| [42] | Bansal, K., Rawat, M.,K., Jain, A., Rajput, A., Chaturvedi, T.,P., Singh, S., 2009, Development of satranidazole mucoadhesive gel for the treatment of periodontitis, AAPS PharmSciTech,10(3),716–723. |
| [43] | Jones, D.,S., Woolfson, A.,D., Brown, A.,F., 1997, Textural, viscoelastic and mucoadhesive properties of pharmaceutical gels composed of cellulose polymers, Int. J. Pharm.,151, 223 - 233. |
| [44] | Tan, Y.,T.,F., Peh, K.,K., Al-Hanbali, O., 2000, Effect of Carbopol and polyvinylpyrrolidone on the mechanical, rheological and release properties of bioadhesive polyethylene glycol gels, AAPS PharmSci. Tech., 1, 1-10. |
| [45] | Cevher, E., Taha, M.,A.,M., Orlu, M., and Araman, A., 2008, Evaluation of mechanical and mucoadhesive properties of clomiphene citrate gel formulations containing carbomers and their thiolated derivatives, Drug Deliv.,15, 57— 67. |
| [46] | Deshpande, A.,A., Rhodes, C.,T., Danish, M., Intravaginal drug delivery, 1992, Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm., 18, 1225—1279. |
| [47] | Richardson, J., Illum, L., 1992, Routes of delivery: Case studies: (8) The vaginal route of peptide and protein drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 8, 341—366. |
| [48] | Rao, M.Y., Vani, G., and Chary, R.,B.,R., 1998, Design and evaluation of mucoadhesive drug delivery system, Indian Drugs, 35, 558-565. |
| [49] | Lin, H., Gebhardt, M., Bian, S., et al, 2007, Enhancing effect of surfactants on fexofenadine HCl transport across the human nasal epithelial cell monolayer. Int J Pharm. 2007;330:23–31. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML