-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Safety Engineering
p-ISSN: 2325-0003 e-ISSN: 2325-0011
2014; 3(2): 31-36
doi:10.5923/j.safety.20140302.01
Risk Assessment Methodology: Quantitative HazOp
Erick Galante1, Daniele Bordalo2, Marcele Nobrega3
1Department of Chemical Engineering, IME, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
2Núcleo de Pesquisas em Sistemas e Gestão de Engenharia da Escola Politécnica, UFRJ, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
3SSMA, Braskem, Duque de Caxias, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Correspondence to: Erick Galante, Department of Chemical Engineering, IME, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Risk management can be defined as a systematic application of management policies, procedures and practices, which include identifying, analyzing, evaluating, monitoring and reviewing risk. Usually, the combined risk identification, analysis and evaluation are folded into what is known as risk assessment. As examples of risk assessment methods, one should quote the HazOp (Hazards and Operability Study) and the PHA (Preliminary Hazard analysis). PHA was originally proposed by the US military in the MIL-STD 882, in 1973, which undertook five reviews over time. Currently, the up-to-date version is the MIL-STD 882-E. The aim of this methodology is to be a semi-quantitative technique to assess risk using a risk matrix. On the other hand, the study of hazards and operability (HazOp) is a qualitative method developed to identify risks and operational problems through the deviations effects from design conditions in industrial process plants. It has been used effectively at any stage of the life of plants. Traditionally, a HazOp study and PHA are two sessions held separately, producing two databases. Considering an integrated approach, proposed by this work, the results combine upsides from PHA and HazOp and after determining deviations, through guidewords, the team determines its possible causes and consequences. Thus, it is possible to systematically identify the ways in which the equipment constituting the industrial process may fail or be improperly operated, which would lead to unwanted operating situations, as well as categorize risk in order to prioritize the measures. As a conclusion, this work provides a hybrid methodology between HazOp and PHA, by integrating HazOp and risk matrixes. The HazOp brings structure, procedure and its criteria (mainly the use of nodes, keywords and deviations), while the use of risk matrix brings to this hybrid technique the capability to prioritize risks/deviations, in other to provide information to a more detailed implementation plan.
Keywords: Risk assessment, HAZOP, Risk Assessment Code, and Quantitative Risk Assessment
Cite this paper: Erick Galante, Daniele Bordalo, Marcele Nobrega, Risk Assessment Methodology: Quantitative HazOp, Journal of Safety Engineering, Vol. 3 No. 2, 2014, pp. 31-36. doi: 10.5923/j.safety.20140302.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Risk management can be defined as the collection of culture, processes and structures that are directed towards realizing potential opportunities whilst managing adverse effects [1-4]. It can be defined as a systematic application of management policies, procedures and practices. The risk management also incorporates several other tasks, such as identifying, analyzing, evaluating monitoring and reviewing risk. Usually the combined identification, analysis and evaluation tasks are folded into what is known as risk assessment.Risk assessment is carried out throughout the use of methods, tools and risk assessment scheme. There are an unlimited number of methods and each of those has its strengths and weakness. Hammer [1] presents several schemes, which could be, after some analysis is folded into tow larger groups, regarding the approach and the method of record the results: analysis in trees and in spread sheets. The schemes of risk analysis in trees are focused on determine a chain of events; while the spread sheets methods address to the full scope of risk assessment (identification, analysis and evaluation). As examples, one should quote the HazOp [5] and the PHA (Preliminary Hazard analysis). The Preliminary Hazard Analysis (PHA) was originally proposed by the US military in the Mil-Std 882 in 1973 [6-8], which undertook five reviews over time. Currently the up-to-date version is the MIL-STD 882-E [8]. The aim of a PHA is to be a semi-quantitative technique to assess risk using a risk matrix.On the other hand, the hazards and operability (HazOp) analysis qualitative method developed to identify risks and operational problems through the effects of deviations from design conditions in industrial process plants. It has been used effectively at any stage of the life of plants. Traditionally, a HazOp study and PHA are two sessions held separately, producing two databases. In the integrated approach proposed by this work, the result combines PHA and HazOp.Therefore, this paper aims to provide s a hybrid risk assessment tool, between HazOp and the PHA, by integrating these methods and risk matrixes. HazOp brings structure, procedure and its criteria (mainly the use of nodes, keywords and deviations), while the use of risk matrix brings to this hybrid technique the capability to prioritize risks/deviations, in other to provide information to a more detailed implementation plan.
2. Background Knowledge
- Risk assessment is part of a risk management program. A risk management program is a bigger initiative carried by an enterprise to control risks and avoid accidents. Hollnagel [3], quoted by Aven and Steen [9], has stated that safety management must not only be reactive, but also proactive. Furthermore, Hollnagel [3] stated that conventional view on safety (risk) management considers performance variability of any kind as a threat and something that should be avoided. The result is often the use of constraining means (in particular for human performance variability) such as barriers, interlocks, rules, procedures, and automation.Aven [10] suggested a risk framework to make the distinction between risk as a concept per se and risk description. According to Aven [10], risk exists "objectively", in the sense of "broad inter-subjectivity" as explained by the following arguments [9, 11, 12].Regardless of the framework, risk management is usually described as containing four stages: identification, analysis, evaluation and mitigation.Risk assessment is carried out throughout the use of any suitable method of study. Hammer [1] presents several methods, which could be, after some analysis be folded into tow larger groups, regarding the approach and the method of record the results: analysis in trees and in spread sheets.The schemes of risk analysis in trees are focused on determine a chain of events. The TNO Red Book [5] presents the fault tree analysis technique, which is a valid example of “analysis in trees” scheme. Fault trees can increase its degree of complexity using a statistical approach (mean and standard deviation for each probability used in the calculations).The other type of scheme is the use of spreadsheets that can operate in various ways. Some of them are used for some preliminary identification, such as the HazID [13-17], while others aim to determine a hierarchy among risks, such as the Hazard Matrix [18], while others address the full scope of the risk management, such as HazOp [19] and PHA [8].
2.1. PHA: Preliminary Hazard Analysis
- Preliminary Hazard Analysis (PHA) is a qualitative technique, widely used in processes of chemical and petrochemical, industries. It is structured to identify the potential hazards arising from the installation of new process units or operating units existing, dealing with hazardous materials.PHA technique is applied during risk analysis systems in the design phase and/or project, especially in new technologies uses that require further information about their risks. Through this technique, a superficial analysis of the risks are still in the design phase of the process, so that the necessary changes due to the risks identified do not imply in significant costs, and easier implementation.This technique examines risks and process deviations, aiming to determine causes and effects in a qualitative approach. This qualitative approach (causes and effects) can be quantified by the use of a risk matrix and its parameters of frequency and severity. Therefore, the results are qualitative, not providing numerical estimates [8].Based on this information, preventive or mitigation of identified hazards may be suggested to eliminate or reduce the causes harmful effects resulting from the different accident scenarios analyzed.The PHA’s scope comprehends hazardous events whose causes have their origin in the installation analyzed, encompassing both the failures of components or systems, as any maintenance or operational errors (human errors).The process of conducting a PHA consists on the following steps:1. Subdividing the studied facility in different modules;2. Defining system boundaries;3. Determining hazardous materials in the system and its process conditions and/or storage;4. Completing the worksheets PHA meetings of the analysis group.PHA results are recorded in spread sheets. A typical PHA spread sheet has eight columns, described as follows:
2.1.1. First Column: Hazard
- This column contains the identified hazards for the analyses module in study. In general, hazards are accidental events have the potential to cause damage to the facilities, operators, people or the environment. Therefore, hazards in general, refer to events such as release of toxic and flammable material, burst contained, among others.
2.1.2. Second Column: Causes
- These causes may involve both intrinsic failures of equipment (leaks, cracks, instrumentation, etc.), as well as human errors in operation and maintenance.
2.1.3. Third Column: Method of Detection
- Installation modes available for the detection of danger identified in the first column are listed in this column. Detection of the occurrence of danger can either be performed by instrumentation (alarms pressure, temperature, etc.), such as through human perception (visual, smell, etc.).
2.1.4. Forth Column: Effect/Consequences
- Here accident effect and/or consequences are listed. The main effects of accidents involving toxic and flammable substances include, for example, among others: formation of toxic cloud, fire puddle of flammable, training torch (jet fire), fire cloud of flammable vapor, vapor cloud explosion product flammable, confined explosion with possible generation of missiles and environmental contamination.
2.1.5. Fifth Column: Frequency Parameter
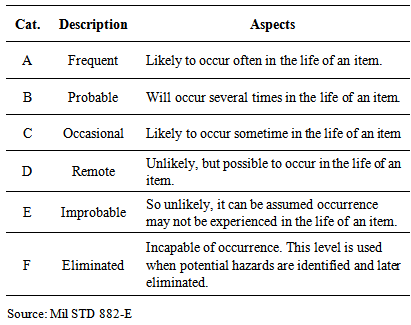
- An accident scenario is defined as the combination of the identified hazard, its causes and each of its effects. According to PHA method, accident scenarios are categorized by its frequency, which provides a qualitative indication of the expected frequency of occurrence as defined in Table 1.
|
2.1.6. Sixth Column: Severity Parameter
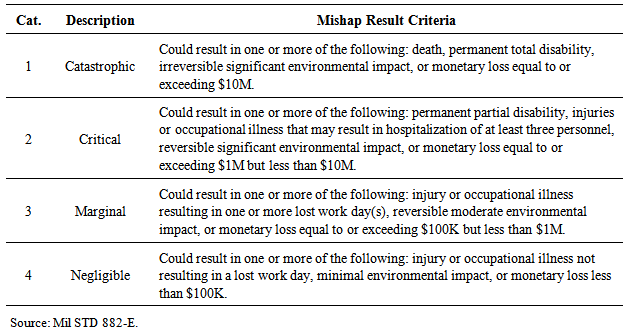
- Accident scenarios are classified into categories of severity, which provide a qualitative indication of the severity of the consequences of each of the scenarios identified. Table 2 present a possible set of parameters for severity.
|
2.1.7. Seventh Column: Risk Assessment Code
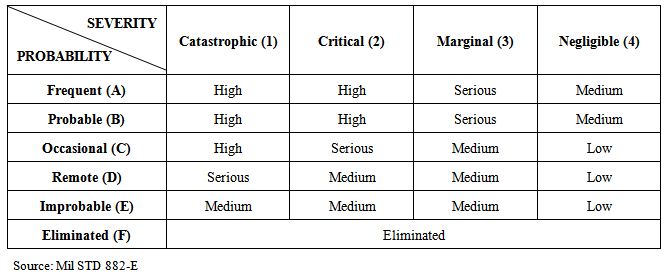
- Combining frequency category, Table 1, with severity, Table 2, one gets the risk matrix as shown in Table 3, which provides a qualitative indication of the risk level for each scenario identified in the analysis.
|
2.1.8. Eighth Column: Control Measures
- This column contains the measures that should be taken to reduce the frequency or severity of the accident or any comments pertaining to the accident scenario under study.
2.2. Classic HAZOP
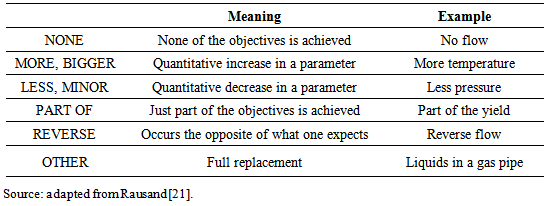
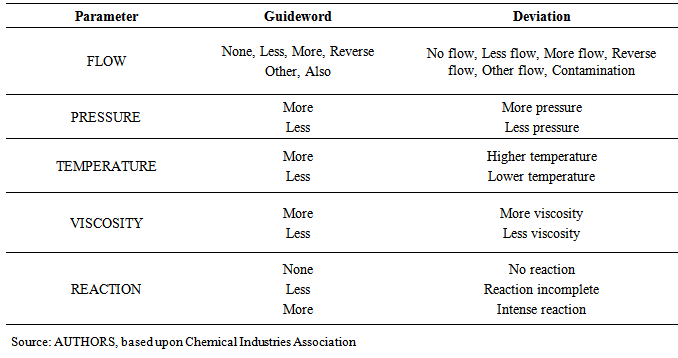
- The Hazard and Operability study (HazOp) is a methodology widely used qualitative risk that was developed to identify risks and operational problems through the effects of deviations from design conditions in industrial process plants [19]. It has been used effectively at any stage of the life of plants.According to Aven [9, 10], since it is complete, systematic and relatively easy to apply, HazOp is a technique for analyzing risks and deviations within a chemical process plant.The technique was originated in the “Division of Organic Chemistry heavy ICI, a major British and international chemical company, where in 1963 a team of three people met three days a week during four months to study the design of a new phenol and acetone from cumene factory [20]. Since then, the method has been improved in many works. Besides it was initially developed to analyze chemical process systems, it was later extended to other types of systems and also for complex operations.A HazOp study is a disciplined procedure to identify how a process can deviate from its design conditions. The application comes from a systematic critical review of process and engineering conditions to evaluate the potential for malfunction of individual parts and/or equipment, and indirect effects on the facility as a whole [19].The HazOp study both the security problems in order to identify the hazards that can endanger operators and equipment installation, as well as the problems of operability, which, although not dangerous, can cause loss of production or affect the product quality or the efficiency of the process. Therefore, HazOp identifies both problems that may compromise facilities’ safety as those that may cause loss of continuity or loss of the product specification.HazOp application is based on formulation questions in a structured and systematic approach, through the appropriate use of guidewords applied to critical points related to the process under analysis. From the guidewords and process parameters, deviations can be identified and further analyzed. Table 4 shows a series of standard guidewords for basic application of HazOp, as presented by Rausand [21].
|
|
3. HAZOP: Quantitative Approach
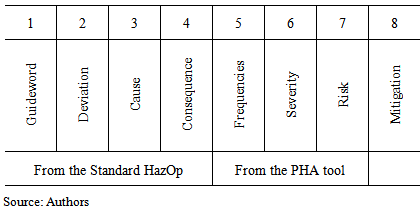
- Traditionally, a HazOp study and PHA are two sessions held separately, producing two databases. HazOp technique is guided by guide words application (such as no more less) to each process variable (e.g., temperature, flow, pressure) generating the deviation of operating standards (such as low- flow, the temperature). On the other hand, PHA allows the definition of risks priorities through the use frequency and severity categories to determine a risk value.In this quantitative approach for a HazOp, the aim is for integrating it with a risk matrix. The core of this method is use the HazOp identification and diagnosis method (parameter, guideword and deviation investigation for each node). From that, the causes and consequences related to each deviation are investigated. Upon the completion of this part of the process, one should use the PHA and risk matrix method to convert causes into frequencies, severities into consequences and, thus, determine a risk parameter (or RAC – Risk Assessment Code) to allow put risks in order of relevance.This modified HazOp should be build around the information (columns) presented in table 6. The first part of the analysis comes from a classic HazOp (columns 1 to 4), followed by the risk assessment originated from PHA (columns 4, 5 and 6). The last part is common to both classic utilization of HazOp and PHA: mitigations. However, in this case the mitigations can be put in order of relevance using the RAC.
|
4. Conclusions
- As a conclusion, this work provides a hybrid methodology between HazOp and the PHA. This risk assessment method combines the strengths of of both HazOp (systematic investigation of deviations, causes and effects) and PHA (possibility to determine an order of relevance for risks). The HazOp contributes with its structure, procedure and its systematic approach (mainly the use of nodes, keywords and deviations), while the use of risk matrix brings to this technique the capability to prioritize risks and deviations, in other to provide information to a more detailed implementation plan.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- We would like to acknowledge our colleagues and co-workers for all the support during this methodology compilation.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML